e. 2nd/3rd Tri Path P1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
which is the most common type of nonlethal fetal
a) Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type 2
b) Thanatophoric skeletal dysplasia
c) heterozygous achondroplasia
d) achronogenesis
c) heterozygous achondroplasia

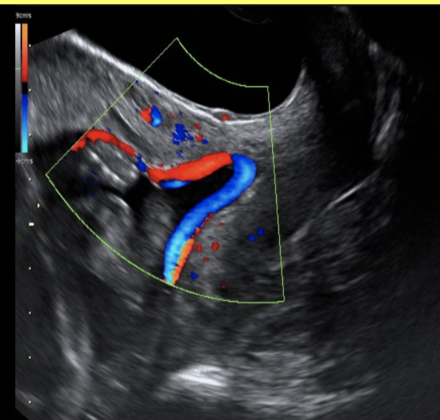
what are the expected US finding in vasa previa
.
a) the internal os is covered by a large blood clot caused by placenta abruption
b) the internal os is covered by the umbilical vessel attachment to a low lying or marginal placenta
c) the internal os is completely covered by the base of the placenta
d) placenta percreta where the endometrium has invaded the myometrium + serosa causing hemorrhage
b) the internal os is covered by the umbilical vessel attachment to a low lying or marginal placenta
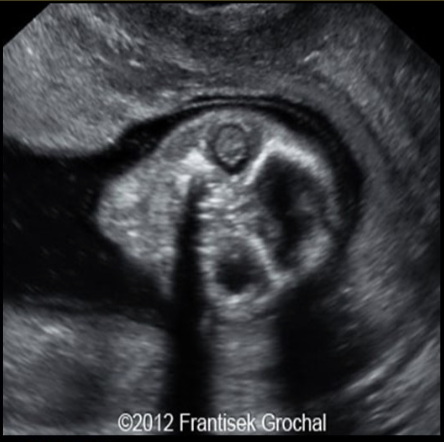
in the 2nd trimester, documenting a normal lens in each eye on the fetal US can rule out
.
the anechoic eye is the normal one
.
a) arhinia
b) holoprosencephaly
c) stigmatism
d) cataracts
d) cataracts

a maternal hx of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism will usually have what effect on the fetus
a) macrosomia, hepatomegaly
b) no effect
c) fetal demise
d) hydrops
.
transplacental passage of maternal thyroid-stimulating antibodies —> fetal hyperthyroidism, heart failure, IUGR, and hydrops fetalis
c) fetal demise

a trident hand is commonly seen w/which skeletal abn
.
a) heterozygous achondroplasia [dwarfism basically ]
b) spina bifida occulta
c) ostenogenesis imperfecta 2 [brittle bone disease]
d) spina bifida aperta
a) heterozygous achondroplasia
in twin to twin transfusion, the donor twin shows ___
.
in twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence, the donor twin shows ____
.
a) pleural effusion, ascites
b) growth restriction, hydrops
c) congestive heart failure, no cardiac structure
d) polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios
b) growth restriction, hydrops
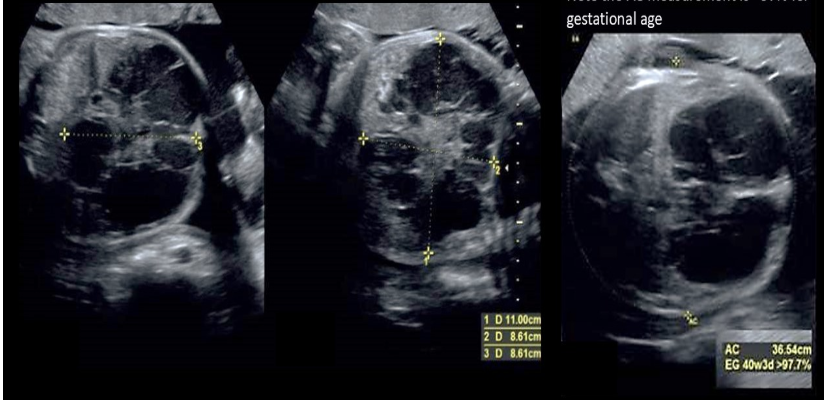
a pt has scan for 26w.
.
the head circumference, biparietal diameter, and femur length measure 25.5w.
.
the abd circumference measure 28.5w
.
a) asymmetric IUGR
b) hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
c) symmetric IUGR
d) hydrops
b) hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma

what about Dandy Walker malformation is true
.
a) DMW is more commonly an isolated finding w/o other defects
b) is frequently assoc w/agenesis of corpus callosum; malformation of the heart, face, limbs, and digits
c) a neonate w/DMW will usually develop normal intelligence + no long terms effects on brain function
d) DMW is caused by cystic dilation of the 3rd ventricle
b) is frequently assoc w/agenesis of corpus callosum; malformation of the heart, face, limbs, and digits

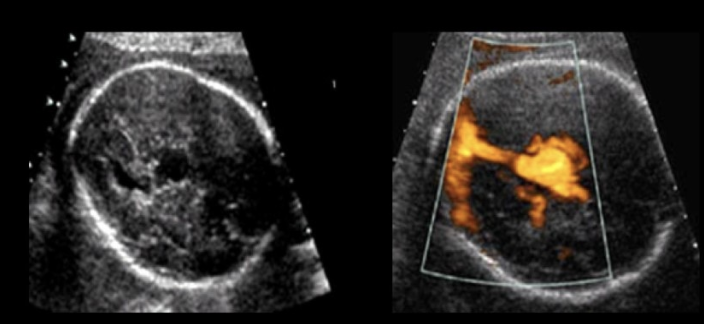
while evaluating the fetal brain of 27w, you see an anechoic space midline in the cerebrum.
.
the space appears to communicate w/an anechoic tubular structure coursing inferiorly. color doppler shows low velocity, swirling flow in the structures
.
a) vein of galen pseudoaneursym
b) aqueductal stenosis
c) dandy walker malformation
d) vein of galen aneurysm
d) vein of galen aneurysm

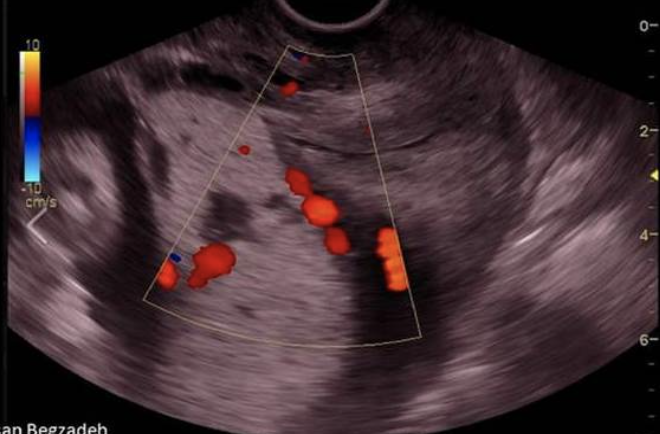
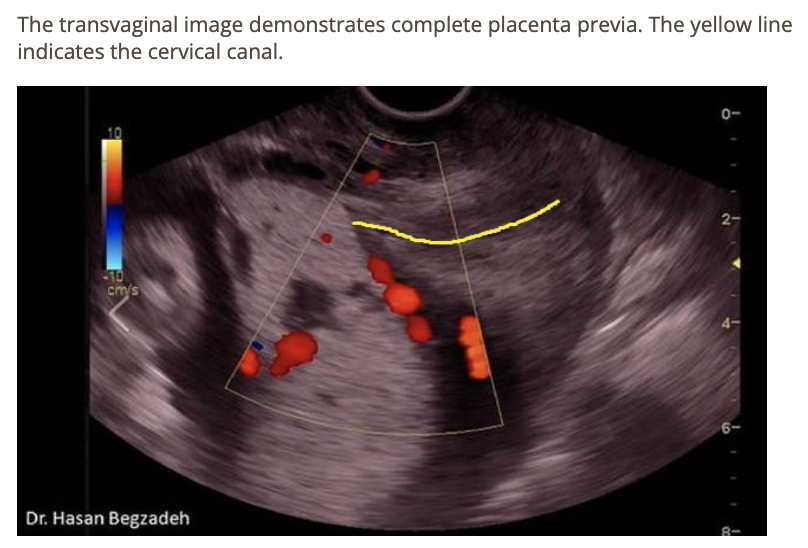
which describes the findings
a) there is large amount of meconium funneled toward the cervix
b) a chorioangioma has formed at the internal os
c) the maternal bladder is too full accurately
d) complete placenta previa
d) complete placenta previa
tetralogy of fallot consists of a group of 4 primary cardiac defects that include
right ventricular hypertrophy
VSD
pulmonary stenosis
and ___
.
a) small left ventricle
b) aortic coarctation
c) overriding AO
d) interrupted IVC
c) overriding AO
encephalocele + polydactyly + polycystic kidneys + microcephaly is noted. these findings are most suggestive of
.
a) trisomy 13
b) meckel gruber syndrome
c) trisomy 18
d) turner syndrome
b) meckel gruber syndrome

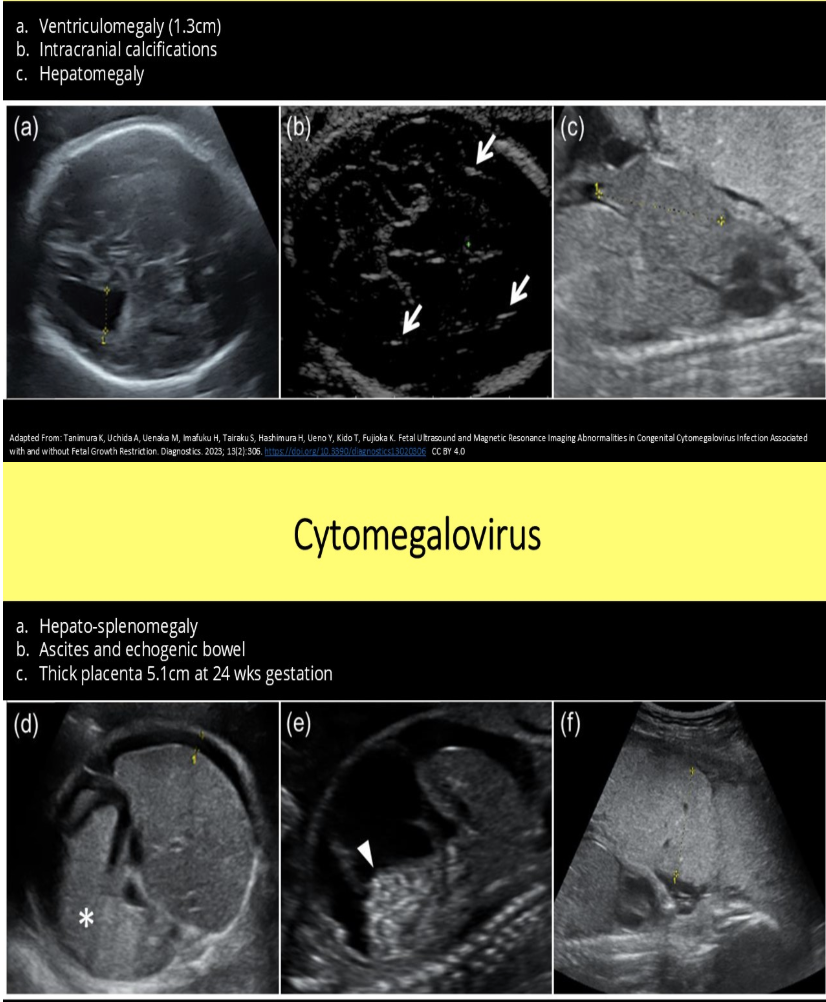
the most commonly reported intrauterine infection in pregnancy is
a) staphylococcus
b) cytomegalovirus
c) HIV
d) PID
b) cytomegalovirus
which is not considered a critical finding on a fetal US
a) placental abruption
b) circummarginate placenta
c) umbilical cord knot
d) cervical pregnancy
b) circummarginate placenta

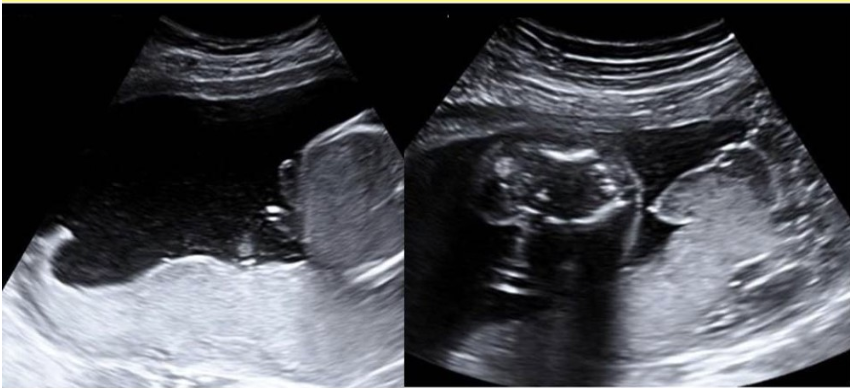
a circumvallate placenta
a) causes placental thickening assoc w/fetal hydrops
b) is caused by back folding of the placenta + fetal membranes toward the chorionic surface
c) is commonly assoc w/chromosomal anomalies
d) causes placental insufficiency + IUGR
b) is caused by back folding of the placenta + fetal membranes toward the chorionic surface

you are doing a follow-up limited scan because the stomach + kidneys at 15 weeks weren’t seen. on today’s exam, you see a single normal kidney but the stomach remains barely visible.
.
borderline polyhydramnios + rocker bottom feet is present.
.
the head measures 3 standard deviations lower than the abdomen and femoral measurements.
a) Ellis Van Creveld
b) trisomy 13 [pateau]
c) trisomy 18 [edward]
d) Noonan
c) trisomy 18

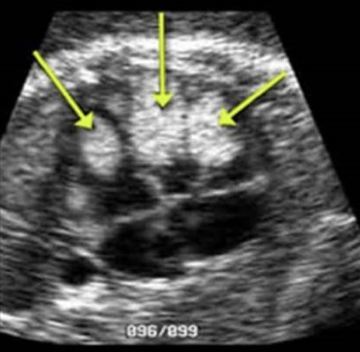
what are the arrows pointing to on this 4 chamber heart view
a) hypoplastic left heart
b) multiple echogenic intracardiac foci
c) rhabdomyoma
d) pulmonary sequestration
c) rhabdomyoma

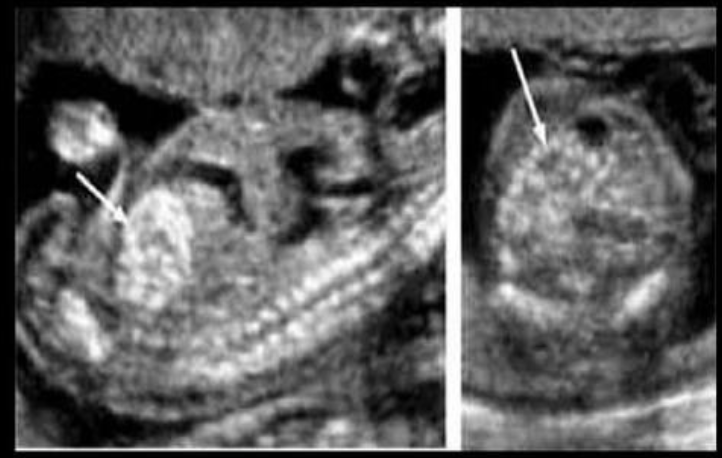
which is most commonly assoc w/echogenic fetal bowel
.
a) holt oram syndrome
b) noonan sydrome
c) trisomy 21
d) trisomy 13
c) trisomy 21

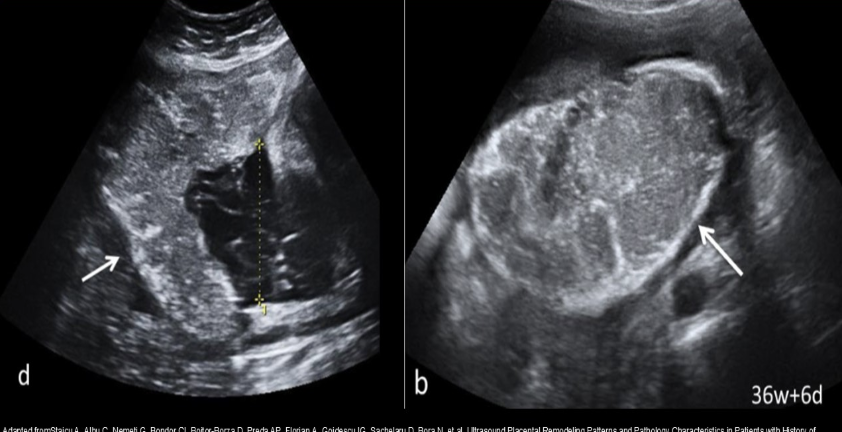
which placental grade shows the cotyledons on US exam
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
d) 3

which is true about sono appearance of fetal bowel
a) dilated bowel can be differentiated from a dilated ureter by identifying peristalsis in the bowel segment
b) as the fetus ages, the bowel becomes more hypoechoic
c) anal atresia will lead to inability to see the fetal bowel due to collapse + atrophy of digestive tract
d) fetal bowel is not normally seen until after 22 weeks
a) dilated bowel can be differentiated from a dilated ureter by identifying peristalsis in the bowel segment

which is not an expected post-partum complication
a) thrombosis/embolism
b) metritis
c) hemorrhage
d) gestational diabetes
d) gestational diabetes
which is least likely to be assoc w/placental abruption
a) placental lakes
b) cocaine use
c) fibroids
d) smoking
a) placental lakes

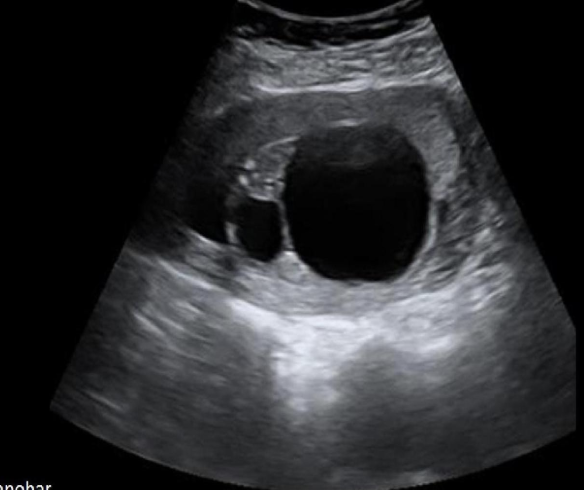
a) duodenal atresia
b) esophageal atresia
c) posterior urethral valves
d) UPJ obstruction
c) posterior urethral valves

which describes Asymmetric IUGR
.
a) the limbs are abn shortened w/relatively normal HC + AC
b) HC measures more than 2 standard deviations smaller than AC
c) AC measures more than 2 standard deviations smaller than HC
d) all parts of the fetus to be reduced in size by more than 2 standard deviations for current gestational age
c) AC measures more than 2 standard deviations smaller than HC
which is correct of fetal hydrops
a) Fetal ascites, scalp edema, and skin edema are common sono signs of fetal hydrops
b) If the fetal hydrops is caused by Rh Incompatibility, it is labeled as non-immune.
c) Immune hydrops can be caused by over 120 different diseases/abnormalities/congenital defects
d) Non-immune and immune fetal hydrops can be distinguished from one another by their very different sonographic appearance/characteristics.
a) Fetal ascites, scalp edema, and skin edema are common sono signs of fetal hydrops

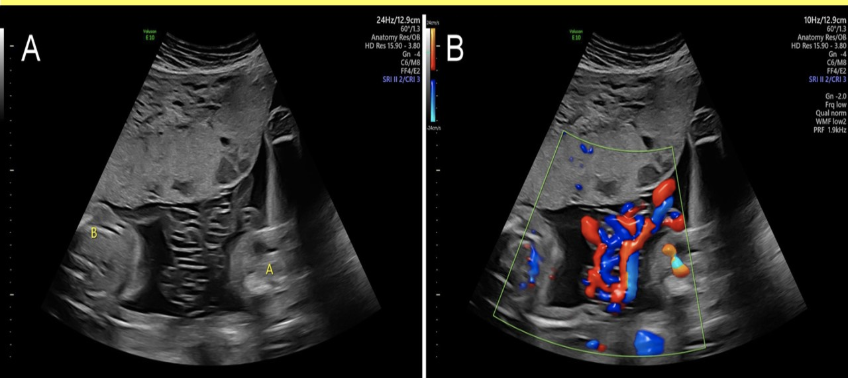
___ twins have the highest incidence of umbilical cord knotting
a) conjoined
b) monochorionic/diamniotic
c) monochorionic/monoamniotic
d) dichorionic/diamniotic
c) monochorionic/monoamniotic
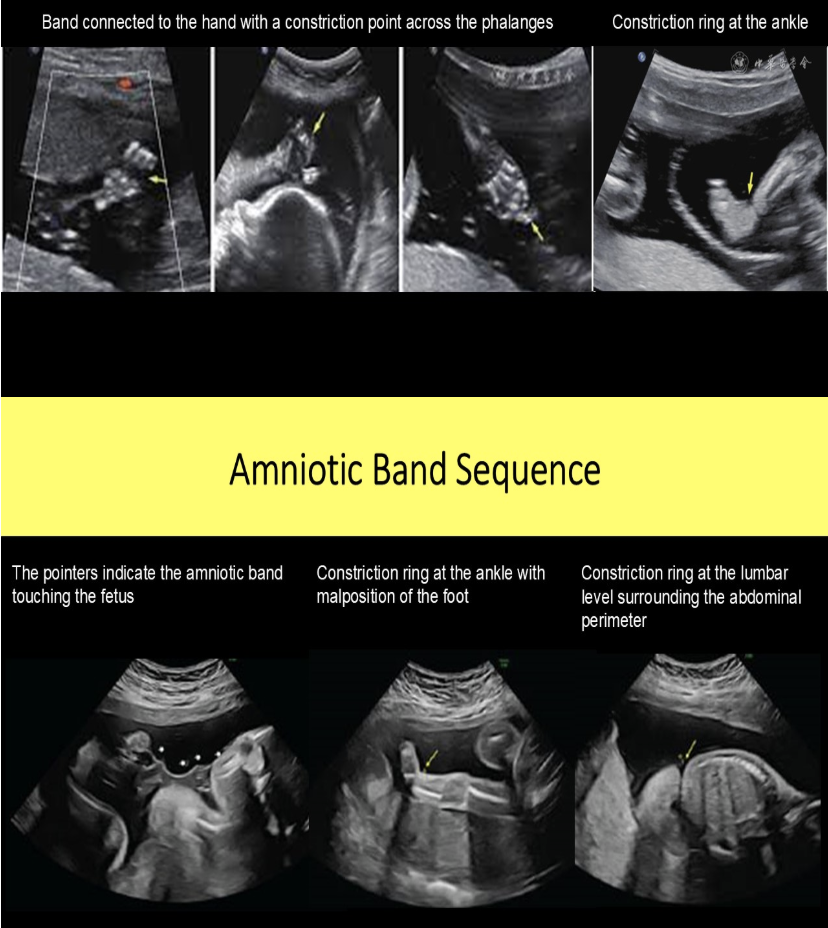
while performing a scan on a 21 week fetus, you see ectopia cordis, club foot, and asymmetric cleft lip/palate.
.
a) pentalogy of cantrell
b) amniotic band sequence
c) tetralogy of fallot
d) patau syndrome
b) amniotic band sequence
![<p>pt has her 1st US at 22w. a twin pregnancy w/1 placenta. fetus A shows increased C/T [<span>cardiothoracic</span>] ratio, mild pleural effusion, and anasarca. <strong>No cardiac activity can be identified in fetus B</strong>. there is no obvious cranial or cerebral structure</p><p>.</p><p>a) fetus A - hydrops, fetus b - triploidy</p><p>b) vanishing twin syndrome</p><p>c) twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence</p><p>d) dichorionic/diamniotic twins</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fbd920ad-1949-4d4a-9448-3a7a1985f5f7.png)
pt has her 1st US at 22w. a twin pregnancy w/1 placenta. fetus A shows increased C/T [cardiothoracic] ratio, mild pleural effusion, and anasarca. No cardiac activity can be identified in fetus B. there is no obvious cranial or cerebral structure
.
a) fetus A - hydrops, fetus b - triploidy
b) vanishing twin syndrome
c) twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence
d) dichorionic/diamniotic twins
c) twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence

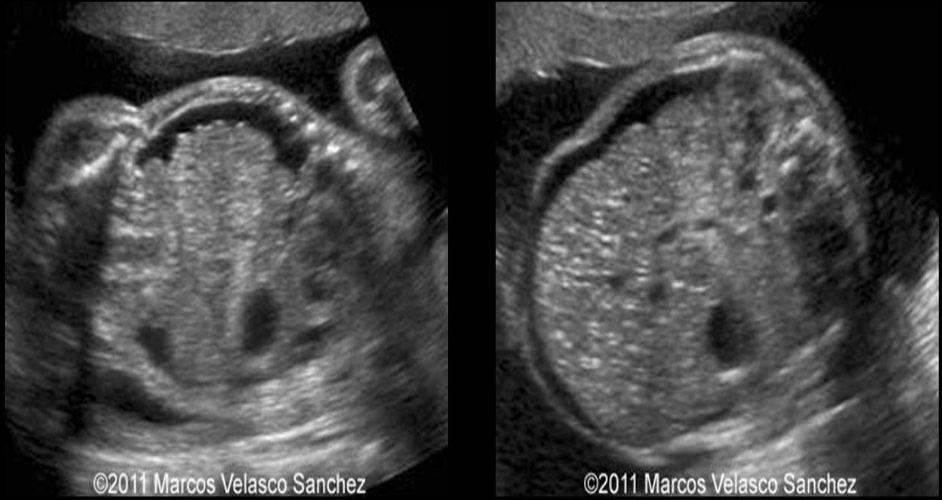
a) echogenic bowel
b) toxoplasmosis infection
c) mesenchymal hamartoma
d) omphalocele
b) toxoplasmosis infection

![<p>what is the most common cause for a shift of cardiac axis/position</p><p>a) diaphragmatic [bochdalek] hernia</p><p>b) ectopia cordis</p><p>c) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation</p><p>d) chromosomal anomalies</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2db53c30-a3cd-423d-aed9-1ed913758368.png)
what is the most common cause for a shift of cardiac axis/position
a) diaphragmatic [bochdalek] hernia
b) ectopia cordis
c) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
d) chromosomal anomalies
a) diaphragmatic hernia
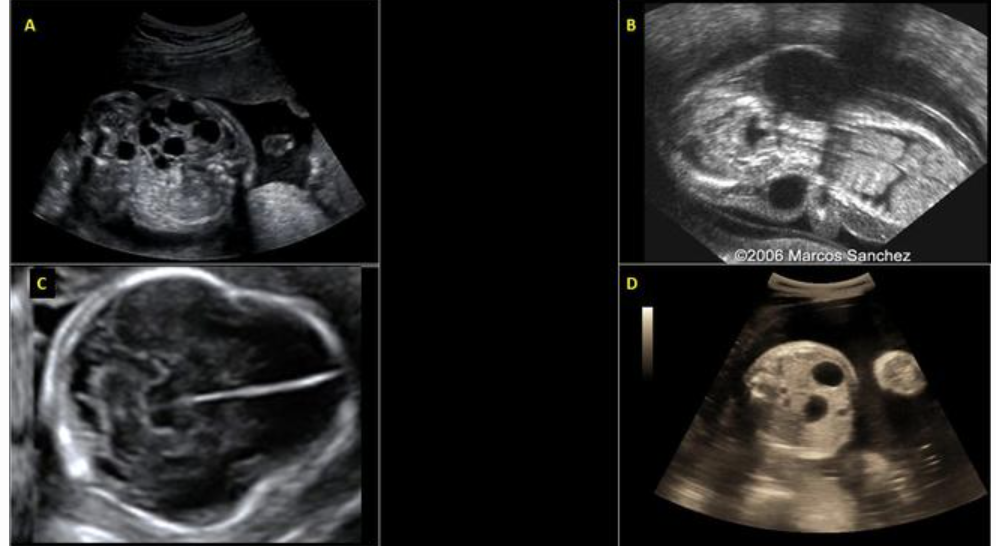
trisomy 21 is suspected. which image is suggestive of this?
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
d) D

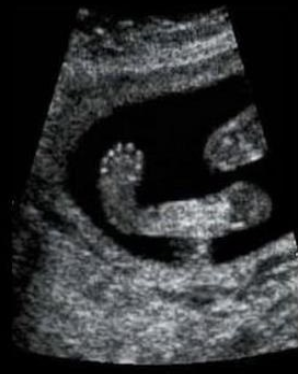
a) club foot + syndactyly
b) arthrogryposis + polydactyly
c) club foot + polydactyly
d) rocker bottom foot + polydactyly
c) club foot + polydactyly
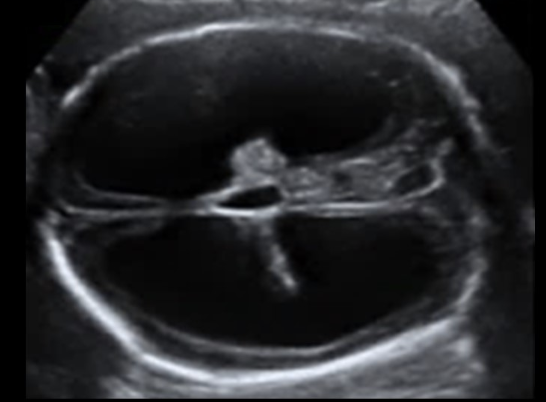
which is not a cause for this abn
a) anencephaly
b) aqueductal stenosis
c) chiari malformation
d) teratoma
a) anencephaly

which trisomy is commonly assoc w/radial ray anomalies
a) 13
b) 18
c) 21
d) 23
b) 18

severe chest + lung hypoplasia is suspected if the thoracic circumference is
.
a) <5th percentile
b) <15th percentile
c) <18th percentile
d) <25th percentile
a) <5th percentile
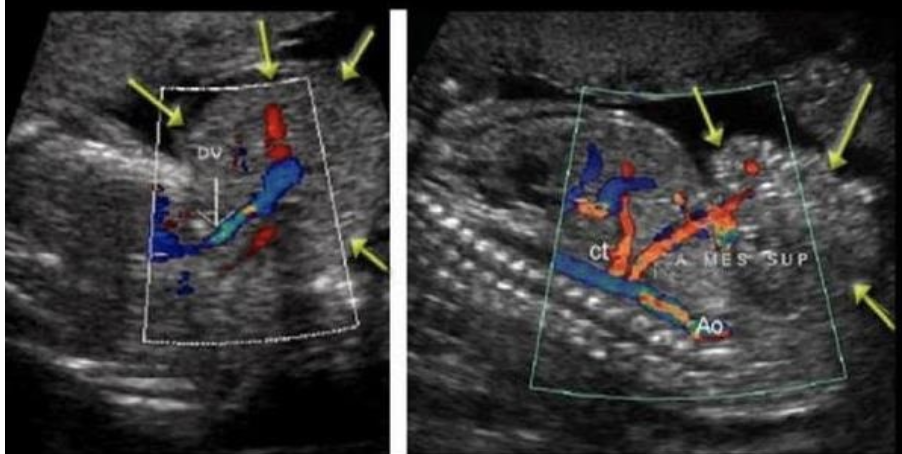
a solid mass is attached to the ventral wall of a 22w fetus.
.
there is NO abd wall or fetal skin covering the mass
.
but there’s abd vasculature shared between the fetus + the mass
.
a) parasitic conjoined twins
b) gastroschisis
c) omphalocele
d) prune belly syndrome
b) gastroschisis

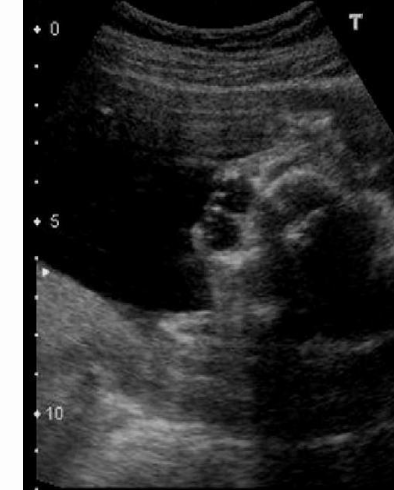
this is ___ which is a common finding in
a) cystic hygroma, monosomy x
b) hypertelorism, trisomy 21
c) cerebellar agenesis, dandy walker syndrome
d) hypotelorism, trisomy 13
d) hypotelorism, trisomy 13
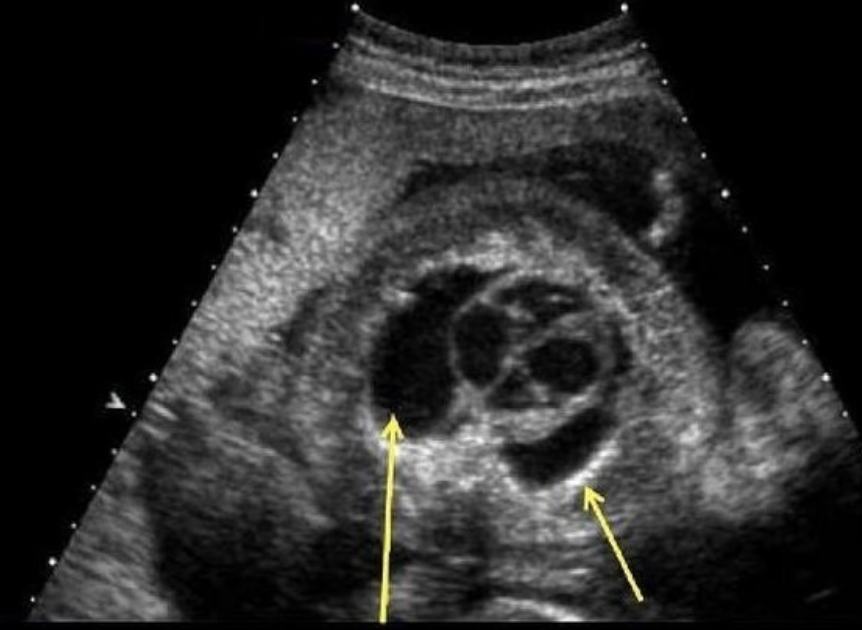
a) pericardiac effusion
b) pleural effusion
c) hydronephrosis
d) ascites
b) pleural effusion

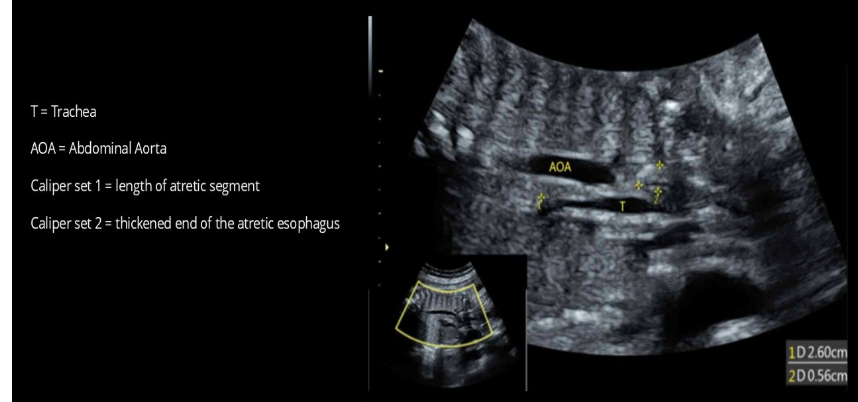
esophageal atresia is a significant indication for trisomy
a) 13
b) 18
c) 20
d) 21
b) 18

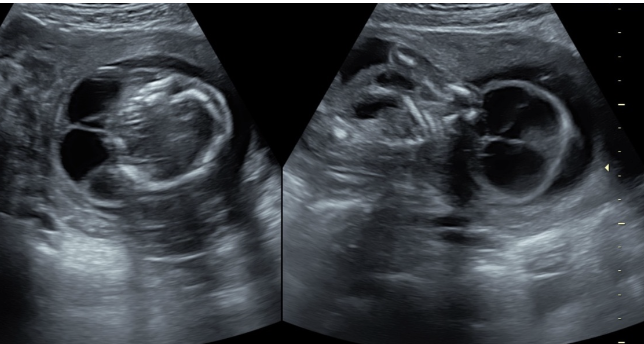
cystic hygroma = abnormal accumulation of lymphatic fluid under the skin
.
if an isolated cystic hygroma is present, AFP levels will be ____
.
if cystic hygroma is present w/Turner syndrome, AFP levels will be ___
.
a) decreased, increased
b) normal, decreased
c) normal, increased
d) increased, decreased
b) normal, decreased

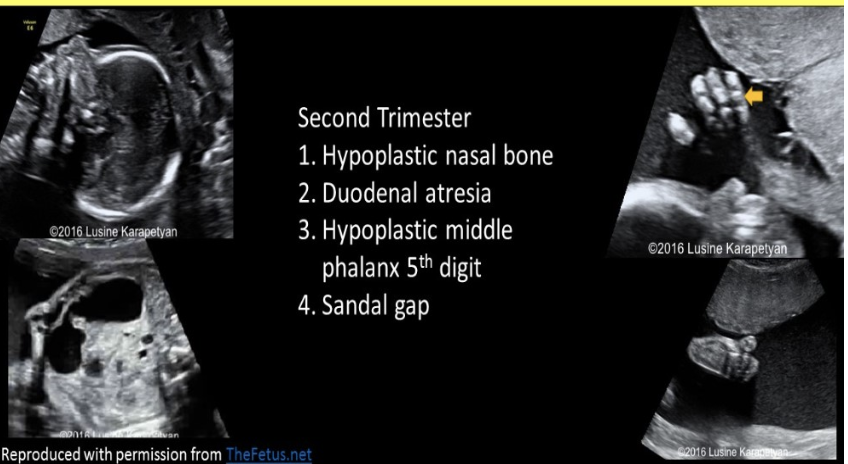
hypoplasia of the ___ is a soft marker of trisomy 21
a) distal phalanx of the 5th digit
b) middle phalanx of the 3rd digit
c) distal phalanx of the 3rd digit
d) middle phalanx of the 5th digit
d) middle phalanx of the 5th digit
![<p>a) holoprosencephaly [levels of cerebral agenesis]</p><p>b) lissencephaly [smooth brain]</p><p>c) iniencephaly [head retroflexion]</p><p>d) schizencephaly [split/cerebral brain]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a1ef6c90-6690-492a-938f-cb0e2056ade2.png)
a) holoprosencephaly [levels of cerebral agenesis]
b) lissencephaly [smooth brain]
c) iniencephaly [head retroflexion]
d) schizencephaly [split/cerebral brain]
d) schizencephaly

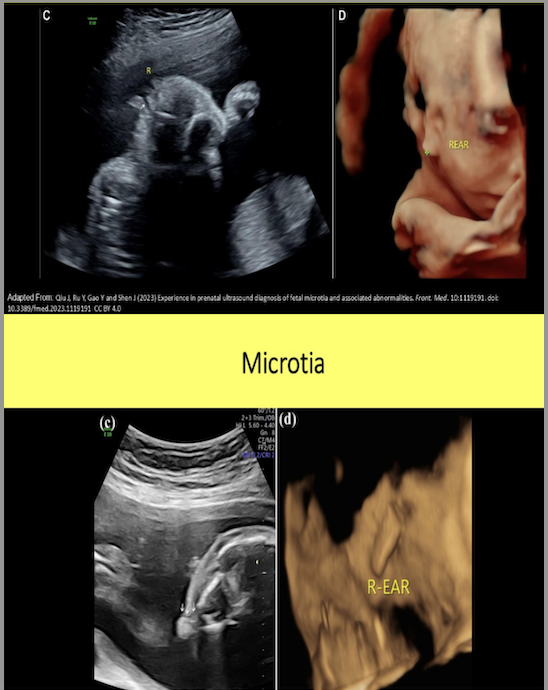
microtia (small lowset ears) is a strong indicator of
a) triploidy
b) trisomy 21
c) trisomy 18
d) turner syndrome
b) trisomy 21
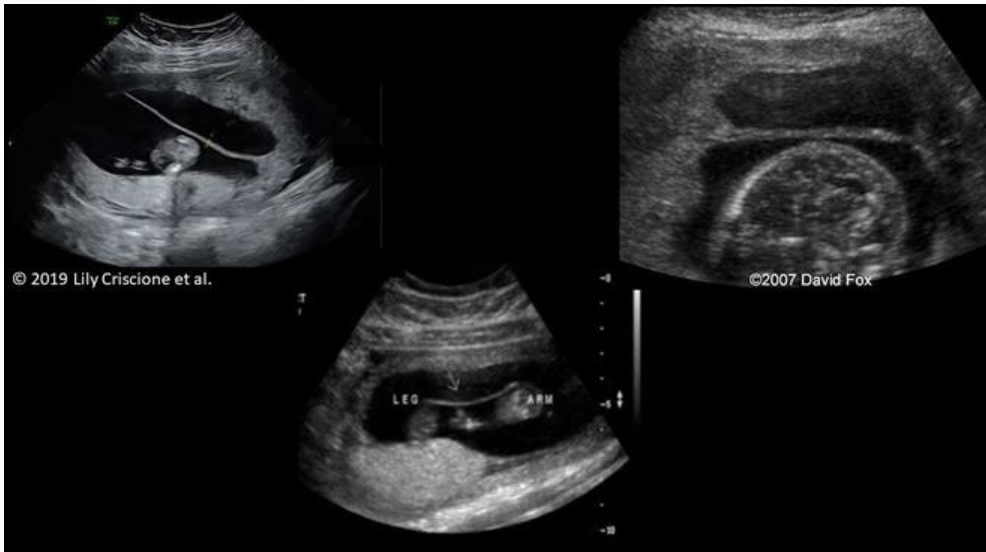
which is uterine synechia
a) top left
b) top right
c) bottom middle
b) top right

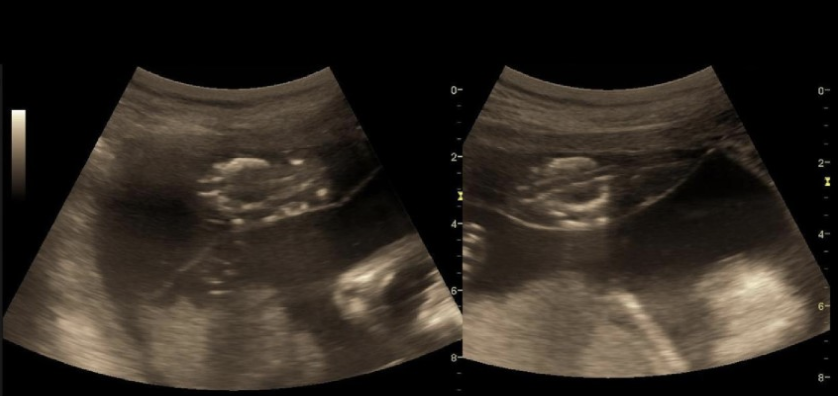
a monochorionic diamniotic twin pregnancy shows 2 female fetuses w/normal fetal heart rates.
.
fetus A is 25% larger than fetus B.
.
fetus A has polyhydramnios. fetus B has oligohydramnios
.
a) vanishing twin syndrome
b) molar twin pregnancy
c) twin reversed arterial perfusion sequence
d) twin to twin transfusion
d) twin to twin transfusion

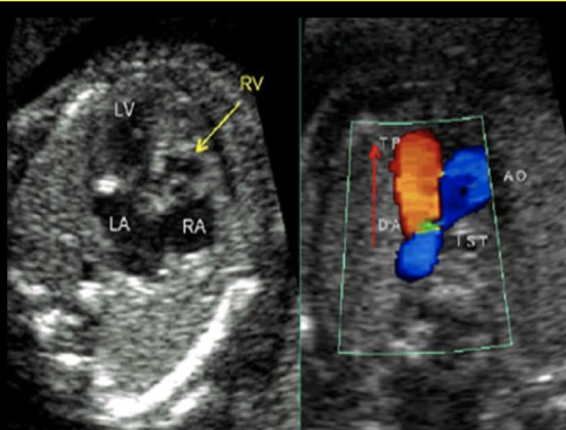
a small, undeveloped right ventricle, right atrium, and pulmonary artery are collectively referred to as
a) noonan syndrome
b) ebstein anomaly
c) double outlet right ventricle
d) hypoplastic right heart syndrome
d) hypoplastic right heart syndrome

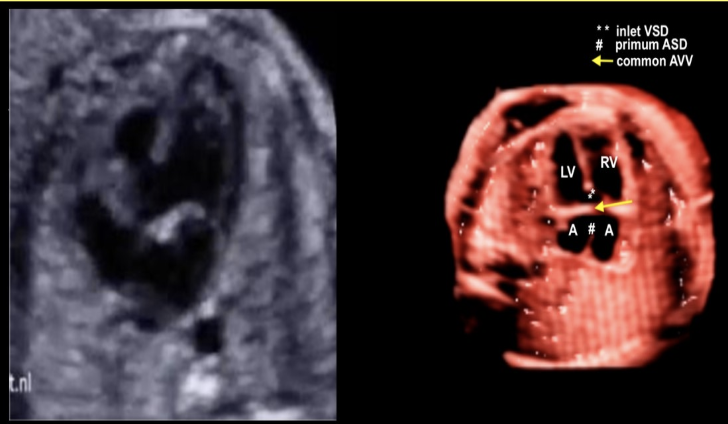
the most common cardiac defect seen w/trisomy 21
a) patent ductus arteriosus
b) ventricular septal defect
c) AV canal defect or AVSD
d) atrial septal defect
c) AV canal defect or AVSD

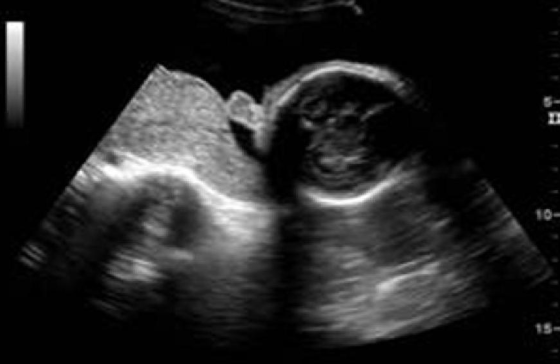
what intracranial anomaly is commonly assoc w/
a) holoprosencephaly
b) lissencephaly
c) dandy walker malformation
d) vein of galen aneurysm
a) holoprosencephaly

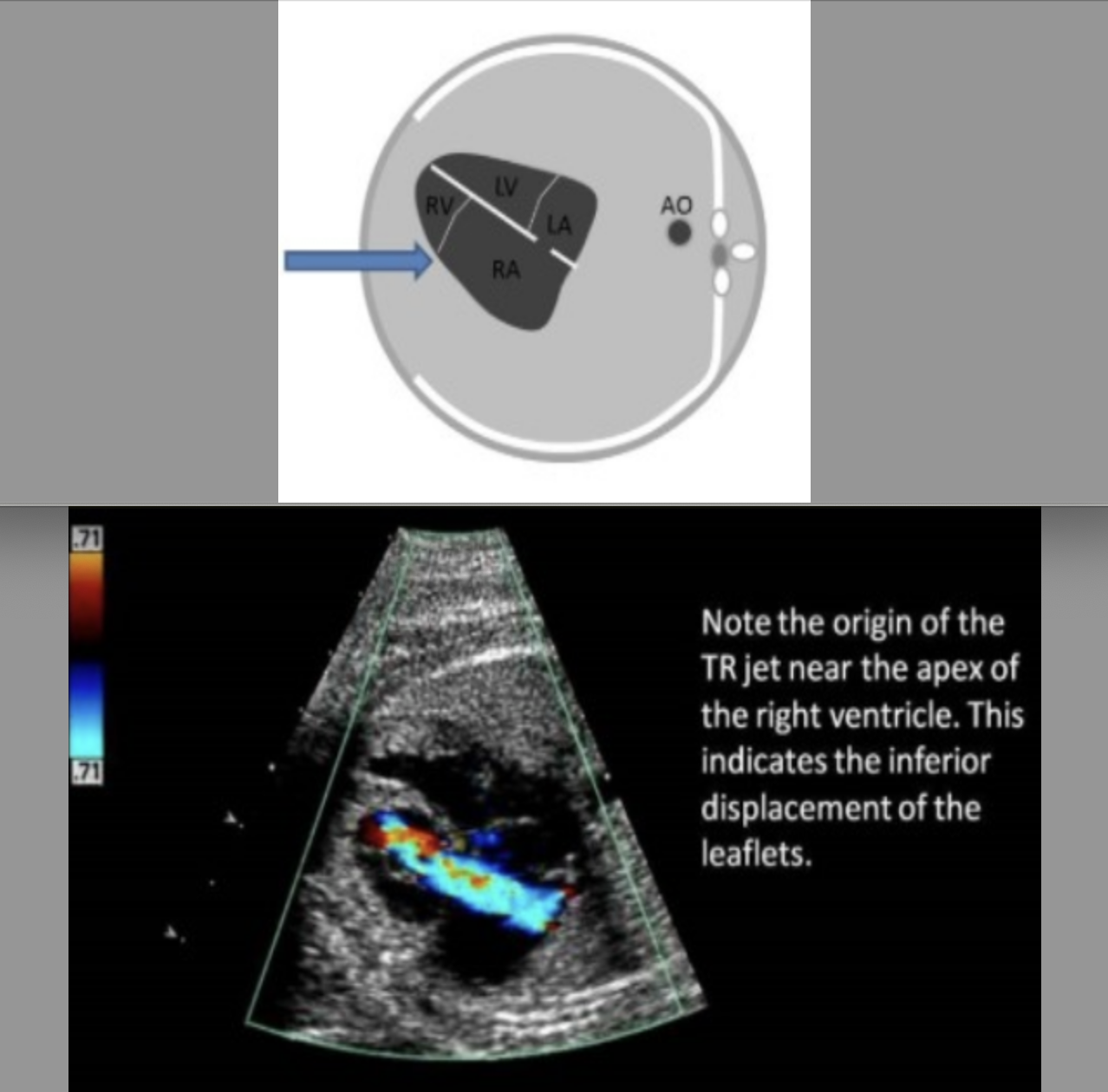
ebstein anomaly is
.
a) abn placement of tricuspid valve more inferiorly into the apex of right ventricle
b) abn placement of tricuspid valve more inferiorly into the apex of left ventricle
c) abn placement of the mitral + tricuspid valves more inferiorly into the apex of the ventricles
d) abn placement of the mitral valve more inferiorly into the apex of left ventricle
a) abn placement of tricuspid valve more inferiorly into the apex of right ventricle
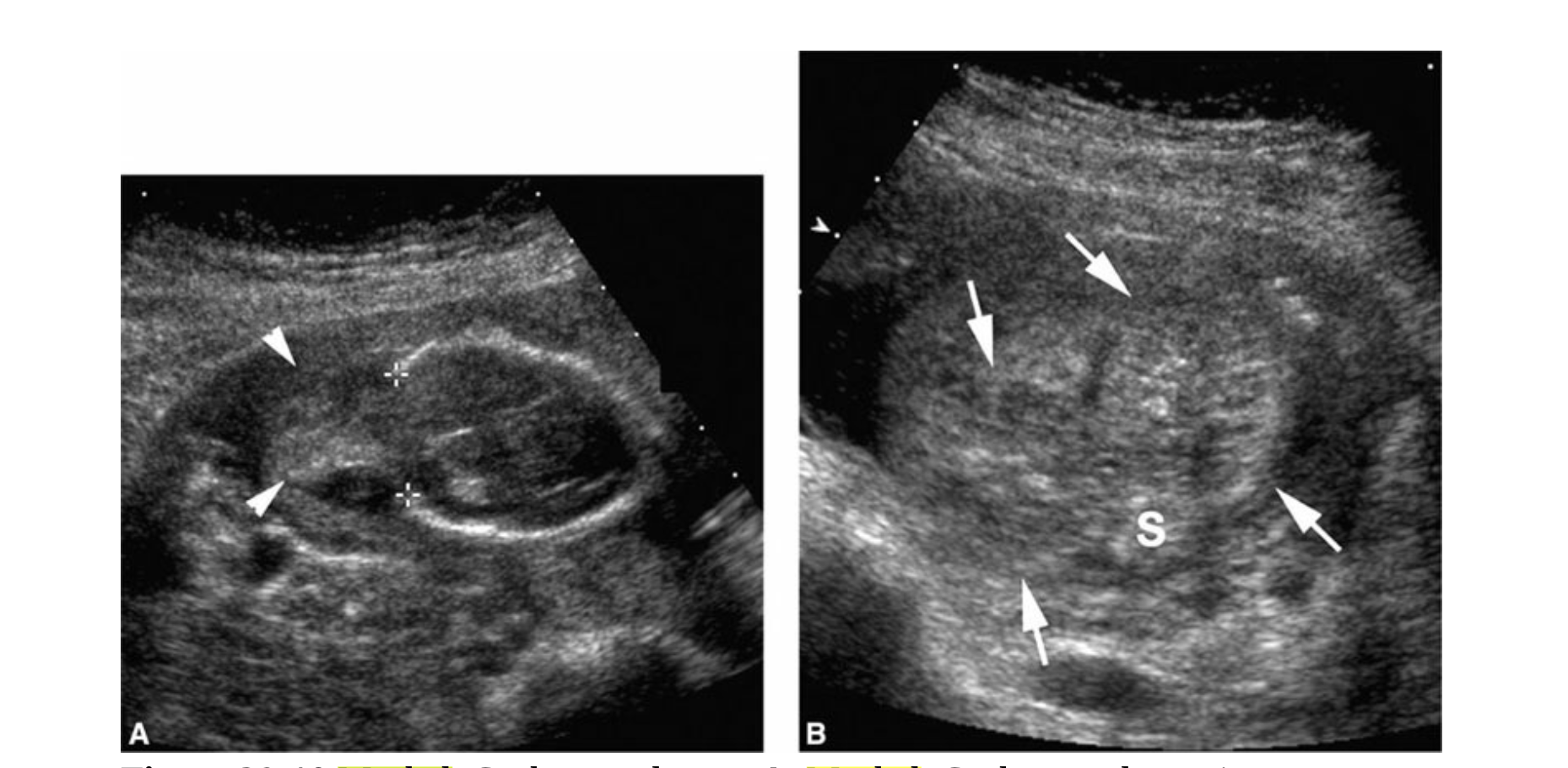
which syndrome is commonly assoc w/this renal abn on this coronal image
a) turner
b) down
c) edward
d) potter
d) potter

which is true regarding autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
a) requires 2 abn genes
b) occurs unilaterally
c) assoc w/early fetal demise
d) at least one parent has ADPKD
d) at least one parent has ADPKD

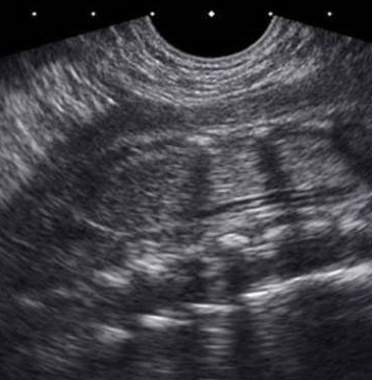
what is seen on this coronal view of thoracic + lumbar spine
a) normal lung tissue
b) enlarged echogenic kidney
c) renal agenesis
d) abn splaying of vertebral bodies
c) renal agenesis

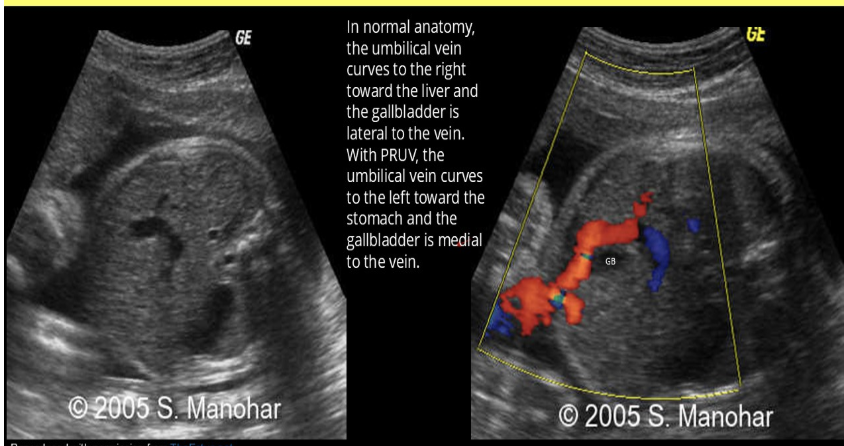
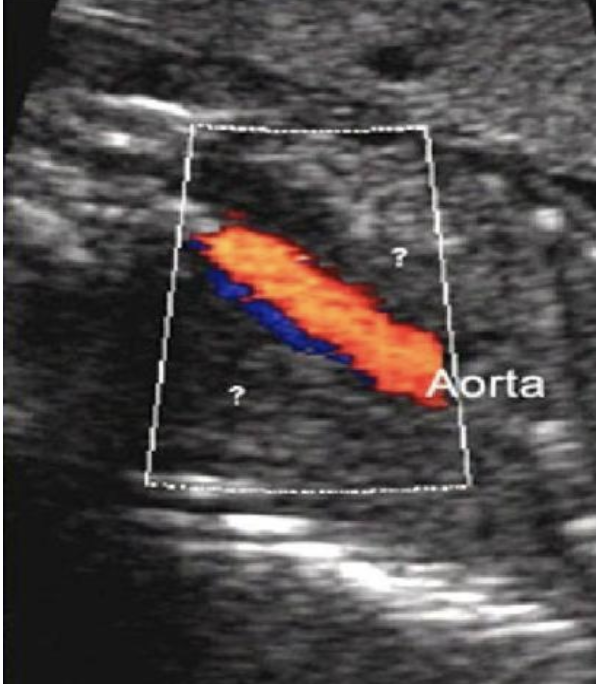
when evaluating the AC of a 30w fetus, you see
.
the umbilical vein curves to the left to the stomach + GB is medial to vein
.
AC + skin thickness measurements are normal
.
a) persistent right umbilical vein
b) absent ductus venosus
c) situs inversus
d) normal anatomy
a) persistent right umbilical vein

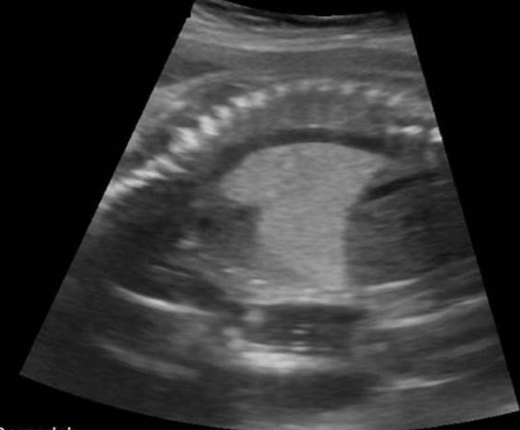
a) diaphragmatic hernia
b) normal lung tissue in 3rd trimester
c) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation type 2
d) Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation type 3
d) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation type 3

![<p>a pt comes in for 20w measuring 12 days behind where they should be according to their 1st trimester scan.</p><p>.</p><p>the cranial bones appear <strong>less echogenic</strong>. the humerus + femur appear <strong>slightly bowed</strong>. the small bones in the extremities are also somewhat difficult to identify due to <strong>decreased echogenicity</strong></p><p>.</p><p>a) achondroplasia [dwarfism basically]</p><p>b) thanatophoric dwarfism</p><p>c) IUGR</p><p>d) osteogenesis imperfecta [brittle bone disease]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fbe77660-bbe1-43f7-bb9b-bb1595684505.png)
a pt comes in for 20w measuring 12 days behind where they should be according to their 1st trimester scan.
.
the cranial bones appear less echogenic. the humerus + femur appear slightly bowed. the small bones in the extremities are also somewhat difficult to identify due to decreased echogenicity
.
a) achondroplasia [dwarfism basically]
b) thanatophoric dwarfism
c) IUGR
d) osteogenesis imperfecta [brittle bone disease]
d) osteogenesis imperfecta

polyhydramnios is dx when the 4 quadrant fluid level is greater than xxx or greater than 8cm in a single pocket
.
a) 15cm
b) 28cm
c) 12cm
d) 25cm
d) 25cm

![<p>a pt at 20w for suspected <strong>Eagle Barrett syndrome </strong>[prune belly] which fetal structure should be closely evaluated</p><p>a) kidneys + bladder</p><p>b) amniotic bands</p><p>c) fetal brain</p><p>d) stomach + bowel</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/603eecc9-1982-4885-b55e-96765a8690ec.png)
a pt at 20w for suspected Eagle Barrett syndrome [prune belly] which fetal structure should be closely evaluated
a) kidneys + bladder
b) amniotic bands
c) fetal brain
d) stomach + bowel
a) kidneys + bladder

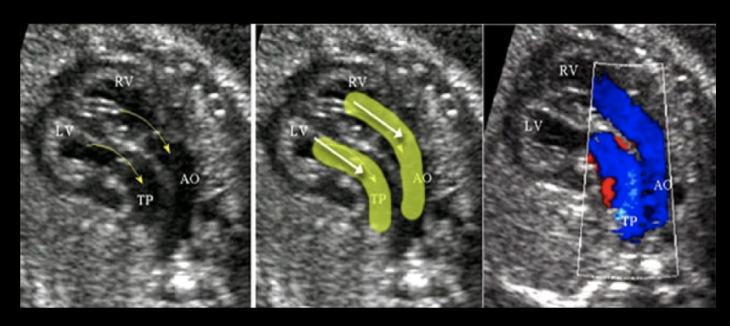
if the LVOT + RVOT are parallel as they exit the fetal heart
a) complete transposition of the great vessels
b) truncus arteriosus
c) tetralogy of fallot
d) normal cardiac outflow anatomy
a) complete transposition of the great vessels

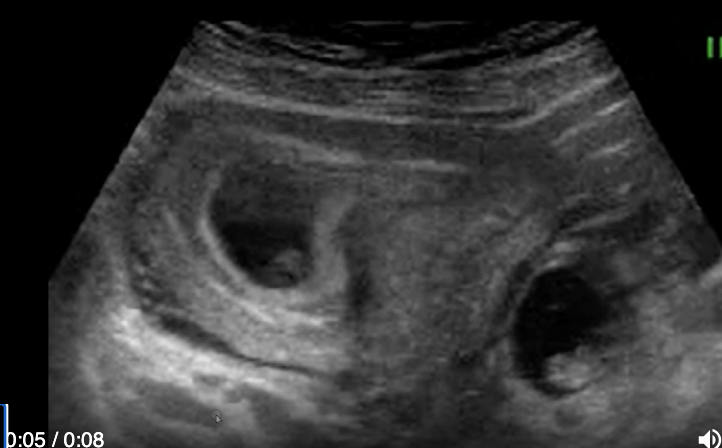
a pt has higher than expected bHCG. her LMP was 8 weeks ago
a) normal twin pregnancy
b) heterotopic pregnancy
c) twin pregnancy in bicornuate uterus
d) twin pregnancy in septate uterus
b) heterotopic pregnancy

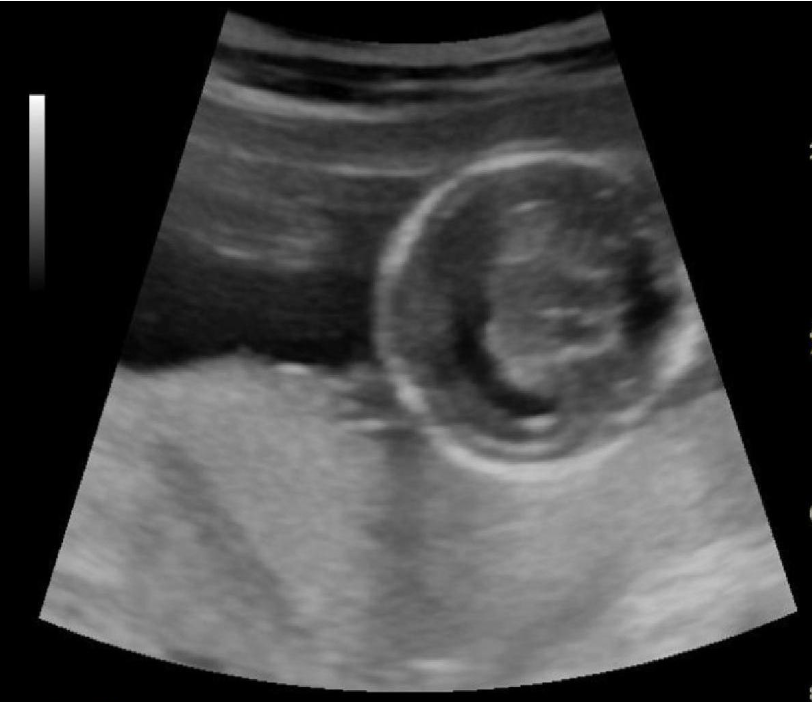
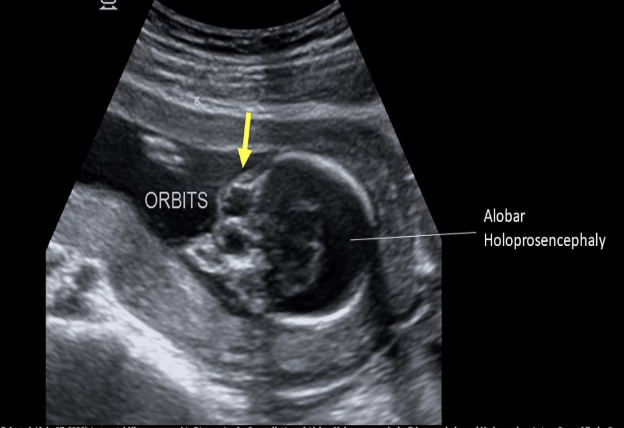
____ is displayed and it’s a common finding
a) aqueductal stenosis, trisomy 21
b) alobar holoprosencephaly, trisomy 13
c) dandy walker malformation, spina bifida
d) lobar holoprosencephaly, monosomy x
b) alobar holoprosencephaly, trisomy 13

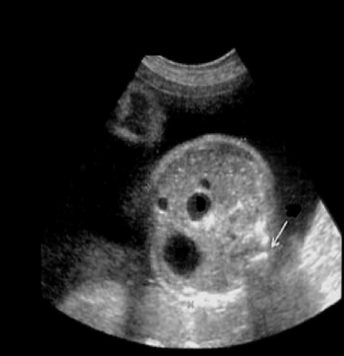
all could cause this expect
a) anal atresia
b) esophageal atresia
c) duodenal atresia
d) mesenteric mass
b) esophageal atresia

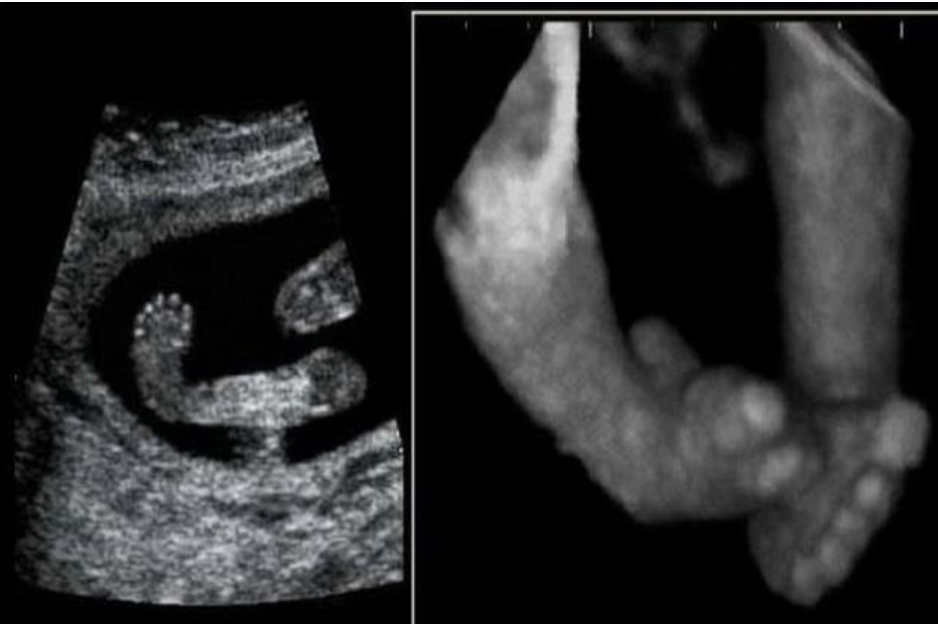
what fetal anomaly is this
a) syndactyly
b) club foot
c) rocker foot bottom
d) clinodactyly
b) club foot

![<p>a) no cavum septum pellucidum</p><p>b) acrania</p><p>c) encephalocele [herniation of intracranial contents through (occipital) skull opening ]</p><p>d) anencephaly</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e0faa964-be06-46aa-b232-34729262b0c1.png)
a) no cavum septum pellucidum
b) acrania
c) encephalocele [herniation of intracranial contents through (occipital) skull opening ]
d) anencephaly
d) anencephaly

what is the most commonly identified fetal chest mass
a) diaphragmatic hernia
b) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
c) pulmonary sequestration
d) cardiac sarcoma
b) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation

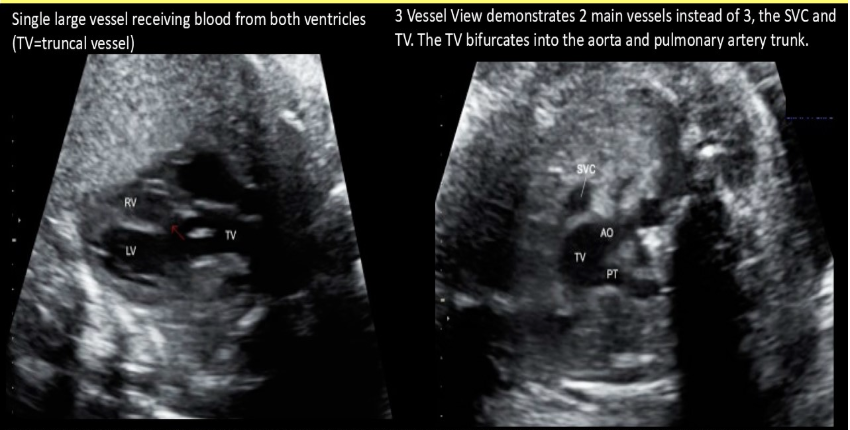
you’re scanning a 28w fetal heart. a single large trunk vessel exits the heart + pulmonary artery appears to branch from it instead of from the right ventricle
.
a) truncus arteriosus
b) total anomalous pulmonary venous return
c) partial anomalous pulmonary venous return
d) double outlet left ventricle
a) truncus arteriosus

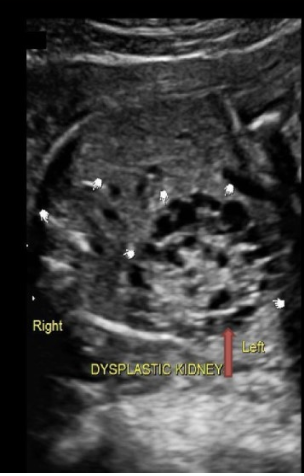
which characteristics indicates multicystic kidney disease
.
a) multiple communicating cysts that connect to a dilated ureter
b) multiple noncommunicating cysts that DO NOT connect to a dilated ureter
c) multiple microcysts that cause increased echogenicity of the kidney
d) multiple cysts that replace the renal sinus w/normal renal cortex
b) multiple noncommunicating cysts that do not connect to a dilated ureter

![<p>what is <strong>anasarca</strong> [skin edema >5mm] commonly seen with</p><p>.</p><p>a) achondrogenesis</p><p>b) IUGR</p><p>c) fetal hydrops</p><p>d) thanatophoric dwarfism</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/55cdebad-60e6-4598-bd82-c7e18cb4da56.png)
what is anasarca [skin edema >5mm] commonly seen with
.
a) achondrogenesis
b) IUGR
c) fetal hydrops
d) thanatophoric dwarfism
c) fetal hydrops

which skeletal anomalies usually occurs as an isolated finding
a) rhizomelia
b) phocomelia
c) arthrogryposis
d) talipes equinovarus [club foot]
d) talipes equinovarus

![<p>an <strong>encephalocele [</strong>Herniation of intracranial contents through **occipital opening in skull<strong>] </strong>can be easily be mistaken for</p><p>. assoc w/Meckel Gruber </p><p>. </p><p>a) gastroschisis</p><p>b) porencephaly</p><p>c) epignathus</p><p>d) cystic hygroma [Abn accum of lymphatic fluid under the skin]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/467556e5-7b45-4549-8ef1-e2170448b764.png)
an encephalocele [Herniation of intracranial contents through **occipital opening in skull] can be easily be mistaken for
. assoc w/Meckel Gruber
.
a) gastroschisis
b) porencephaly
c) epignathus
d) cystic hygroma [Abn accum of lymphatic fluid under the skin]
d) cystic hygroma

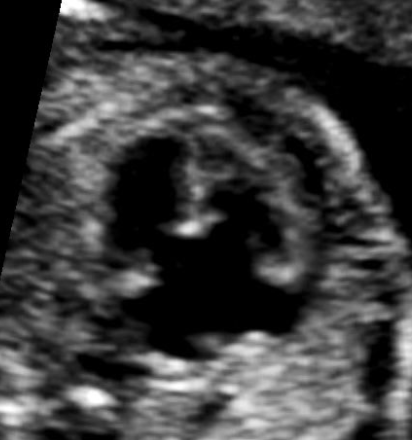
the findings are
a) hypoplasia left heart
b) normal 4 chamber heart
c) atrioventricular septal defect
d) tetralogy of fallot
c) atrioventricular septal defect

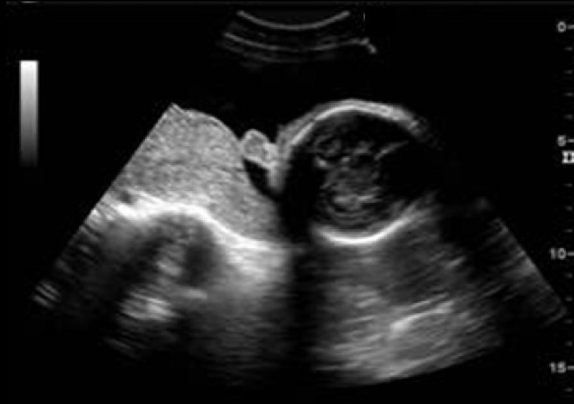
a) frontal bossing
b) normal fetal profile
c) micrognathia
d) proboscis
d) proboscis


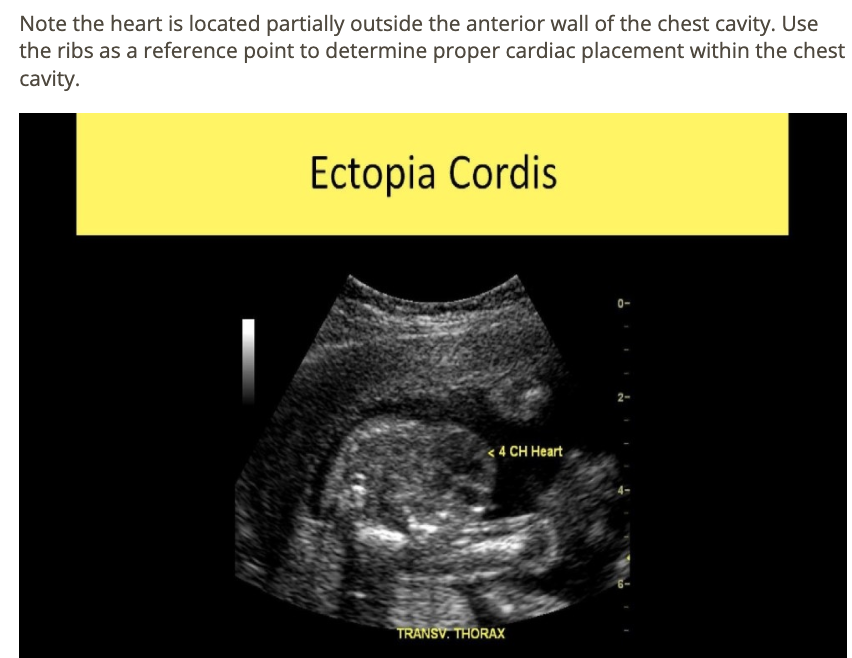
a) gastroschisis
b) ectopia cordis
c) normal heart w/oblique view of thorax
d) omphalocele
b) ectopia cordis
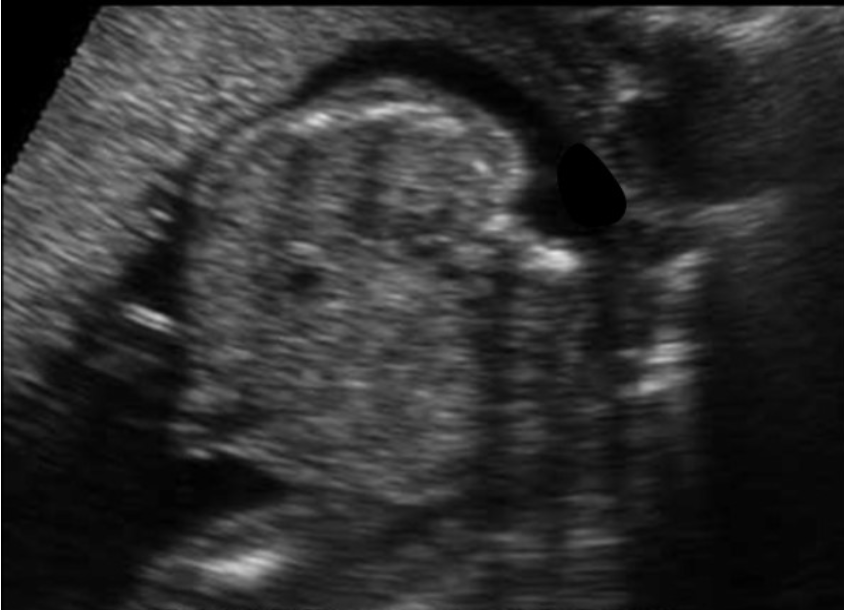
a) there are no kidneys identified on either side of the normal lumbar spine
b) there are 2 normal kidneys seen but there is cystic hygroma too
c) there are normal kidneys seen on either side of normal lumbar spine
d) there are 2 normal kidneys but spina bifida too
d) there are 2 normal kidneys but spina bifida too
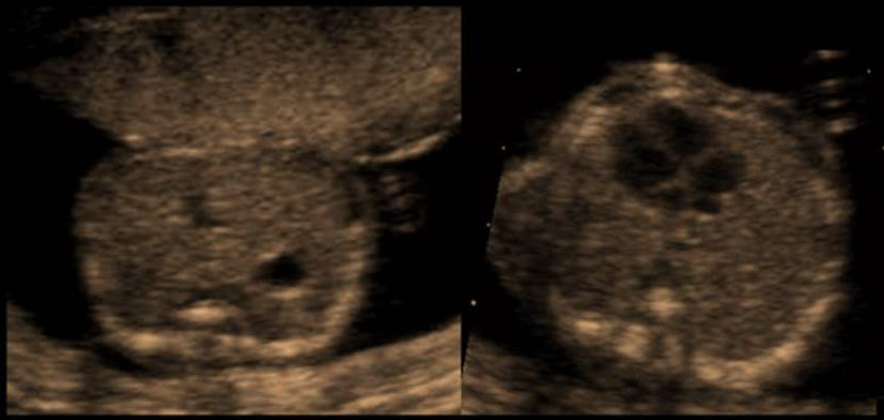
a) the heart is abnormally small but the stomach appears normal
b) complete situs inversus
c) partial sinus inversus
d) normal 4 chamber heart + stomach
c) partial sinus inversus

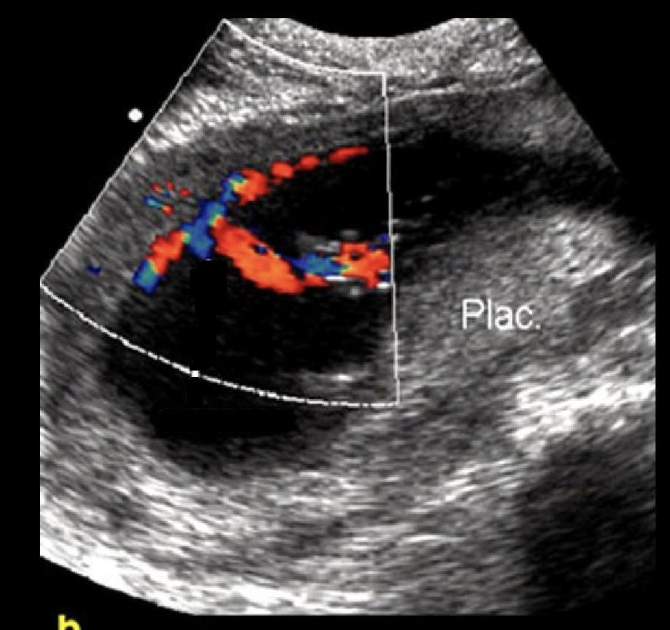
pt w/22w GA fetus. this is placental cord insertion
.
a) velamentous cord insertion
b) marginal cord insertion
c) cyst originating from the umbilical cord
d) a normal placental cord insertion
a) velamentous cord insertion

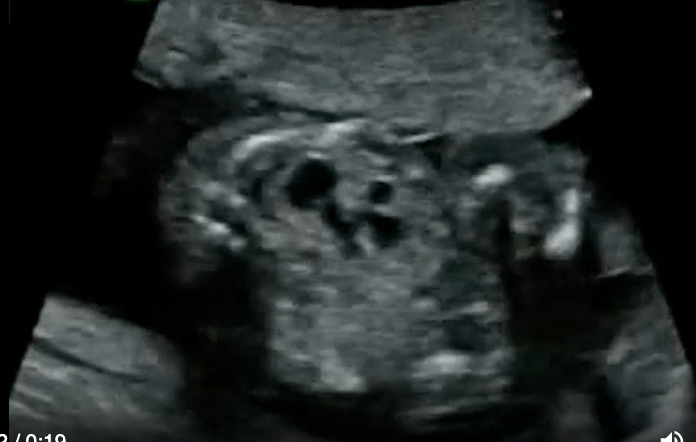
a) duodenal atresia
b) posterior urethral valves
c) unilateral multicystic dysplastic kidney
d) autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
c) unilateral multicystic dysplastic kidney

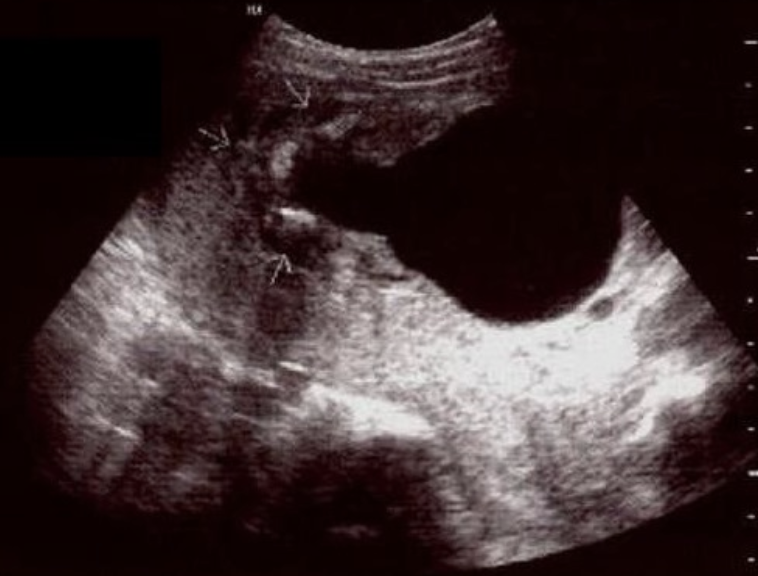
a) most likely a female fetus
b) fetus probably has potter syndrome
c) fetus probably has turner syndrome
d) most likely a male fetus
d) most likely a male fetus

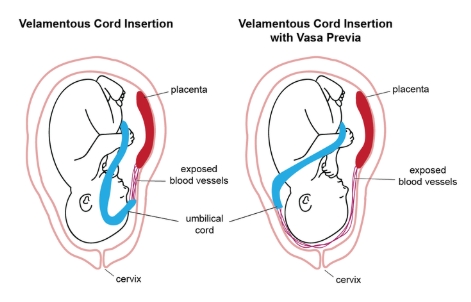
common complications of a velamentous cord insertion include
vasa previa
IUGR
xxx
.
a) choriocarcinoma
b) placental abruption
c) complete molar pregnancy
d) cord entanglement
b) placental abruption

most forms of skeletal dysplasia shows a foreshortened femur throughout pregnancy
.
except ___ that typically has a normal femur length until later in the 2nd trimester
.
a) osteogenesis imperfecta
b) campomelic dysplasia
c) Thanatophoric skeletal dysplasia
d) heterozygous achondroplasia
d) heterozygous achondroplasia

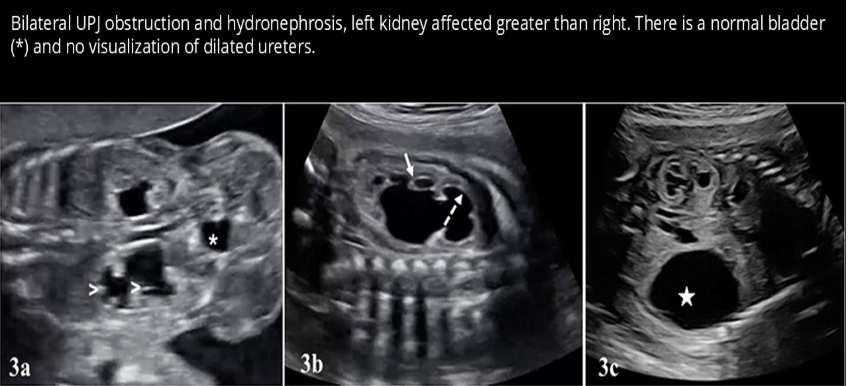
which condition is the most common cause of hydronephrosis in a fetus
a) ureteropelvic junction obstruction
b) posterior urethral valves
c) bladder exstrophy
d) aqueductal stenosis
a) ureteropelvic junction obstruction
which facial anomaly is commonly assoc w/beckwith wiedemann syndrome
a) frontal bossing
b) proboscis
c) macroglossia
d) midface hypoplasia
c) macroglossia
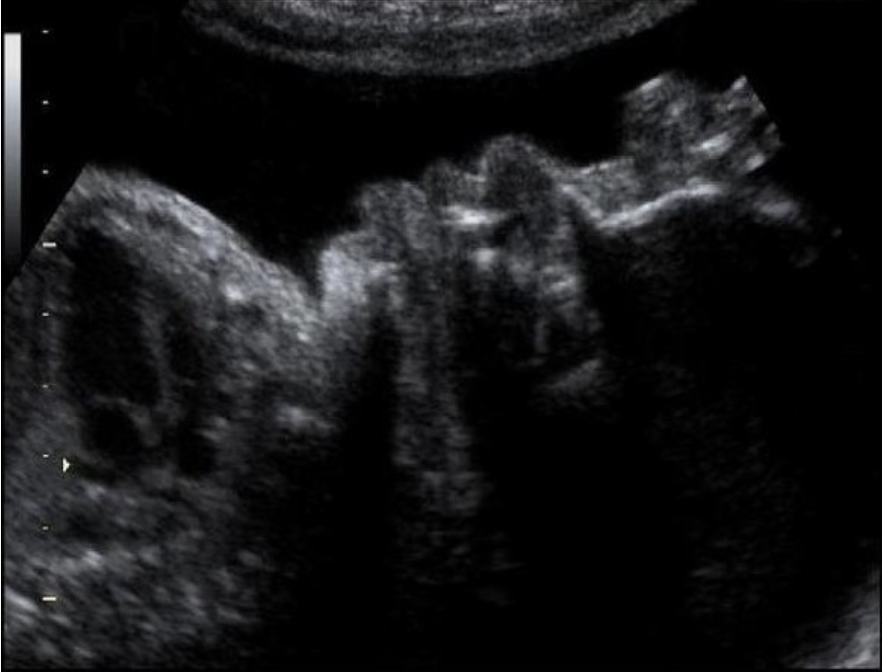
which describes sono appearance of possible intestinal atresia in a 29w fetus
a) small bowel loops dilated at 3mm luminal diameter
b) decreased or absent peristalsis of bowel
c) hyperechoic bowel w/increased peristalsis
d) pleural effusion, megacystitis + ascites
b) decreased or absent peristalsis of bowel

symmetric IUGR occurs when
a) HC measures more than 2 standard deviations smaller than AC for the current GA
b) the limbs are abn shortened w/relatively normal HC + AC
c) AC measures more than 2 standard deviations smaller than HC for the current GA
d) all parts of the fetus to be reduced in size by more than 2 standard deviation for current GA
d) all parts of the fetus to be reduced in size by more than 2 standard deviation for current GA
macrosomia describes a fetus weighing more than
a) 3,000g
b) 10lbs
c) 4,000g
d) 2,000g
c) 4,000g
which anomaly is almost always assoc w/tracheoesophageal fistula
. assoc w/trisomy 18
.
a) esophageal atresia
b) megacystitis
c) duodenal atresia
d) bochdalek hernia [left side hernia w/bowel + stomach + LLL]
a) esophageal atresia

all can cause a false positive dx of club foot except
a) oligohydramnios
b) uncooperative fetus
c) 8cm intramural fibroid
d) footling breech position
b) uncooperative fetus

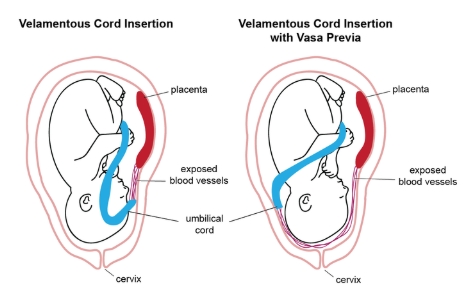
what delivery complication is most commonly assoc w/velamentous cord insertion
.
a) meconium peritonitis
b) vasa previa
c) fetal respiratory distress
d) premature rupture of membranes
b) vasa previa

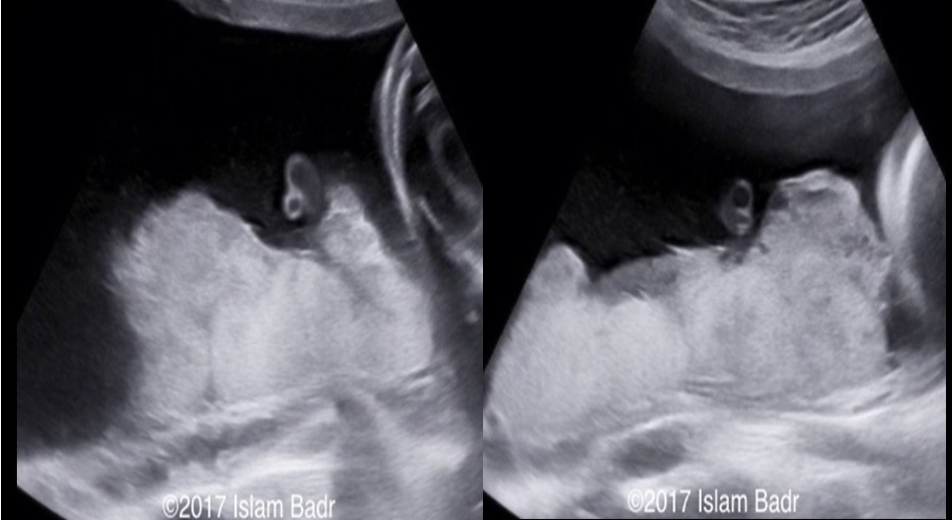
a) normal grade 2 placenta
b) circumvallate placenta
c) placenta previa
d) placental abruption
b) circumvallate placenta
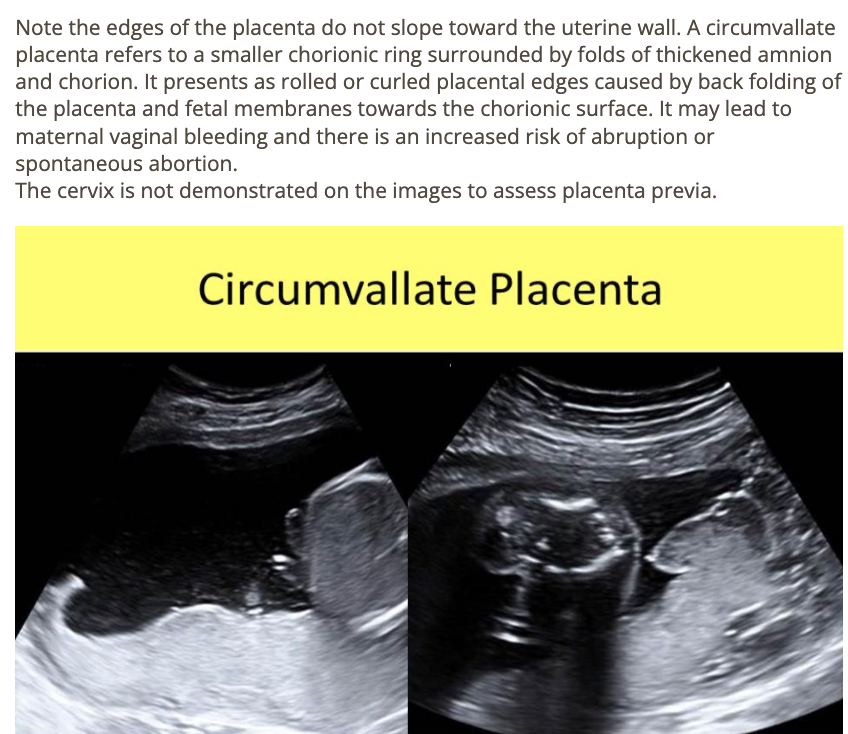
if you identify hypoplastic left heart in a female fetus, what fetal syndrome should be suspected
a) edwards
b) turner
c) triploidy
d) noonan
b) turner
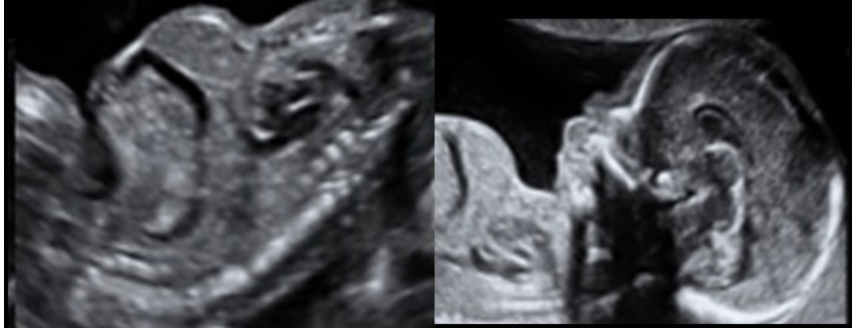
what is the most common cause of death in lethal skeletal dysplasia
.
a) umbilical cord knot
b) renal failure
c) pulmonary hypoplasia
d) hypoplastic heart
c) pulmonary hypoplasia

monochorionic twins over 16w GA should be evaluated every 2 weeks for possible complications.
.
Doppler evaluation of the ___ for discordant flow resistance
.
Doppler evaluation of the ___ for discordant flow velocities
.
must be included in the exams
.
a) middle cerebral artery, umbilical artery
b) umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery
c) uterine artery, umbilical artery
d) ductus venosus, uterine artery
b) umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery

which is true about micrognathia? it is seen w/
a) polyhydramnios in 70% of cases due to dysphagia
b) oligohydramnios in 70% of cases due to dysphagia
c) oligohydramnios in 70% of cases due to assoc renal anomalies
d) polyhydramnios in 70% of cases due to assoc renal anomalies
a) polyhydramnios in 70% of cases due to dysphagia

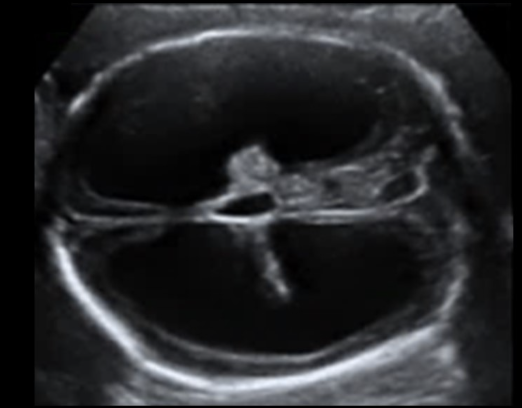
what is the most common cause for hydrocephalus
a) spina bifida
b) aqueductal stenosis
c) mass effect from neuroblastoma
d) chiari malformation
b) aqueductal stenosis

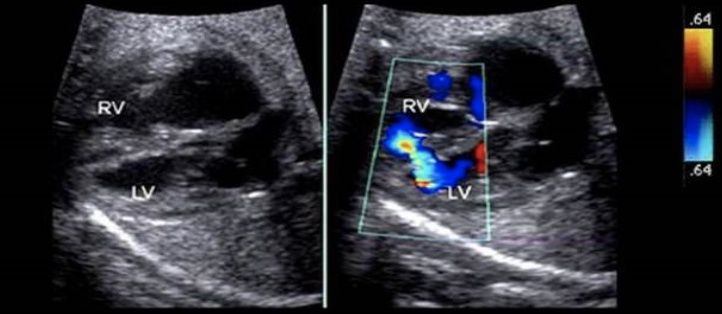
what is this cardiac defect
a) patent foramen ovale
b) aortopulmonary window
c) sinus venosus ASD
d) muscular VSD
d) muscular VSD

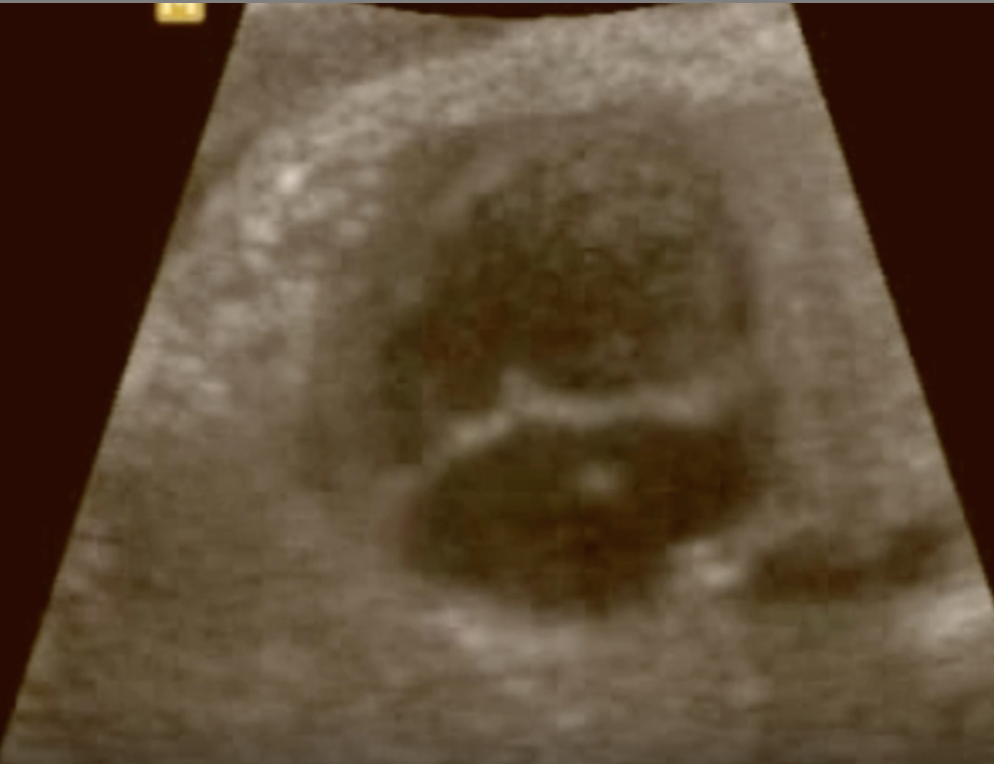
a) turner syndrome
b) trisomy 13
c) trisomy 18
d) trisomy 21
d) trisomy 21

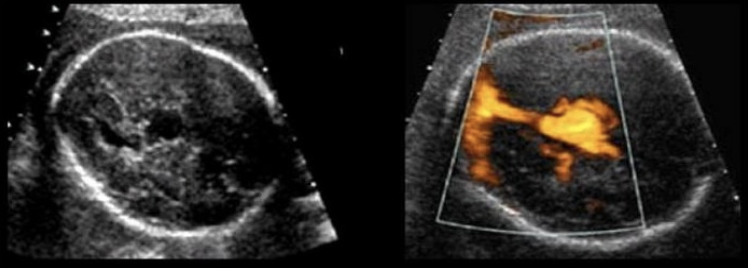
this is ___ and it’s assoc w/xxx
.
a) vein of galen aneurysm, congestive heart failure
b) dilated 3rd ventricle, spina bifida
c) agenesis of corpus callosum, triploidy
d) middle cerebral artery aneurysm, fetal demise
a) vein of galen aneurysm, congestive heart failure

while scanning a 22w fetus, you see normal long bones in lower extremities but the feet are very small w/shortened tarsals + metatarsals
.
a) rhizomelia
b) clinodactyly
c) phocomelia
d) acromelia
d) acromelia
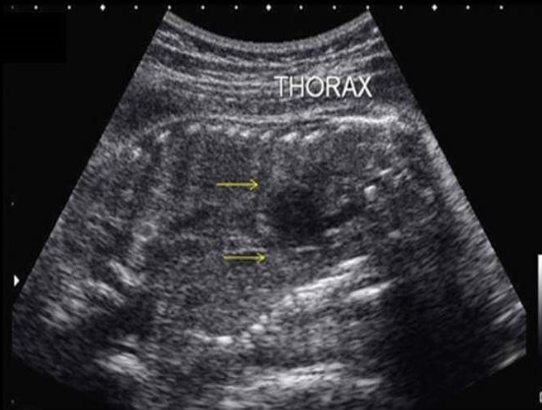
a) congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation + pulmonary sequestration
b) potter syndrome + diaphragmatic hernia
c) vein of galen malformation + cardiomegaly
d) thanatophoric skeletal dysplasia + osteogenesis imperfecta
d) thanatophoric skeletal dysplasia + osteogenesis imperfecta

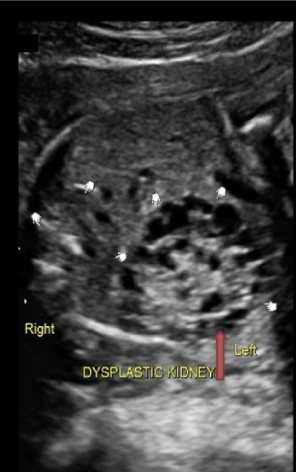
what urinary anomaly is caused by urinary obstruction in the 1st trimester and leads to renal cyst formation + ureteral atresia
a) potter syndrome
b) multicystic kidney disease
c) infantile PCKD
d) adult PCKD
b) multicystic kidney disease

![<p>a) diaphragmatic [Bochdalek ] hernia</p><p>b) normal thoracic activity</p><p>c) cardiomegaly</p><p>d) cognenital cystic adenomatoid malformation</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d46cff50-88de-4db3-a5e8-086fe63722c9.png)
a) diaphragmatic [Bochdalek ] hernia
b) normal thoracic activity
c) cardiomegaly
d) cognenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
a) diaphragmatic hernia
