Fungal Like Organisms (Protists and Chromist) Phyla not apart of the fungi kingdom
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
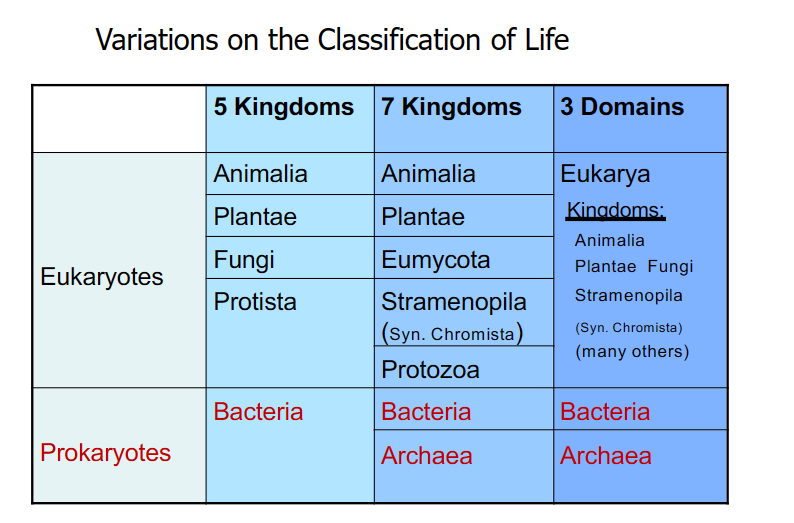
What are Protists and Chromists?
Before Chromista was erected, any eukaryotes that weren’t animals, plants, or fungi were place in Protista.
\
Chromists is a new group; that arose ancestrally eukaryote- eukaryote chimaeras that arose by symbiotic enslavement of a eukaryote (red algae)
(eukaryotes merged to make Chromists; one eukaryote enslaves another.)
\
Protists are a garbage can group; arose ancestrally **monophyletically** by the origin of the eukaryote cell and a prokaryote cell and its enslavement of a symbiotic purple bacteria to make mitochondria.
(prokaryote cell is purple bacteria that turn into mitochondria)
\
These groups look similar but are distinct, they have **converged** (not related but share characteristics)
\
Chromists is a new group; that arose ancestrally eukaryote- eukaryote chimaeras that arose by symbiotic enslavement of a eukaryote (red algae)
(eukaryotes merged to make Chromists; one eukaryote enslaves another.)
\
Protists are a garbage can group; arose ancestrally **monophyletically** by the origin of the eukaryote cell and a prokaryote cell and its enslavement of a symbiotic purple bacteria to make mitochondria.
(prokaryote cell is purple bacteria that turn into mitochondria)
\
These groups look similar but are distinct, they have **converged** (not related but share characteristics)
2
New cards
Myxomycota
Known as slime molds(move like slime)
\
Not important as plant parasites
\
Can colonize grass blades (hanging out in glass blades)
\
More of a visual problem than a plant pathogen
\
Probably a chromist
\
Not important as plant parasites
\
Can colonize grass blades (hanging out in glass blades)
\
More of a visual problem than a plant pathogen
\
Probably a chromist
3
New cards
The slime mode; a member of the class Myxomycetes, aka the dog vomit fungus
**Fuligo**
4
New cards
Badhamia uticularis
eats fungi decomposing wood
5
New cards
Physarum cinereum is found in
the grass
6
New cards
Life cycle of Myxocete
Has diploid and haploid stage
\
Start at mature fruiting bodies
\
Start at mature fruiting bodies
7
New cards
Plasmodiophormycota
Plasmodiophara brassicae
causes club root of cabbage family
\
Spongospora subterranea
causes powdery scab of potato and transports potato mop top virus
causes club root of cabbage family
\
Spongospora subterranea
causes powdery scab of potato and transports potato mop top virus
8
New cards
Club roots of Brassicas
Occurs only on Brassicas(mustards aka cabbages)
\
Favored by cool, wet soil and low pH
\
Survives ten or more years in the soil
\
Very difficult to manage
\
\
Favored by cool, wet soil and low pH
\
Survives ten or more years in the soil
\
Very difficult to manage
\
9
New cards
Crop rotation
Main reason we switch crops is to stop and kill pathogens.
10
New cards
Plant cells with A B C
A: Host cell with profiles of multiple young sporogenic plasmoida.
\
B and C: Cells fillied..
\
B and C: Cells fillied..
11
New cards
Start with resting spores
Disease cycle of clubroot
\
Thursday, March 2, 2023 at 12:26:11 PM (panopto.com)
\
Thursday, March 2, 2023 at 12:26:11 PM (panopto.com)
12
New cards
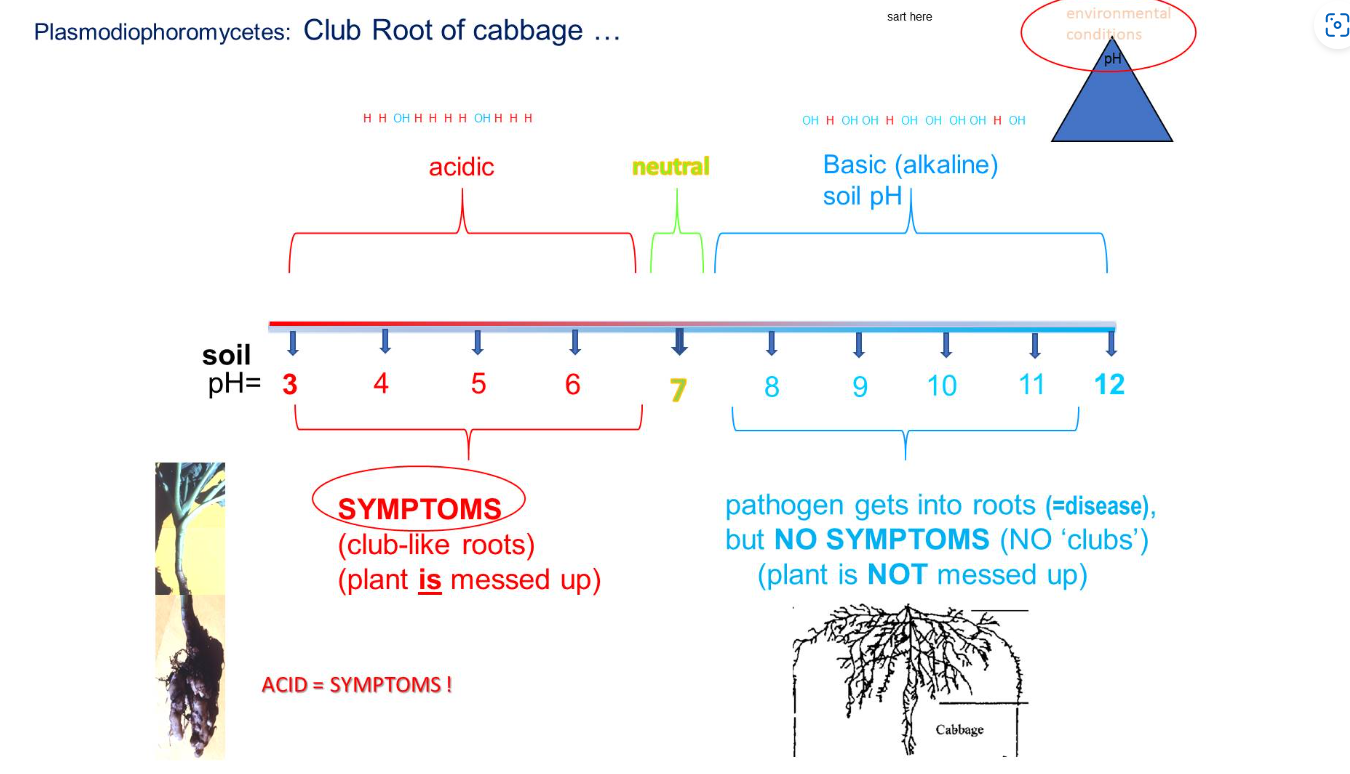
Best way to manage club root of cabbage
Change pH in the soil
\
Soil usually in 5-6 pH range
\
Club like roots appear in said range.
\
Change pH with lime and get the soil to 8 the pathogen gets into roots and will infect soil but no symptoms will arise.
\
Soil usually in 5-6 pH range
\
Club like roots appear in said range.
\
Change pH with lime and get the soil to 8 the pathogen gets into roots and will infect soil but no symptoms will arise.
13
New cards
Best way to manage club root of cabbage
grow resistant crops
14
New cards
Powdery scab of potato
Caused by Spongospora subterranea
\
Spongospora can survive for 18 years in the soil without the hosts
\
Spongospora can damage the potato directly and transmit the potato mop top virus, which was 1st discovered in the US in 1992
\
crop rotation doesn’t work on this as spores only wake up when potato is cropped; they can detect the chemicals in the soil.
\
Spongospora can survive for 18 years in the soil without the hosts
\
Spongospora can damage the potato directly and transmit the potato mop top virus, which was 1st discovered in the US in 1992
\
crop rotation doesn’t work on this as spores only wake up when potato is cropped; they can detect the chemicals in the soil.
15
New cards
Resting Sturctures
Soil-borne plant pathogens are those that survive in the soil and primarily cause diseases of roots, crown, and fruit on the ground.
\
In order to survive, they produce various structures that are discussed below.
\
In order to survive, they produce various structures that are discussed below.
16
New cards
**Oospores**
Sexual spores produced by oomycetes; they can survive for many years in the soil
17
New cards
Chlamydospores
Thick-walled microscopic resting spores that allow fungi and oomycetes to survive long periods of time(years) in the soil
\
Shown here in chains, but single cells
\
Shown here in chains, but single cells
18
New cards
Sclerotia (Sclerotium, singular)
Not a spore; more like a mushroom
\
A compact mass of hyphae, usually with a rind
\
Most sclerotia are large enough to see the eye
\
Can survive many years in the soil
\
Produced by ascomycetes and basidiomycetes.
\
A compact mass of hyphae, usually with a rind
\
Most sclerotia are large enough to see the eye
\
Can survive many years in the soil
\
Produced by ascomycetes and basidiomycetes.
19
New cards
Resting structures of smuts are
Teliospores but smuts aren’t soil-born soil-borne pathogens and teliospores only survive on top of the ground.
20
New cards
Resting structures of rusts are
Teliospores; overwinter in plant material on top of the ground
21
New cards
Summary of resting structures
Sclerotia multicellular, vegatative and macroscopic
\
Chlamydospore: thick-walled spore, vegatitive and microscopic
\
Oospore: sexual and microscopic
\
Zygospore: sexual and microscopic
\
Teliospore: asexual and microscopic produced by smuts and rusts(basidiomycetes)
\
Chlamydospore: thick-walled spore, vegatitive and microscopic
\
Oospore: sexual and microscopic
\
Zygospore: sexual and microscopic
\
Teliospore: asexual and microscopic produced by smuts and rusts(basidiomycetes)