C5: Bivariate correlational research
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What was the ‘eavesdropping on happiness’ experiment by Mehl et al.?
Relationship between deep talk & well-being?
deep talk: observed engagement in conversation
well-being: self- & other-rated questionnaires
Results: positive relationship
What was Cacioppo et al.’s research on relationship satisfaction & partner meeting?
Research question: Are people who met their partner online happier in their relationship than those who met their partner offline?
satisfaction: questionnaire
question: online or offline? (categorical variable)
Results: people who met their partner online are significantly happier, but effect size was not big
What was Siddarth et al.’s research on sitting & brain thickness?
Research question: is there a relationship between the number of hours a person sits while working and thickness of certain brain regions
hours sitting: question
thickness brain regions: MRI
Results: negative relationship
Based on the previous examples, what is bivariate correlational research?
Bivariate correlational research examines the relationship between two variables to determine if they are related & to what degree.
What determines if a study is correlational or not?
The variables measured, NOT statistical test
Refresher: briefly explain construct, statistical, internal & external validity.
Construct validity
how well was each variable measured?
Statistical validity
how well does the data support the conclusions?
Internal validity
can we draw conclusions about causality?
External validity
can we generalize to other people, places, times & contexts?
What is the importance of an effect size for the statistical validity?
Large correlation = large effect size = accurate predictions & typically more important = higher likelihood of statistically significant effect
the larger the correlation, the larger the effect size, the more accurate the predictions
significance alone not relevant, effect size more relevant because it says how important a difference is
Are only large effect sizes important?
No, there are exceptions
even small effect sizes can be important
ex. effect aspirin on heart conditions: lower likelihood of getting heart condition, very small effect, but in reality impact is large because you’re able to save a couple of people’s lives, outcome is also important
Small effects can accumulate
ex. if you engage in deep talk daily, well-being starts to get better & better → accumulated effect can be large
Explain what a confidence interval (CI) of 95% means.
= Accuracy of estimate
95% of confidence intervals will contain the true population parameter
ex. r = .06, 95% CI = [.05, .07]
the wider the interval, the less certainty we have what the true population parameter is if .06 is inaccurate, ex. CI = [0, 50]
the smaller the interval, the more accurate
How does the sample size affect the CI?
The larger the sample, the smaller the 95% CI
How can you use the 95% CI to determine whether an effect is statistically significant or not?
If 95% CI doesn’t contain 0 (from H0) → effect statistically significant
If 95% CI does contain 0 (from H0) → effect statistically insignificant
What does p < .05 mean?
p < .05 → reject H0 (accept Ha)
p < .05 → effect size statistically significant
What does statistical significance (i.e. a p value of < .05) imply? (2 things)
Likelihood is <5% that we’d find this effect (or an even larger effect) in our sample, if there were no effect in the population
Likelihood is <5% that we draw an incorrect conclusion in our sample (there’s an effect), while there’s no effect in reality, in population
What is the relationship between effect size & statistical significance?
The larger the effect size, the higher the likelihood that p < .05
positive relationship
What is the relationship between sample size & statistical significance?
The larger the sample size, the higher the likelihood that p < .05
positive relationship
doesn’t necessarily mean that effect size is large
Which 3 things can negatively influence the statistical validity & the conclusions drawn based on statistics?
Presence of outliers
Range restriction
Linear relationship assumption
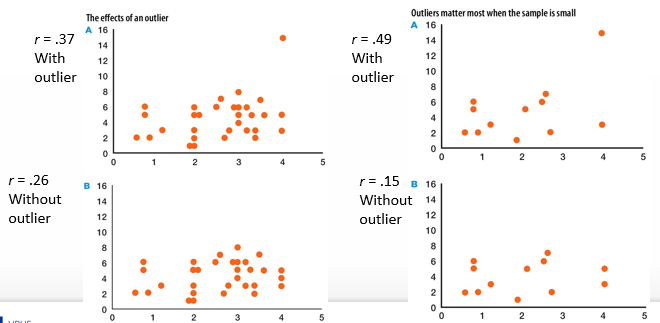
How can the presence of outliers influence the statistical validity & the conclusions drawn based on statistics? When is this problem worse?
Correlation including the outlier will be inflated, higher than without outlier
Problem worse with small samples
How can range restriction influence the statistical validity & the conclusions drawn based on statistics?
Range restriction reduces the strength of a correlation in a sample, compared to the population
ex. only getting data from people who scored >1800 on SATs, because they’re the ones who can go to university
really small SD or variance
→ Every estimate weaker because of range restriction

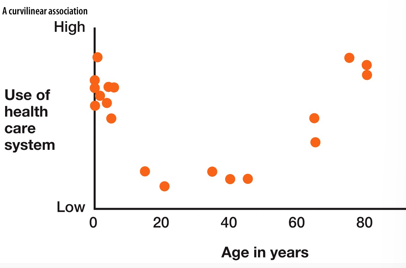
How can a linear relationship assumption influence the statistical validity & the conclusions drawn based on statistics? How can we solve this?
Correlation assumes a linear relationship. If relationship is curvilinear, a correlation may not accurately reflect the relationship between two variables
→ Visualize data in papers
→ Use a different test, or take the square of one of the 2 variables & correlate
What is internal validity about & which 3 conditions have to be met?
Can we draw conclusions about causality?
Conditions:
Covariance
a relationship between 2 variables
Temporal precedence
directionality problem
do we know which one came first in time?
if we can’t tell, we can’t speak about causation
Internal validity
third-variable problem
is there C variable that’s associated with both A & B, independently?
if there is, we can’t speak about causation
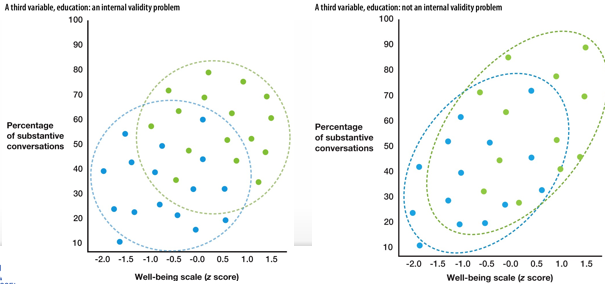
How can the presence of a third variable be spotted?
Inspect data!
Control for 3rd variable C
if there is NO relationship between A & B → 3rd variable
if there still is a relationship between A & B → not a 3rd variable
Is external validity important when investigating relationships?
Not really prioritized when looking at relationships
sometimes even restrictive samples used
But if you can replicate effects in different samples, it will strengthen external validity
What is a moderator & what role do they play in evaluating external validity?
Moderators tell us whether results generalize to different groups, contexts…
to what extent can we generalize results?
Z is a moderator when a relationship between 2 variables depends on the value of Z
ex. relationship group conversations & extraversion: is there a difference between the sexes?
→ gender could be a moderator
significant effect for females, insignificant effect for males → (positive) relationship depends on gender
→ we can generalize to females, but not to males
What is the difference between a moderator & a third variable?
If Z is a moderator, then the relationship between X & Y will be different for different values of Z
ex. relationship between extraversion (X) & amount of group conversations (Y) stronger for women than for men (Z)
If Z is a third variable, the only reason why we observe a relationship between X & Y is because they are both related to Z
ex. there is a relationship between extraversion (X) & amount of group conversations (Y), because both variables correlate with gender (Z)
if we control for Z as a 3rd variable, then the relationship between X & Y would disappear