Base Ten and Fractions
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Scientific Notation
numbers expressed as the product of a base-10 number and a number between 1 and 10
Example:
2.56 x 10 = 25.6
4.32 x 10-4 = 0.000432
Non-proportional Manipulatives
objects that are not proportional to each other with respect to shape and size. Often, all of the items are the same size.
Example:
Counting Tokens

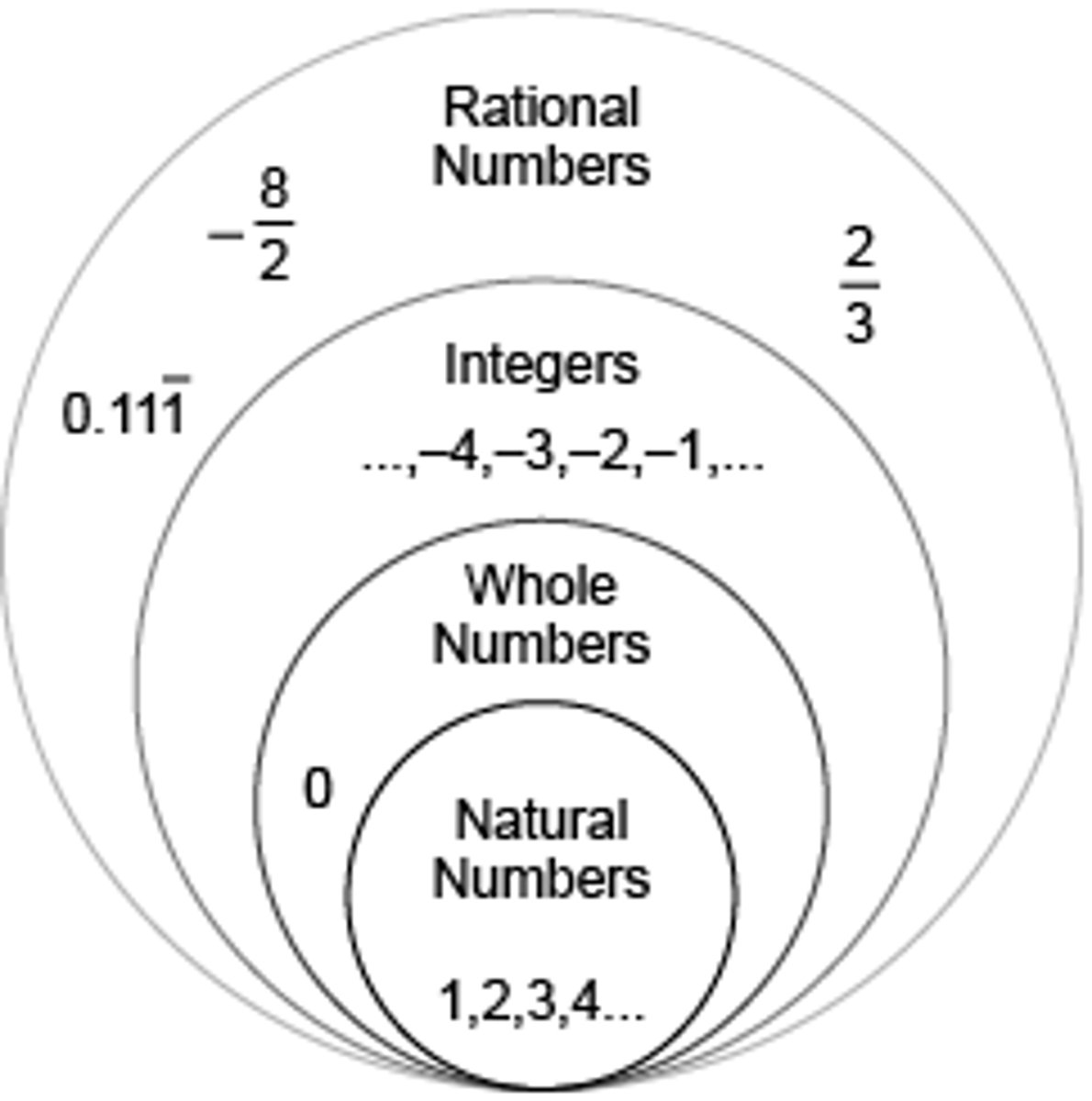
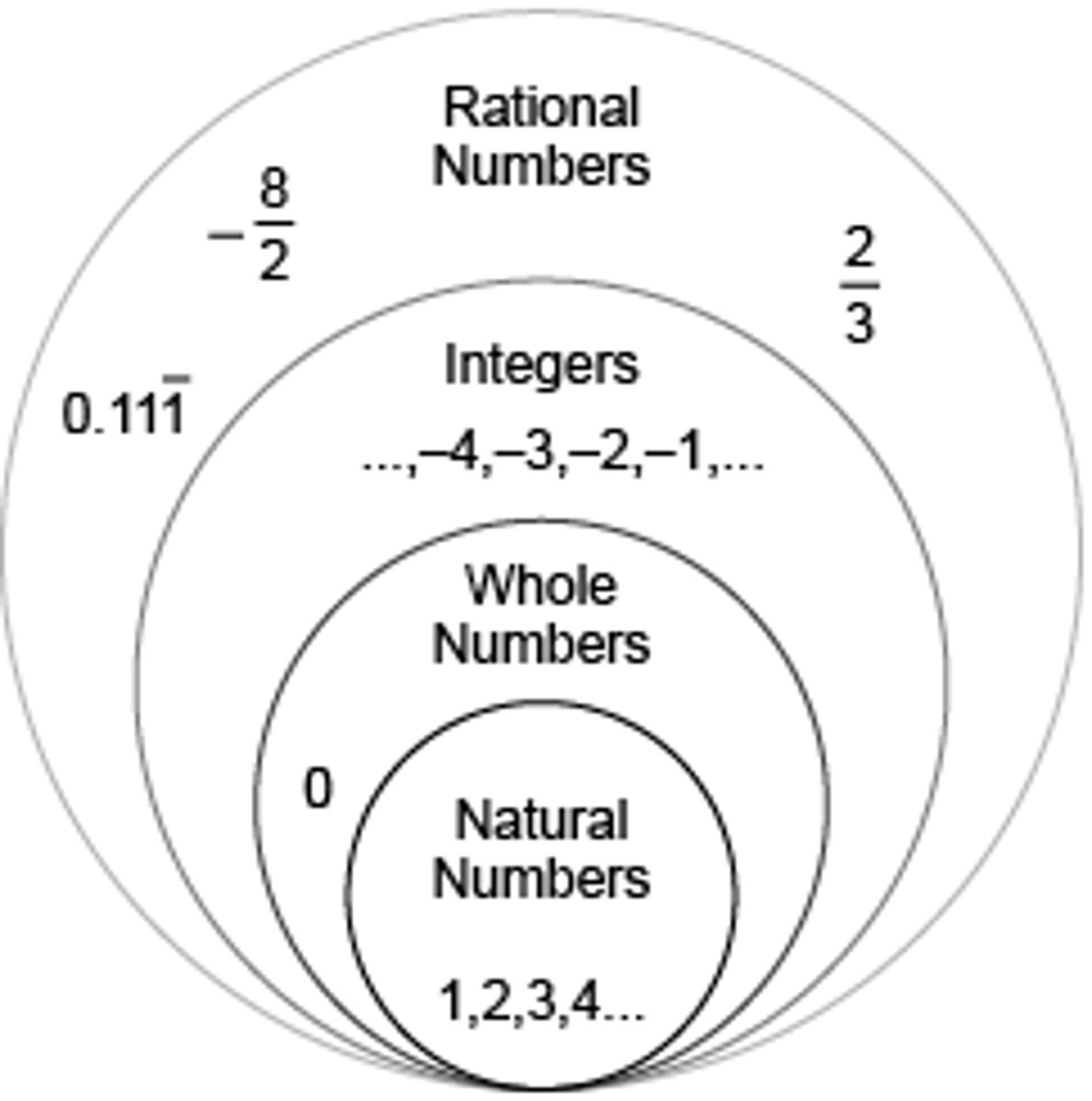
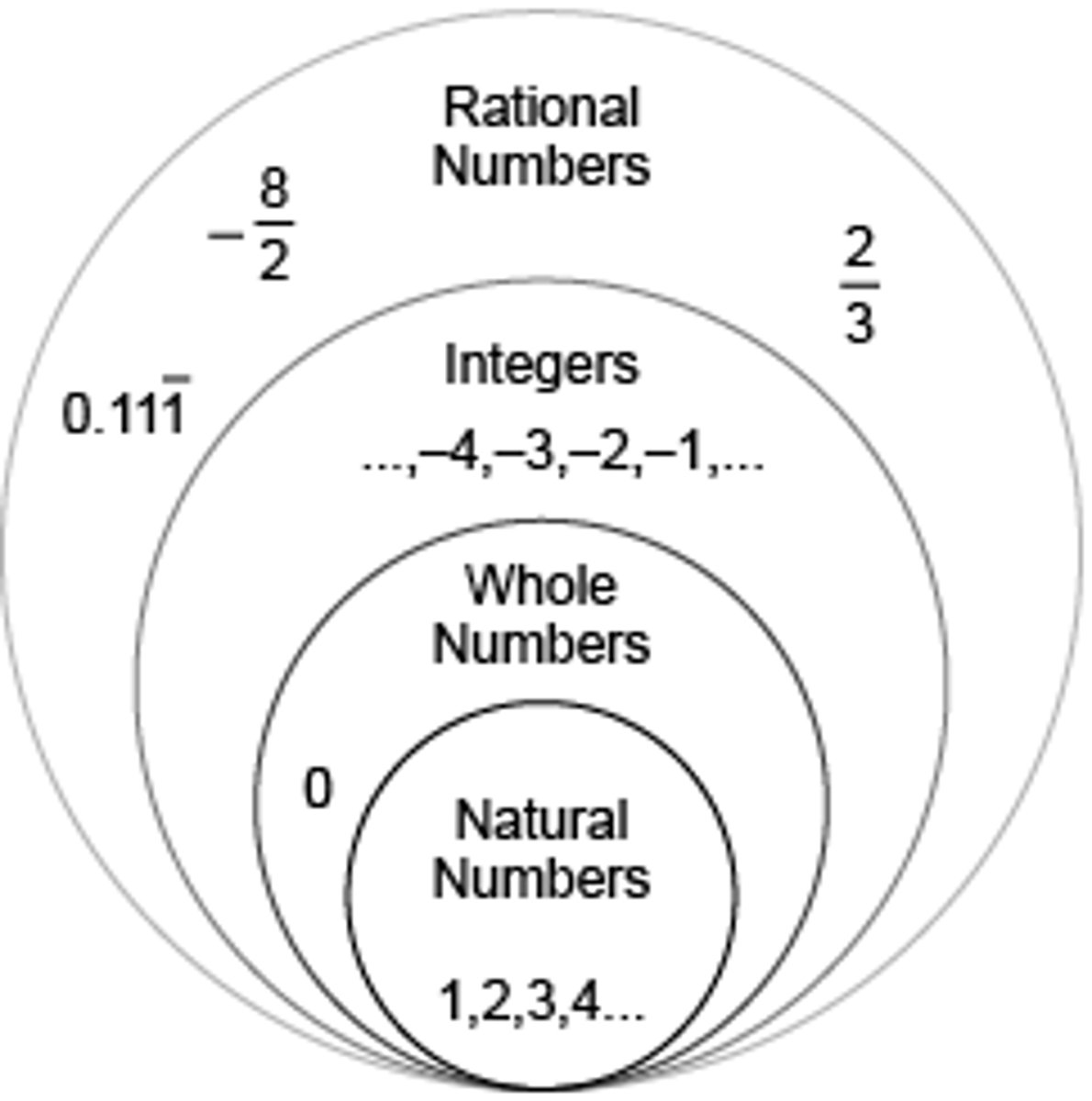
Natural Numbers
set of counting numbers starting at 1 and increasing by 1s up to infinity; sometimes called "counting numbers"
Example:
1, 2, 3, 4....
Number Line
a straight line where each number is equal distance from the next one
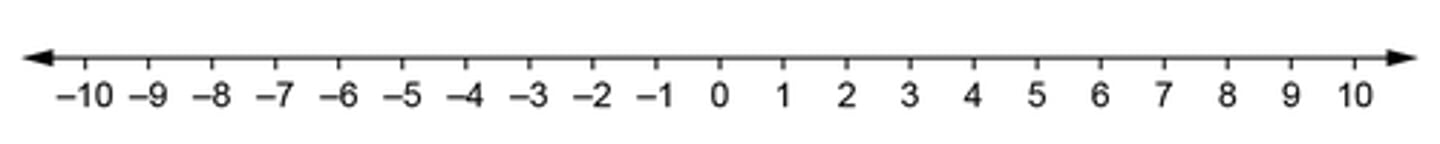
Sum
the result of adding two or more numbers, a total
Example:
addend + addend = sum
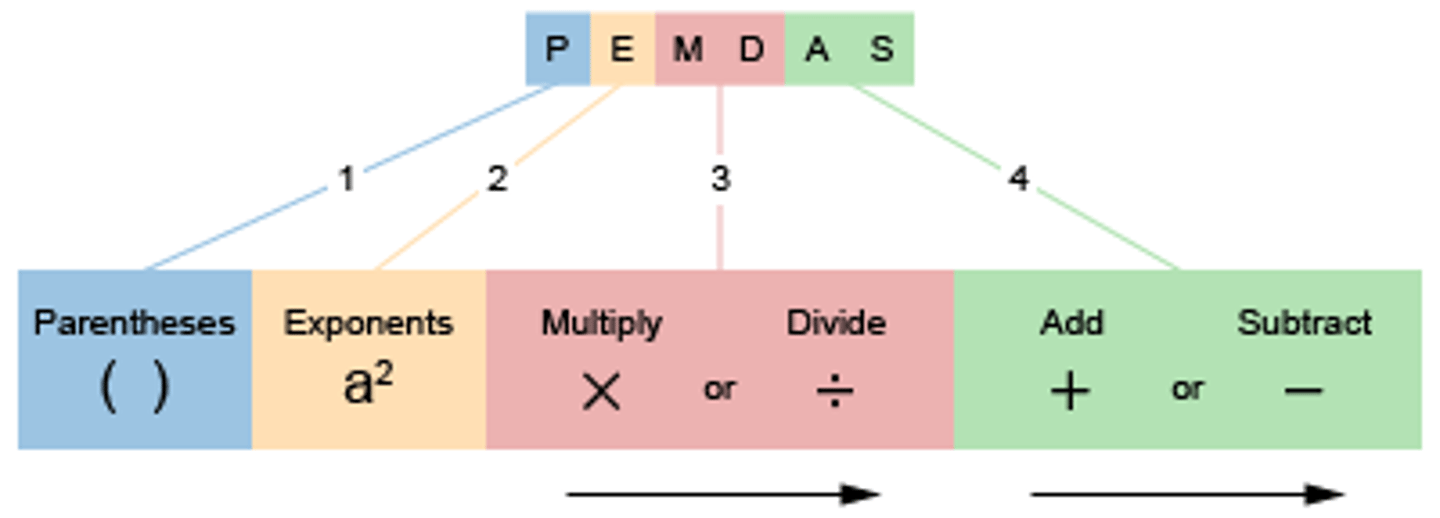
Order of Operations (PEMDAS)
the set order in which multi-step equations must be solved: Parenthesis, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (left to right), Addition and Subtraction (left to right)
Addend
a number that is added to another number
Example:
addend + addend = sum
Dividend
A number that is divided by another number (divisor) to find the quotient
Example:
dividend ÷ divisor = quotient
Rounding
A number is simplified to its closest multiple of 10, 100, 1,000, etc.
Example:
26 rounds UP to 30
Integers
infinite set of positive and negative counting numbers and zero
Example:
–2, –1, 0, 1, 2
Concrete Operational Stage
the third stage of Piaget's Theory of Cognitive development, occurring from 7 years old to adolescence, in which children begin to think logically and use inductive reasoning
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers; the smallest number two or more numbers will divide into evenly
Example:
For 12 and 15, LCM = 60
Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60
Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60
Expanded Form / Expanded Notation
break apart each digit in the number and show the digits' true value
Example:
4,358→4000+300+50+8
Irrational Numbers
real numbers that CANNOT be represented exactly; they can not be shown as a ratio of two integers nor placed on a number line
Example:
pi (π)
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) / Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
the greatest factor that is common to two or more numbers; the largest number that will divide evenly into two or more numbers
Example:
For 12 and 15, GCF = 3
Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Factors of 15: 1, 3, 5, 15
Improper Fraction
A fraction where the numerator is larger than the denominator
Example:
3/2
Closure Property
The sum of two real numbers is a real number.
The product of two real numbers is a real number.
Example:
2.5+3=5.5
Reciprocal Fraction
the inverse or "flip" of a fraction in which the numerator and denominator switch places
Example
1/2 → 2/1
Quotient
The result of dividing two numbers
Example:
dividend ÷ divisor = quotient
Fraction Decomposition
Breaking down a fraction into smaller fractions that total to the original
Example:
2/3 = 1/3 + 1/3
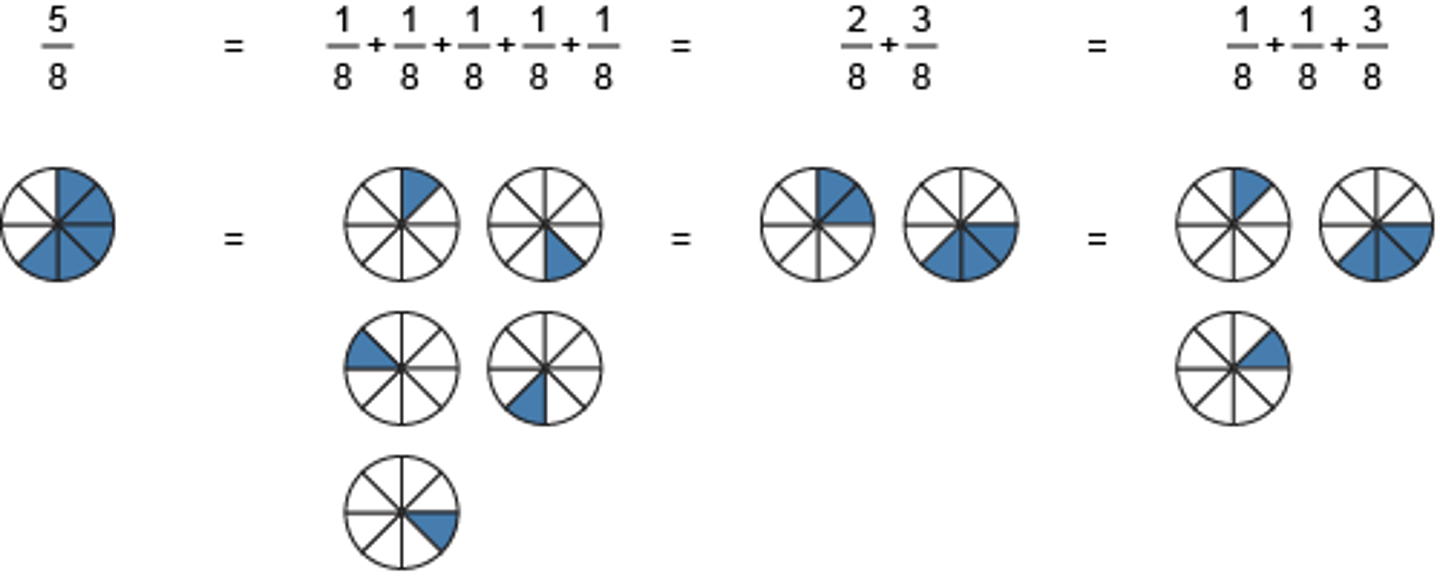
Divisor
A number that divides another number (dividend) to find the quotient
Example:
dividend ÷ divisor = quotient
Commutative Property
An operation is commutative if changing the order of terms does not change the outcome
Example:
a+b=b+a
Factors
Values that are multiplied to get another number.
Example:
Some factors of 12 are 3 and 4 because 3 × 4 = 12
3×4=12
Zero Product Property
When a real number is multiplied by 0, the result is 0.
Example:
5 x 0 = 0
Associative Property
An operation is associative if regrouping the terms does not change the outcome
Example:
(a + b) + c= a + (b + c)
Real Numbers
numbers that have a specific value
Example:
-2, 3, 1/2, 3.2, √2
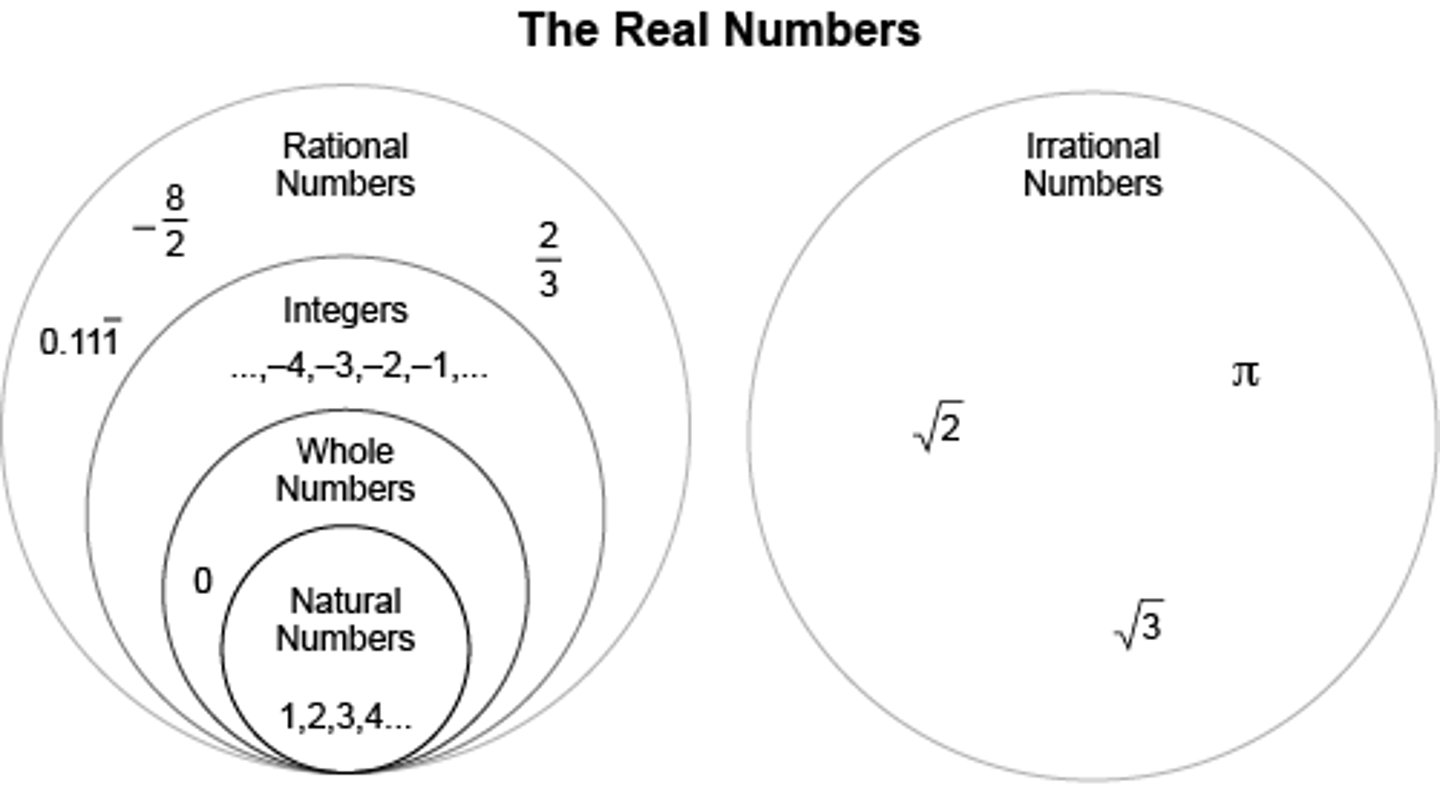
Whole Numbers
Infinite set of natural numbers and zero
Example:
0,1,2,3, ...
Base 10 Number System
Our number system. Each place location for a number has a value that is a power of 10
Example:
10, 100, 1000, 10000

Numerator
the top term of a fraction

Proportional Manipulatives
objects that are proportional to each other with respect to shape and size
Example:
Tangrams

Difference
the result of subtracting one number from another
Example:
x − y = difference
Unit Fraction
a fraction composed of 1 over any rational number; the inverse of a whole number
Example:
1/2 or 1/19
Multiplicative Identity Property
a number that, when multiplied by x, yields x. These are one or forms of one such as x/x
Example:
6 x 1 = 6
Benchmark Fraction
an easily remembered fraction that can be used to make problems simpler
Example:
1/10, 1/4, 1/2, etc.
Fraction Composition
Adding fractions to come up with a larger one
Example
1/4 + 1/4 + 1/4 = 3/4
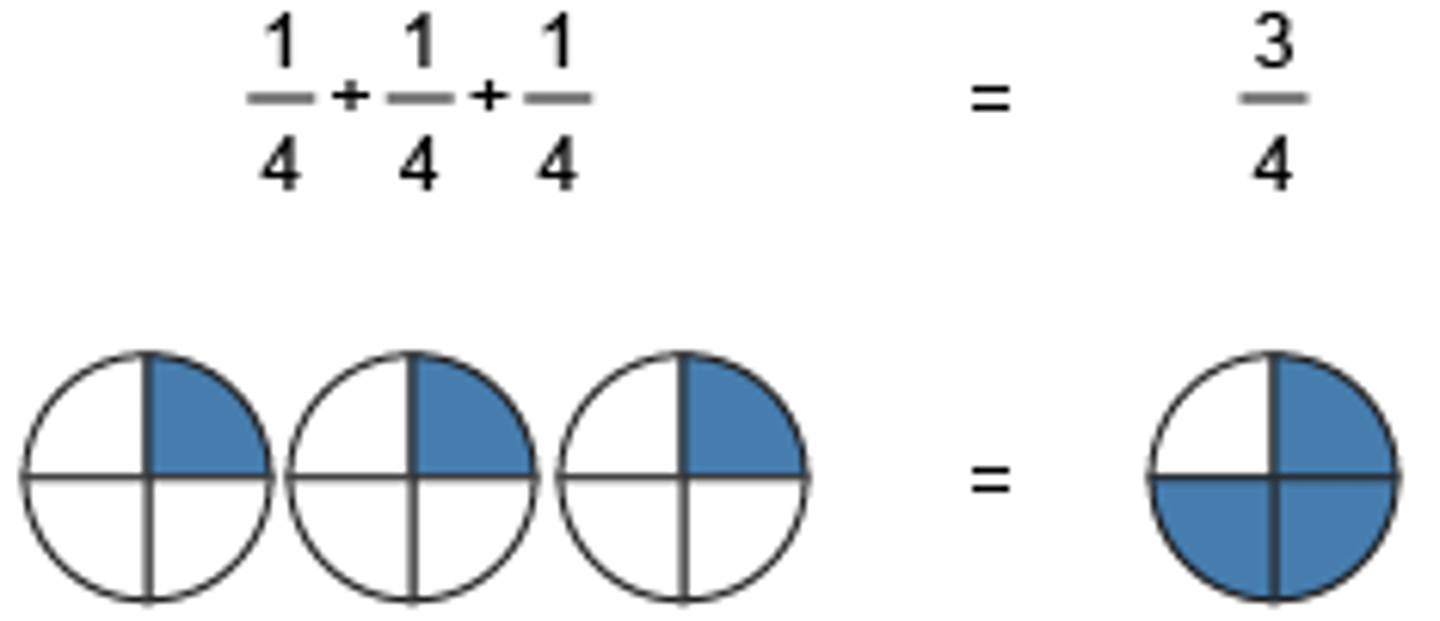
Denominator
the bottom term of a fraction

Mixed Number
A whole number with a fraction
Example:
3 1/2
Distributive Property
a number in front of a group of terms will multiply all terms in the grouping individually
Example:
a(b + c) = ab + ac
Manipulatives
objects used by students to illustrate and explore mathematical concepts, such as to represent numbers in an equation
Example:
Blocks, Coins
Multiplier
a number that multiplies another number (multiplicand)
Example:
multiplicand × multiplier = product
Common Denominator
when 2 fractions share the same total parts of whatever item or items are being represented
Example:
1/3 and 2/3
Multiplicand
a number that is multiplied by another number (multiplier)
Example:
multiplicand × multiplier = product
Additive Identity Property
a number that, when added to any element x in a set, always yields x. Zero itself is sometimes referred to as the additive identity.
Example:
5+0=5
Product
the result of multiplying two or more numbers
Example:
multiplicand × multiplier = product