AP. Human Geo CH.1 Part 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:08 PM on 9/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
Abiotic
Composed of nonliving or inorganic matter.
2
New cards
Absolute location
Description of the position of a place in a way that never changes, such as geographic coordinates of latitude and longitude.
3
New cards
Acculturation
The process of changes in culture that result from the meeting of two groups, each of which retains distinct cultural features.
4
New cards
Assimilation
The process by which a group's cultural features are altered to resemble those of another group.
5
New cards
Atmosphere
The thin layer of gases surrounding Earth.
6
New cards
Behavioral geography
An approach to human geography that emphasizes the importance of understanding the psychological basis for individual human actions in space.
7
New cards
Biosphere
All living organisms on Earth, including plants and animals, as well as microorganisms.
8
New cards
Biotic
Composed of living organisms.
9
New cards
Cartogram
A map in which the projection and scale are distorted in order to convey the information of a variable.
10
New cards
Cartography
The science of making maps.
11
New cards
Choropleth map
A map in which areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the variable.
12
New cards
Citizen science
Scientific research by amateur scientists.
13
New cards
Climate
The long-term average weather condition at a particular location.
14
New cards
Concentration
The extent of a feature's spread over a given area.
15
New cards
Connection
The relationships among people and objects across the barrier of space.
16
New cards
Conservation
The sustainable management of a natural resource to meet human needs.
17
New cards
Contagious diffusion
The rapid, wide-spread diffusion of a feature or trend through-out a population.
18
New cards
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
Informally Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The time in the zone encompassing the prime meridian, or 00 longitude;
19
New cards
Cultural ecology
A geographic approach that emphasizes human-environment relationships.
20
New cards
Cultural Landscape
An approach to geography that emphasizes the relationships among social and physical phenomena in a particular study area.
21
New cards
Culture
The body of customary beliefs, mate-rial traits, and social forms that together constitutes the distinct tradition of a group of people.
22
New cards
Density
The frequency with which some-thing exists within a given unit of area.
23
New cards
Diffusion
The process by which a feature spreads from one place to another over time.
24
New cards
Distance decay
The diminished importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with increasing distance from its origin.
25
New cards
Distribution
The arrangement of something across Earth's surface.
26
New cards
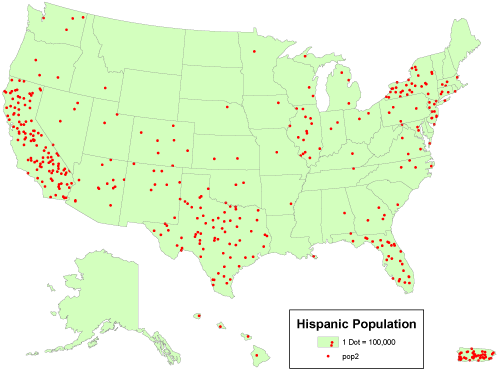
Dot distribution map
A map that depicts data that consists of discrete observations. Each dot represents a predetermined number of observations, which could be one or many.
27
New cards
Ecology
The scientific study of ecosystems.
28
New cards
Ecosystem
A group of Living organisms and the abiotic spheres with which they interact.
29
New cards
Environmental determinism
A nineteenth-and early twentieth-century approach to the study of geography which argued that the general laws sought by human geographers could be found in the physical sciences. Geography was therefore the study of how the physical environment caused human activities.
30
New cards
Expansion diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in an additive process.
31
New cards
Formal region (or uniform region)
An area in which most people share in one or more distinctive characteristics.
32
New cards
Functional region (or nodal region)
An area organized around a node or focal point.
33
New cards
Geographic information science (GIScience)
Analysis of data about Earth acquired through satellite and other electronic information technologies.
34
New cards
Geographic information system (GIS)
A computer system that captures, stores, queries, and displays geographic data.
35
New cards
Geotagging
Identification and storage of a piece of information by its precise latitude and longitude coordinates.
36
New cards
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that determines the precise position of some-thing on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
37
New cards
Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
38
New cards
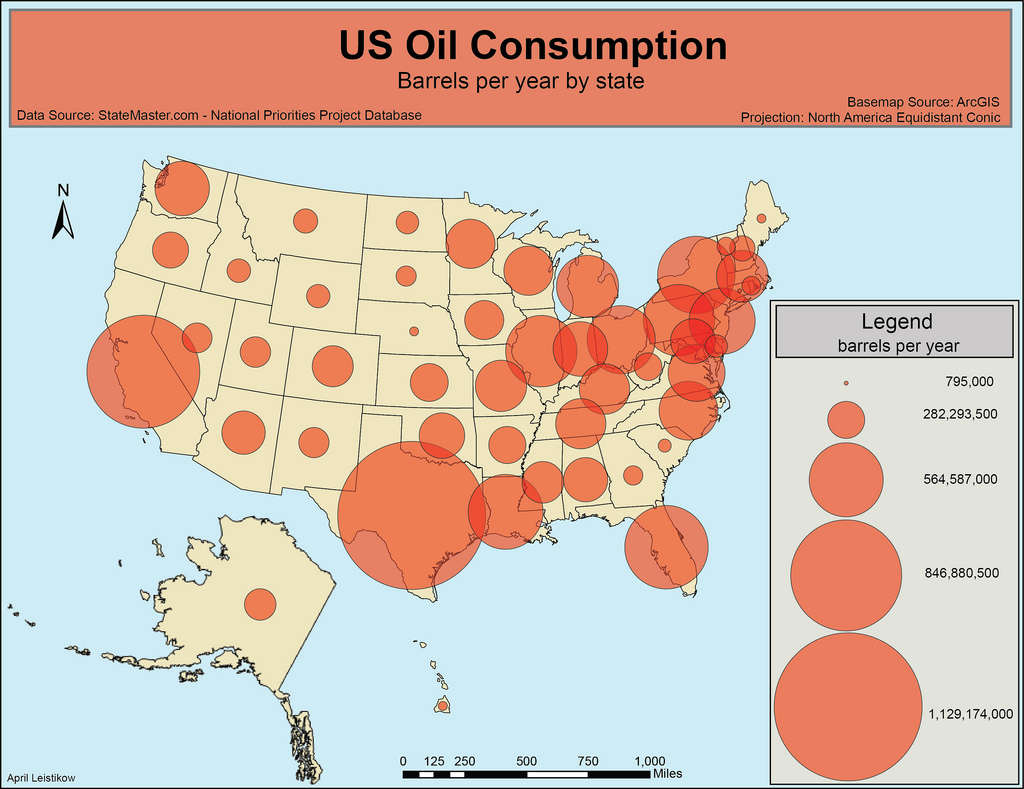
Graduated symbol map
A map that dis-plays symbols that change in size according to the value of the variable.
39
New cards
Hearth
A place from which an innovation originates.
40
New cards
Hierarchical diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places.
41
New cards
Humanistic geography
An approach to human geography that emphasizes the different ways that individuals form ideas about place and give those places symbolic meanings.
42
New cards
Hydrosphere
All of the water on and near Earth's surface.
43
New cards
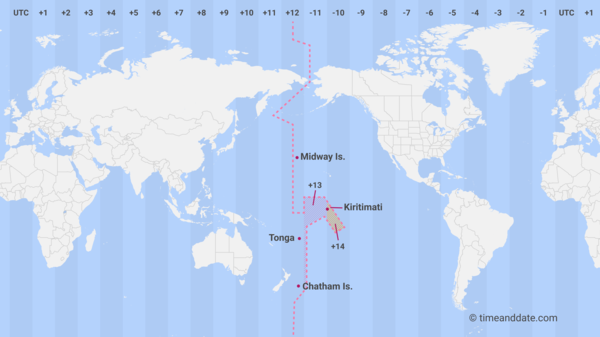
International Date Line
An arc that for the most part follows 180 longitude. When the International Date Line is crossed heading east (toward America), the clock moves back 24 hours, or one entire day. When it is crossed heading west (toward Asia), the calendar moves ahead one day.
44
New cards
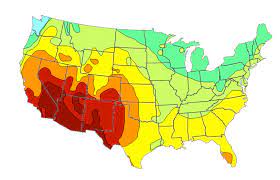
Isoline map
A map that connects places of a particular value by lines.
45
New cards
Latitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of parallels drawn on a globe and measuring distance north and south of the equator (00).
46
New cards
Lithosphere
Earth's crust and a portion of upper mantle directly below the crust.
47
New cards
Location
The position of anything on Earth's surface.
48
New cards
Longitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians drawn on a globe and measuring distance east and west of the prime meridian (00).