AP Chem Unit 9
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Standard sign (little degree symbol) , can be on the top of Deltha H , S , or G
With the standard sign, these are calculated at 25 C (298K) temp
Entropy, S, of a system is?
The measure of randomness or dispersion of the system; the greater the dispersion of a system, the greater its entropy.
(Zero entropy is defined as a solid crystal at 0 K, and because 0k has never been reached experimentally)
Standard Entropy Change , Delta S, change in dispersion
Delta S= Sum of S of products - Sum of S of reactants
More dispersion Positive
Less dispersion negative
You can predict Delta S sign by phase changes
Solid < liquid < Gas
If the reaction has more molecules (coefficients ) on the product side, when all the states are the same, the?
Delta S is Positive, because More dispersion
If state & molecules are both the same, you can also account for ions, ?
Yes, more ions more dispersion
However you can only count ions/ molecules if you are looking at the ________ phases
Aqueous or gas
Gibbs free energy G
Determines whether process is thermodynamically favored or not,
We always use thermodynamically favored in AP chemistry
Standard Free energy change, DELTA G
Delta G = Sum of G of products - sum of G of reactants
Delta G = negative, thermodynamically favored
Delta G= positive, thermodynamically unfavored
Delta = 0, equilibrium
How to find Delta G, use this equation:
IMPORTANT relates favorability (Delta G, H ,S)
Delta G = Delta H - T * delta S
T = Kelvin

You can always use Delta G= Delta H - T * Delta S
To find if reactions are favored, and at which temp are favored,
But here is graph just in case
U don’t really need to remember this you can just manipulate formula

Delta G and phase change, if we need to find phase transition temperature , what do we do.
Since phase transition temperature is equally stable in either of 2 phase, WE CAN SET DELTA G = 0 at that temperature, If we have data regard thermodynamic properties at the point of fusion or vaporization we can determine boiling point or melting ponit


Standard free energy change and the equilibrium constant (Given)
While this R is same, BE VERY CAREFUL YOU ARE USING CORRECT VALUE FOR R, use 8.31 j/mol

Reduction potential Zn 2+ + 2e- → Zn(s) E= -0.76 V
Every Half reaction has an electric potential, or voltage associated. (Always Given)
You can always read them in reverse and flip the sign on the voltage to get oxidation potentials
The larger the potential for a half reaction, the _____ likely it is going to occur
more
For a galvanic / voltaic cell always has a _____ cell potential.
Postive
Add the two potentials to calculate for the _________________.
Calculate the potential of a redox reaction. (Positive for galvanic, negative for electrolytic)

Rule when manipulating Half-reactions
Never multiply the potential for a half reaction by a coefficient, even you if multiplied on one side.

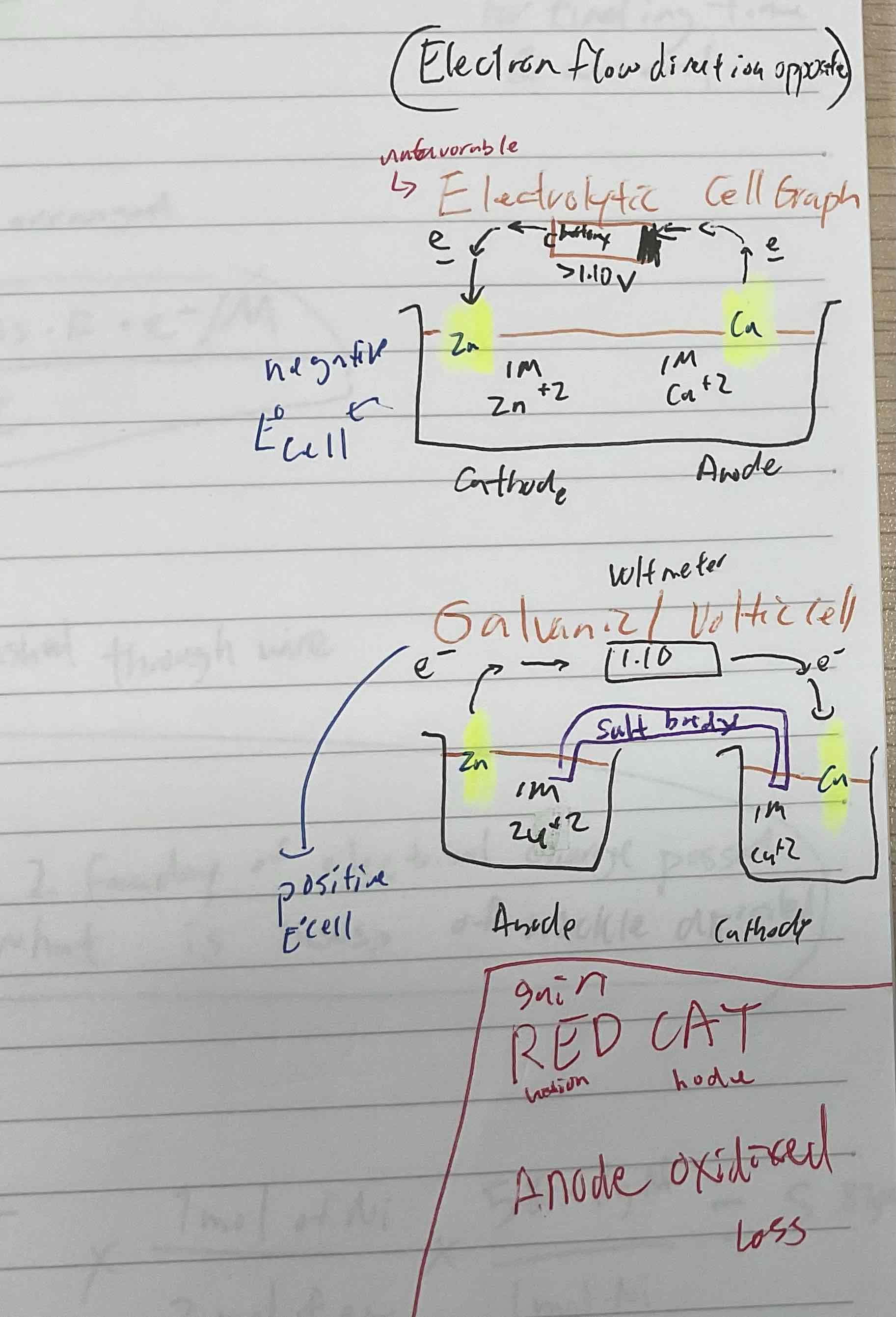
Galvanic / Voltaic Cell
A favored redox reaction is used t generate a flow of current.
If salt bridge removed, the voltage would drop to zero, because would become electrically imbalanced
Voltage flow keeps on going until anode runs out
Overall E always postive
AN OX, RED CAT , OIL RIG
Mnemonic device to help remember
Anode has oxidation ANOX
Reduction happens in cathode RED CAT
Oil oxidation is loss electron
Rig reduction is gain electron
Current
The flow of electrons from one place to another
In galvanic cell, current flow from _______ to ______.
Anode to cathode
Ion in salt bridge flow _____ to______
_______ to ____
Anion to anode
Cation to cathode
Galvanic cell is like a ______ functioning
A electrolytic cell is like ______ a battery
Battery
Recharging

Electrolytic cell
Is like running a galvanic cell backward,
Overall E is always negative
Outside force is used to force an unfavored redox reaction to take place
Non standard conditions, if concentration would cause cell potential to deviate.
(Q = K), dead battery, The voltage of the cell would drop to zero.
Any change to the cell that would cause the reaction quotient to increase ( such as an increase concentration of a product),
Would cause the reaction quotient to become closer to the equilibrium constant and would thus decrease the cell potential

Ernest equation (NO Calculation required)
You can use it to mathematically justify the change in cell potential under non-standard conditions.
Increasing reactant quotient would cause Q term to increase, which would cause E cell to decrease
Electroplating
Use stoichiometry to calculate electroplating problems,
Electroplating is a process where well use electrical current and see how much metal “plates out”

Current (A) = ?
Amps = Coulombs / time (seconds)
Moles of electron to coulombs
1 mole of e- = 96500

Voltage and favorability equation (given)
Delta G= - n FE
Make sure you can do calculations with this
