Ventilation and Ventilatory Tests
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Respiratory Therapy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is Tidal Volume (VT)?
It's the volume of air inspired or expired during each respiratory cycle.
- Measured in L or mL.
- Corrected to BTPS.
What is respiratory rate (RR)?
It's the number of breaths per minute or how many breaths you breath in one minute.
- Normal range 12-20 breaths/min.
- Called "breathing frequency" or "respiratory frequency" (fb).
How can Tidal Volume be directly measured?
By simple spirometry.
Patient breaths into a volume-displacement or flow-sensing spirometer.
It can also be measured from an integrated flow signal.
What are two stimuli measured in ventilatory response?
High CO2
Low O2
Difference between Alveolar Ventilation (VA) and alveolar dead space.
Alveolar Ventilation is the gas that participates in gas exchange.
Alveolar dead space reaches the alveoli, but does NOT participate in gas exchange because there is no perfusion.
What are the two variables that can affect Minute Ventilation?
Tidal Volume
Respiratory Rate
In anatomical dead space, what can we do to decrease dead space?
Tracheostomy because it will bypass upper airways.
What is qualitative capnography?
A visual indication analysis of exhaled carbon dioxide levels through color change, providing insights into ventilation status.

Factors that can affect EtCO2?
Alveolar ventilation
Pulmonary perfusion
CO2 production
Normal capnography tracing and its components.
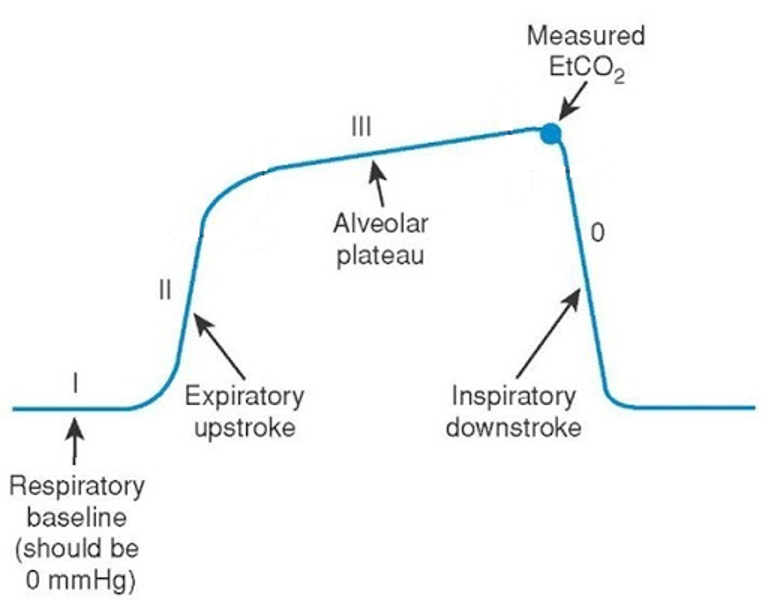
In what other way can VT be estimated?
By means of respiratory inductive plethysmography (RIP), without a direct connection to the patient’s airway.
Where is a atomic dead space located in the respiratory tract?
Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi.
What is physiologic dead space composed of?
Anatomic dead space + alveolar dead space due to non-functional or poorly perfused alveoli.
Pulmonary disorders that cause a decreased VT.
Severe restrictive patterns
Pulmonary fibrosis
Neuromuscular diseases (Myasthenia gravis, ALS, Guillain-Barré syndrome).
Low VT and rate usually result in…
Alveolar hypoventilation.
If dead space increases…
The lungs must breath more air overall (↑ VE) to keep alveolar ventilation normal.
What is physiologic dead space composed of?
Anatomic dead space + alveolar dead space
Is tidal volume (VT) alone a good indicator of adequacy of alveolar ventilation (VA)?
No. Tidal volume should ALWAYS be considered in conjunction with respiratory rate and minute ventilation (VA).
Increases or decreases in the respiratory rate are indications of…
A change in the ventilatory status. RR with VT may be used as an index of ventilation.
What causes increased respiratory rate (RR)?
Hypoxia
Hypercapnia
Metabolic acidosis
Decreased lung compliance
Exercise
Rapid breathing rates and low tidal volumes causes…
Increased VD
What two components indicate adequacy of ventilation?
Minute ventilation (VE) and ABGs.
Minute ventilation (VE) increases in response to…
Hypoxia
Hypercapnia
Metabolic acidosis
Anxiety
Exercise
As the difference between arterial and mixed-expired CO2 increases…
The volume of “wasted” ventilation rises.
What can cause increased dead space and VD/VT ratio?
Pulmonary embolism and pulmonary hypertension.