EMC Unit 2
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
History of EMS, Ethics/Legalities, Anatomical Postitions, Anatomy/Quadrants
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What were people transported to the hospital in before ambulances?
Hearses
When did care begin before EMS?
once the Pt got to the hospital
What did we learn from that led to EMS change?
The wars (Korea, Vietnam, etc)
What did the Highway Safety Act of 1966 do for the EMS
Allowed the DOT (Department of Transportation) the ability to develop the EMS
What TV show led to the widespread paramedic units we have today?
Emergency!
How many paramedic units were in North America in 1972?
12
By 1977, how far away (in minutes) was the average American from an ambulance or paramedic unit?
10 minutes
What are the levels of Emergency Response Training from least to most in-depth/complex?
Emergency Medical Responder (EMR)
Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)
Advanced EMT (AEMT or AMT)
Paramedic
What is the Golden Hour?
The prime first hour when the Pt should receive care to have the best chance for survival
What are Standing Orders?
A set of protocols that do not require checking with a base doctor to enact
What is Standard of Care?
The expected care to be provided by EMT
What is Duty to Act?
Your legal obligation to provide care
What is Scope of Practice?
Actions/Care EMTs are legally allowed to perform (varies by state)
What should you do if the Pt is a child and the parent is refusing to allow you to help the Pt who is clearly in need of help and the adult seems altered or otherwise unable to make that decision?
Call the cops
When do you have Implied Consent?
If the patient is altered, unable to respond, or a minor without a guardian present
What should you make sure to do if a Pt refuses treatment?
Make sure they are of sound mind, understand the consequences, and DOCUMENT
What is a DNR?
Do Not Resuscitate order that can limit the amount of care that can be provided (NOTE: Each if different, so begin/continue care until it is consulted and can be abided by specifically)
What are the 4 obvious signs of death where and EMT can declare death?
Decapitation, rigor mortis (2-12 hours after death), decomposition, or lividity (blood pooling from the effects of gravity)
What is Anatomical Position?
Standing up facing forward with feet and palms facing front
What in an Anterior view?
From the front
What is a Posterior view?
From the back
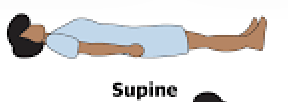
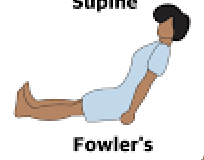
What does it mean to be Supine?
Laying on your back, stomach up
What does it mean to be Prone?
Laying on your stomach, back up
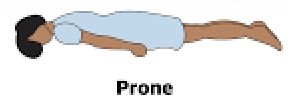
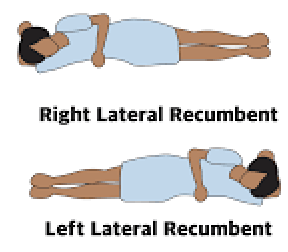
What is Recumbent Position?
Recovery Position: Laying on your side (right of left will be dictated in the name as applicable) with bottom arm reaching up under head, the other across body and bent to be palm on the floor and top leg bent at an angle to keep the body from rolling forward
What is Fowler’s Position?
Sitting with back elevated to 45-60 degrees from the ground/seat
What is Trendelenburg Position?
Laying on the back with legs elevated above the head

When should you use Fowler’s Position?
If the Pt is having difficulty breathing/chest pain or experiencing n/v
When would you not use Trendelenburg Position?
If the Pt has a suspected head/spine injury
What are the 5 parts of the spine in order from top to bottom including how many vertebrae are in each section
Cervical - 7
Thoracic - 12
Lumbar - 5
Sacrum - (fused) 5
Coccyx - (fused) 4
What is Mechanism of Injury?
The forces/factors that cause a traumatic injury
Using the blank diagram and the list of words, indicate where they are

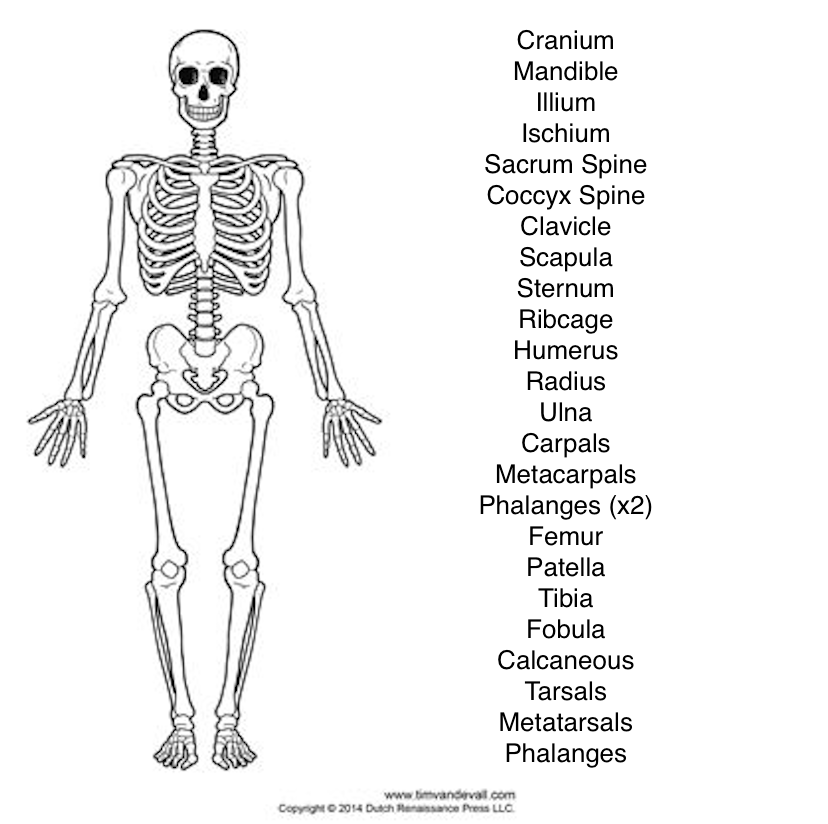
Using the blank diagram and the list of words, indicate where they are
See photo (Look at red ink as applicable and only those with a numbered box with the exception of the ischium)

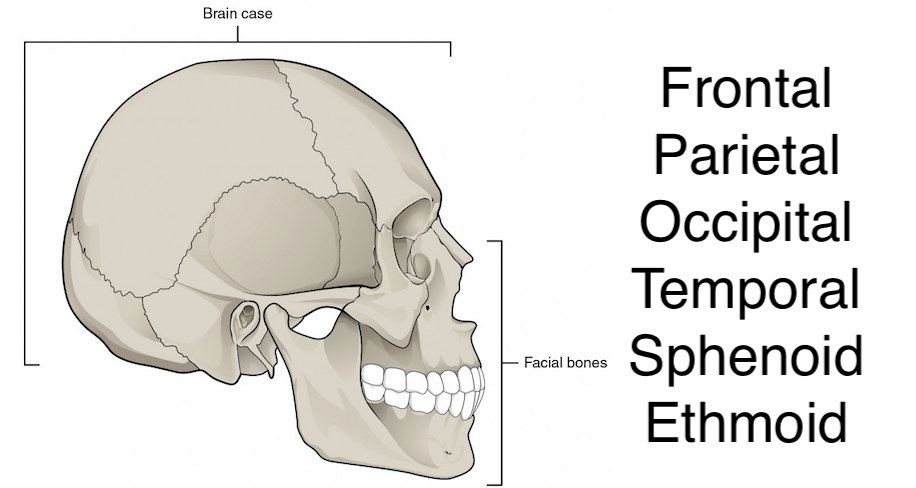
Using the blank diagram and the list of words, indicate where they are
See photo (Note the numbers in parenthesis that note how many parts there are in total, with the exception of the Ethmoid which has one)

What quadrant(s) is the liver in?
URQ & ULQ
What quadrant(s) is the gallbladder in?
URQ
What quadrant(s) is the bile duct in?
URQ
What quadrant(s) are the kidneys in?
URQ & ULQ
What quadrant(s) is the colon in?
Everywhere
What quadrant(s) is the small intestine in?
everywhere
What quadrant(s) is the pancreas in?
URQ
What quadrant(s) is the appendix in?
LRQ
What quadrant(s) is the uterus in?
LRQ & LLQ
What quadrant(s) is the bladder in?
LRQ & LLQ
What quadrant(s) are the ovaries in?
LRQ & LLQ
What quadrant(s) is the rectum in?
LRQ & LLQ
What quadrant(s) is the anus in?
LRQ & LLQ
What quadrant(s) is the spleen in?
ULQ
What quadrant(s) is the stomach in?
ULQ
What quadrant(s) is the diaphragm in?
URQ & ULQ
What us considered in the center of all of the quadrants and serves to divide the abdomen into four quadrantsq
the umbilicus (the belly button)