Rates of Reaction, RATE OF REACTION
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
rate of reaction
change in concentration of a reactant or product / time
Activation energy
(Ea) the minimum energy required for colliding reactant molecules to successfully react
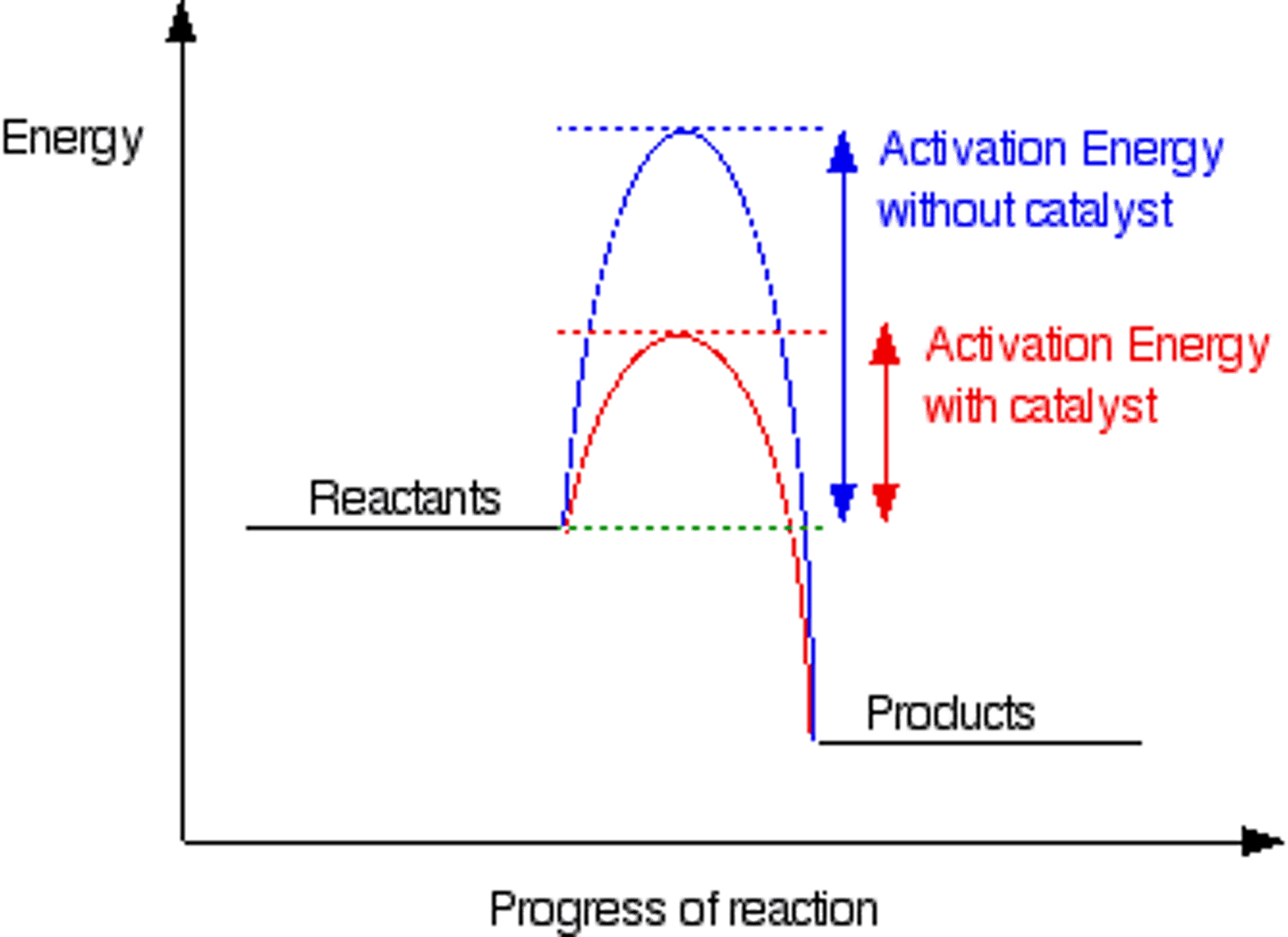
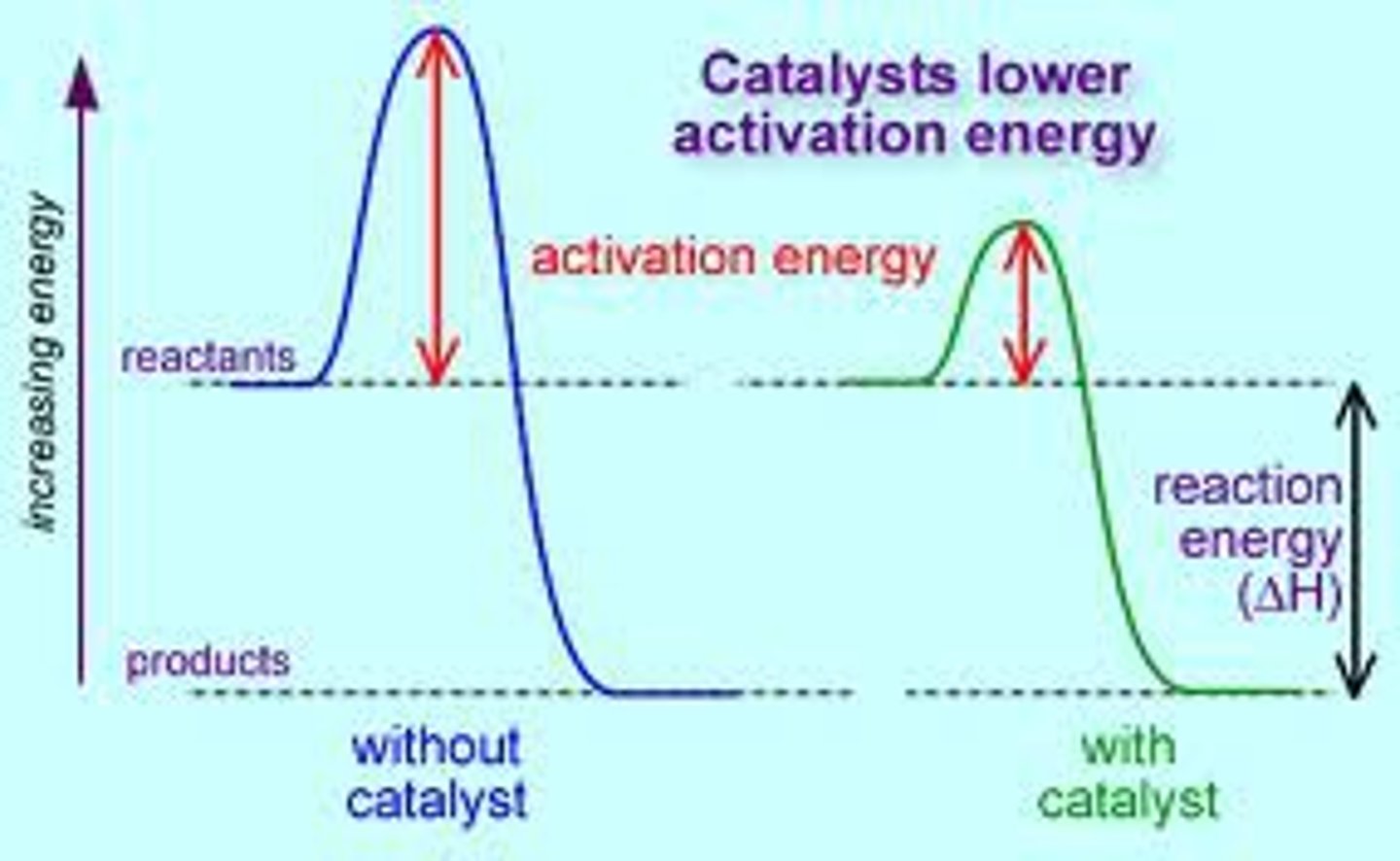
Catalyst
material that reduces the activation energy (and so the number of successful reactant collisions) without being used up or changed
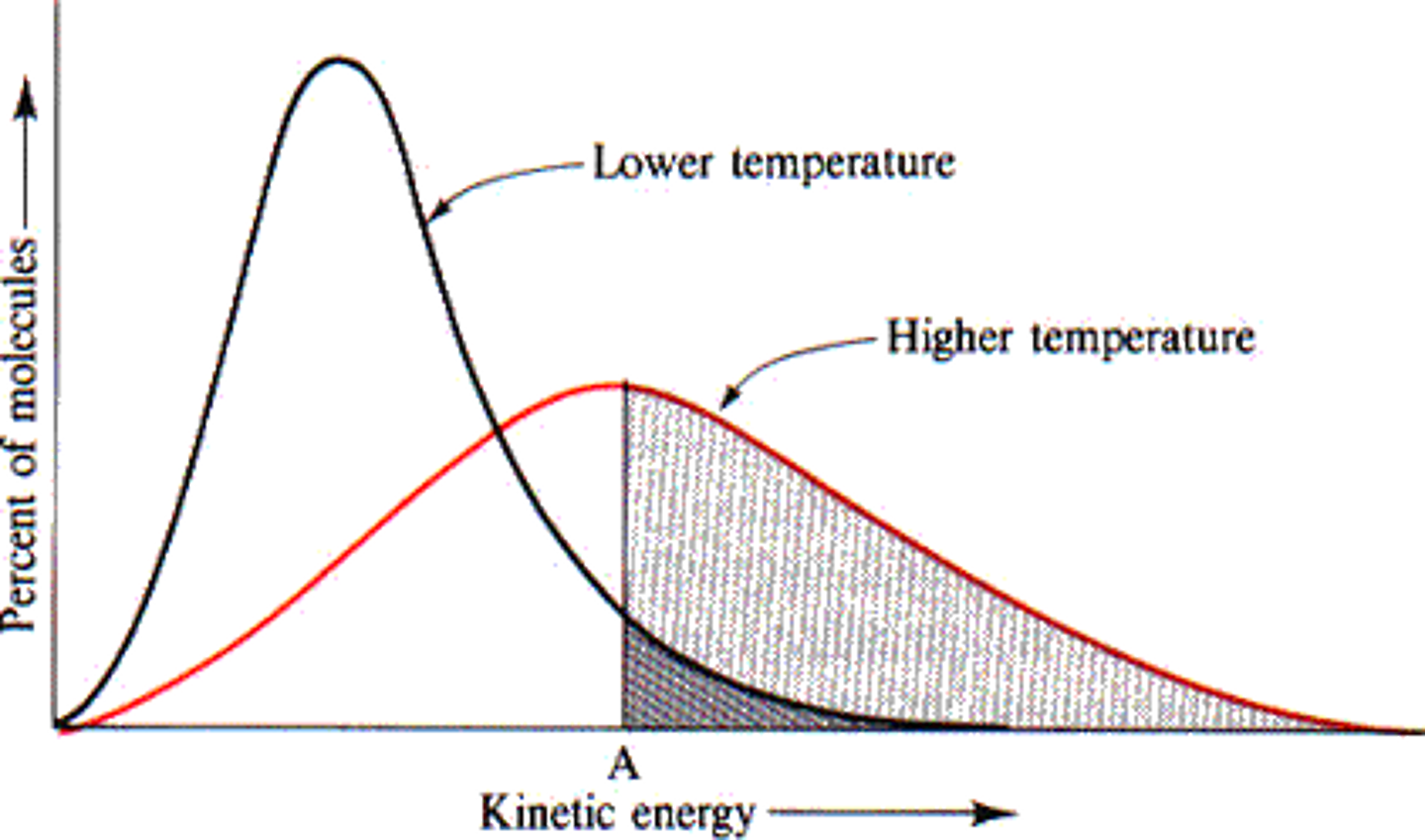
increase temperature
increase rate because speed of the particles increases (the frequency of collisions increases), so the chance of successful collisions increases
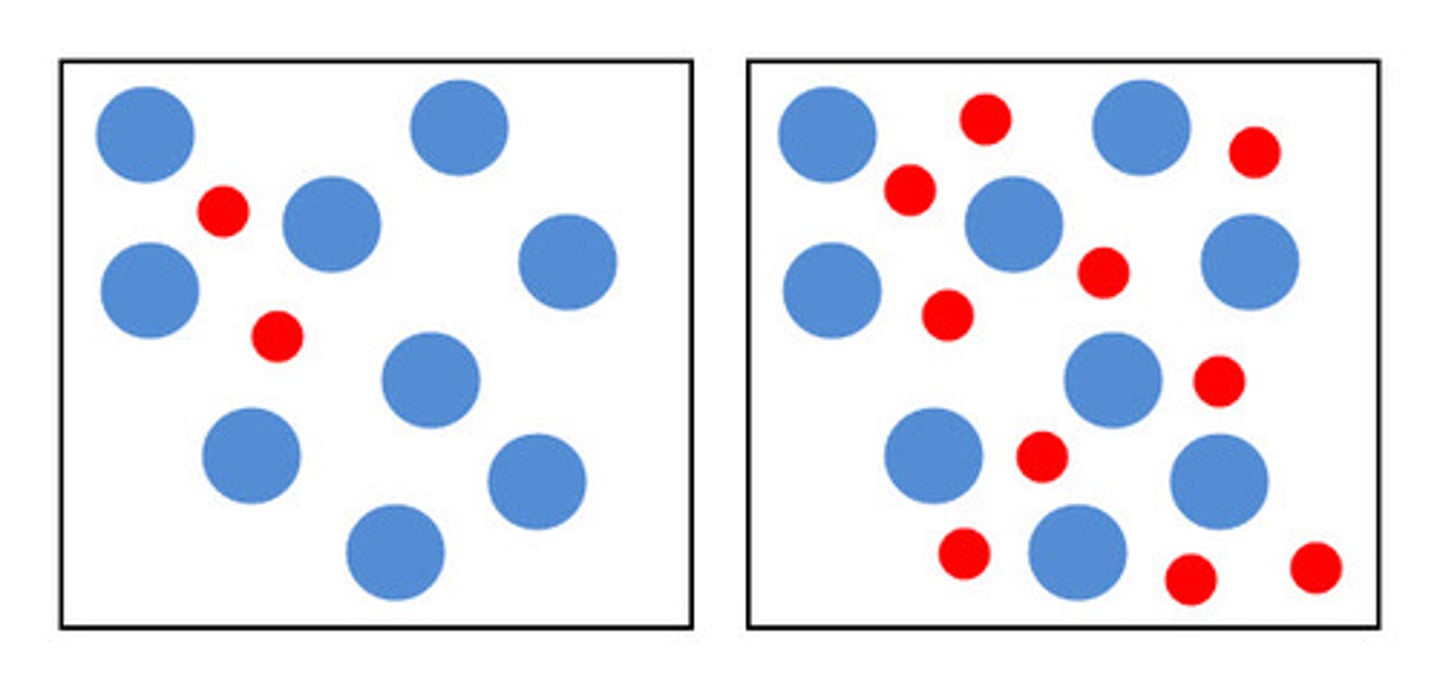
increase concentration
increase rate because the number of particles increase (the frequency of collisions increases), so the chance of successful collisions increases.
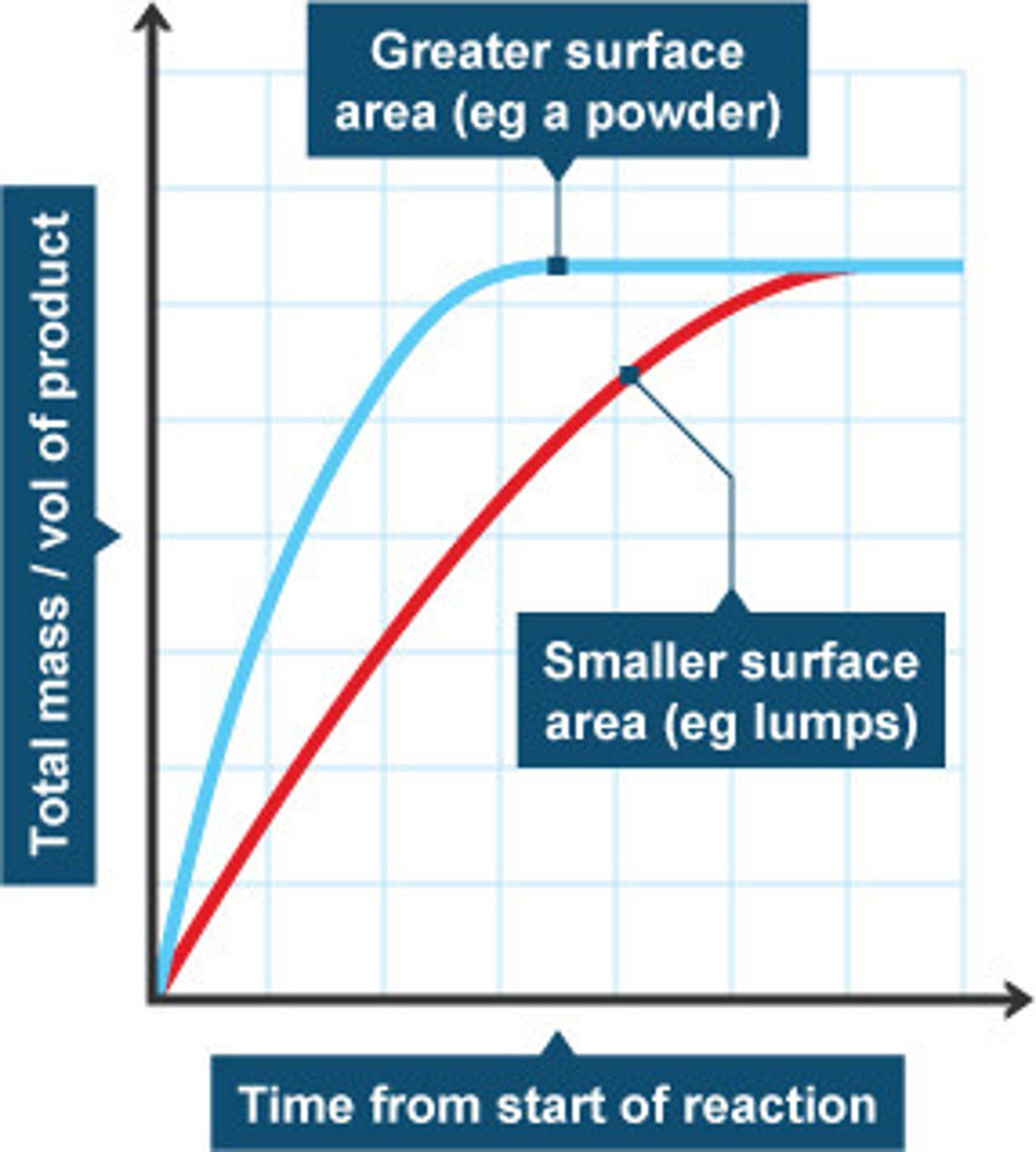
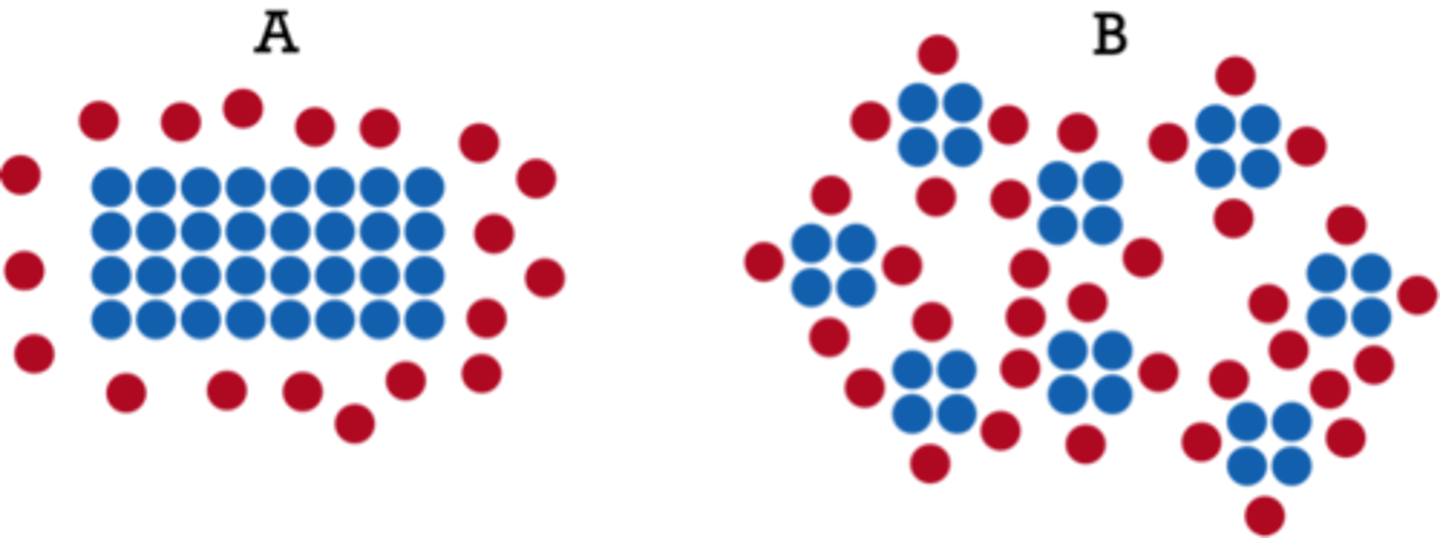
increase surface area
increase rate because the number of exposed/available (solid) reactant molecules increases so the frequency of collisions increases, so the chance of successful collisions increases.
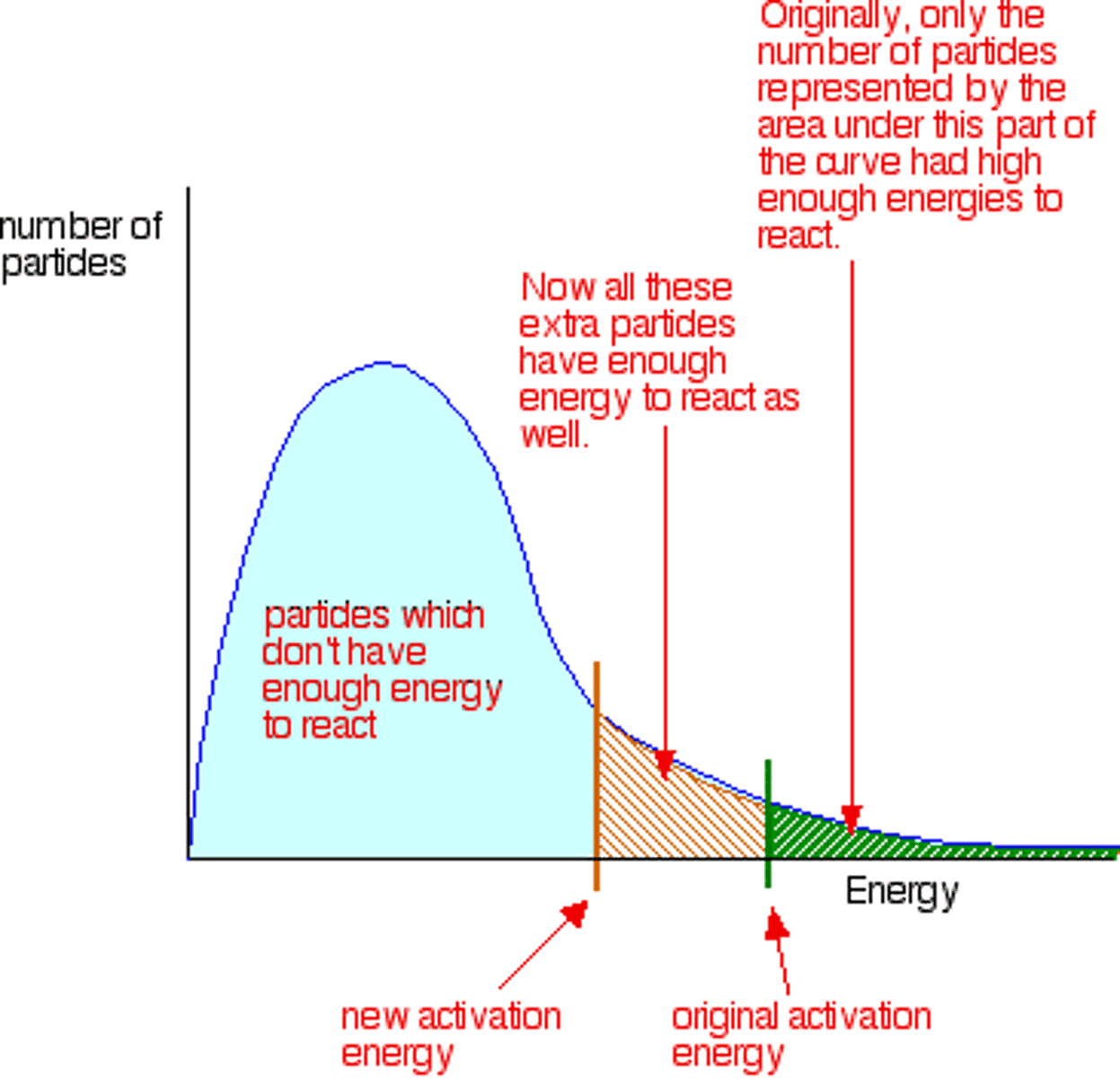
addition of a catalyst
increase rate because (activation energy is reduced) there is an increase in the proportion of particles with the kinetic energy equal to the activation energy so the frequency of successful collisions increases.
Concentration
Amount of solute dissolved in a solvent
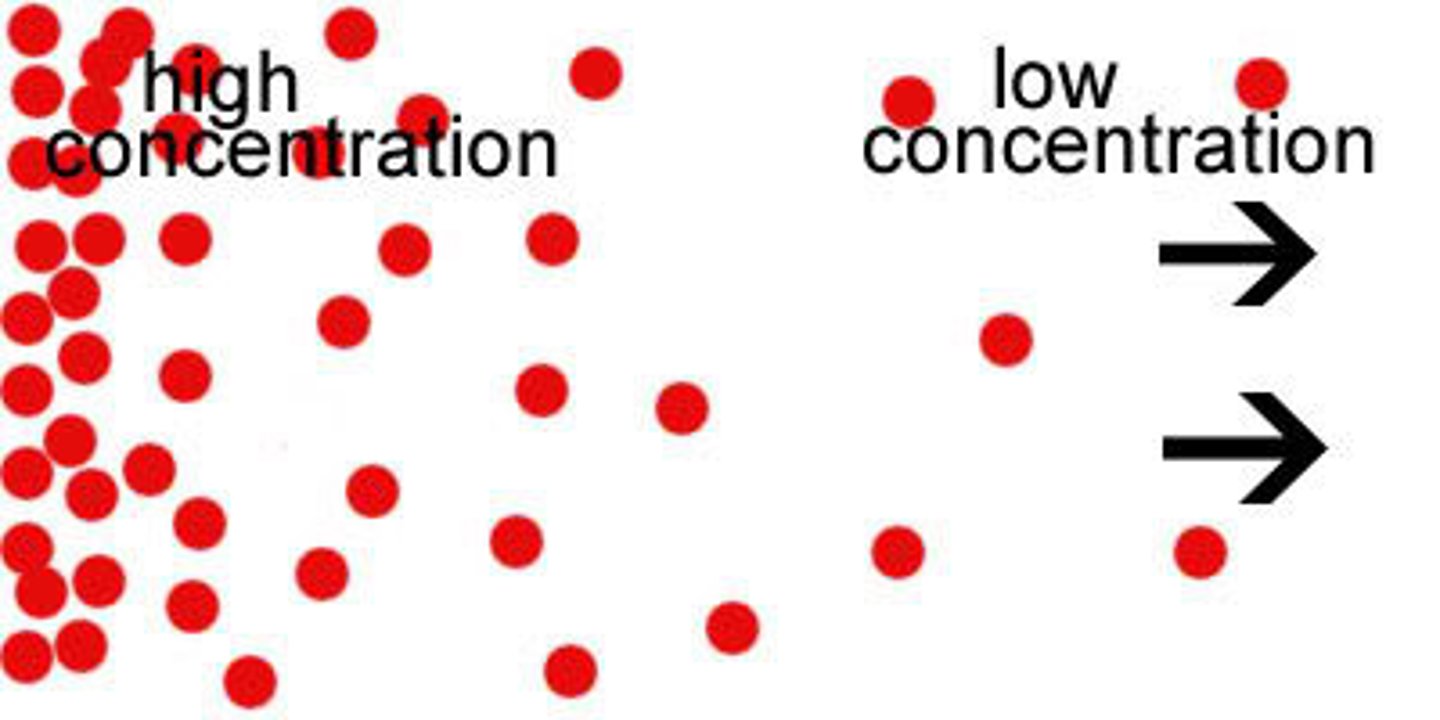
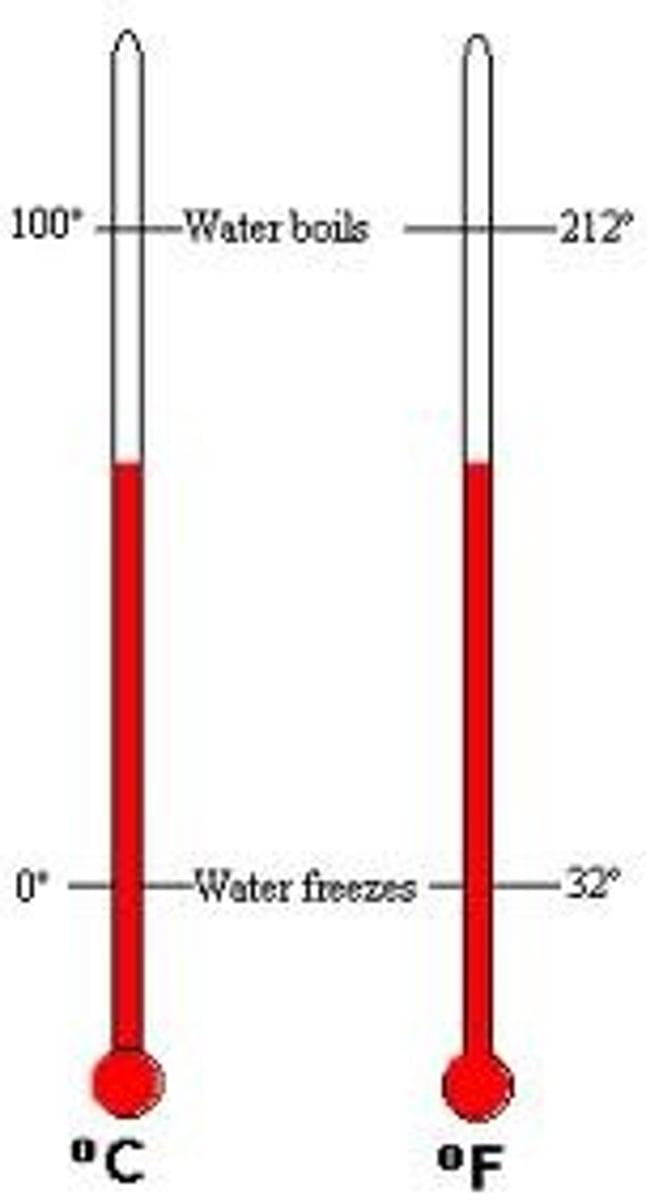
Temperature
A measure of how fast the particles in an object are moving. It is related to the kinetic energy of the particles.
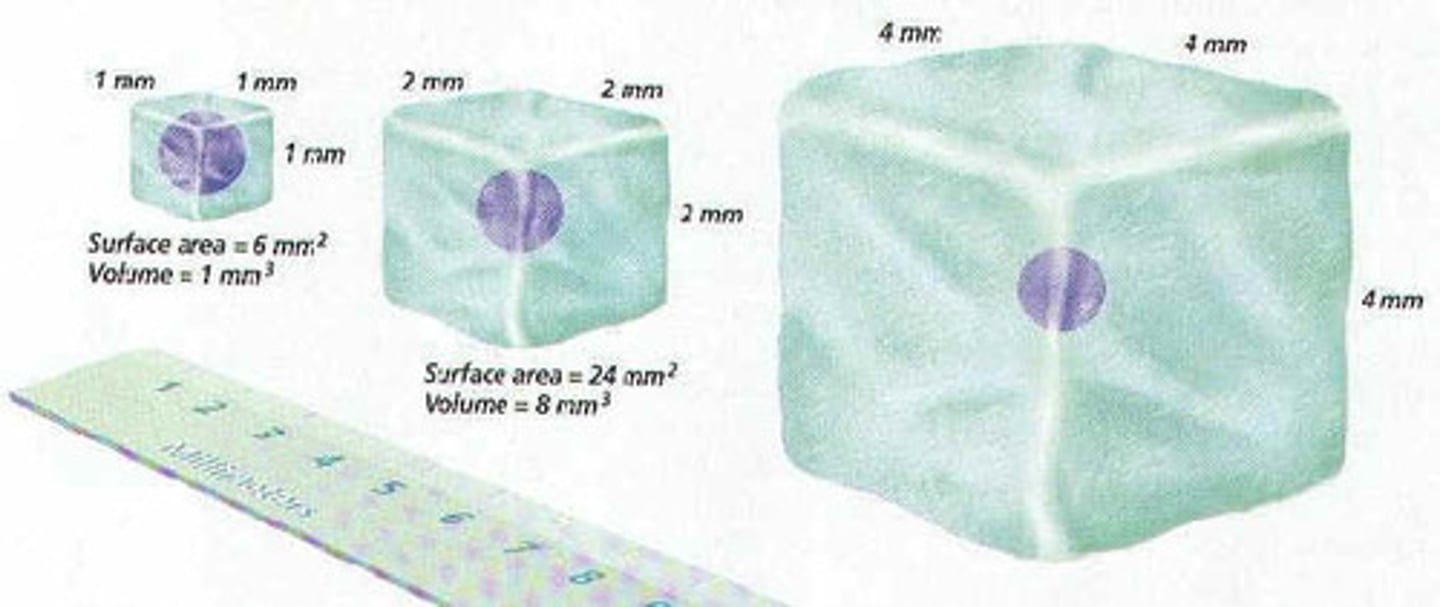
Surface Area
The amount or number of areas of an object that is exposed to reaction.
Endothermic reaction
A reaction in which energy is absorbed or enters

Exothermic reaction
Releases heat. Energy exits

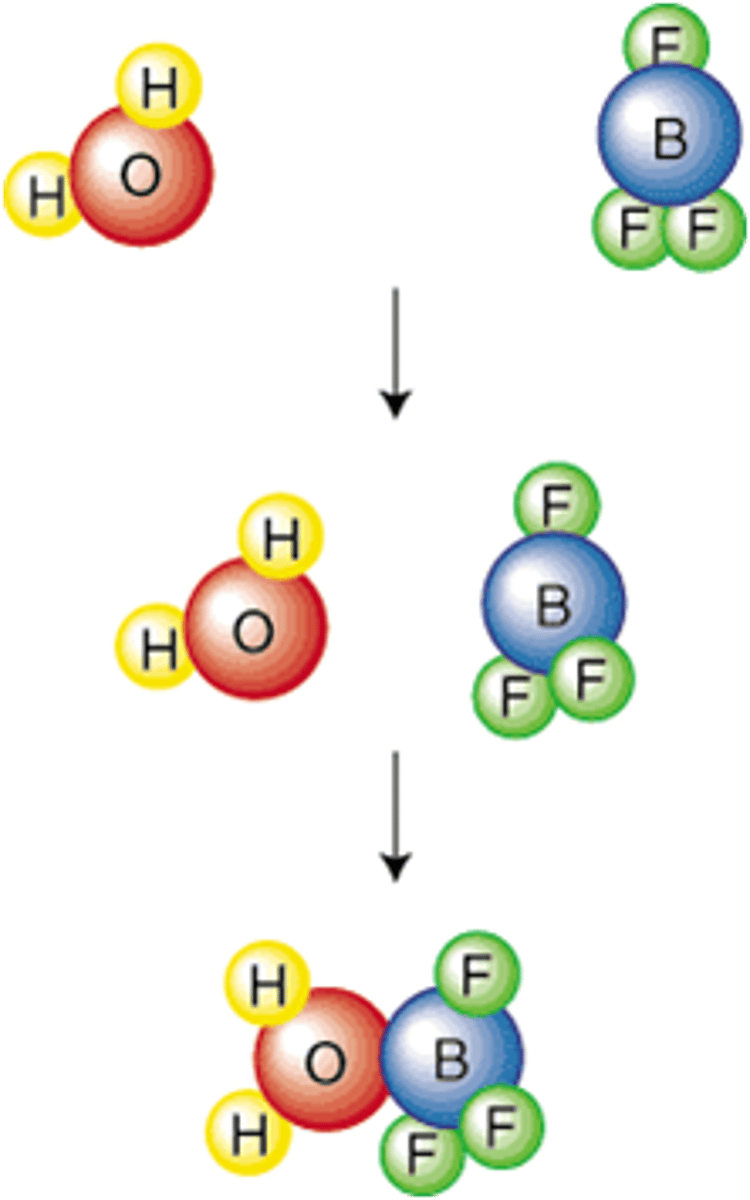
Collision Theory
States that atoms, ions, and molecules must collide in order to react
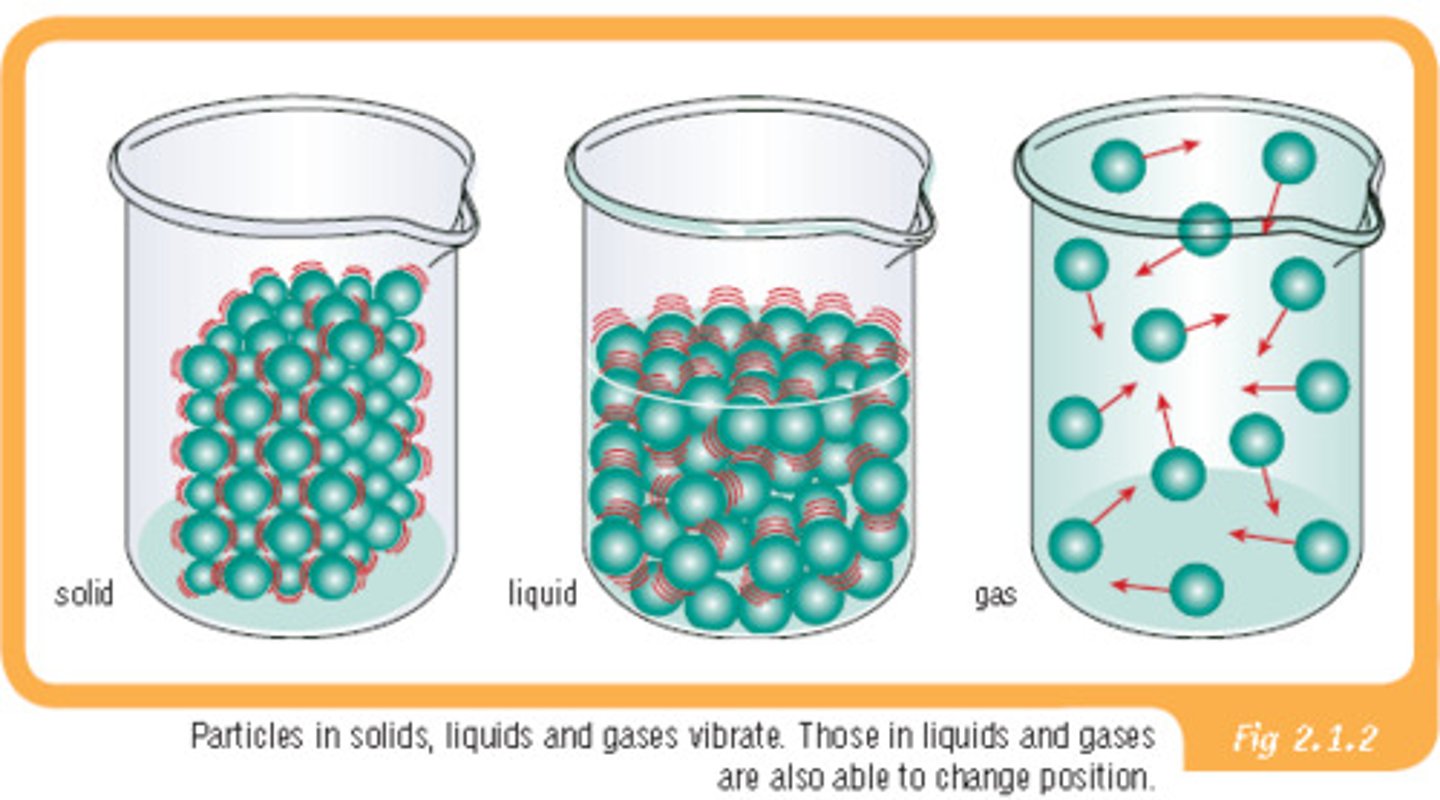
Kinetic Theory
Atoms are always in motion
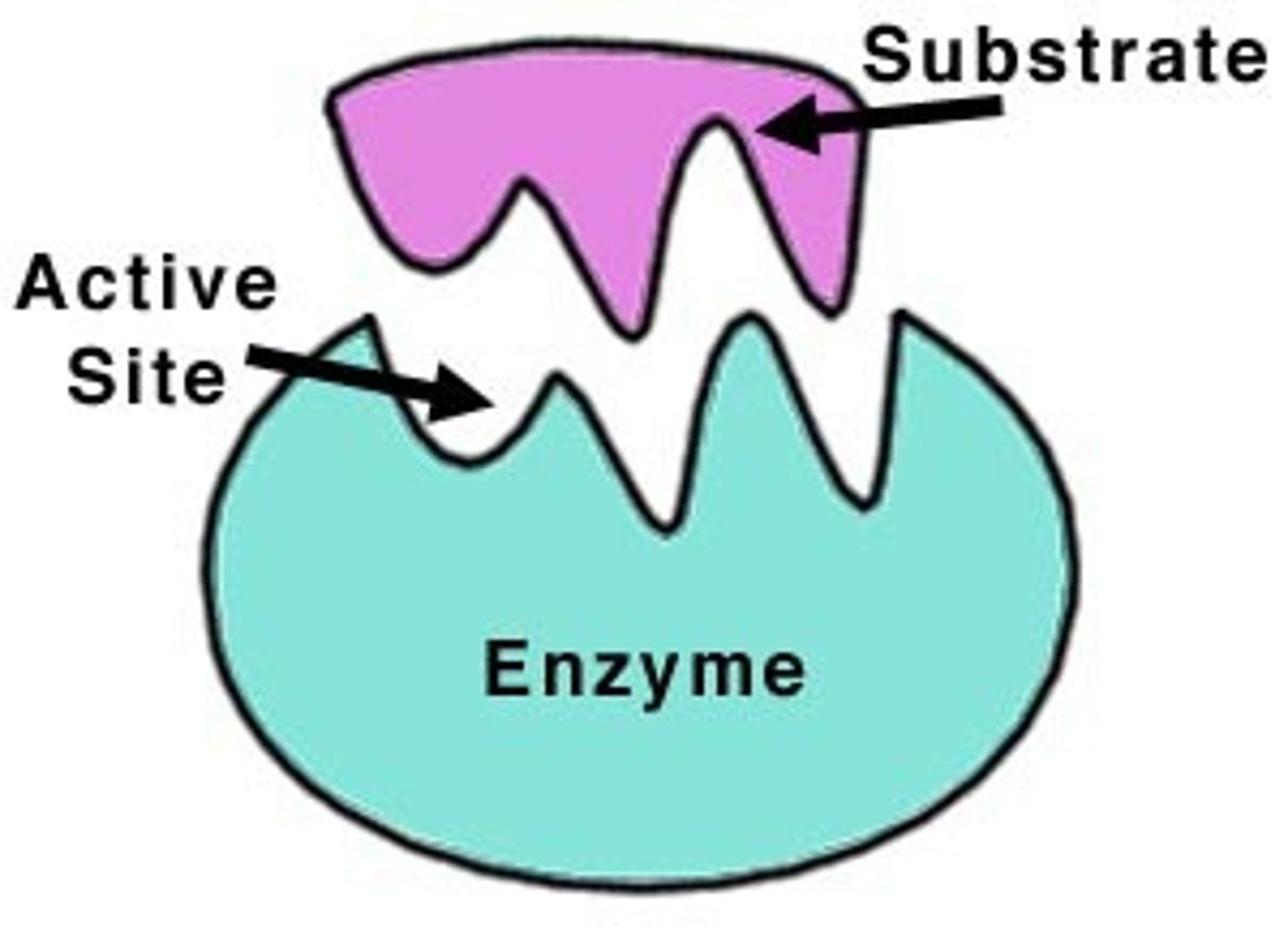
Enzymes
Biological catalysts; speeds up reactions in living things