Key 37 and more- Ventricular Ectopic and Questions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Ventricular Ectopic is
abnormal heartbeats from the ventricle
Three beats pattern = Ventricular Trigeminy
Symptoms and sign of Ventricle Ectopic
asymptomatic
sense of missed/ skipped beat
Unsustained palpitation
Dyspenia
Dizziness
sign: Broad QRS complex
Causes of Ventriculars Ectopics
Benign and Pathological
Benign:
Naturally, anxiety, caffiene, alcohol, stress, cocaine
Pathological
MI
Cardiomyopathies
Medications
______ and ______ should not be given for patients with CKD, CHD, IHD
NSAIDS - ibuprofen
COX 2 inhibitor - celecoxib
These drugs can worsen HF and renal function
Base on MI complication for pricarditis we give full dose NSAIDs
NSAIDS inhibits systhesis of prostaglandin, thus decrease____, retain more salt and water
eGFR
Thiazide Diuretic and Loop Dieuretics Decrease clearence of uric acid leading to____
GOUT( hyperuricemia)
A patient with chronic heart failure developed gout. A medication for his gout is prescribed. A few days later, the patient came back to the hospital complaining of worsening of his Heart Failure symptoms (SOB, Orthopnea).
The likely cause of this patient's gout
→ Thiazide like diuretics (e.g. bendroflumethiazide) or Loop Diuretics (Both can cause hyperuricemia (Gout) and both can be used to treat volume overload caused by Heart Failure)The likely cause of this patient's worsening of SOB and Orthopnea → NSAIDs (e.g. Ibuprofen) that was prescribed to treat his gout.
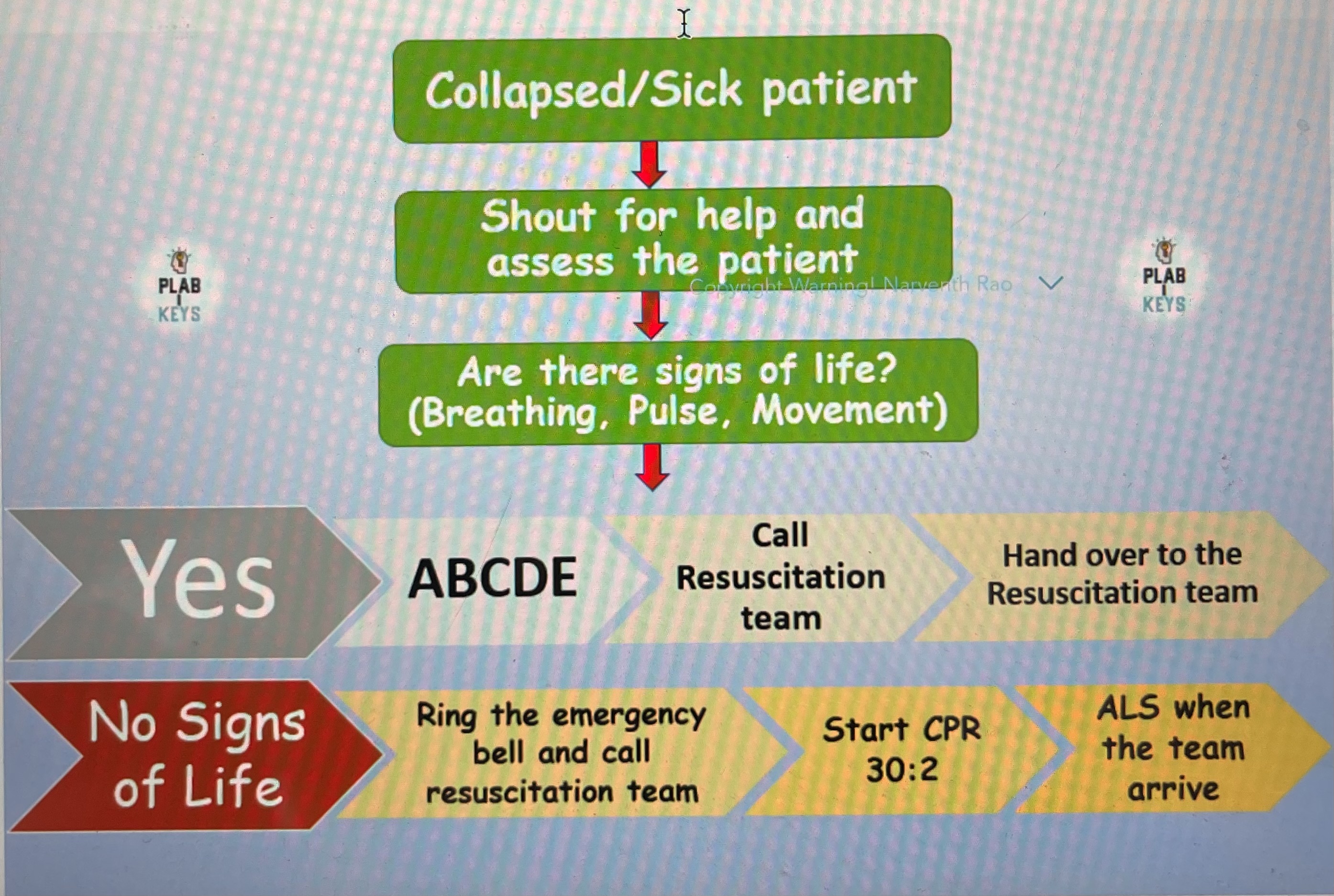
In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
Collapse /sick patient
Shout for help and assess patient
Are there sign of life ? (Breathing, pulse)
If YES what to do? If NO what to do?
No sign
Ring emergency bell call resus team
Start CPR 30:2
Get defib
ALS(advance life support) when resus team arrive
UK guidelines recommendation of Alcohol consumption:
No more than 14 units a week
No more than 3 units a day
with at least 2 alcohol-free days a week
If someone drinks 7 units of alcohol a week and smoke 20 cigarette a day, we should refer him to
→ Smoking Cessation Clinic.
This is because his alcohol intake is insignificant as per NICE whereas his smoking is significant.
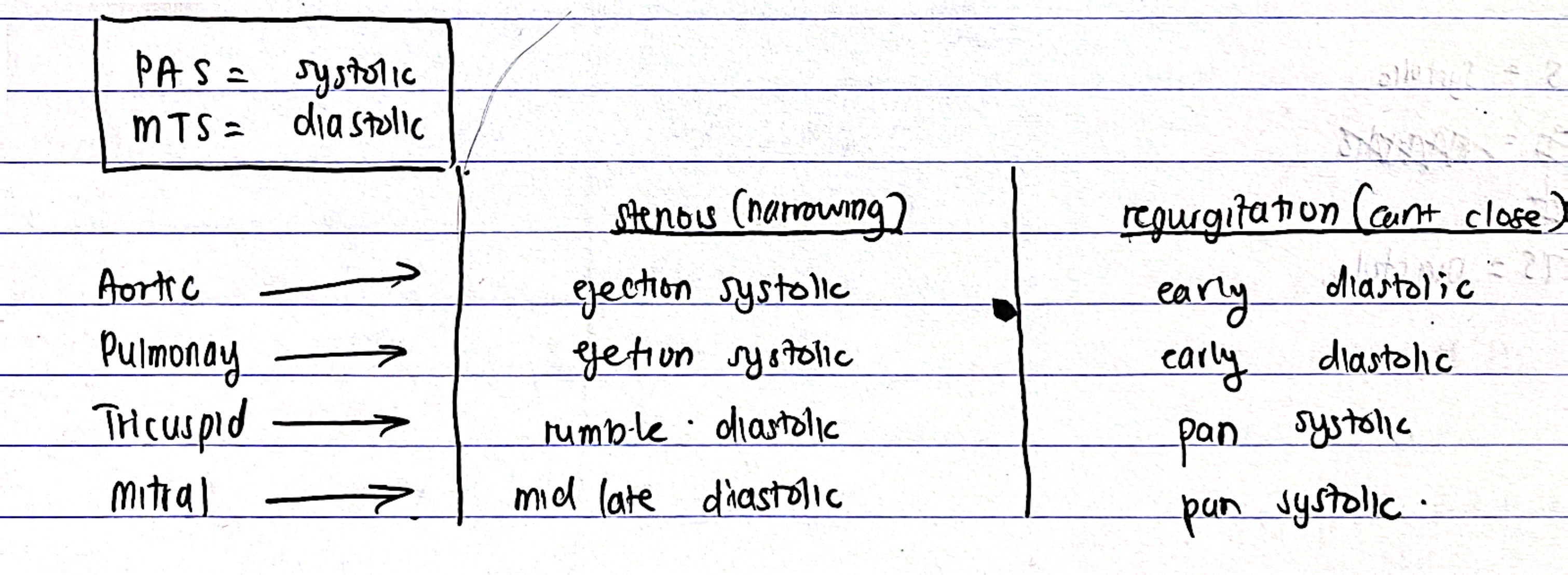
Heart Murmurs
PAS(PA stenosis) - systolic murmur
MTS(MT stenosis) - diastolic murmur
*remember one side only, regurgitation is opposite
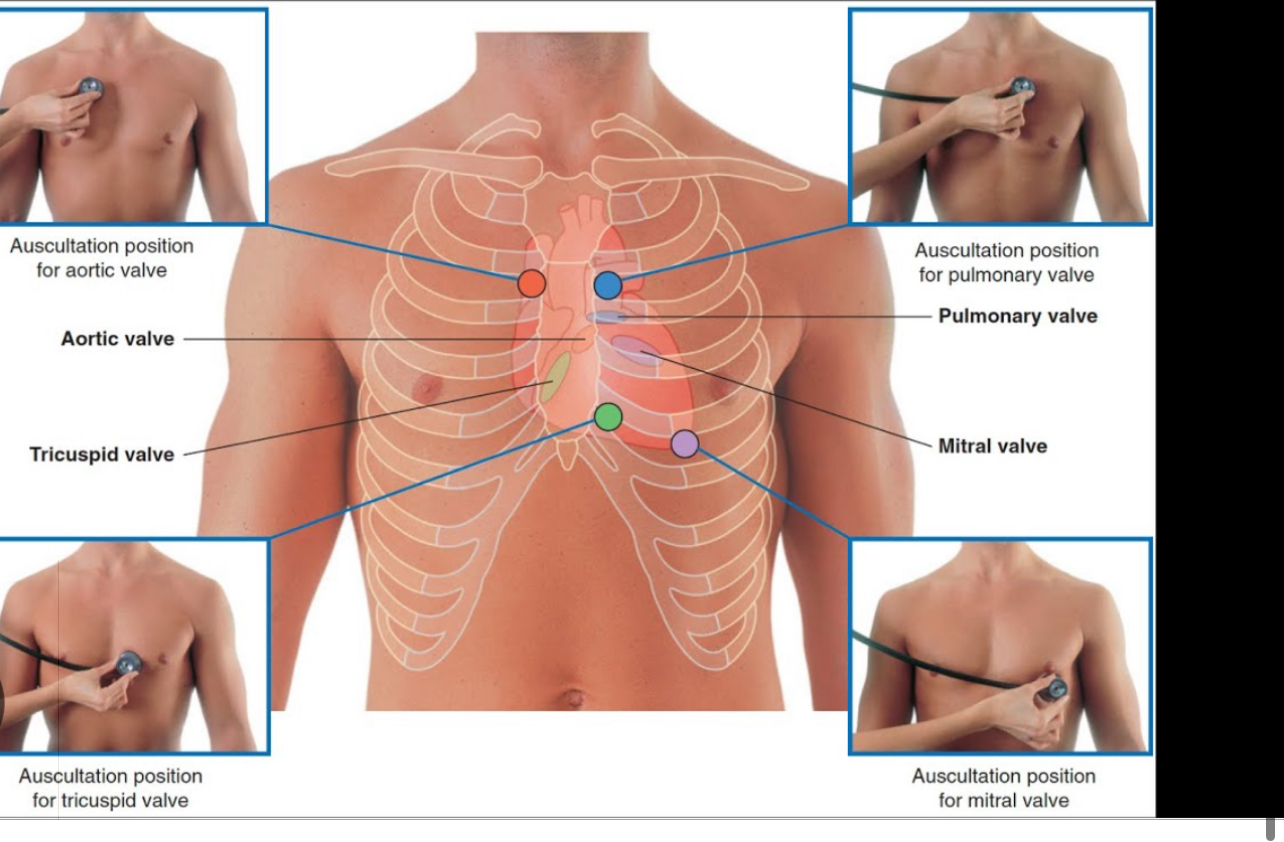
Points of Auscultation for Hearts Murmurs all
From PAMT stenosis and regurgitation
Pulmonary - Left 2nd ICS
Aortic - Right 2nd ICS
Mitral Stenosis - Apex of Heart (5th ICS mid claviculr line (MR - apex same but radiates to axialla
Triscuspid - 4-5th ICS left sternum border
A Young adult presents with frequent fainting attacks since childhood and prolonged QT. There are sinus rhythm and normal P-R interval. No Hx of arrhythmias or sudden death. Diagnsis?
TDP
An elderly patient with a Hx of stroke presents with exertional dyspnea.
ECG shows Atrial Fibrillation. Chest X-ray shows Straight left heart border. what is the likely diagnosis?
→ Mitral Stenosis.
Straight left heart border because:
Mitral Stenosis blocks LV filling, increase Left Atrium pressure causes LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTROPHY. CXR shows straight left side heart border.
This causes: blood return back to lungs, pulmonary congestion then Right Ventricular failure( hepatomegaly, Ascites, Edema)
The most common cause of Mitral Stenosis is________
Rheumatic Fever
What causes left atrial hypertrophy?
Mitral Stenosis
Features of Mitral Stenosis
Mid late diastolic murmur(low pitched) during expiration
Loud S1, opening snap
Atrial Fibrillation
lEft heart Murmur is heard during_____.
rIght heart murmurs is heard during___.
E - expiration
R - inspiration
ECG, CXR and Echo of Mitral Stenosis
ECG - sign of right ventricular hypertrophy
P mitrale/ bifid p wave (P wave with 2 humps)
Afib
CXR - Left Atrium Enlargement/ straighten left border of heart
Echo - Thickening if Mitral Valve Leaflets/ mitral valve tissue
Decrease Ejection Fraction + Decrease Wall Thickness=
Increase EF + Increase Septal Wall Thickness =
DILATED Cardiomyopathy
HYPERTHROPHIC Cardiomyopathy
What is Dilated Cardiomyopathy?
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a condition in which the heart muscle becomes stretched and weakened
*All chambers but, particularly the left ventricle, leading to poor pumping ability (reduced ejection fraction)
Symptoms of SVT and TDP
SVT - lightheadness, palpitations, recurrence
TDP - episode faintings
An elderly patient suddenly fell unconscious, he recovered completely within a few minutes, he remembers the event very well, he did not trip, he felt hot and flushed after the episodes but he did not feel dizzy or sweaty before the fall.
Best investigation?
12 lead ECG
Analysis cause of fall:
Cardiac Cause (Arrythmias)
Postural Hypotension
fall usually follow a standing from a sitting + dizzi before fall
Hypoglycaemia
felt sweaty and dizzy + not recovered till glucose administered
Seizure
someone eyewitness + post-ictal features like confusion and drowsiness.
Analysis and Causes of Falls
Causes:
Cardiac Cause (Arrythmias) - stokes adams attack
feel hot and flushed
Postural Hypotension
fall usually follow a standing from a sitting + dizzi before fall
Hypoglycaemia
felt sweaty and dizzy + not recovered till glucose administered
Seizure
eyewitness + post-ictal features like confusion and drowsiness.
An elderly patient fell and collapsed "syncope"
. He was transferred to the A&E
and now he is fully conscious. ECG shows irregular rhythm. What is the next best investigation?
Echocardiogram
Holter ECG/ 24 hour ecg
*but this case no need holter ecg cause normal ecg already show pathology.