Endothermic and Exothermic Processes
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
System
The part of the world being studied (e.g., the chemicals in a beaker, a salt, or water).
Surroundings
Everything else around the system (e.g., the air, tabletop, thermometer, or beaker walls).
Universe
The combination of the system and the surroundings.
First Law of Thermodynamics (Conservation)
Energy lost by the system is gained by the surroundings, and vice versa (qsys = -qsurr).
Endothermic Process
A process where heat is absorbed by the system from the surroundings.
Exothermic Process
A process where heat is released by the system to the surroundings.
Sign of q (Heat) for Endothermic
Positive (+q); heat enters the system.
Sign of q (Heat) for Exothermic
Negative (-q); heat leaves the system.
Sign of ΔH (Enthalpy) for Endothermic
Positive (+).
Sign of ΔH (Enthalpy) for Exothermic
Negative (-).
Work (w)
Energy needed to move something against a force (e.g., expanding gases pushing a piston).
Equation for Work
w = -P\ΔV (Work = negative Pressure times change in Volume).
Sign of w (Work) for Expansion
Negative (-w); the system pushes on the surroundings (volume increases).
Sign of w (Work) for Compression
Positive (+w); the surroundings push on the system (volume decreases).
Conversion: L·atm to Joules
1 Latm = 101.325 Joules.
Temperature and Energy Relationship
Temperature changes in a system indicate energy changes.
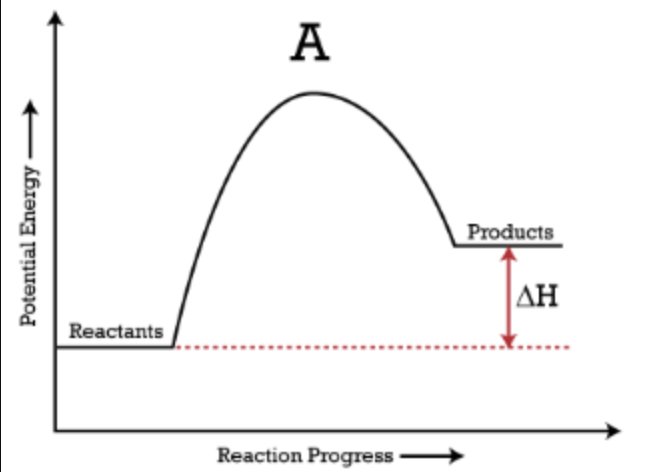
Potential Energy Diagram: Endothermic
The curve goes "uphill"; products are higher in energy than reactants.
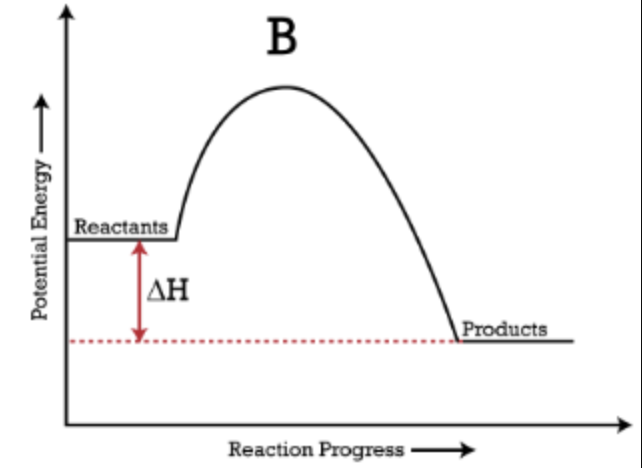
Potential Energy Diagram: Exothermic
The curve goes "downhill"; products are lower in energy than reactants.
Phase Changes: Endothermic
Melting, Boiling, Vaporization, Sublimation (Solid -> Gas).
Phase Changes: Exothermic
Freezing, Condensation, Deposition (Gas -> Solid).
Bond/Interaction Rule: Breaking
Breaking bonds or separating particles requires energy (Endothermic).
Bond/Interaction Rule: Forming
Combining materials or forming bonds releases energy (Exothermic).
Heating Curve slopes vs. plateaus
Sloped lines indicate temperature change (heating); flat lines (plateaus) indicate phase changes where potential energy changes.
Solution Formation: Step 1 (Solvent)
Solvent expands by overcoming intermolecular forces; this is Endothermic.
Solution Formation: Step 2 (Solute)
Solute expands by overcoming intermolecular forces; this is Endothermic.
Solution Formation: Step 3 (Mixing)
Solute and solvent recombine; this is Exothermic.
Temperature Drop in a Solution
Indicates an Endothermic process (the system absorbed heat from the water/thermometer, causing the temp to read lower).
Temperature Rise in a Solution
Indicates an Exothermic process (the system released heat into the water/thermometer).
Freeze Drying (Concept)
Involves Freezing (Exothermic) followed by Sublimation (Endothermic) where ice changes directly to gas.
Born-Haber: Enthalpy of Sublimation
M(s) -> M(g); Endothermic (requires energy to turn solid to gas).
Born-Haber: Ionization Energy
M(g) -> M+(g) + e-; Endothermic (requires energy to remove an electron).
Born-Haber: Enthalpy of Dissociation
Bond breaking; Endothermic.
Born-Haber: Lattice Energy
Formation of solid lattice from gaseous ions; Exothermic (releases energy).
Orange Tree Protection Concept
Farmers spray water on trees before a freeze; as water freezes (Exothermic), it releases heat which is absorbed by the oranges to prevent them from freezing.
Dissolving CaCl2 (Calcium Chloride)
An exothermic process often used to melt ice on roads (the heat released helps melt the ice).
Gas Expansion Cooling
When a compressed gas expands rapidly (like whipped cream leaving a can), the system does work and absorbs heat, causing the canister to feel cold (Endothermic from the can's perspective).