AP Psych: Unit 2
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from the myers textbook. 2.1 Perception - 2.8 Intelligence and achievement
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Selective Attention
Focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
Inattentional Blindness
Failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
Change Blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment
Perceptual Set
mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another
experience → expectations
gestalt
A german word for ‘organized whole’
Tendency for people to integrate information into meaningful wholes.
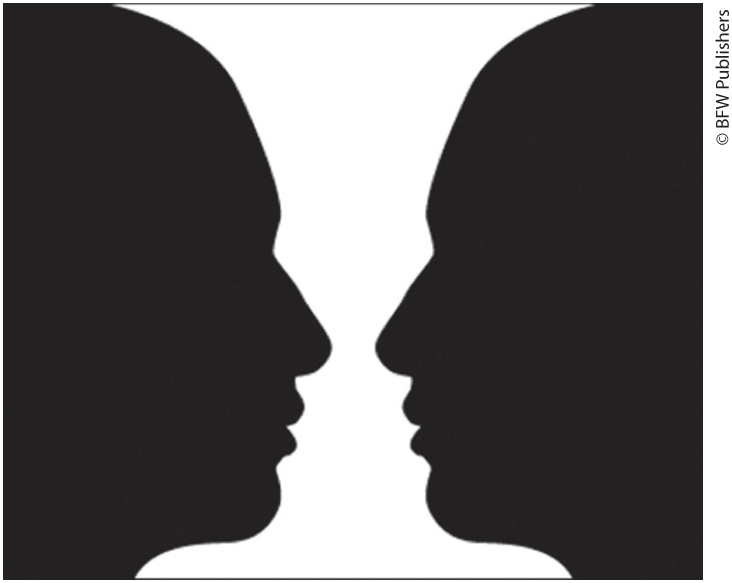

Figure-ground
Organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings
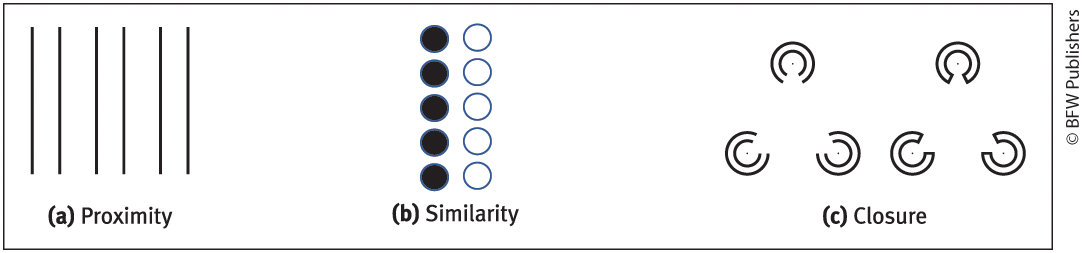
Grouping
Perceptual tendency to group stimuli into coherent groups
depth perception
ability to see objects in three dimensions; although the image in the retina is 2D; It allows us to judge distance
Visual cliff experiment
Experiment on infants in a lab where there was a ‘visual cliff’ that imitated depth, the toddlers were coaxed by their parents into going towards them however many of them refused to do so, indicating that they had depth perception
Cocktail party effect
Ability to attend to only one voice as opposed to many when focused on a conversation, for example you are able to single out someone calling your name whilst talking to someone
Binocular cues
A depth cue, depends on the use of both eyes
Retinal disparity
Cue for percieving depth, by comparing both retinal images, the brain computes the distance. The greater the difference between two images, the closer the object is.
Convergence
A cue to nearby objects’ distance, enabled by combining both retinal images
Monocular cues
Depth cues available to each eye seperately
Stroboscopic movement
an illusion of continuous moving images experienced when viewing a rapid series of images
Phi phenomenon
Illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession
Autokinetic effect
Illusory movement of a still spot of light in a dark room
Perceptual constancy
Perceiving objects as unchanging (color, brightness, shape, size) even as illumination and retinal images change
Color constancy
Perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color even in different illumination that alters the wavelength
Perceptual adaptation
Ability to adjust to changed sensory input
Cognition
Focus on mental activities like thinking, knowing, remembering, memorizing
Metacognition
‘beyond cognition’ Cognition of our cognition; keeping track of and evaluating our mental processes.
Students that keep monitor and track their learning do better in school.
Concepts
Mental groupings of similar objects, events, people, ideas
Prototype
mental image or best example of a category
E.g: Which is more birdlike, a crow or penguin?
Schemas
Jean Piaget’s proposal, a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
Assimilate
Interpreting new experiences in terms of existing experiences
Accomodate
Adjusting current schemas to incorporate new information
Creativity
ability to create new and valuable ideas
Convergent thinking
narrowing available problem solutions to determine the single best
E.g: SATs
Divergent thinking
Ability to consider many different options, creative thinking that can diverge into many ways
Executive functions
cognitive skills that work together, enabling us to generate, organize, plan and implement goal-directed behavior
Algorithms
methodical, logical procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem
Heuristics
Simpler thinking strategy, allows us to make judgements and solve problems efficiently.
E.g: experiences and knowledge from past give you a solution quicker
Insight
Sudden realization of a problem’s solution
Confirmation bias
Tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore contradictory evidence
Fixation
Inability to see a problem from another perspective, obstacle to problem solving
mental set
tendency to approach a problem in one particular way that has been successful in the past
Intution
effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought in comparison to conscious reasoning.
Represantativeness heuristic
judging the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent or match certain prototypes. May lead us to ignore relevant information
Avaliablity heuristic
judging likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; when instances come suddenly to mind, we think they are more common than we think.
Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct, overestimate our the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments
Belief perseverance
persistence of own initial conceptions even when it’s basis is discredited
Framing
The way an issue is posed; affects decisions and judgments
Nudge
framing choices in a way so people make beneficial decisions
Memory
persistence of learning over time through, encoding, retrieving and storage of information
Recall
Retrieving information from earlier (fill in the blank questions)
Recognition
Identifying items previously learned (multiple choice question)
Relearning
Learning something more quickly, saving time when learning something again
Hermann Ebbinghaus created experiment about relearning using nonsense syllables
Encoding
Getting information into the brain
Storage
retaining encoded material
Retrieval
getting memory out of storage
Parallel processing
processing multiple aspects of stimuli
Sensory memory
immediate and brief recording sensory information in the memory system
(first step of Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin three stage memory model)
Short-term memory
brief activated memory of a few items that are later forgotten or stored
George A. Miller proposed that people can remember seven items at a time, like the 7 seas, 7 colors,
Long-term memory
Relatively permanent archive of the memory system, like knowledge, experience and skills
working memory
newer understanding of short-term memory: active processing of incoming sensory information and information retrieved from long-term memory.
Central executive
coordinated activities like phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad
Phonological loop
briefly holds auditory information
Visuospatial sketchpad
briefly holds information about objects’ appearance and location in space. (mental maps, where you parked car, route from home to school)
Neurogenesis
formation of new neurons
Eric Kandel researched about this on sea slugs
Long-term potentiation
increase in nerve cell firing potential after brief stimulation. (neural basis for learning + memory)
Explicit memories
retention of facts and experiences that we consciously know
Effortful processing
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Automatic processing
unconscious encoding of information, e.g space, time, location, familiar info
Implicit memories
retention of learned skills and classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection (riding a bike)
Iconic memory
Encoding visual information
Echoic memory
Encoding auditory information
Chunking
Organizing information into familiar, managable units; happens automatically (recalling phone numbers)
Mnemonics
memory aid, vivid imagery and organizational devices (never eat soggy waffles= N E S W)
Spacing effects
tendency for distributive study or practice to yield better results than massed study and practice.
(so don’t and study for 5 hours straight because you will not retain the information, sorry.)
Testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving rather than simply rereading (repeated self testing after learning new information)
Shallow processing
encoding on a basic, elementary level based on structure of word
Deep processing
encoding semantically, based on meaning of the word.
(best for retention of information)
Semantic memory
Explicit memories of facts or general knowledge
Episodic memory
explicit memories of experiences events
Hippocampus
part of the limbic system, processes explicit memories for storage
Memory consolidation
neural storage of long-term memory
Flashbulb memory
a clear memory of emotionally significant events
Priming
Activation (usually unconsciously) of certain associations predisposing one’s memories or response.
Encoding specificity principle
idea that cues and contexts specific to a memory will be most effective in recalling it.
Mood-congruent memory
tendency to recall experiences that connect to current mood; either good or bad.
Serial position effect
Tendency to recall last few items in a list initially than the first few after a delay.
Interleaving
retrieval practice strategy involves mixing the study of different topics
(switch between study topics so that you’re not bored C:)
Anterograde amnesia
Inability to form new memories after an event
E.g: When someone can’t remember anything after a car accident but can recall past events
Proactive interference
Difficulty in learning new information due to old information interfering
E.g: Struggling to remember a new phone number because you keep recalling an old one
Retrograde interference
Difficulty in retrieving old information due to new information learned
E.g: Forgetting names of old classmates after learning the names of new classmates.
Repression
Unconsciously blocking out painful memories or traumatic event
Reconsolidation
The process of stabilizng a memory after it is recalled
E.g: When recalling a past experience, the memory may change slightly each time.
Misinformation effect
Tendency for memories to be corrupted by misleading information
Source amnesia
Faulty memory of how, when and where information was obtained or learned
Déjà vu
Eerie sense of “i’ve experienced this before”
Cues from current situation might unconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience
Intelligence
A person’s ability to learn from experiences, solve problems and use knowledge to adapt to new social situations
General intelligence (g)
Idea by Charles Spearman, that a person’s intelligence is measured by every task on an intelligence test and contains all mental abilities.
Factor analysis
Statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items on a test. Identifies different dimensions of performance that underlie a person’s total score.
Fluid intelligence (gf)
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease with age, especially during late adulthood.
Crystallized intelligence (gc)
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age.
Cattell-Horn-Caroll (CHC) Theory
the theory that our intelligence is based on g as well as specific abilities, bridged by Gf and Gc.
Savant syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill, such as in computation or drawing.
grit
Passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals.
emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions.