Edexcel IGCSE Physics - Cosmology
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
how has the universe evolved over time?
it has expanded from an infinitely dense and extremely hot point; it is still expanding and cooling
what is the main theory for how the universe evolved?
big bang theory
what are the 2 main pieces of evidence that support the big bang theory?
cosmic microwave background radiation
red shift of galaxies
what happens if a wave source moves relative to an observer?
there is a change in the observed frequency and wavelength
what is the change in observed frequency and wavelength called?
the doppler effect
what colour of light has the lowest frequency?
red
what colour of light has the highest wavelength?
red
describe the doppler effect in terms of light
if a light source is moving away from you, the waves behind will spread out and the observed wavelength will increase, decreasing the frequency meaning that the light is shifted to the red end of the spectrum
the opposite will happen if a light source is moving towards you
how is the doppler effect of light seen in the universe (not galaxies)?
the light from distant stars is red-shifted - the light has a longer observed wavelength than we would expect stars to emit - only happens if the stars are moving away from earth
what is the doppler effect for galaxies generally called?
red shift of galaxies
what are absorption spectra?
different elements absorb different frequencies/wavelengths of light
when a light is passed through a sample of an element, dark lines appear on the spectrum where the wavelengths have been absorbed
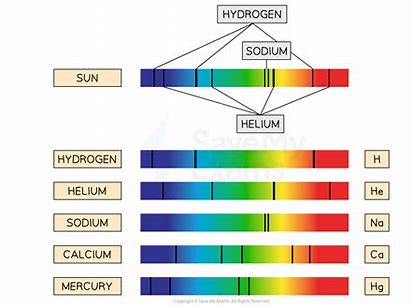
what is the red-shift of galaxies?
when we look at light from distant galaxies (compared to light from the sun/another galaxy), they have the same patterns of lines on their absorption spectra
however, these patterns are at lower frequencies/higher wavelengths - they have been shifted towards the red end of the spectrum
why does red-shift of galaxies provide evidence for the big bang?
more distant galaxies have a greater red shift than nearer galaxies - they have a bigger observed increase in wavelength
this shows that more distant galaxies are moving away faster than nearer ones
this suggests that the whole universe is expanding
this is present wherever you look - galaxies are moving away from each other as well
which model is commonly used to demonstrate red shift of galaxies?
a balloon and pompoms
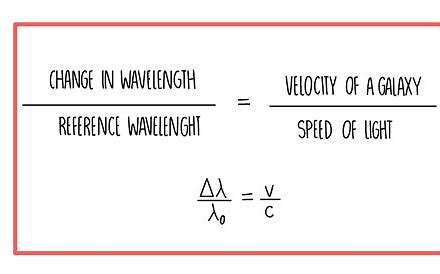
what equation is used to calculate red shift?
what is cosmic microwave background radiation?
low frequency microwave radiation that is detected in all directions and comes from all parts of the universe in all directions
why is cosmic microwave background radiation evidence for the big bang?
it suggests that the universe expanded from a single point
this radiation has also dropped in frequency, suggesting that the universe has cooled