ib econ- 2.2: supply
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credit https://www.econinja.net/microeconomics/2-2-supply
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what is supply?
the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to provide/sell in a time period
what is the law of supply?
states that there is a positive relationship between quantity supplied and price, ceteris paribus
what are the assumptions underpinning the laws of supply?
the law of diminishing marginal returns
increasing marginal costs
what is the law of diminishing marginal returns?
the idea that as factors of production increase to produce more supply, the added return of each additional resource diminishes. hence, firms are only willing to supply more if they can charge higher prices.
what are increasing marginal costs?
owing to the law of diminishing marginal returns, the added productive gain of employing more workers decreases, but their costs do not- hence the cost of each new resource will increase.
draw the basic supply diagram
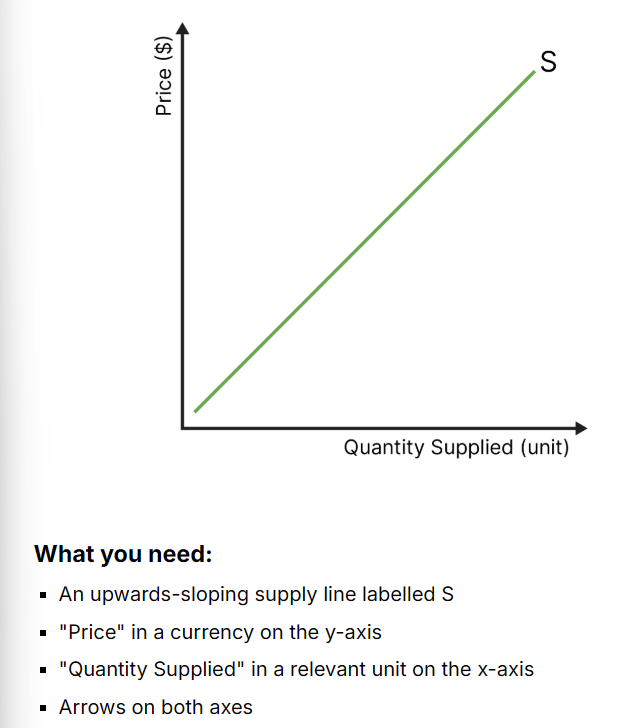
what does the market supply refer to?
the combined supply by every individual firm in a market at a price level.
what are the non-price determinants of supply?
changes in costs of factors of production
prices of related goods
indirect taxes and subsidies
future price expectations'
changes in technology
number of firms
how do changes in costs of factors of production affect supply?
if the costs of producing a good increase, firms will produce less of it and vice versa
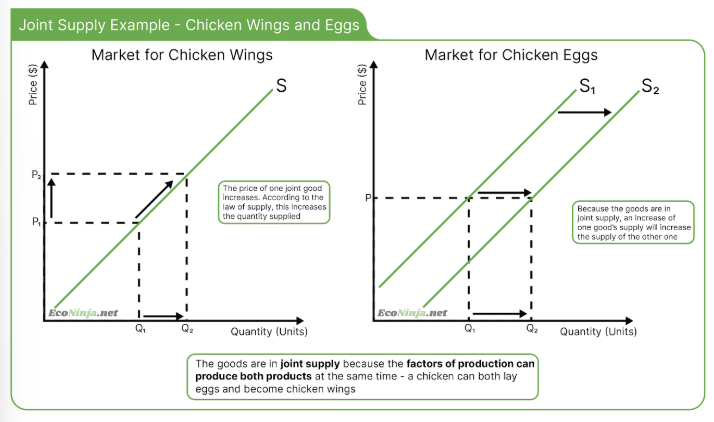
how do changes in prices of complementary goods affect supply?
joint supply: when the production of one good automatically aids the production of another good (e.g. chicken breasts and chicken eggs)
competitive supply: when the production of one good competes with the production of another good. (e.g. if you are a fruit farmer you can have apple trees or orange trees- they compete against each other, more apples=less oranges)
how do indirect taxes and subsidies affect supply?
indirect taxes = taxes on consumption rather than income (shifts supply to the left)
subsidies are government funded financial assistance that reduce the costs of production (shifts supply to the right)
how do future price expectations affect supply?
if firms expect the price to increase in the future, they will increase production, shifting the supply curve to the right
how do changes in technology affect supply?
if improvements in technology result in the production of goods being more efficient, firms will be willing to supply than before. this shifts the supply curve to the right.
how does the number of firms in a market affect supply?
if the number of firms in a market increases, the total market supply increases (and vice versa)
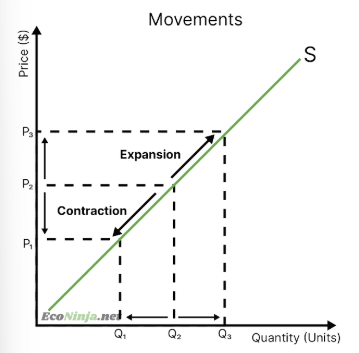
what are movements along the supply curve called and what are they?
contractions are movements down and left on the supply curve - a lower quantity is supplied due to a lower price
expansions are movements up and right on the supply curve- a higher quality is supplied due to a higher price
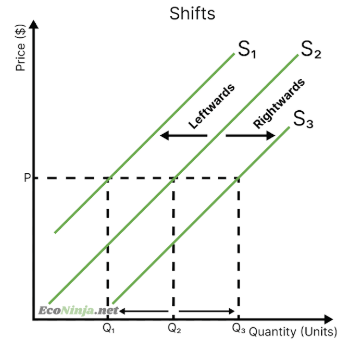
what are shifts of the supply curve called and what are they caused by?
leftwards shifts are caused by unfavourable non-price events
rightwards shifts are caused by favourable non-price events
caused by one or multiple non-price determinants of supply
draw a contraction or expansion along the supply curve
draw a leftwards or rightwards shift of the supply curve