ACCT I Practice (LO2-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
A company using accrual accounting may report revenue on the income statement even if it does not collect cash. This statement is
True
When a company earns revenue on account
Which of the following shows how recognizing revenue on account will affect a company's financial statements?
assets= +
lib= NA
eq= +
rev= +
exp= NA
net inc= +
Stmnt CF= NA
When a company collects cash from accounts receivable,
total assets are not affected
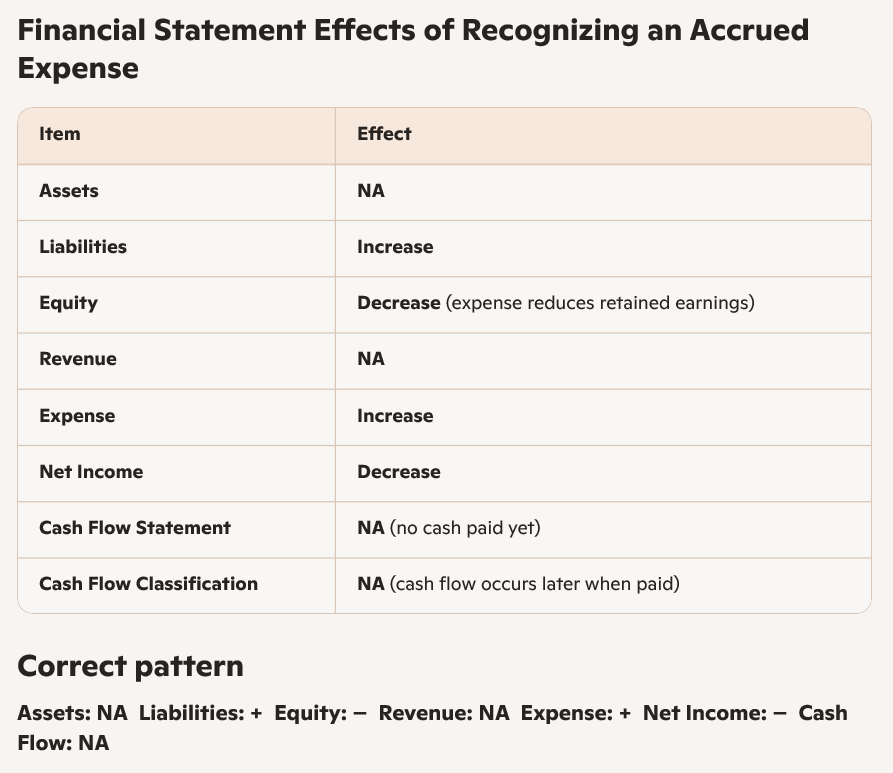
If a company recognizes accrued salary expense:
the liability account, accounts payable, increases.
stockholders' equity decreases.
assets are not affected.
On December 31, Year 1, Hilton Company recognized $600 of accrued salary expense. Hilton paid cash to the employees in Year 2. Which of the following shows how these events will affect Hilton’s ledger accounts on December 31, Year 1?
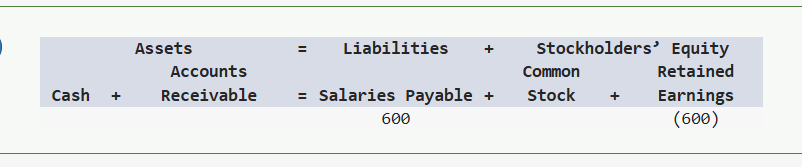
Which of the following shows how recognizing accrued expense will affect a company’s financial statements? The letters “NA”, “OA” and “FA” indicate that the component of the equation is “Not Affected”, “Operating Activities” and “Financing Activities” respectively.
In Year 1, Day Company incurred $350 of utility expense on account. Day paid cash for this expense in Year 2. Which of the following shows how these events will affect Day’s accounting equation in Year 2?

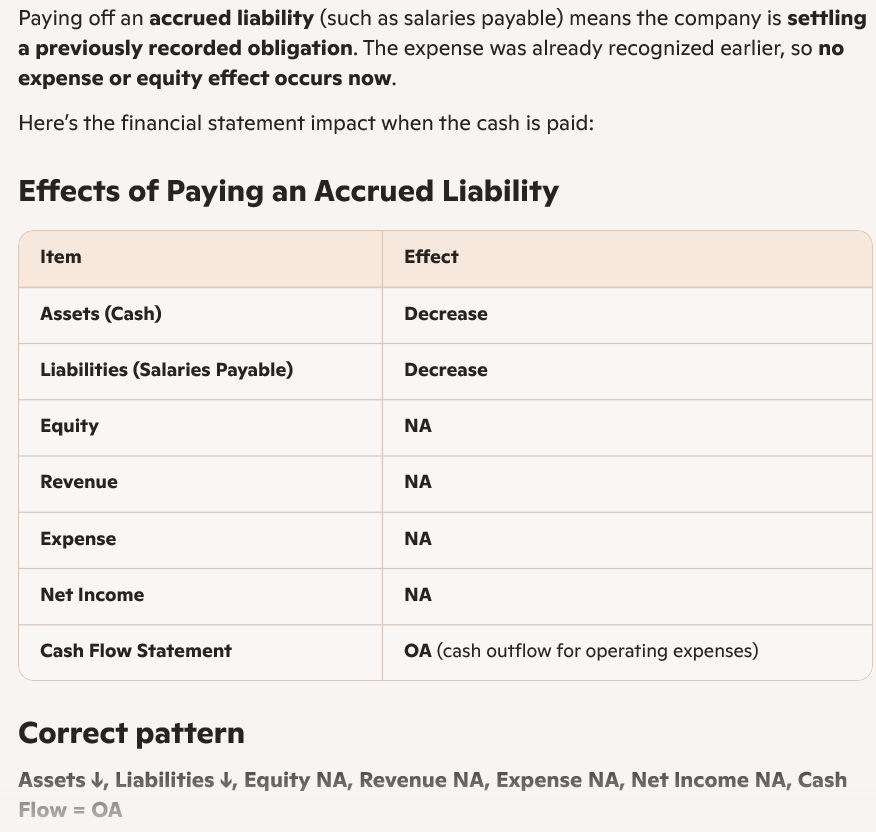
Which of the following shows how paying off an accrued liability such as salaries payable will affect a company’s financial statements? The letters “NA”, “OA”, “IA” and “FA” indicate that the component of the equation is “Not Affected”, “Operating Activities”, “Investing Activities” and “Financing Activities” respectively.

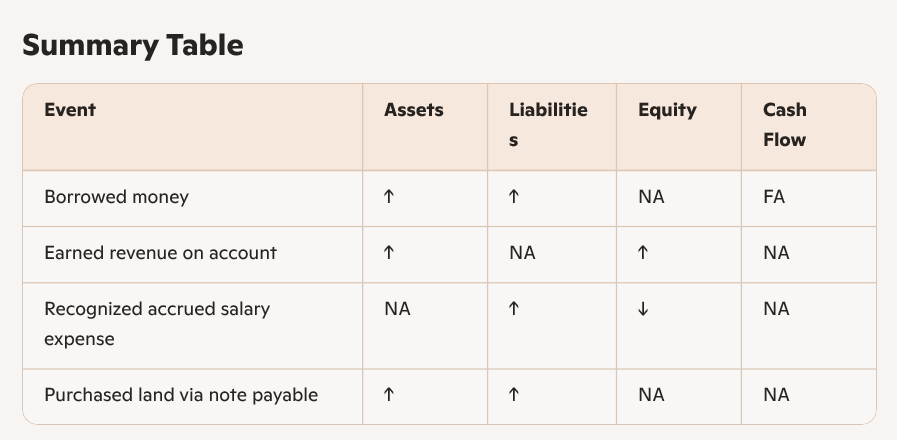
Knopp Company experienced an event that had the following effects on its financial statements: The letters “NA” indicate that the component of the equation is “Not Affected”.
Recognized accrued salary expense
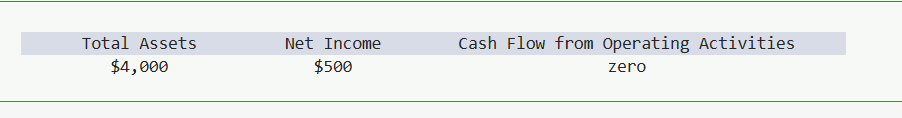
During year 1, Xing Enterprises experienced the following events.
(1) Earned $4,000 of revenue on account
(2) Incurred $3,500 of expenses on account
Based on this information the amount of total assets, net income, and cash flow from operating activities appearing on the year 1 financial statements is
Paying cash to settle a salaries payable obligation will affect which section of the statement of cash flows?
Operating activities
Investing activities
Noncash activities
Financing activities
Paying cash to settle a salaries payable is simply paying off an accrued operating expense, so it is treated as an operating activity on the statement of cash flows.
It’s not investing (no long‑term assets involved)
It’s not financing (no borrowing or equity transactions)
It’s not a noncash activity (cash is actually paid)
Correct Answer: Operating activities
If you want, I can also show the full accounting‑equation impact for this transaction.
The amount of revenue shown on the income statement may differ from the amount of cash inflow from operating activities shown on the statement of cash flows. This statement is
True or False
TRUE
Revenue on the income statement is reported when it is earned, following the accrual basis of accounting.
Cash inflow from operating activities on the statement of cash flows is reported when cash is actually received.
Because revenue and cash collection often occur in different periods, the two amounts frequently differ.
If you'd like, I can illustrate this with a quick example showing how revenue on account creates this timing difference.
Buckley Company started in Year 1 by issuing stock for $17,000 cash. During Year 1, Buckley earned $12,500 of revenue on account. The company collected $6,000 cash from accounts receivable and paid $4,000 cash for operating expenses. Based on this information alone, the balance in accounts receivable as of December 31, Year 1 is:
Step‑by‑step
Buckley earned $12,500 revenue on account → this creates Accounts Receivable.
During Year 1, the company collected $6,000 of that receivable.
Ending Accounts Receivable = Revenue on account − Cash collected
A/R End of Year 1 = 12,500 - 6,000 = 6,500
Correct Answer: $6,500
Jay Company started Year 2 with a beginning balance of $10,000 in accounts receivable. During the year, revenue on account amounted to $25,000. Cash collections of accounts receivable amounted to $5,000. Expenses for the period were $2,100. The company paid dividends of $450. Based on this information alone, what is the ending balance in accounts receivable for Year 2?
Accounts Receivable Roll‑Forward
You start with:
Beginning A/R: 10,000
Plus revenue on account: +25,000
Less cash collections: −5,000
Ending A/R = 10,000 + 25,000 - 5,000 = 30,000
Expenses and dividends do not affect accounts receivable.
Correct Answer: $30,000
Nest Company started Year 2 with a beginning balance of $7,000 in accounts receivable. During the year, revenue on account amounted to $13,000. The company incurred $3,000 of expenses on account and paid dividends of $500. If the company had an ending balance in accounts receivable of $2,000, how much cash was collected from customers?
Let’s break this one down using the accounts‑receivable roll‑forward you’ve been mastering.
Given
Beginning A/R = 7,000
Revenue on account = +13,000
Ending A/R = 2,000
Cash collected = ?
Expenses on account and dividends do not affect accounts receivable.
Set up the A/R equation
Beginning A/R + Revenue on account - Cash collected = Ending A/R
Plug in the numbers:
7,000 + 13,000 - Cash collected = 2,000
Combine:
20,000 - Cash collected = 2,000
Solve:
Cash collected = 20,000 - 2,000 = 18,000
Correct Answer: $18,000
If you want to keep sharpening these, I can walk you through a tougher multi‑year version next.
Sheldon Company began Year 2 with $1,500 in accounts payable. During the year, the company incurred utility expense of $3,500 on account. The company paid $2,000 on accounts payable by year end. The company also paid a cash dividend of $500. At the end of Year 2, what is the balance in Sheldon’s accounts payable?
Let’s run the accounts payable roll‑forward — the cleanest way to solve this type of problem.
Given
Beginning A/P = 1,500
Utilities incurred on account = +3,500
Cash paid toward A/P = −2,000
Dividends do not affect A/P
Accounts Payable Equation
Ending A/P = Beginning A/P + Expenses on account - Cash paid
Plug in the numbers:
Ending A/P = 1,500 + 3,500 - 2,000 = 3,000 ]
Correct Answer: $3,000
If you want to keep sharpening these, I can walk through a version that mixes both A/R and A/P in the same problem.
Rushmore Company started the year with $5,000 in accounts payable. During the year, the company provided services on account for $45,000. Rushmore incurred $36,000 expenses on account during the year, and by year end the balance in accounts payable was $24,000. Assuming that these are the only accounting events that affected Rushmore, how much of the accounts payable did the company pay off during the year
Given
Beginning A/P = 5,000
Expenses incurred on account = +36,000
Ending A/P = 24,000
Cash paid toward A/P = ?
Revenue on account does not affect accounts payable.
Set up the A/P equation
Beginning A/P + Expenses on account - Cash paid = Ending A/P
Plug in the numbers:
5,000 + 36,000 - Cash paid = 24,000
Combine:
41,000 - Cash paid = 24,000
Solve:
Cash paid = 41,000 - 24,000 = 17,000
Correct Answer: $17,000
If you want to keep practicing, I can walk through a version that mixes both receivables and payables in the same scenario.
Owens Company started Year 2 with $10,000 in accounts payable. On March 1, Owens incurred expenses of $6,000 on account. If the ending balance of accounts payable was $4,000. How much of the accounts payable did Owens pay off during the year?
Given
Beginning A/P = 10,000
Expenses incurred on account = +6,000
Ending A/P = 4,000
Cash paid = ?
Set up the equation
Beginning A/P + Expenses on account - Cash paid = Ending A/P
Plug in the numbers:
10,000 + 6,000 - Cash paid = 4,000
Combine:
16,000 - Cash paid = 4,000
Solve:
Cash paid = 16,000 - 4,000 = 12,000
Correct Answer: $12,000
Olly & Sons is a construction company. The company started the year with $90,000 in the land account. During Year 2, Olly & Sons purchased multiple lots of land. The first lot cost $25,000, the second lot cost $28,000 and the third lot cost $31,000. The company sold one lot that had a cost of $50,000 for $50,000. What is the ending balance in the land account?
Given
Beginning land balance = 90,000
Purchases during Year 2:
+25,000
+28,000
+31,000
One lot sold with cost of 50,000 → land is recorded at cost, so reduce land by 50,000.
Compute ending land balance
[ 90,000 + 25,000 + 28,000 + 31,000 - 50,000 ]
Add purchases:
[ 90,000 + 84,000 = 174,000 ]
Subtract the cost of land sold:
[ 174,000 - 50,000 = 124,000 ]
Correct Answer: $124,000
How the sale affects the income statement and cash flows.
XYZ Company ended Year 1 with accounts receivable of $100,000. On February 1, Year 2, XYZ provided services on account for $40,000. On May 1, Year 2, XYZ provided services for $20,000 cash. On November 1, Year 2, XYZ provided services on account for $70,000. What is the ending balance in accounts receivable as of December 31, Year 2?
Run the accounts receivable roll‑forward, which is exactly the right tool for this scenario.
Given
Beginning A/R (end of Year 1) = 100,000
Services on account (Feb 1) = +40,000
Services for cash (May 1) = 0 effect on A/R
Services on account (Nov 1) = +70,000
No cash collections mentioned → assume none occurred
Compute ending A/R
[ 100,000 + 40,000 + 70,000 = 210,000 ]
Correct Answer: $210,000
Accounts receivable will appear on which of the following financial statements?
Accounts receivable shows up only on the Balance Sheet.
Where Accounts Receivable Appears
Financial Statement | Does A/R Appear? | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Balance Sheet | Yes | Listed as a current asset because it represents money customers owe the company. |
Income Statement | No | Revenue may create A/R, but A/R itself is not reported here. |
Statement of Cash Flows | No | Only cash collections from A/R appear (as Operating Activities), not the A/R balance. |
Statement of Stockholders’ Equity | No | A/R does not directly affect equity. |
Accounts payable will appear on which of the following financial statements?
Income statement
Balance sheet
Statement of cash flows
Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity
Correct Answer: Balance sheet
Accounts payable is a current liability — money the company owes to suppliers.
It is not reported on the income statement, cash flow statement, or statement of changes in stockholders’ equity.
Quick Table
Financial Statement | A/P Appears? | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Income statement | No | Expenses may create A/P, but A/P itself isn’t listed. |
Balance sheet | Yes | Reported as a current liability. |
Statement of cash flows | No | Only cash payments to suppliers appear (Operating Activities), not the A/P balance. |
Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity | No | A/P doesn’t directly affect equity. |
Garcia Company recognized revenue on account. The recognition will affect which of the following financial statements?
Income statement and the balance sheet
Income statement
Balance sheet
Statement of cash flow
The moment Garcia Company recognizes revenue on account, two things happen:
Revenue increases → affects the income statement
Accounts receivable increases → affects the balance sheet
No cash is received yet, so the statement of cash flows is not affected.
Correct Answer: Income statement and the balance sheet
If you want to walk through the journal entry and see how it flows through each statement, I can map that out too.
Mary Company collected cash from an account receivable. The recognition of the cash collection will affect which of the following financial statements?
Income statement and the balance sheet
Income statement and the statement of cash flows
Balance sheet and the statement of cash flows
Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity
When Mary Company collects cash from an account receivable, the company is simply converting one asset (A/R) into another (Cash). No revenue is recorded, and no expense is recorded.
That means:
Balance sheet is affected → Cash ↑, Accounts Receivable ↓
Statement of cash flows is affected → Cash inflow from Operating Activities
Income statement is not affected
Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity is not affected
Correct Answer: Balance sheet and the statement of cash flows
If you want, I can map this into a quick T‑account view to reinforce how the asset exchange works.
Paying cash to settle a salaries payable obligation will affect which section of the statement of cash flows?
Operating activities
Investing activities
Noncash activities
Financing activities
Paying cash to settle a salaries payable is simply paying off an accrued operating expense, so it is treated as an operating activity on the statement of cash flows.
It’s not investing (no long‑term assets involved)
It’s not financing (no borrowing or equity transactions)
It’s not a noncash activity (cash is actually paid)
Correct Answer: Operating activities