Unit 6: Gilded Age/Progressive/Frontier/Imperialism
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Populism
A political movement that supports the concerns of ordinary people.
Urbanization
Rapid population shift from rural areas to urban areas due to industrialization.
Imperialism
A policy extending the country’s power and influence through military force.
Laissez-Faire
Minimal government intervention.
Tenement
An overcrowded and run-down building, often in urban areas.
Aquisition
The act of gaining possession of land or territory.
Assimilation
The process where a person or group adopts the culture of another group.
Capitalism
An economic system characterized by private ownership and free markets.
Horizontal Integration
The buying or merging of similar companies across one industry.
Recall
A vote to remove an elected official by the public.
Referendum
Direct vote by the people on a proposal, a law, or a political issue.
Initiative
Power of the people to directly propose and enact laws.
Vertical Integration
The buying or merging of companies across all levels of production.
Political Machine
Party organization that recruits members by incentives (money)
Conservation
Policy that stated that the U.S. should save some of its land for national parks but also use some of its resources.
Monopoly/Trust
A single company has an unreasonable amount of control over a market.
Social Darwinism
A belief that certain people are naturally better and become powerful.
Gospel of Wealth
The rich have a responsibility to spend their money for the greater good.
Old Immigrants
Came to America (1820-1890) from Northwestern Europe.
New Immigrants
Came to America (1890-1920) from Southern, Eastern Europe, and Asia.
Sitting Bull
Leader of the Lakota Sioux people.
Samuel Gompers
Labor leader of the American Federation of Labor.
Ida B. Wells
A journalist and activist who shed light on conditions of African Americans in the South, specifically lynchings.
Emilio Aguinaldo
Filipino led his country to independence by fighting against Spain and then the Americans.
Henry Ford
Inventor of the Model T automobile and introduced the assembly line.
Boss Tweed
Leader of the Democratic political machine Tammany Hall.
Thomas Nast
Political cartoonist who brought down Tammany Hall and Boss Tweed.
Cornelius Vanderbilt
The Commodore who built his wealth on railroads and shipping.
Ida Tarbell
Muckraking writer of “The History of Standard Oil” which caused a trial to break it.
Upton Sinclair
Muckraking writer of “The Jungle” which brought about changes in food.
WEB DuBois
Believed that African Americans should demand Civil Rights; started in NAACP.
Booker T. Washington
Founder of the Tuskegee Institute that helped blacks with self-help.
Thomas Edison
Inventor of hundereds of electrical products in the late 1800s.
John Rockefeller
Robber Baron who made his fourtune from his monopoly of oil refineries.
JP Morgan
Robber Baron who controlled the financial institutions and part of many Trusts.
Andrew Carnegie
Robber Baron who made his fourtune from his monopoly of the steel industry.
Jane Addams
An activist on the frontline of the settlement house movement.
NAACP
Organization that advocates for civil rights and social justice.
Teddy Roosevelt
Progressive Era President who added millions of acres for conservation.
Assembly line
A way to build complex items as it moves from person to person on a conveyor belt.
Barb Wire
Clusters of short, sharp spikes set at intervals to make a fence.
Telephone
A system of transmitting voices over a distance using wire or radio.
Railroad
A system of tracks with trains.
Steel
A metal alloy made up of iron and carbon (incredibly strong).
Oil
A fossil fuel and nonrenewable energy source used for power.
Electricity
A form of energy from charged particles.
Telegraph
A device that sends information over long distances converting the message into electric impulses.
Advertising
The promotion of a commercial product or service.
Philippine-American War
Fight over Independence instead of a change in colonial rulers.
Chinese Exclusion Act
Law which did not allow immigrants from China to enter the United States.
Tammany Hall
Political Machine in New York City led by the corrupt Boss Tweed.
Ellis Island
Entry point for many New Immigrants from Europe.
Settlement Houses
Organization that provides services to the poor and immigrants.
Little Big Horn
Indian battle led by Crazy Horse in which they wiped out the 7th Calvary.
Wounded Knee
Indian massacre after the Ghost Dance about the killing off of the buffalo.
Angel Island
Entry point for many New Immigants from Asia.
AFL
Labor union of skilled workers (mostly white men).
Roosevelt Corollary
The U.S. had the responsibility to preserve and protect the western hemisphere (can be anywhere now).
Spanish-American War
Conflict between U.S. and Spain over the explosion of the USS Maine.
Great White Fleet
The U.S. Navy’s nickname at the turn of the century.
Uncle Tom’s Cabin
Book about an enslaved person, depicted as saintly and dignified.
How the Other Half Lives
Book that depicted slum life and how the poor lived in tenement houses.
The jungle
Book that exposed the meat packing industry; led to the Meat Inspection Act.
The History of Standard Oil
Book that exposed the negatives of monopolies and led to an anti-trust case.
Muckrackers
Writers in the Progressive Era who exposed poverty and corruption in society.
Yellow Journalism
“Sensationalism of the news” which used emotions rather than facts.
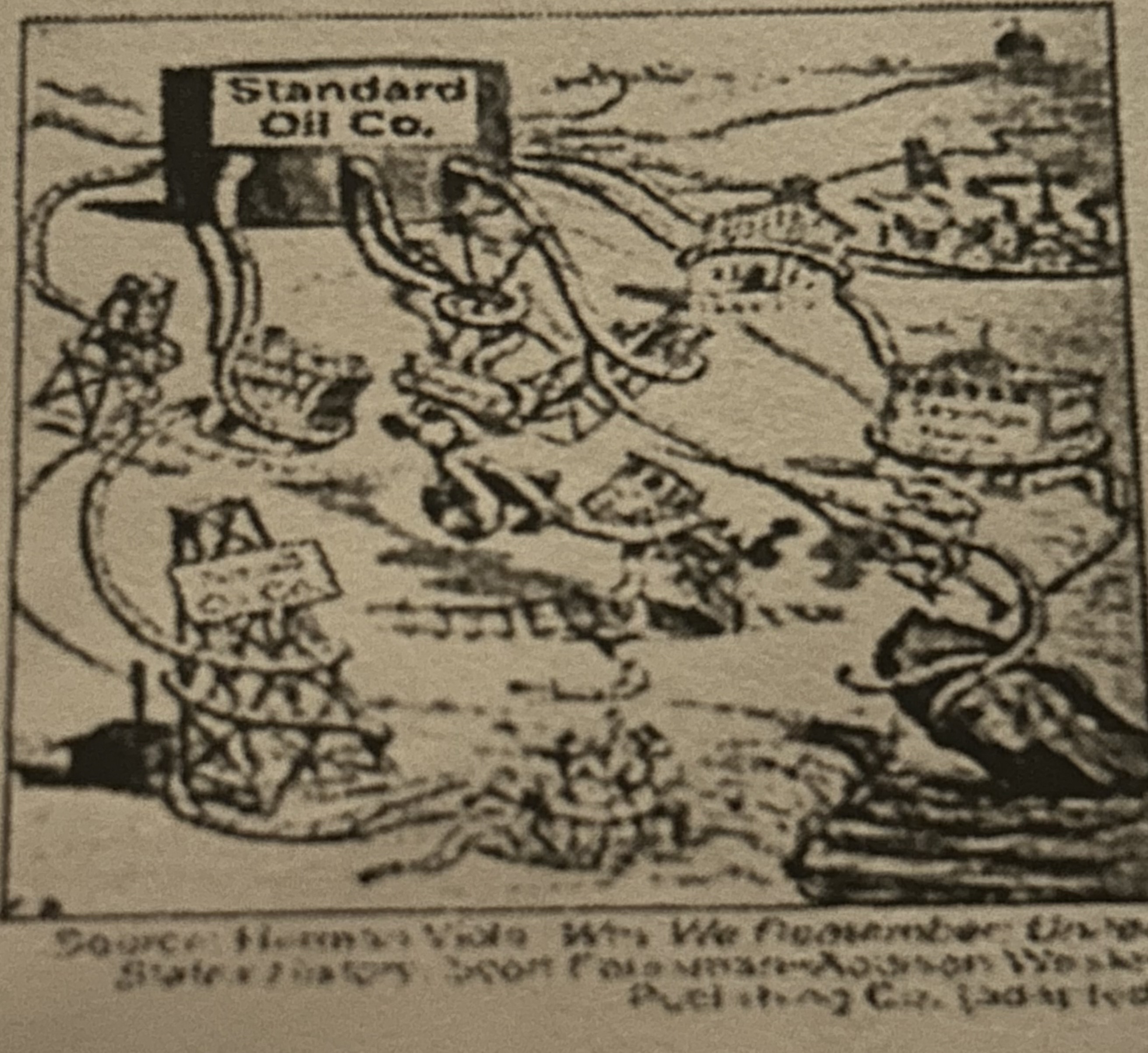
What does this picture depict?
Monopoly
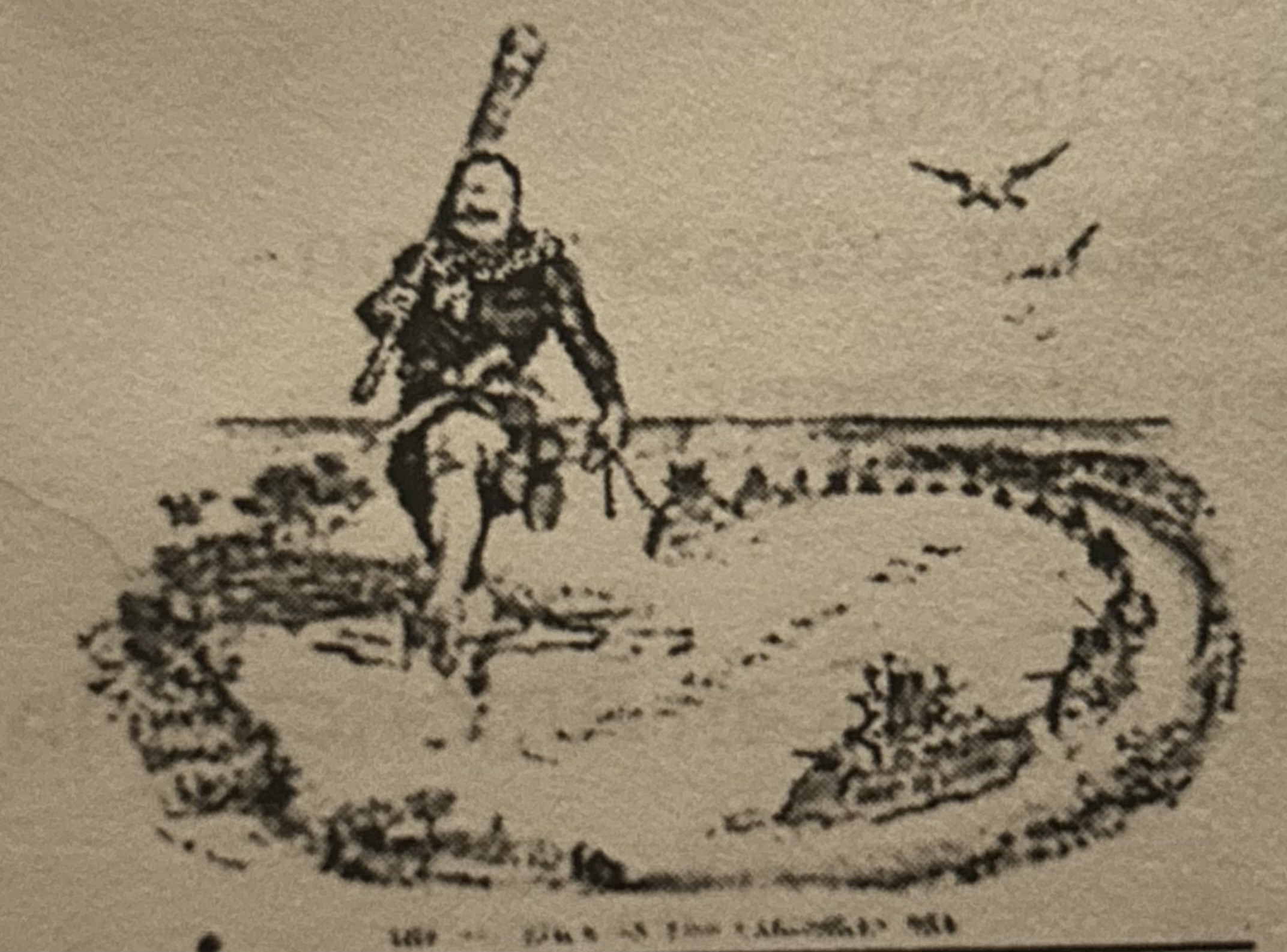

What does this picture depict?
Teddy Roosevelt Coorelary

What does this picture depict?
Tenements
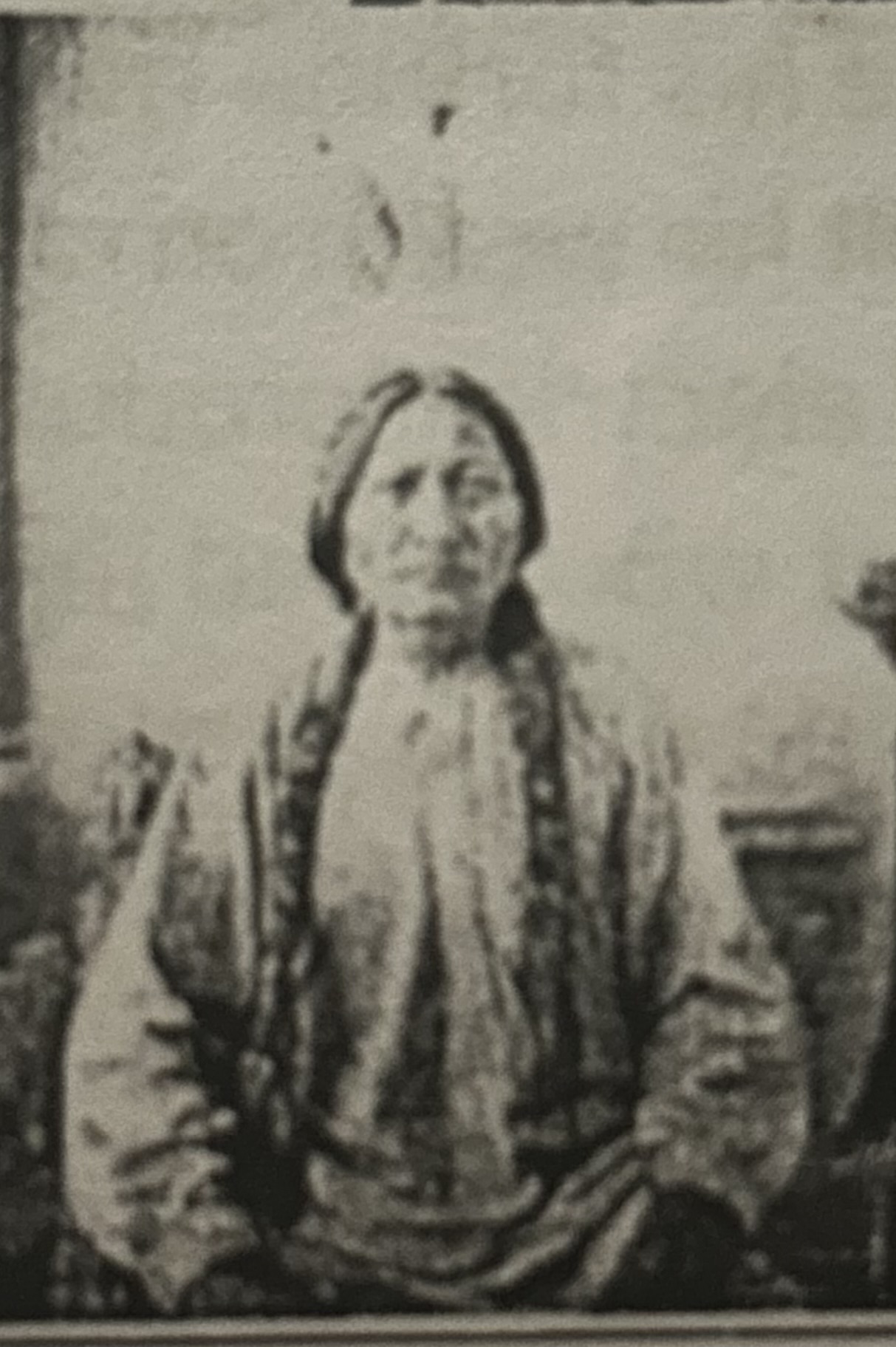

What does this picture depict?
Sitting Bull

What does this picture depict?
Boss Tweed
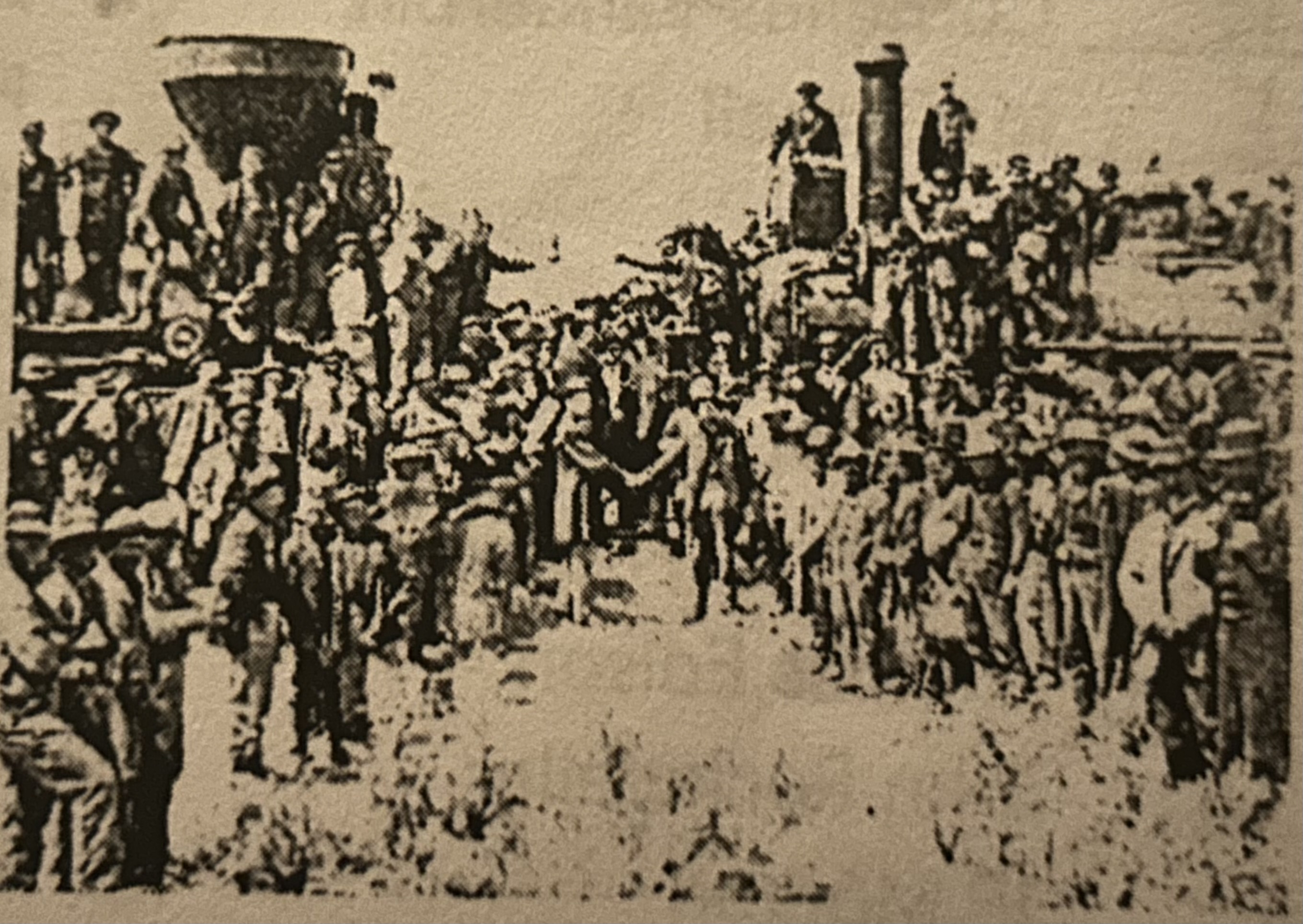

What does this picture depict?
Transcontinental Railroad
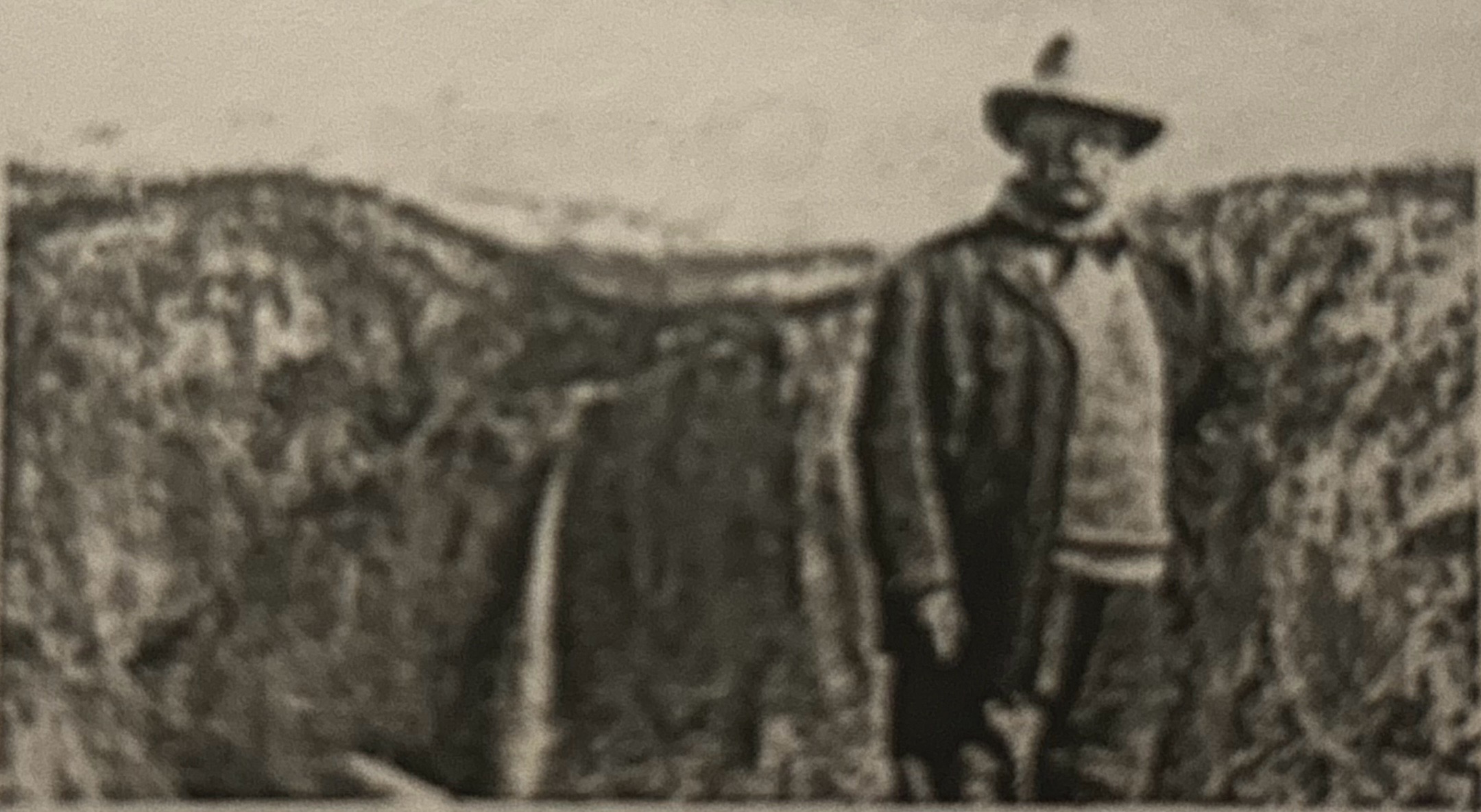

What does this picture depict?
Teddy Roosevelt at Yellowstone park