Nervous Tissue
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Central Nervous System
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Cranial Nerves
Autonomic nervous system ganglia
Spinal nerves
Axon
Initial segment: part of axon closest to axon hillock. Most impulses arise at junction between axon hillock and initial segment (trigger zone)
Propagates impulse away from cell
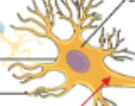
Multipolar Neurons
Multiple processes: several dendrites and one axon
Most neurons in brain and spinal cord are ___
Bipolar Neurons
Two processes: one dendrite and one axon
Unipolar Neurons
One process: dendrites and axon fuse together
Sensory/Afferent Neurons
Convey (deliver) into CNS
Motor/Efferent Neurons
Convey action potentials away from the CNS
Interneurons/Association Neurons
Process incoming sensory information from sensory neurons and elicit (trigger) motor response by activating appropriate motor neurons
99% of neurons are ___
Nerves
Bundle of parallel axons found in peripheral nervous system
Epineurium (Surround, Tissue Type)
Surrounds entire nerve
Dense irregular CT
Perineurium (Surround, Tissue Type)
Surrounds fascicles (bundles of axon)
Dense irregular CT
Endoneurium (Surround, Tissue Type)
Separates and insulates each axon
Areolar CT
Neuroglia/Glial Cells (Characteristics)
Found in CNS and PNS
Support, nurture and protect neurons and maintain interstitial fluid that bathes them
Smaller than neurons, but 5-50 times more numerous
Do not generate or propagate action potential
Can multiply & divide in mature nervous system
Astrocytes
Largest and most numerous of the neuroglia in the central nervous system that compose the blood brain barrier
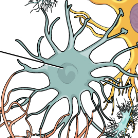
Oligodendrocytes
Found in CNS that form and maintain myelin
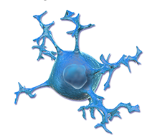
Microglia
Function as phagocytes, remove cellular debris & phagocytize microbes and damaged nervous tissue
Ependymal Cells
Produce, monitor & assist in circulation of cerebrospinal fluid
Myelin Sheath
Multilayered lipid and protein covering
Insulates (enclose) axon and increases speed of nerve impulse
Pump
Moves substances against concentration gradient (low → high)
Requires energy
Channel
Moves substances down its concentration (high → low)
Passive process
Receptive Segment
Dendrites and cell body
Chemically gated channels found at K+ and Cl-
Excitatory neurotransmitter is released and inside of cell becomes more positive
Inhibitory neurotransmitter is released and inside of cell becomes more negative
Initial Segment
Axon hillock
Voltage gated
Determine if threshold membrane potential -55mV is reached
Conductive Segment
axon hillock to synaptic knob
voltage gate
Action potential propagates along the length of an axon to nerve signal/impulse
Transmissive Segment
Synaptic knob
Voltage-gated
Calcium channels open enabling calcium to move down its gradient into the synaptic knob
Calcium ions bind to synaptic vesicles and triggers release of neurotransmitters
Resting Membrane Potential
Relative difference in charge across the plasma membrane of resting, excitable cell
Value is -70 millivolts
Depolarization
Occurs when the inside of a cell becomes more positive than the resting membrane potential +30mV
Repolarization
Occurs when the inside of the cell returns to a negative value -70mV
Graded Potential
Occurs in the receptive segment of neuron (dendrites, cell body)
Decreases in intensity
Action Potential
Generates in the initial segment of the axon and propagates along the axon
Happens when voltage gated channels open from reaching minimum voltage, this triggers successive channels to open all while the intensity is maintained.
Schwann Cells/Neuroclemmocytes
Found in PNS that form myelin sheath around axons of neurons