IGCSE Physics P1.1-P1.4
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
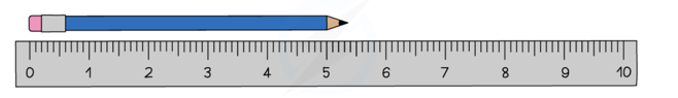
Describe the use of rulers to find a length
Used to measure small distances of a few centimetres (cm)
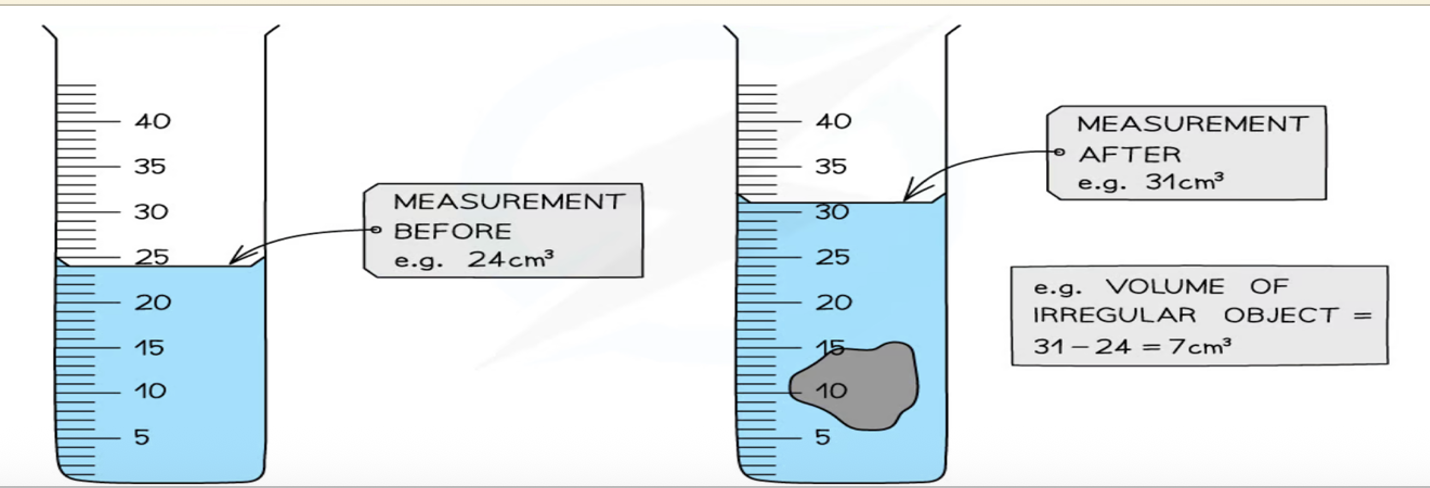
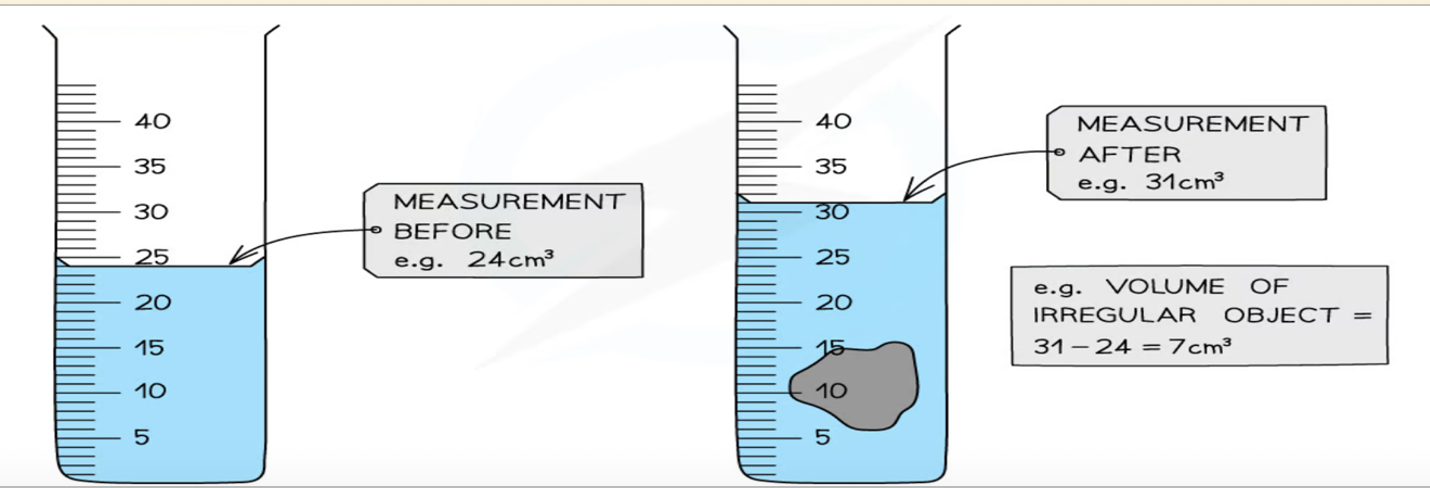
Describe the use of measuring cylinders to find a volume (displacement)
Used to measure the volume of liquids or to find the volume of irregular solids using the displacement method.
Describe how to measure a variety of time intervals using clocks and digital timers
Stop-clocks and stopwatches are used to measure time intervals.
Identify start time for the lap. Identify finish time for the lap.
Calculate total time to complete the lap (end of lap – start of lap).
Determine an average value for a short interval of time by measuring multiples (include period of oscillation of a pendulum)
Small distances (e.g. thickness of paper):
Measure the thickness of a stack of many sheets with a ruler.
Divide total thickness by the number of sheets.
Short time intervals (e.g. pendulum period):
Measure the time for many oscillations with a stopwatch.
Divide total time by the number of oscillations.
State the difference between a scalar quantity and a vector quantity
A scalar quantity has only magnitude (size).
A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
State examples of scalar quantities
Distance (m), speed (m/s), time (s), mass (kg), energy (J), or temperature (°C).
State examples of vector quantities
Force (N), weight (N), velocity (m/s), acceleration (m/s²), or gravitational field strength (N/kg).
Define speed
Speed is the distance travelled per unit time (scalar quantity).
State the equation used for an object moving at constant speed
v (speed) = s (distance) ÷ t (time)
Define velocity
Velocity is the speed in a given direction (vector quantity).
State the equation average speed
Average speed = total distance moved ÷ total time taken
On a distance–time graph, what does the gradient represent?
The gradient represents the velocity of the object.
On a speed/velocity–time graph, what does the gradient represent?
The gradient represents the acceleration of the object.
On a speed/velocity–time graph, what does the area under the graph represent?
The area under the graph represents the distance travelled.
Describe what an object moving with increasing speed is doing
Accelerating
Describe what an object moving with decreasing speed is doing
Decelerating
Calculate speed from the gradient of a straight-line section of a distance–time graph
Speed or velocity = gradient = change in Y ÷ change in X
Define acceleration
Acceleration is the change in velocity per unit time (vector quantity).
State the equation for acceleration
Acceleration = change in velocity ÷ change in time
State the approximate value of the acceleration of free fall, g, near the Earth’s surface and explain why it is considered constant
It is approximately 9.8 m/s², constant due to gravity.
State the term mass
Mass is a measure of the quantity of matter in an object.
Unit: kg.
Scalar quantity.
An object’s mass remains the same anywhere in the universe.
State the term weight
Weight is the gravitational force that acts on an object with a mass.
Unit: Newtons.
Vector quantity.
An object’s weight changes from planet to planet depending on the gravitational field strength g.
Define gravitational field strength (g)
Gravitational field strength g is the amount of gravitational force acting on an object per unit of its mass (vector quantity).
The value of g changes from planet to planet.
Use the equation for weight
W = m × g,
g = W ÷ m,
m = W ÷ g
Describe and use the concept of weight as the effect of a gravitational field on a mass
The bigger and closer the objects, the stronger the gravitational field strength.
What does g represent on Earth’s surface and what is its value?
g represents both acceleration of free fall (9.8 m/s²) and gravitational field strength (9.8 N/kg).
Define density
Density is the mass per unit volume.
Use the equation for density
ρ (density) = m (mass) ÷ V (volume).
m = ρ × V.
V = m ÷ ρ.
Describe how to find the density of a liquid
Calculate the mass: mass of cylinder full of liquid – mass of empty cylinder.
Measure the volume (read from the cylinder).
Calculate density using formula.
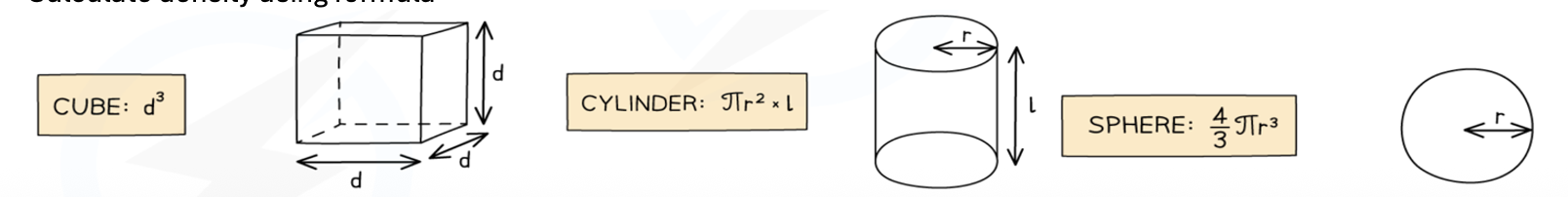
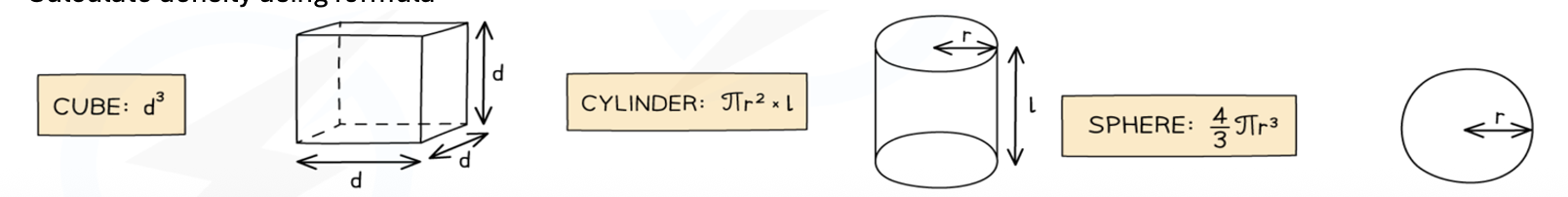
Describe how to find the density of a regularly shaped solid
Measure the mass using a balance.
Calculate the volume.
Calculate density using formula.
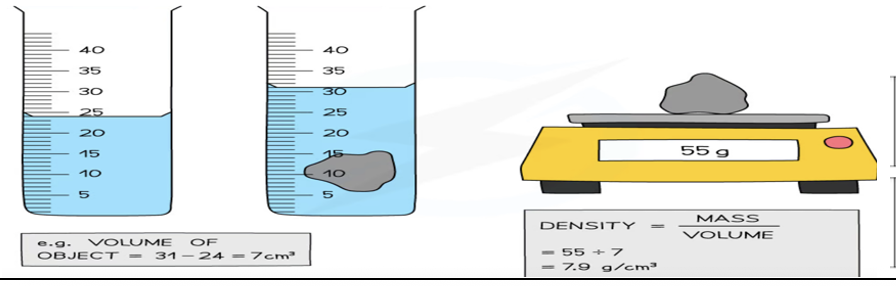
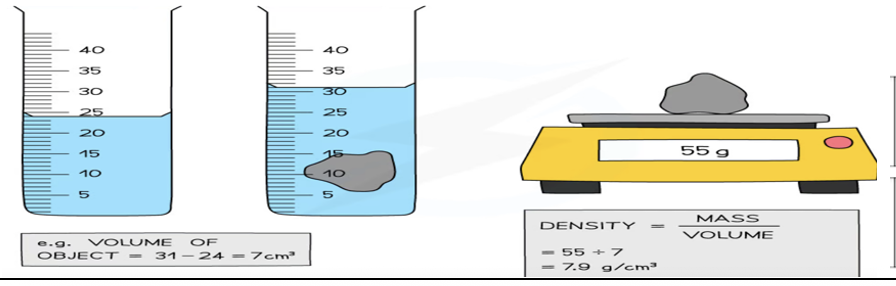
Describe how to find the density of an irregularly shaped solid which sinks in a liquid (volume by displacement)
Measure the mass of the solid using a balance.
Find the volume of the solid using the displacement method: volume = (water level with object) – (water level without object).
Calculate the density using the formula.
Determine whether an object floats or sinks based on density data
Density of object > density of liquid = sink
Density of object < density of liquid = float