AP Psych Unit 2
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering core concepts from Unit II: Research Methods in psychological science.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it (the 'I knew it all along' phenomenon).
Critical Thinking
Thinking that questions assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions rather than blindly accepting arguments.
Theory
An explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events.
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory.
Operational Definition
A carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used to measure a variable in a study.
Replication
Repeating the essence of a research study with different participants or in different situations to see if findings generalize.
Case Study
Descriptive technique focusing on one person or group to reveal universal principles; may not generalize. Also notes limitations in generalization.
Naturalistic Observation
Describing behavior by observing it in its real-world environment without manipulating the situation.
Survey
A method that looks at many cases at once by asking people to report their attitudes or behaviors; relies on random sampling for representativeness.
Sampling Bias
A flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample.
Population
All cases in a group being studied from which samples may be drawn (not always a whole country).
Random Sample
A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion.
Correlation
A measure of how two factors vary together and how well one predicts the other.
Correlation Coefficient
A number from -1.0 to +1.0 that indicates the strength and direction of a linear relationship.
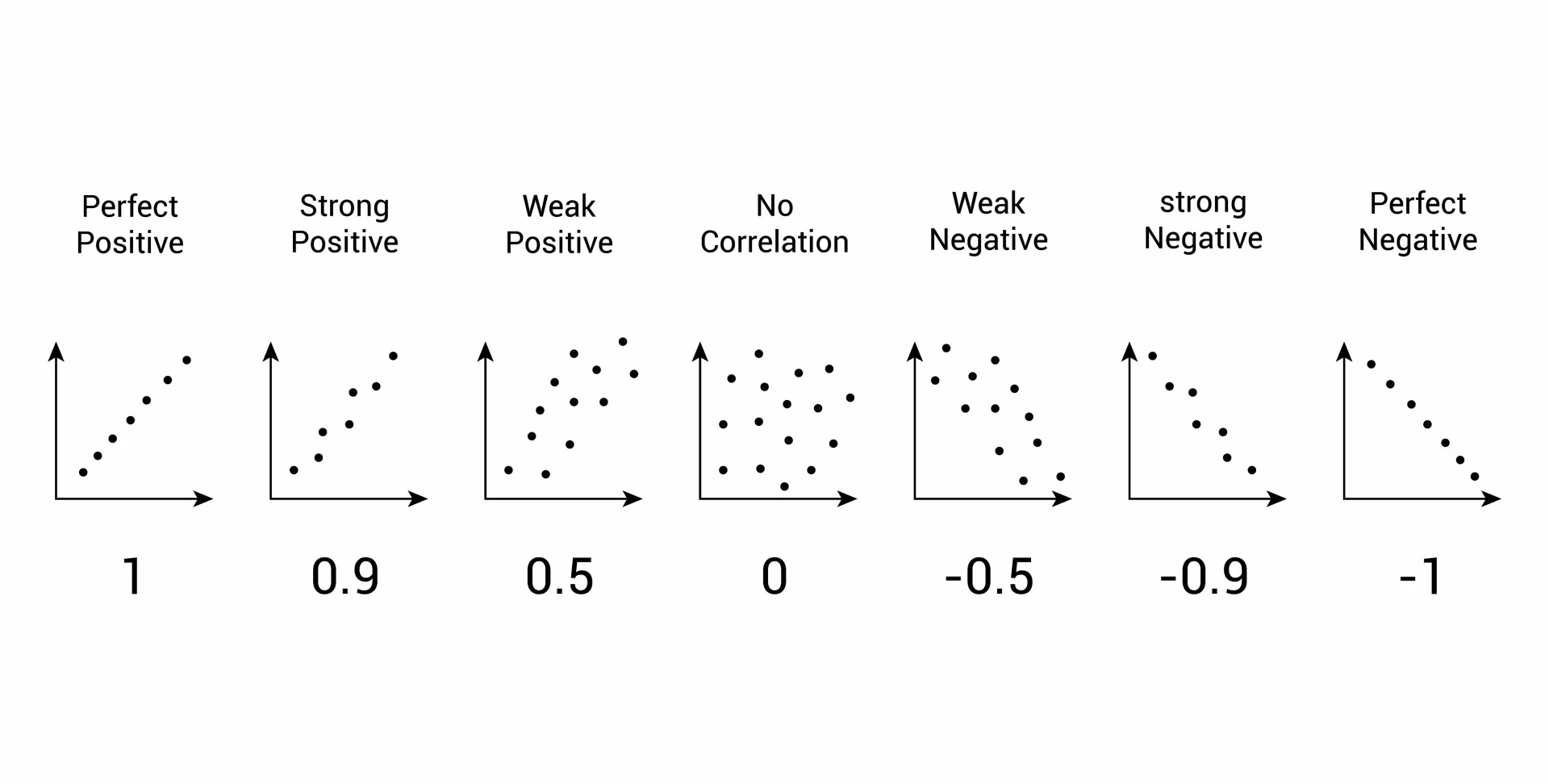
Scatterplot
A graph of data with two variables; the slope shows direction and the scatter shows strength of the relationship.

Illusory Correlation
Perceiving a relationship between variables even when no real relationship exists.
Experiment
A research method that manipulates one or more factors (independent variables) to observe the effect on behavior (dependent variable) with random assignment to control confounds.
Experimental Group
The group that receives the treatment in an experiment.
Control Group
The group that does not receive the treatment, used for baseline comparison.
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance to minimize preexisting differences.
Double-Blind Procedure
An experimental procedure in which neither participants nor researchers know who is in which group, to prevent bias.
Placebo Effect
A change in a participant’s behavior due to the belief that they are receiving a treatment, not the treatment itself.
Independent Variable
The experimental factor that is being manipulated to observe its effect.
Dependent Variable
The outcome factor that is measured in the experiment.
Confounding Variable
A factor other than the IV that might produce an effect in an experiment.
What is the main limitation of correlational studies?
They cannot determine cause and effect relationships
What is the primary purpose of a double-blind procedure in a clinical trial for a new psychological treatment?
To prevent the placebo effect