addition reactions
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
organic chemistry 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
what is Hydrohalogenation
treatment of alkene with HX (Cl, Br, I)
X added to double bond
Regioselectivity of hydrohalogenation
Markonikov
Markonikov addition
addition of a polar molecule to an asymmetric alkene, the (H) attaches to the C with more H, while the other group (such as X, OH, or OR) attaches to the C with fewer H.
anti-Markonikov addition
addition of a polar molecule to an asymmetric alkene, the (H) attaches to the C with fewer H, while the other group (such as X, OH, or OR) attaches to the C with more H.
Regioslectivity of hydrohalogenation with ROOR
anti-Markonikov
Steps of a hydrohalogenation
Proton transfer
Nucleophilic attack
Do hydrohalogenations form enantiomers
Yes - depends on carbocation formation/rearrangement
what does Acid-catalyzed hydration add
addition of OH and H
Steps for acid-catalyzed hydration
Proton transfer
nucleophilic attack
Proton transfer
Regiosleectivity for acid-catalyzed hydration
Markonikov
Hydrohalogenation reagents
HX
Hydrobromination reagents (anti)
HBr, ROOR
Acid-catalyzed hydration reagents
H3O+ or H2O + H2SO4
Oxymercuration-demercuration reagents
1) Hg(OAc), H2O
2) NaBH4
Hydroboration-oxidation reagents
1) BH3 - THF
2) H2O2, NaOH
Hydrogenation reagents
H2, Pt
Bromination reagents
Br2
Halohydrin formation reagents
Br2, H2O
Anti-dihydroxilation reagents
1) RCO3H
2) H3O+
Syn-dihydroxilation cold reagents
KMnO4, NaOH cold
Syn-dihydroxilation reagents
1) OsO4
2) NaHSO3, H2O
Ozonolysis reagents
1) O3
2) DMS
Hydrohalogenation adds
Halogen and H
Catalyzed Hydrogenation adds
H2
what is Halogenation
Adds 2 halogens
Steps of acid catalyzed hydration
1) Proton transfer
2) Nucleophlic attack
3) Proton transfer
How does concentration affect acid-catalyzed hydration?
The more H2O (diluted H2SO4) will favor formation of alcohol
The less H2O (conc. H2SO4) will favor the alkene
Does acid-catalyzed hydration produce enantiomers?
Yes
Regioselectivity of oxymercuration-demercuration
Markonikov
what does oxymercuration-demercuration add
OH and H
Regioselectivity of Hydrobroration-oxidation
anti-markonikov
Stereoselectivity of hydroboration-oxidation
syn-addition (same plane)
what does hydroboration-oxidation add
OH and H in a syn manner
What does catalytic hydrogenation add
2 Hydrogens
stereospecificity for catalytic hydrogenation
syn addition
Heterogeneous catalyst
Pt, Ni, Pd
What does halogenation add
2 halogens across alkene
stereospecificity of halogenation
anti-addition
what does halohydrin formation add
Halogen and OH
where does OH go in halohydrin formation
in the most substituted position
what does anti-dihydroxilation add
2 OH in anti manner
what does syn-dihydroxilation add
2 OH in a syn manner
what happens in an ozonolysis reaction
double bond is split to form two C=O
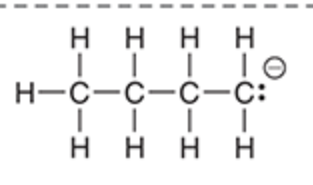
Will this base deprotonate a terminal alkyne
Yes
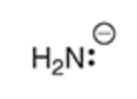
Will this base deprotonate terminal alkyne
yes
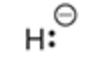
Will this base deprotonate a terminal alkyne
yes
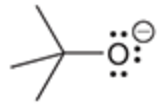
will this base deprotonate a terminal alkyne
no
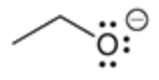
will this base deprotonate a terminal alkyne
no
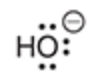
will this base deprotonate a terminal alkyne
no
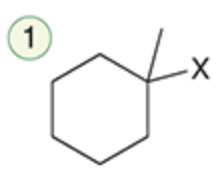
name the reaction that makes this
Hydrohalogenation (Markonikov)
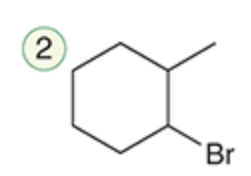
name the reaction that makes this
Hydrohalogenation (Anti-Markonikov)
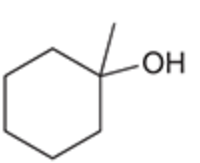
name the reaction that makes this
Acid-catalyzed hydration
Oxymercuration-demercuration
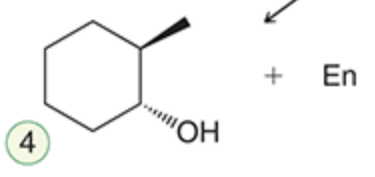
name the reaction that makes this
Hydroboration-oxidation
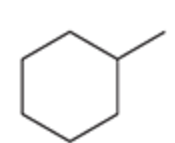
name the reaction that makes this
Hydrogenation, catalyzed hydration
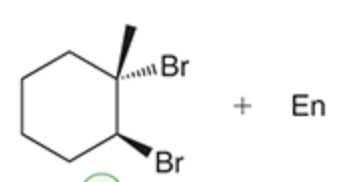
name the reaction that makes this
Bromination/Halogenation
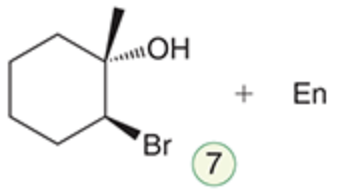
name the reaction that makes this
Halohydrin formation
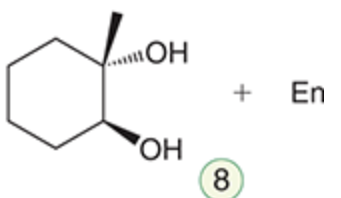
name the reaction that makes this
anti-dihydroxylation
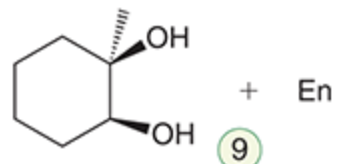
name the reaction that makes this
syn-dihydroxylation
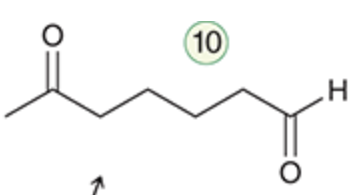
name the reaction that makes this
ozonolysis
SN2 _____ be performed in tertiary alkyl
cannot
Regioselectivity of E2 reactions
Favor Zaitsev product
Zaitsev product definition
more substituted alkane
what is alkyl treated with for substitution
nucleophile
what is alkyl treated with for elimination
base
what is key about the configuration of a substitution reaction
it undergoes an inversion of configuration due to back side attack
What type of nucleophile is needed for SN2 reaction
strong nucleophile
Name 5 strong nucleophiles
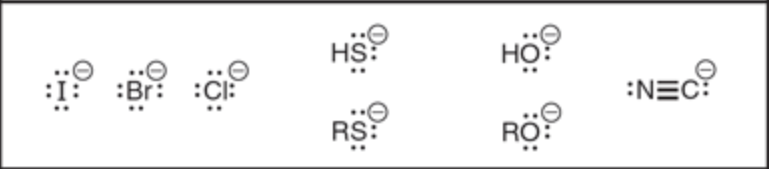
Name 2 weak nucleophiles

Hoffman product definition
less substituted product
chemicals that are Strong Base/Strong Nucleophile
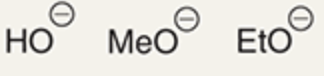
chemicals that are weak base/strong nucleophile
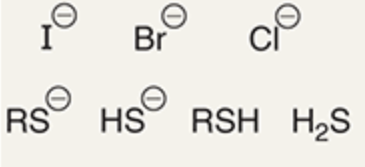
chemicals that are weak base/weak nucleophile

chemicals that are strong base/weak nucleophile

strong base/weal nucleophile will favor
E2
strong base/strong nucleophile will favor
SN2 and E2
weak base/strong nucleophile will favor
SN1 and SN2
weak base/weak nucleophile will favor
SN1 and E1
Catalytic hydrogenation with Lindlar-P2 catalyst
alkyne to cis alkene
Catalytic hydrogenation with H2/Pt in alkyne
alkyne to trans alkane
radical anion
intermediate with both a negative charge and a unpaired electron
convert terminal alkyne to trans alkene
catalytic hydrogenation with Lindlar catalyst
convert internal alkyne into trans alkene
1) Na
2) NH3
HBr/ROOR in alkyne
Anti-markonikov addition, creates cis and trans
reagents to go from alkyne to dihalide
excess HX OR
1) NaNH2/NH3
2) H2O
What does acid catalyzed tautomerization of an alkyne produce
an enol that turn into a ketone
What does base catalyzed tautomerization of an alkyne produce
an enol that turn into an aldehyde
Regioselectivity of acid-catalyzed tautomerization
Markonikov
Regioselectivity of base-catalyzed tautomerization
Anti-markonikov
What reagents are used for acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkyne
1) H2SO4, H2O
2) HgSO4
What reagents are used for base-catalyzed hydration of an alkyne
1) R2BH, disialmyborane or 9-BBN
2) H2O2, NaOH
Raegents for halogenation of alkenes
excess Halogen, CCl4
What does the ozonolysis of an internal alkyne produce
2 carboxylic acids
what does ozonolysis of an terminal alkyne produce
co2 and carboxylic acid
how to go from alkyne to alkene
H2, lindlar catalyst or
Na, NH3
How to go from alkene to alkane
H2, Pt
How to go from alkene to alkyne
1)Br2, CCl4
2) xs NaNH4
3) H2O
What does heterolytic cleavage form
ions
What does homolytic cleavage form
radicals
What determines the stability of a radical
hypercojungation —> the amount of alkyl groups
reaction that forms individual radicals
homolytic cleavage