Care of Developing Fetus
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Ovum
from ovulation to fertilization.
Zygote
from fertilization to implantation
Fetus
from 8 weeks until term
Conceptus
developing embryo and placental structures throughout pregnancy
Age of viability
earliest age at which fetuses survive if they are born is generally accepted as 24 weeks or the point a fetus weighs more than 500-600 grams
Fertilization
union of an ovum and spermatozoon. referred to as conception, impregnation or fecundation.
outer third of the fallopian tube, ampullar portion
where fertilization occurs
24-48 hours
Viability of ovum
48-72 hours
Spermatozoon life span
2.5ml of fluid containing 50-200 million spermatozoa per ml or an average of 400 million sperm cells per ejaculation
average semen ejaculation
Graafian follicle
Where the ovum is released in the ovary
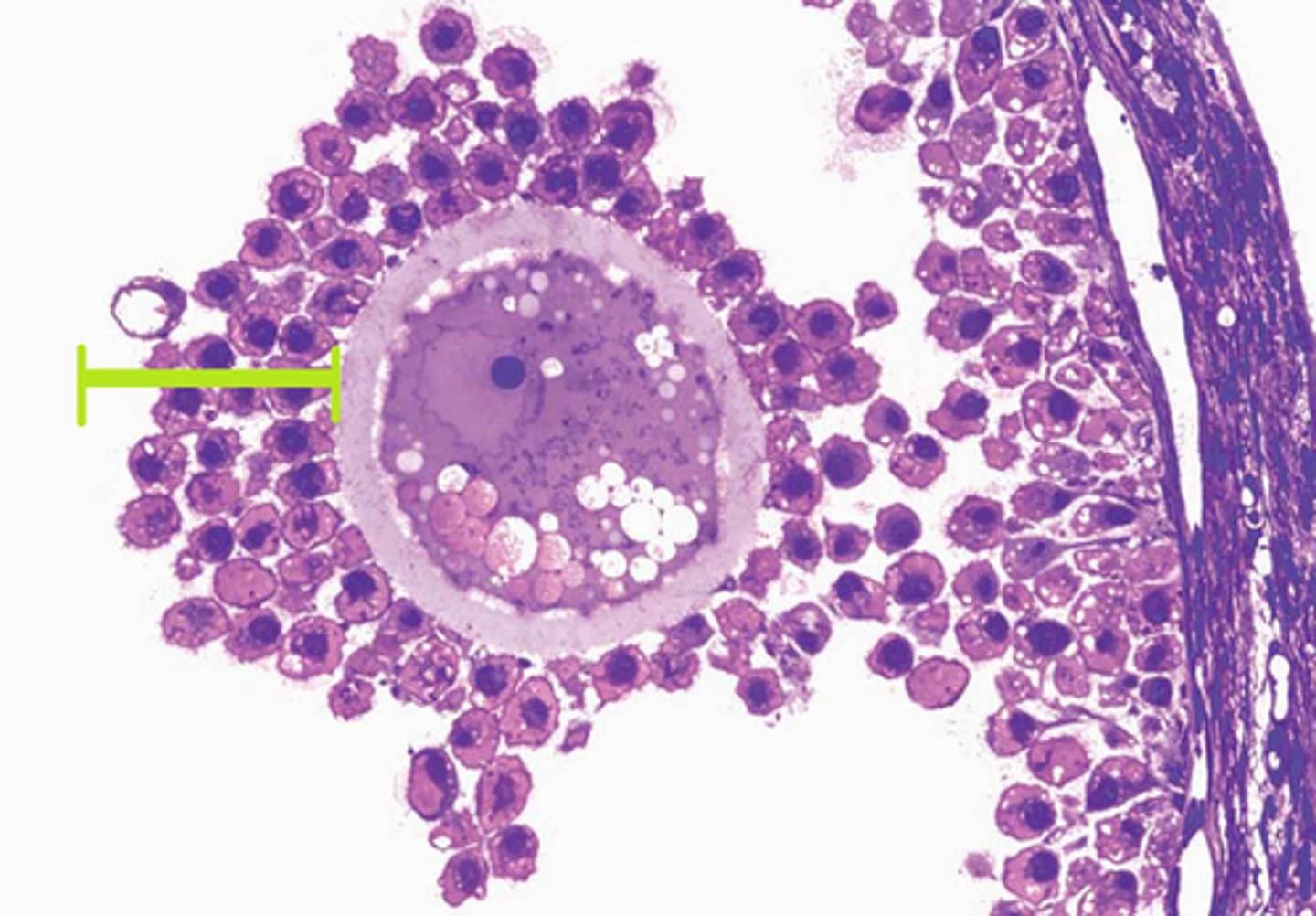
zona pellucida and corona radiata
protective structures surrounding primary oocyte
zona pellucida
a protective mucopolysaccharide layer which is a thick, transparent coating rich in glycoproteins that surrounds an oocyte.
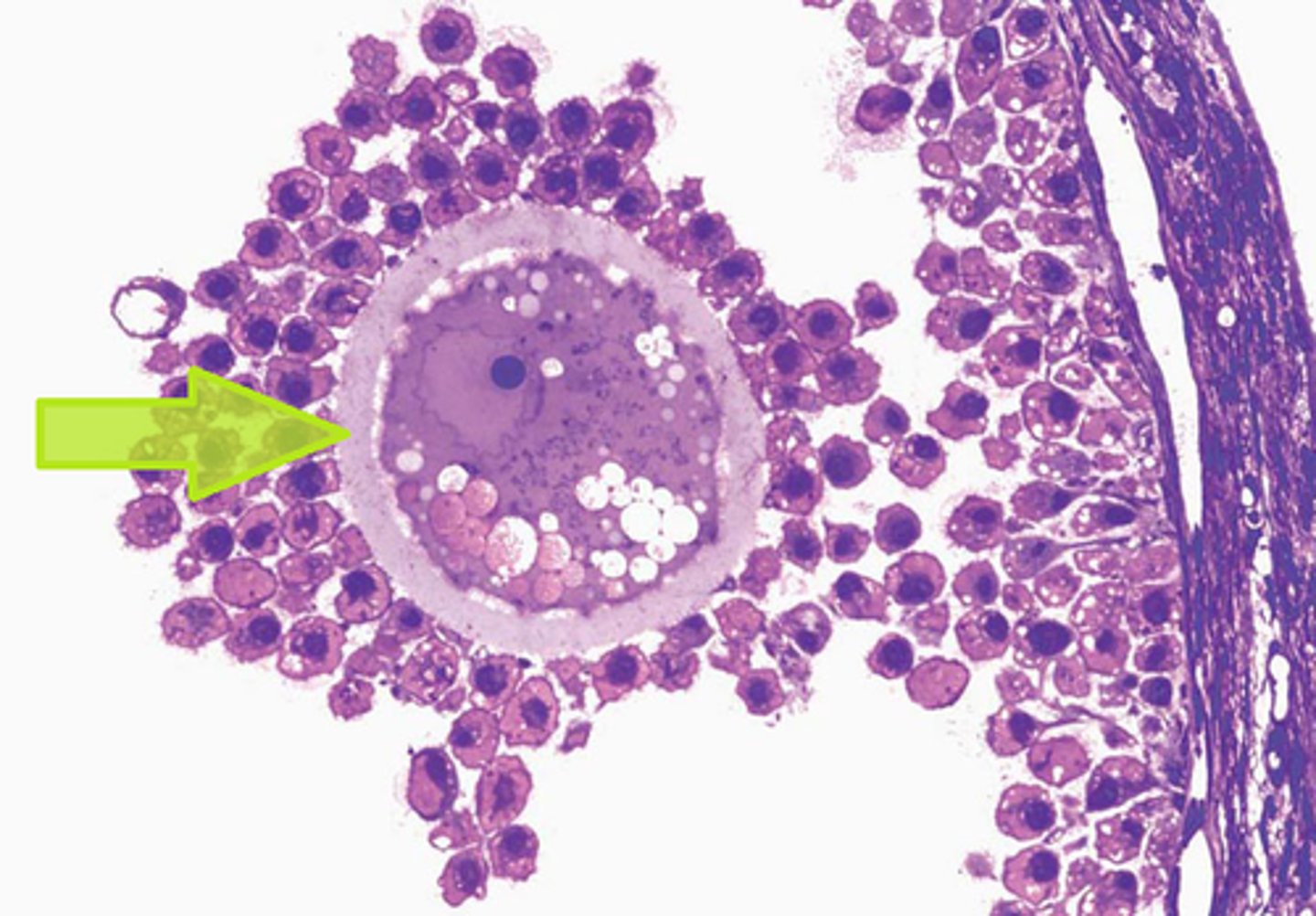
corona radiata
The layer of granulosa cells that surround an oocyte after is has been ovulated.
fimbriae
hairlike structures at the fallopian tube openings, create currents to propel the ovum into the fallopian tube.
3-4 days
how many days does the zygote travels from the ampulla of the fallopian tube to the uterus
morula stage
the zygote undergoes mitotic cell division with 16-50 undifferentiated cells.
blastocyst
A fluid-filled sphere formed about 5 days after fertilization of an ovum that is made up of an outer ring of cells and inner cell mass. This is the structure that implants in the endometrium of the uterus and differentiates into three germ layers.
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
3 primary germ layers of embryo
Ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, Adrenal Medulla, nerves, and outer layer of skin
Mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into Kidneys and Ureters, Reproductive System, Bone & Cartilage, Muscles, Vasculature, Lymphatics, Spleen Adrenal Cortex
Endoderm
the inner germ layer that develops into the lining of the digestive and respiratory systems, Liver, Bladder, and Urethra
trophoblast
The outer layer of cells that develops in the germinal period. These cells provide nutrition and support for the embryo. forms the placenta and other support structures.
corpus luteum
Endocrine tissue which produces hormones, estrogen, and progesterone which prepares the uterine lining for receiving an embryo
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
trophoblast absorbs nutrients from the endometrium and secretes what to maintain the corpus luteum
Cytotrophoblast (inner layer)
Proliferates upon implantation, forming primary chorionic villi used in early genetic testing (chorionic villus sampling).
Syncytiotrophoblast (outer layer)
Supports the cytotrophoblast and facilitates nutrient, waste, and gas exchange between maternal and fetal systems.
Implantation
contact between the growing structure and the uterine endometrium that occurs between 8-10 days after fertilization (or about 8 days after ovulation)
Decidua
specialized layer of endometrium that forms the base of the placental bed. most ideal site for implantation
prolactin, renin, corticotrophin releasing hormone (CRH), growth hormone, prostaglandin, oxytocin, and endothelin-1
hormones released by decidua
•Decidua vera or parietalis-
•Decidua basalis or placentalis
Decidua capsularis-
Layers of Decidua:
Decidua vera or parietalis
the remaining portion of the uterine lining
Decidua basalis or placentalis
forms the maternal portion of the placenta
Decidua capsularis
the layer which encloses the blastocysts after implantation
Chorionic villi
tiny projections of placental tissue that look like fingers and contain the same genetic material as the fetus. allow for the absorption of gases and nutrients from the maternal blood supply while eliminating fetal waste
Chorionic frondosum
villi at the embryonic pole in contact with decidua basalis. Later form the fetal side of the placenta
Chorion leave "bald chorion"
villi not involved with implantation that gradually degenerates, becoming thin and eventually forming the chorionic membrane
Fetal membrane
surrounds the fetus during pregnancy and is a thin tissue composed of two layers, the chorion and the amnion.
Chorion
among the vital membranes that form the amniotic sac. has tail-like structures (chorion villi) for providing extra protection to the embryo. facilitates the exchange of nutrients between the mother and child during the pregnancy period.
Amnion
contains a thin transparent fluid called amniotic fluid in which the embryo is suspended
Amniotic Fluid
acts as a cushion and protects the fetus from any mechanical jerks. It maintains even pressure and protects the fetus from damage. composed of 99% water and 1 % solid particle
ranges from 500-1200 ml averaging at 1000ml.
Amniotic Fluid volume range
7.00-7.25
Amniotic fluid pH
1.005-1.025
specific gravity of amniotic fluid
Amniotic Fluid
contains albumin, urea, uric acid, creatinine, lecithin sphingomyelin, bilirubin, minerals and suspended materials such as desquamated epithelial cells and vernix caseosa.
Umbilical Cord
originated from the yolk sac and umbilical vessels. connects the fetus to the placenta (carry oxygen and nutrients to the placenta and return oxygenated blood and fetal waste products to the placenta).
Wharton's jelly
gelatinous substance within the umbilical cord, largely made up of mucopolysaccharides to insulate and protect the umbilical cord
Thomas Wharton.
DIscovered Wharton's jelly
50-55 cm long and 2cm in diameter
length of the umbilical cord
350ml/min
rate of blood flow at term
Short cord
Intrapartum hemorrhage due to premature separation of the placenta
Delayed descent of the fetus during labor
Inversion of the uterus
Long cord
Cord presentation
Coiling of the cord around the neck
True knots of the cord
Placenta
A structure that allows an embryo to be nourished with the mother's blood supply. formed from the chorionic villi and decidua basalis. Temporary endocrine organ. Weighing approximately 500 grams at term with a diameter of 15-20cm and 3 cm thick.
700-900ml
Uteroplacental blood flow at term
cotyledons
attaches to the mothers uterine wall. This side is dark red in color and is made up of many lobes (15-20) which adheres to the uterus and connect with mother's circulation.
Zygote growth
development proceeds cephalo-caudal (head-to-tail) direction
Cardiovascular System
one of the 1st systems to become functional in intrauterine life.
single heart tube
forms as early as the 16th day of life and beat as early as 24th day.
6th or 7th week
Septum that divides the heart into chambers develop during
After 28th week
week when sympathetic nervous system matures, the heart rate stabilizes and a consistent heart rate of 110-160 beats/min
Fetal Circulation
fetus derives oxygen and excretes carbon dioxide not from gas exchange in the lungs but from exchange in the placenta
Foramen ovale
connects the left & right atrium, bypassing the lungs
fossa ovalis
remnant of foramen ovale of fetal heart
Umbilical vein
brings oxygenated blood coming from the placenta to the heart and liver
round ligament (ligamentum teres hepatis)
Remnant structure of umbilical vein
Umbilical arteries
carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta. Its obliterated portion will become umbilical ligaments
Ductus venosus
carry oxygenated blood from umbilical vein to inferior vena cava, bypassing the fetal liver
ligamentum venosum or Arantius ligament.
remnant of ductus venosus
Ductus arteriosus
carry oxygenated blood from pulmonary artery to aorta bypassing fetal lung.
ligamentum arteriosum
remnant of ductus arteriosus
Respiratory System
at 3rd week of intrauterine life, exist as a single tube along with the digestive tract
4th week
by the end of what week will a septum begin to divide the esophagus from the trachea.
24th week of pregnancy
Surfactant, a phospholipid substance, is formed and excreted by the alveolar cells of the lungs beginning approximately
lecithin & sphingomyelin
2 components of surfactant
2:1
35 weeks there is a surge in the production of lecithin, which then becomes the chief component by ratio of
8th week
Brain waves can be detected on electroencephalogram by what week
24 weeks
by what week is the ear capable of responding to sound, and the eyes exhibit a pupillary reaction, indicating sight is present
neural plate
3rd week, what becomes apparent? its top portion differentiates into the neural tube, which will form the CNS and the neural crest
Endocrine System
function begins along with neuro system development
6th week
by what week will the intestine become too large to be contained by the abdomen
32 weeks or weighs 1500 grams
swallowing and sucking reflex are not mature until about
meconium
by the 16th week, a collection of cellular wastes, bile, fats mucoprotein, mucopolysaccharides and portions of vernix caseosa, accumulates in the intestines. It is sticky in consistency and appears black or dark green
26 weeks
by what week does fetus begin to store brown fats to be utilized as a source of heat in the 1st hours after birth
36 weeks
at what week does GI secretes enzymes necessary for digestion of CHO, CHON
Fetal Liver
stores glycogen at week 9. Cannot synthesize coagulation factors because of lack of vitamin K
Pancreas
Originate from the foregut and is formed between 5th & 8th weeks.
12th week
Islets of Langerhans develop at what week
20 weeks
Fetus produces insulin beginning at what week
11th week
Fetus can be seen to move on ultrasonography as early as
12th week.
Ossification (natural process of bone formation) of the cartilage into bone begins at abou
4 weeks
at what week does a part of the mesoderm gives rise to the bones and muscles
13 weeks
skeleton begins to calcify at what week
8 weeks
Child's sex can be ascertained as early as __ by chromosomal analysis of fetal cells in the mother's blood stream
34-38 weeks of gestation
testes 1st form in the abdominal cavity and do not descend into the scrotal sac until
Urine
formed by the 12th week and is excreted into the amniotic fluid by the 16th week of gestation
500ml/day
At term, fetal urine is excreted at a rate of up to
oligohydramnios
too little amniotic fluid. Suggests fetal kidneys are not secreting adequate urine and that there is a kidney, ureter or bladder disorder
36 weeks
skin of fetus appears thin and almost translucent until subcutaneous fat begins to be deposited underneath it at about
vernix caseosa
important for lubrication and for keeping the skin from macerating in utero.
lanugo
Skin is covered by soft downy hairs that serve as insulation to preserve warmth in utero