B4: Cell Bio Exam 3
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
337 Terms
week 35
When is surfactant in full production?
glucocorticoids
What can be given to mom to help encourage the infant's lungs to produce surfactant early on if mom is high risk for pre-term birth?
external
(external/internal) respiration:
-exchange of respiratory gases between the cells of an organism and its environment (e.g., respiration/breathing)
internal
(external/internal) respiration:
-utilization of O2 in cellular metabolism (cellular respiration)
1. phonation (speaking, singing, movement of air across vocal cords)
2. provide reservoir for blood for LV
3. filters circulation (clots via DVT, and cancers can get trapped in lungs)
4. have ACE
What are the non-respiratory functions of the lungs?
visceral
Which pleura:
-adheres directly to the lung surface
parietal
Which pleura:
-encases the lungs
-adjacent to the chest wall
-pleural space can be filled with air (pneuemothorax) or fluid (pleural effusion) or blood (hemothorax)
pleurisy
What is inflammation of the pleura, the double-layered membrane that surrounds each lung and the rib cage, creating a friction rub?
pleura
What is double-layered and protects and lubricates the surface of the lungs as they inflate and deflate within the rib cage?
bronchial a.
Which artery in the pulmonary circulation:
-provides nourishment
-bypasses the gas-exchange area
-arises from the aorta and supplies the larger airways
pulmonary a.
Which artery in the pulmonary circulation:
-deoxygenated blood from R heart
-terminates in alveolar capillaries to perfuse the walls of alveoli
-under normal conditions, 100% of the blood from the RV flows through this structure to the pulmonary capillary bed in the walls of the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs (capillaries will take up O2 and give off CO2)
pulmonary capillaries
What component of the pulmonary circulation pick up O2 from alveoli and return it to the heart to pump blood into the body?
Hint: these will enter the pulmonary v. which runs into the LA
lymphatics
What picks up excess fluid within the lung space (favors absorption) to prevent edema?
upper
(upper/lower) respiratory zone:
-columnar epithelium
-ciliated cells to move mucus up and out of the lungs
-goblet cells to produce mucus
-after the 4th branch, there is NO cartilage, so the airways may collapse under pressure here due to the lack of cartilage to help keep them open
Conduction Zone: NO. GAS. EXCHANGE.
-warms and humidifies air
-deposition of particles
-mucociliary clearance
lower
(upper/lower) respiratory zone:
-specialized respiratory epithelium
-single cell barrier between air and blood --> SITE. OF. GAS. EXCHANGE.
Respiratory zone = site of respiration
-large surface area for gas exchange (respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli)
atmospheric (barometric) pressure
What is the gas pressure exerted by air (as temperature increases, so does velocity of particle movement and contributes to an increase in pressure)?
760 mmHg
What is the standard atmospheric pressure (e.g., at sea level)?
decreases
As you move up in height or elevation, the overall atmospheric pressure (increases/decreases)
increases
As you move down in height or elevation, the overall atmospheric pressure (increases/decreases)
60 mmHg
If arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) is below ______ mmHg, you are considered to have hypoxemia
false
T/F: the % of O2 in the atmosphere decreases as you increase elevation
NEVER
the % of O2 in the atmosphere _____ changes (e.g., decreases/increases)
ventilation
What is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lungs?
Ex: hypo- or hyper-
hypocapnia
What is a state of reduced CO2 in the blood?
hypercapnia
What is a condition where there is too much CO2 in the blood?
compliance
What is also known as distensibility, how easily a structure can be stretched (change in volume/change in pressure)?
elastance
What is the retractive (recoil) force generated by distension?
eupnea
What is normal, unlabored ventilation, sometimes known as QUIET BREATHING, or RESTING RESPIRATION, in which expiration is an entirely passive process, employing the elastic recoil of the lungs?
hypopnea
What is abnormally shallow breathing or slow respiratory rate, differing from apnea because there remains some flow of air?
hyperpnea
What is when the increased breathing is required to meet demand, as during and following exercise or when the body lacks O2 and may also occur as a result of sepsis and is usually a sign of the beginning of refractory sepsis?
diffusion
What is the movement of individual molecules from a higher concentration to an area of lower concentration by random movement?
diffusion coefficient
What is the constant of proportionality between the diffusion flux and the concentration gradient in Fick's first law?
Hint: Its magnitude is indicative of the rate of atomic diffusion.
dyspnea
What is difficult or labored breathing; SOB (does not necessarily indicate an issue)?
sleep apnea
What is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep?
hemoglobin saturation
What measures the % of Hb binding sites in the bloodstream occupied by O2?
hypoxemia
What is a deficiency in the concentration of O2 in arterial blood (e.g., PaO2 is low)?
hypoxia
What is an inadequate supply of O2 to the body tissues?
true
T/F: hypoxemia is one cause of hypoxia but not the only cause (e.g., hypoxia can occur from structural abnormalities in the tissue itself)
vasoconstrict
Under hypoxic conditions, the lungs will (vasodilate/vasoconstrict)
true
T/F: it is possible to have low O2 content (e.g., due to anemia) but a high concentration of O2 in the arterial blood
solubility
What is the ability for a given substance, the solute, to dissolve in a solvent?
faster
the higher the solubility, the _____ the rate of diffusion
more
CO2 is ____ soluble than O2
marfan syndrome
Which disorder is caused by a mutation in the fibrillin 1 gene (FBN1) and presents with (+) wrist sign and thumb sign is a risk factor for spontaneous pneumothorax?
spontaneous pneumothorax in marfan syndrome
ID
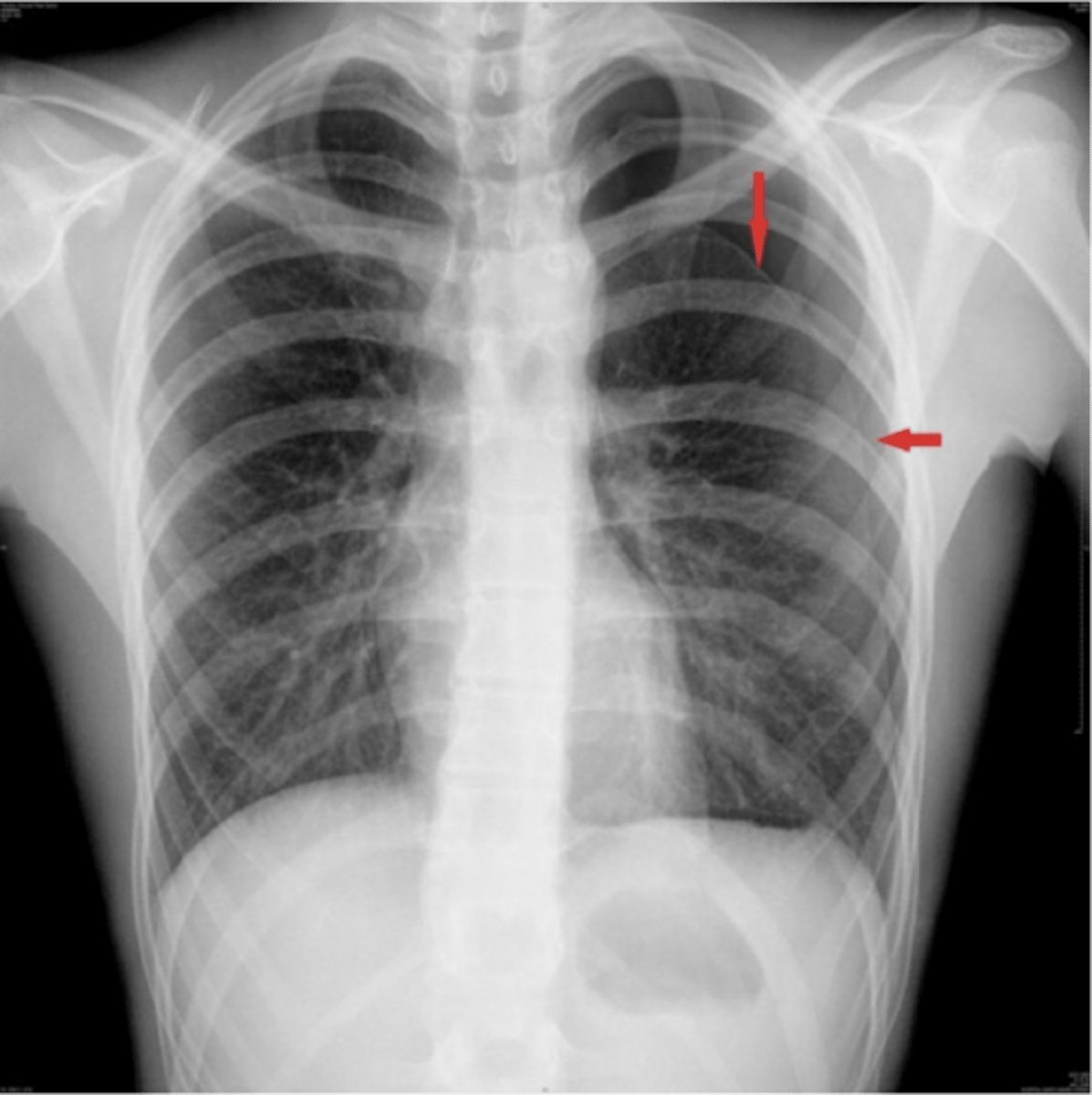
pneumothorax
What is a potential medical emergency caused by the accumulation of air or gas in the pleural cavity, occurring as a result of disease or injury?
Hint: when present, the chest wall will spring OUTWARD and the lungs will COLLAPSE
L pneumothorax
ID
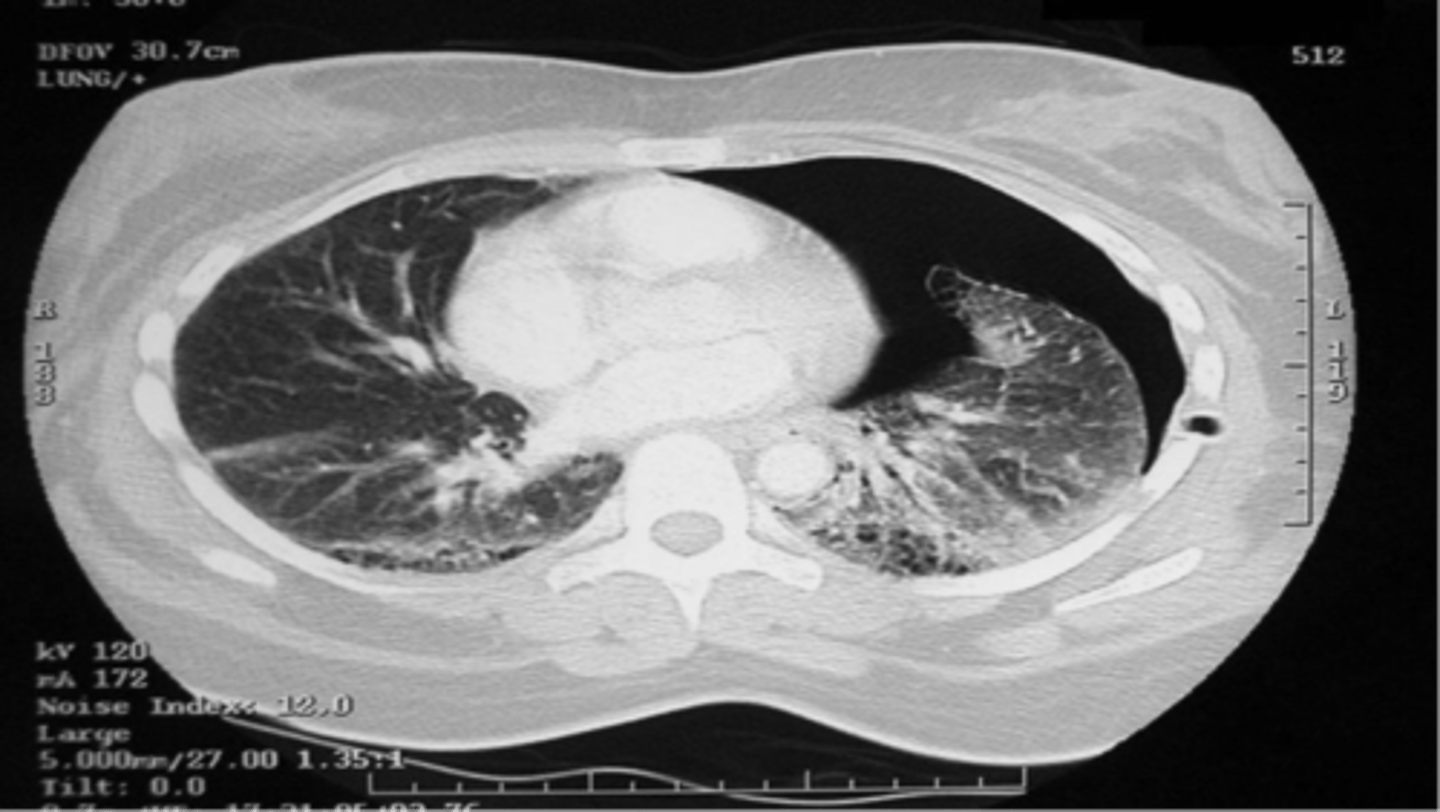
chest tube
How do you treat a pneumothorax?
tension
(tension/non-tension) pneumothorax:
-medical emergency!!!!!
-air accumulates in the pleural space with each breath
-increase in intra-thoracic pressure results in massive shifts of the mediastinum away from the affected lung compressing intra-thoracic vessels
non-tension
(tension/non-tension) pneumothorax:
-less severe because air in the pneumothorax is able to escape
breathing
What begins by negative pressure allowing air to flow into the nasal passages and through the turbinates?
sniff and irritant receptors
What cause you to stop inhaling if they sense something toxic and even cause you to cough or sneeze, important because of the type I pneumocytes in alveoli are very sensitive to toxins?
bronchoconstriction
What is due to an activation of the parasympathetic nervous system in which post-ganglionic fibers release ACh next to Reissessen muscle, a smooth muscle layer surrounding the bronchi, activating M3 receptors on their membrane which will activate intracellular Gq proteins that activate the PLC pathway, which will lead to an increase in intracellular Ca2+ and contraction of the smooth muscle cell, causing the diameter of the bronchus to decrease and increase the resistance within them?
Hint: caused by IRRITATION with allergens or other toxins (e.g., smoke)
bronchoconstriction
What is narrowing of the airways in the lungs (bronchi and bronchioles) from 3 different factors; 1) a spasmodic state of smooth m. in bronchi and bronchioles, 2) an inflammation of airways, and 3) excessive production of mucous due to an allergic reaction or irritation caused by mechanical friction of air (Due to shear stress), overcooling or drying of airways)?
respiratory passages
What are coated in mucus, periciliary fluid, and surfactant which all work to keep the surface moist, trap small particles, and decrease surface tension?
goblet cells
Which cells:
-secrete mucus, which is increased in pts who smoke or exposed to pollutants
ciliated cells
Which cells:
-sweep debris
-terminate at terminal bronchioles in conducting zone
-secrete periciliary fluid
clara cells
Which cells:
-divide, differentiate, metabolize toxic chemicals
-secrete glycosaminoglycans to protect the bronchiole lining
black lung disease
What disorder:
-caused by long exposure to coal dust that progressively builds up into the lungs and is unable to be removed by the body --> causes inflammation, fibrosis, and, in the worse case, necrosis
-common affliction of coal miners and others who work with coal
-similar to both silicosis from inhaling silica dust and to the long-term effects of tobacco smoking
mesothelioma
What is a rare form of cancer that develops from the protective lining that covers many of the body's internal organs (e..g, mesothelium) and is usually caused by exposure to asbestos?
type 1 cell
Which cell of the respiratory zone:
-thin, elongated
-95% of alveolar surface -- within alveoli that participate in gas exchange
type 2 cell
Which cell of the respiratory zone:
-cuboidal
-2% of alveolar surface
-secretes surfactant
-progenitor of type I cells -- replace type I and type II cells
type 3 cell
Which cell of the respiratory zone:
-also known as brush cells
-throughout the airways
-associated with nerves
alveolar macs
Which cell of the respiratory zone:
-scavengers of the surface
-kill bacteria
-produce cytokines and ROS, which can be toxic to type II cells
cystic fibrosis
What disorder:
-mutation in the CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator)
-AR disease
-Sx = coughing, copious phlegm production
-problem is that bacteria that normally inhabit the thick mucus grow out of control and cause pneumonia
-S. aureus, H. influenzae, and P. aeruginosa are the 3 most common organisms causing lung infections in CF patients
-Cl- channel defect in sweat duct causes increased Na+ and Cl- concentration in sweat
-in airway, CF pts have decreased Cl- secretion and increased Na+ and water reabsorption leading to dehydration of the mucus layer coating epithelial cells
-decreased mucociliary action
-mucus plugging of airways
hemoglobin
oxygen binding to ______ is needed in order to transport O2 to tissues because O2 has limited solubility in liquid
true
T/F: once a gas is bound to a substance (e.g., O2 being bound to Hb), it does not exert a partial pressure
myoglobin
What stores O2 in muscle for emergency use, is our reserve source of O2, is higher in slow twitch muscles, is not within normal circulation (thus is a marker for the lysis of cells), can lead to kidney damage, and only binds 1 O2 molecule?
RBCs
Ectopic production of ______ can occur in renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma
yolk sac
Where do RBCs come from in the 1st couple of weeks of gestation?
fetal liver (also spleen/lymph nodes)
Where do RBCs come from in the middle trimester?
bone marrow of all bones
Where do RBCs come from in the last month of gestation and throughout puberty?
bone marrow of rib, sternum, and vertebrae
Where do RBCs come from after puberty?
erythropoietin
RBC production is induced by the production of _____________ by the kidney
decreased
In kidney failure (e.g., renal insufficiency), there will be (increased/decreased/normal) RBC production
acute renal failure
myoglobin can induce:
increase
decreased O2 delivery to the kidneys will (increase/decrease) RBC production by stimulating the renal cortex to produce EPO (erythropoietin)
30 mmHg
What is the PO2 at which hemoglobin is 50% bound by O2?
100 mmHg
What is the PO2 at which hemoglobin is 100% bound by O2?
40 mmHg
What is the venous PO2?
75%
At venous PO2, what percentage of O2 is still bound to Hb?
high
When PO2 is (high/low), O2 binds Hb readily
low
When PO2 is (high/low), O2 dissociates from Hb
sickle cell
What refers to a group of genetic disorders characterized by the production of hemoglobin S due to a single amino acid change on the surface of the Hb beta chain, which causes Hb S to polymerize and stick to Hb A and form aggregates?
methemoglobin
What is a form of Hb, in which the heme group is in the Fe3+ (ferric) state instead of the Fe2+ (ferrous) state of normal Hb?
false
T/F: methemoglobin can carry O2
NADH-dependent enzyme methemoglobin reductase
What is responsible for converting methemoglobin back to hemoglobin?
amyl nitrite
What is administered to treat cyanide poisoning and works by converting hemoglobin to methemoglobin, allowing for the binding of cyanide and the formation of non-toxic cyanomethemoglobin?
cytochrome c oxidase
cyanide poisoning is a form of hypoxia that is not due to hypoxemia because it makes the cells of an organism unable to use O2 through the inhibition of:
fetal
(fetal/adult) hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen, which is why mom can readily pass O2 to baby
true
T/F: the alpha subunit of hemoglobin is always present throughout life
gamma
What is the major second subunit (other than alpha) of Hb during development (e.g., in fetal hemoglobin)?
beta
What is the major second subunit (other than alpha) of Hb after birth (e.g., in adult Hb)?
1. blood pH
2. CO2 levels
3. 2,3-BPG
4. temperature
5. Hb chain composition
What are factors that modify Hb O2 binding affinity?
Bohr effect
What describes the phenomenon by which there is a decrease in the amount of oxygen associated with hemoglobin in response to a lowered blood pH (which occurs due to an increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood)?
a.right
When there is a decrease in pH, the O2 sat curve will shift to the (right/left)
Hint: if pH decreases, what is happening to the concentration of H+?
increase
alkalotic (e.g., decreased [H+] or HIGH pH) conditions will (increase/decrease) O2 relationship with Hb
Bohr effect
What describes the phenomenon by which:
Within the tissues
-Increased [CO2] because of working conditions --> CO2 binding to Hb diminishes O2 binding --> allows for more O2 OFF LOADING
-Hydration of CO2 will lead to increased [H+] and dec. pH because of carbonic anhydrase
-inc [H+] will be taken up by Hb as O2 dissociates
Within the lungs
-CO2 is low, therefore [H+] is low (pH high)
-O2 affinity for Hb is increased
increase
cell metabolism will (increase/decrease) the concentration of 2,3-BPG, thereby decreasing Hb affinity for O2
0.8
What is the normal respiratory exchange ratio (number)?