Unit 5 AP Gov
1/63
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Linkage institutions
organizations that translate inputs from the public into outputs from the policymakers
3 Indirect linkage institutions
parties, interest groups, media
Party competition
battle between Democrats and Republicans for control of public office, this creates a democracy because it creates a choice
Goal of Parties
Endorse candidates for public office, WIN
Party as an organization
people who work for the party, leaders, campaign officials
Party in the government
elected officials who identify as a party, e.g. president
Tasks of linkage institutions
pick policymakers, run/coordinate campaigns, give cues to voters, articulate policies, coordinate policymaking
Party Identification
self-proclaimed preference for one party, influences voter choice
Ticket Splitting
voting for both parties on a ballot
Straight Ticket Voting
voting one party on a ballot
Divided Government
different party in Congress compared to the President
Likely Republican voters
higher income/affluence, college grads, older voters, protestants, suburban areas, smaller cities, southeast
Likely Democratic Voters
lower income, lower education, women , younger voters, Catholics (changing), Jews, Asians, African Americans, large cities, northeast and west coast
Party Organizations
party activists who keep party running between elections and make party rules, decentralized and fragmented
National Convention
Prepare, every four years, write party platform, nominate candidates for Pres and VPres
Officeholders
those who identify with party and hold elective/appointed offices in all three branches and levels of government
Critical elections
new issues appeared that divided the electorate and party coalitions underwent realignment
Party Era 1796-1824
The first party system
Party Era 1828-1856
Jackson and the Democrats vs the Whigs
Party Era 1860-1928
The Republican Era
The Republican Era
The New Deal Coalition
Party Era 1968-Present
The Era of Divided Government
Reasons for 2 Party system
historical, force of tradition, electoral system ,american ideological consensus
Splinter parties
offshoots of a major party
Importance of 3rd Parties
can tip college vote, brought new groups into electorate, safety valves for popular discontent, brought new issues to the political agenda, innovator
Consequences of the 2 party system
Moderation of political conflict, winner take all system, proportional representation problems
Interest Group
organization of people with similar policy goals that tries to influence the political process to achieve those goals
What do interest groups try to influence?
Every branch and every level of government
Iron triangles
composed of key interest groups interested in a particular policy, the government agency in charge of administering the policy, and the members of congressional committees/subcommittees handling the policy
Arrangement of Iron triangle
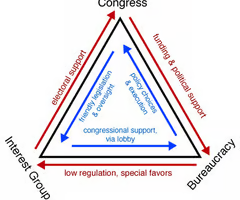
Factors that influence success of interest groups
size, intensity, financial resources
Free-rider problem
when potential members decide not to join, but sit back and let others do the work from which they will still benefit
Single issue group
has narrow interest, dislikes compromise, and single-mindedly pursues its goal at the expense of other goals
Interest group goal
to shape policy
Strategies of interest group to reach goal
lobbying, electioneering, litigation, appeal to public for widespread support
Lobbying
interest groups that directly influence
Lobbyist
political persuaders who are reps of organized groups
How do lobbyists help congresspeople
source of info, help with political strategy, formulate campaign strategy, source of ideas and innovation
Political Action Committees (PACs)
provide a means for groups to participate in electioneering
Amicus curiae briefs
Friend of the court"; written arguments submitted to the courts in support of one side of a case
4 main policy areas
economic issues, environmental issues, equality issues, interest of all consumers issues
Economic groups
concerned with wages, prices and profits
Labor groups
union workers in a specific group
Business groups
support the right to work laws
Right to work laws
outlaw union membership as condition of employment
Equality interests
equal rights for women and minorities
The only guarantee for equal protection of women in constitution
19th Amendment
Public interest lobbies
represent groups that champion causes or ideas in the public interest
Madison's solution to problem in Federalist 10
create an open system in which many groups would be able to participate; groups with opposing interests would counterbalance each other
Mass media
reaches out and profoundly influence not only the elites but the masses
Investigative journalism
use of detective like reporting methods to unearth scandals
Federal Communications Commission
regulates the use of airwaves
Narrowcasting
stations target narrow audiences; bias
Reporting the news
a business in America in which profits shape how journalists decide what is newsworthy, where they get their information from, and how they present it
Trial balloons
info leaked to see what political reaction would be
Political neutrality
limiting an expression of views in the workplace
Talking head
shot of person's face talking directly to camera
Political Activists
depend heavily on the media to get their ideas placed on the government agenda
Media
key linkage institution between people and policymakers
Watchdog function
helps keep government small; expose scandals and intrigues people
Gate keeper
what is news and for how long; sets and swings political agenda
Agenda setter
activists depend on media to get ideas on political agenda
Scorekeeper
who is winning/losing and by how much; horserace
Media functions
gate keeper, agenda setter, scorekeeper, watchdog