SPI Summary
1/450
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
451 Terms
A linear scan has what type of display
Rectangular display, where it has scan lines
A “slice of pie” where scan lines originate from the same location/starting point but travels out in different directions is what type of scan
Sector scan
Sound is 2 types of waves: which are?
Mechanical & Electromagen waves
What are two types of mechanical waves?
Longitudinal Compressional wave
Transversal wave
Compression is a region of
High pressure & high density ( many particles are present on the medium)
Rarefaction is a region of
Low pressure & low density ( fewer particles are present on the medium)
What must be present if sound wants to travel?
a Medium must be present, waves only exits if theres a medium( air, body tissues)
in Longitudinal waves/ compressional waves, how does the particles move?
Moves in the same direction (parallel to the wave) ~ [ pressure variation in the sound wave causes particles of the medium to oscillate(vibrate) back & forth ]
In Transversal wave or shear waves, in what direction do particles move ?
Moves in a perpendicular direction
What are 3 Acoustic Variables that describe a sound wave ?
Pressure - concentration of force into area
Density - concentration of mass
Distance/ Particle Motion/ Vibration - measures distance
( doesnt matter)Temperature - concentration of heat energy
What type of wave that can only go through a media is …
Mechanical
What type of wave can go through a vacuum and media
Electromagnetic
define propagation speed.
Speed of wave as it moves through Medium
Difference between PWD & CWD
PWD has 1 crystal & used for Imaging
CWD has 2 crystals & No image
Define Wavelength
Distance measurement to complete 1 cycle
Equations for Propogation speed (C)
C= F(Y) & C=B/p
Equations for wavelength (y)
Y= C/F & Y= SPL/ n
Define Density
Concentration of Matter
Stiffness
Hardness of Matter
Define Frequency
numbers of cycles something happens in a given period of time
Equations for Frqx
F= # of cycles/ time
F= 1/ T
F= C/Y
As Low As Reasonably achievable (ALARA) is used to ensure the proper equipment settings and helps minimize the exposure time; What are 3 Major factors of controls that help us safely use ultrasound in an exam?
Power
Intensity/ Amplitude
Time
Define whats ultrasound Imaging?
Non-Invasive way of looking inside of the human body to image anatomy which uses a pules-echo technique
Define Pulse echo technique
Pulses of U/S are generated by the TX & sent to the ptx where they produce echoes at organ tissues & the returning echoes are detected by the TX & presented on the display
In Ultrasound how many cycles are in 1 pulse ?
2/3 cycles made up of pressures called compression & rarefaction & have units of pascals (Pa) or mega-Pascals (MPa)
Whats the frequency range for Subsonic / Infrasound?
<20Hz
Whats the frequency range for Audible sound?
20Hz-20,000 Hz
20Hz- 20kHz
20Hz × 10³Hz
Whats the frequency range for Ultrasound?
>20,000 Hz
> 20kHz
>20Hz × 10³ Hz
Whats the Frequency range for Ultrasound?
> 1,000,000 Hz
> 1000 kHz
1MHz
> 10^6 Hz
If I have the frequency of Hz & I want to convert into time what would be the unit?
1/sec
If I have the frequency of KHz & i want to convert it into time what unit would it be ?
1/ms
If my frequency is in MHz & i want to convert it in time what unit would it be ?
1/ microsecond
Define Pulse repetition Frequency
number of pulses that occur in 1 sec
In pulse repetition frequency what equations are there and what units do we use?
PRF= # of pulses / time & PRF= 1/PRP
Units: Hertz, KiloHertz, MegaHertz
Define Pulse Repetition Period
Time measurement from one pulse to the next pulse
What are the equations for Pulse repetition Period and what are its units?
PrP= 1/ PRF & PRP= PD+ LT
Define Pulse duration
Time to complete 1 cycle
What are its formulas for Pulse Duration and what are its units
PD= n (x) T & PD= PRP - LT & PD=n/F
Units: secs,ms, us
Define Listening Time & what formula do we use
Machine is off & not transmitting any pulse
LT = PRP - PD
units; secs,ms,us
Define Period (T) and what formulas do we use
Time it takes to complete 1 cycle
T= 1/F & T= PD/n
Units: secs,ms, us
Define Duty factor & what formula do we use?
Percentage of time that the machine is on
DF= (PD/PRP) x 100
Units: Percentages
Define Spatial Pulse Length , & what formula do we use ?
Length or Distance measured for 1 pulse
SPL= n (x) y
Units: mm
Define bandwidth and what formulas do we use
Its a range or useful frequencies that are created in a short pulse
BW= Of / Q
Define quality factor and what formulas do we use ?
Relates to bandwidth → short pulse same as the # of cycle in that pulse
In quality factor the ______ (lower or higher) numerical value for Q factor the higher the quality of the tx.
Lower
In relation to Bandwidth, the shorter the pulse the ______ (wider/narrower) the bandwidth
Wider
If we increase stiffness what happens to the propagation speed. (Increases or decreases)
Increase
If we decrease stiffness what happens to prop speed ( decrease or increase)
Decrease
How many scan lined make up a single frame ?
96-256
The _____ of each dot corresponds to the echos ____, which in turn produced a gray scale.
Brightness ; strength
Whats it called when the ultrasound pulses goes into the tissues with a set frequency?
(Received frqx / Initial Frqx)
Initial Frqx
Whats it called when there is a pulse that returns back, once it hits the tissue & comes back?
( Received/reflected frqx / Initial Frqx)
Received Reflected Frqx
If the blood direction is TOWARDS the tx, the returning echoes that interact with this blood will have a (low/high) _____ frqx as compared yo the initial frqx, when they return to the tx from the body
Higher
If the blood flow direction is AWAY from the tx, the returning echoes that interact with this blood will have a _____ (high/ low) frqx as compared to the initial frqx when they return to the tx from the body
Lower
Whats are the formulas for Doppler shift equation?
FD= Fr-Fi
Fd= 2(Of)(V)Cos/ C
& units are MHz
How many Doppler displays are there?
Color Doppler
PW
Power Doppler
CW
Define Attenuation
Loss of Amplitude, Intensity, & power as the sound beam travels deeper into the tissues( weakening of sound beam as it propagates through the tissues of the body)
If there is a high frqx, will attenuation be more or less?
Sound beam will attenuate more
If there is a low frqx, will attenuation be more or less?
Sound beam will attenuate less
Define Period or Time(T)
Time it takes to complete 1 cycle & each cycle is made up of 1 compression and 1 rarefraction
Increasing __________ , will have reason to be concerned with bio effects & is the reason why we should use in the ALARA( as low as reasonably achievable) principle.
Out power
(Power + Intensity + Time )
1 of the components with the ultrasound imaging system is controlling the power to the transducer. Which function is it called ?
A. Pulser
B. Transducer
C. Receiver
D. Memory
E. Display
A. Pulser
True or False: Tissue equivalent phantoms are devices made of graphite-filled aqueous gels or urethane rubber materials. Attenuation & propagation speeds in devices are similar to soft tissues
True
According to the ALARA principle, if we encounter an image which is too dark, we should increase the _______ first because it does not increase patient exposure.
Receiver Gain
Research performed within the living body of either a plant or animal is called?
A. In ViVo
B. In vitro
A. in Vivo
Research performed outside the living body and in artificial environment is called ?
In Vitro
True or False: True positive is what we call a study performed which indicates that the patient has the disease and the test is accurate .
True
The velocity of sound for the AIUM mm test object is ?
1,540 m/s
What helps us distinguish the different shades of grey and helps control the contrast resolution ?
Dynamic Range(dB)
What is the typical duty factor for a Continuous wav(CW)?
A. 50%
B. 70%
C. 100%
100%
Which of the following is the time it takes to complete 1 full cycle of its oscillation ?
A. Spatial Pulse Length
B. Wavelength
C. Period
Period
What uses 525 spaced lines & writes the odds first & then the evens?
Interlaced Display
Whats The relationship between between spatial pulse length & wavelength?
Direct
You’re measuring the strength of a sound wave produced by an ultrasound machine. If the sound wave increases by 9dB, approx how much has the original signal power voltage increased?
8
The range between smallest & Largest signal amplitudes received decreases with which receiver function?
Compression
Which system component adjusts the PRF appropriately for imaging depth ?
Pulser
What is the typical range of values for the pulse repetition frequency (PRF) used in real time ultrasound imaging?
1 to 10 kHz
Which terms refers to a shadowing artifact that occurs when the U/S trajectory is changed after hitting a reflector obliquely or at the boundary between 2 different media ?
Refraction Artifacts
What estimates the total output of the U/S beam by measuring the heat produced?
Calorimeter
How would you define the distance that a pulse occupies from its initiation to its completion?
Spatial Pulse Length
Which of the following most accurately characterizes the relationship between Spatial pulse length & number of cycles?
Direct
Which description most accurately characterizes the relationship between spatial pulse length & frequency ?
Inverse
Your Mechanical Index has reached 1.8 & is getting closer to the maximum allowed by the FDA.What would you do to decrease it?
Decrease the ultrasound beam output
Which formula represents pulse repetition period?
1/ PRF
Which of the following is the function of the pulser used to increase the signal to noise ratio ?
Coded Excitation
The US Food and Drug Administration mandates that the Mechanical Index be kept below what value?
1.9
What is the term used to describe the conversion of energy to heat due layers of blood moving to relative to each other?
Friction
What refers to to fluid movement that changes over time from the heart beating ?
Pulsatile Flow
What is the term used to describe the phenomenon where out of phase waves interferes with each other & result in a reduction in amplitude known as cancellation or nullification
Destructive Interference
Which display mode in U/S imaging appears as a chart of upward spikes?
A-Mode
What is the relationship between the quality factor & damping?
The higher the quality factor, the lower the damping
What are 3 major components that contribute to attenuation of an ultrasound wave as it passes through a medium?
Absorption, scattering & reflection
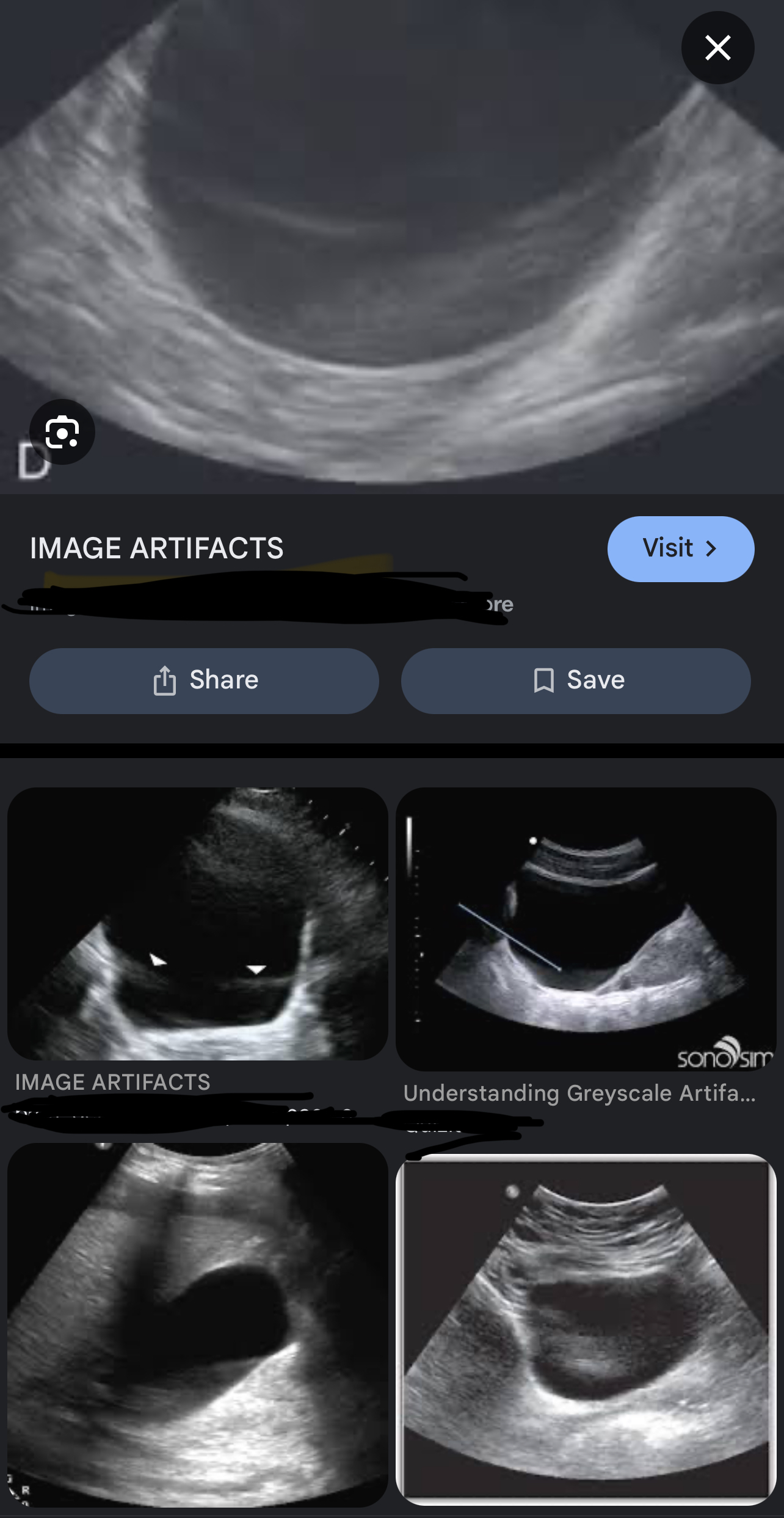
Section Thickness( slice thickness/ Elevational Resolution artifact)
The beam width perpendicular to the scan plane results in section thickness artifact
Which assumption is failed in section thickness & how do we fix it ?
#5 ( image plane is thin) & fix it with 1.5 array tx, harmonics, virtual beam former
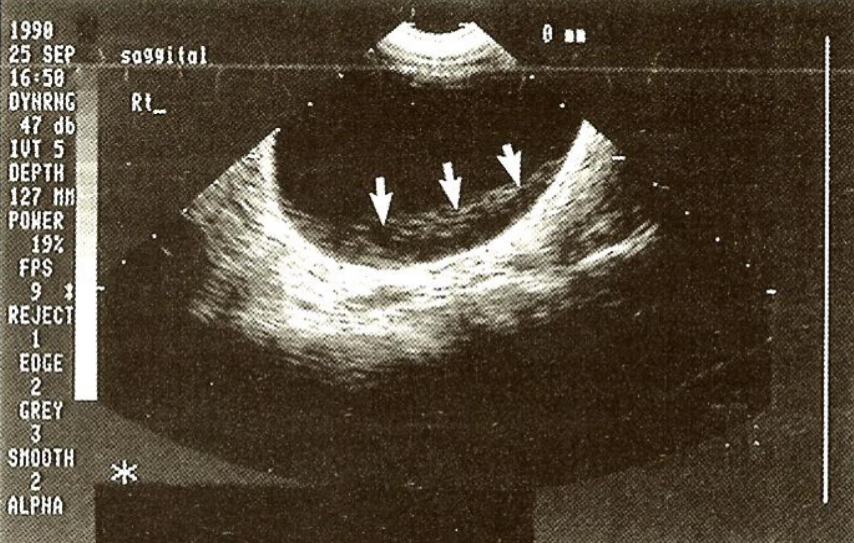
Speckle
an interference pattern resulting from constructive and destructive interference of echoes returning simultaneously from many scatters within the propagating ultrasound pulse at any instant ( a type of artifact has a grainy appearance )
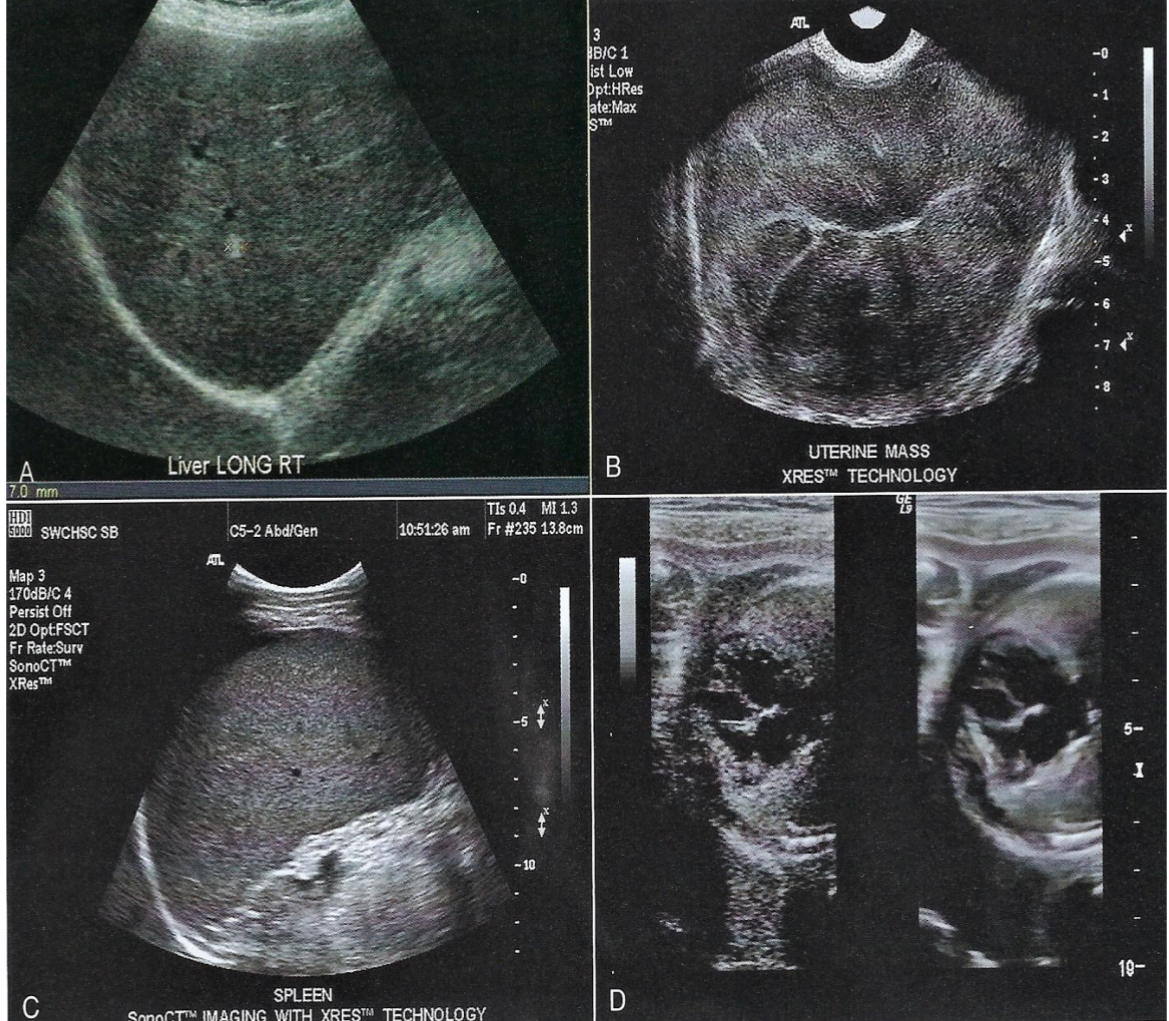
How do we correct speckle artifact and what assumption is failed?
#6: strength (amplitude) of reflection os related to its characteristics
persistence and spatial compounding
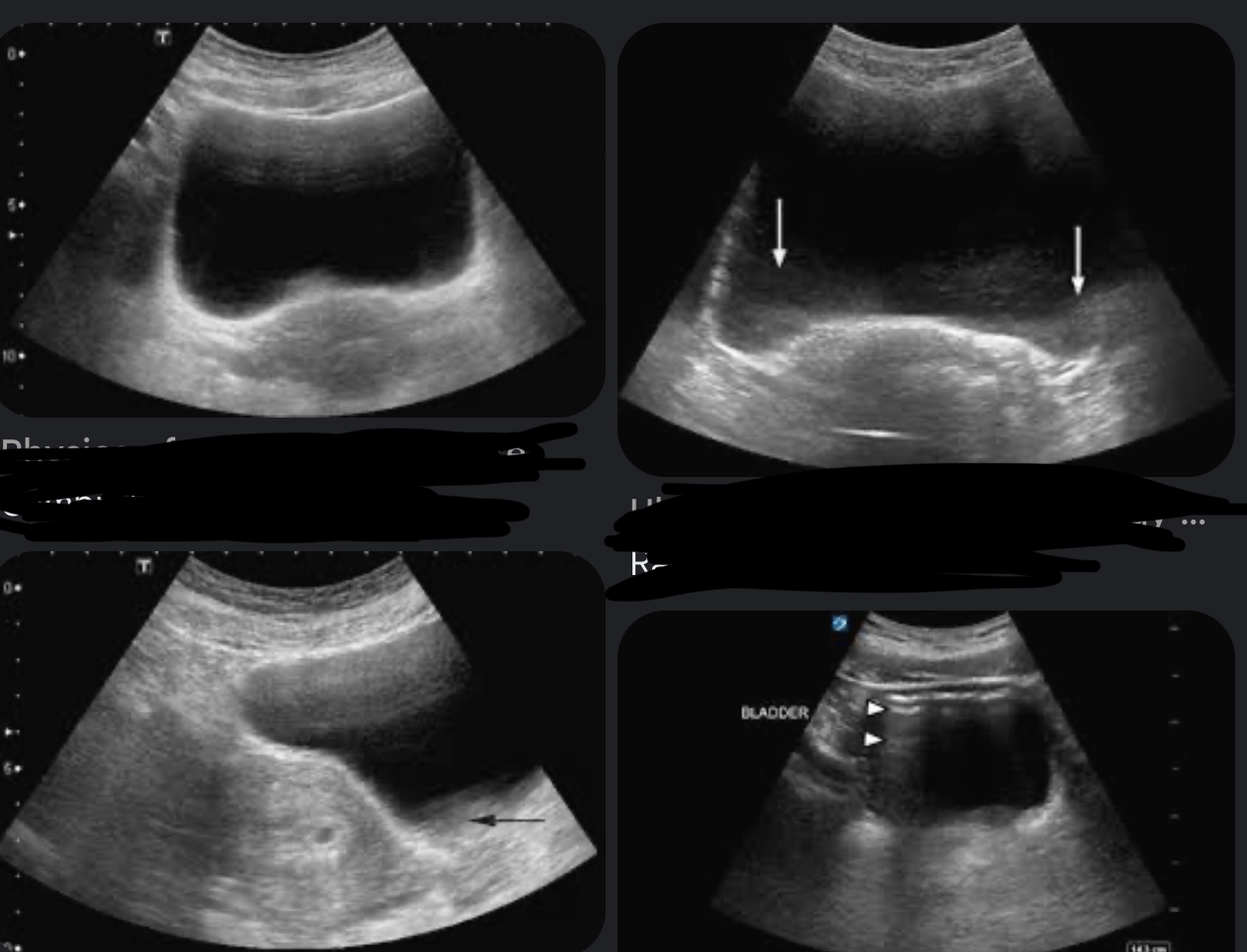
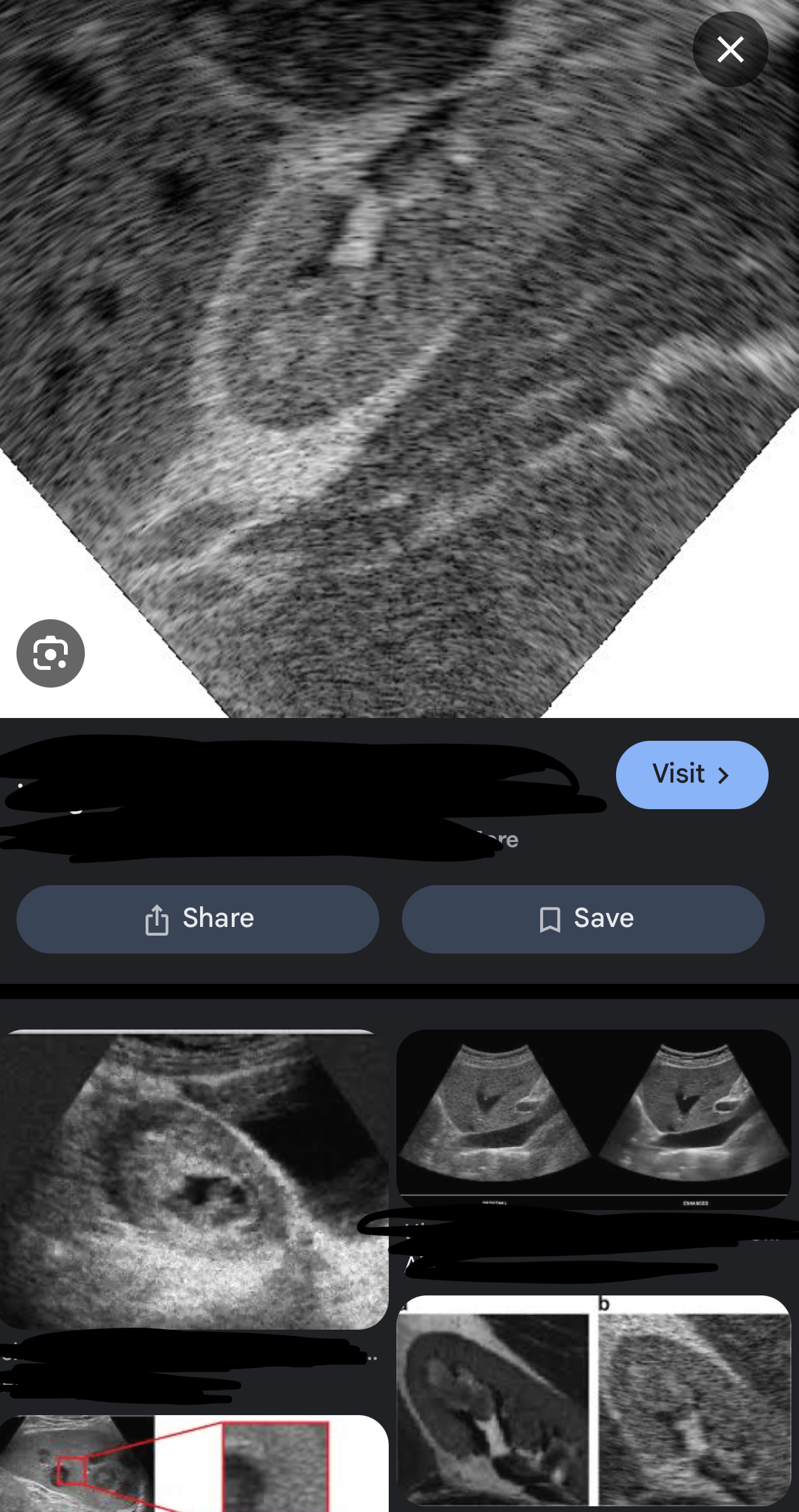
define reverberation
Artifacts that appears on our display monitors as multiple, equally, spaced echoes, caused by the bouncing of sound wave between 2 strong reflectors positioned parallel to the U/S beam
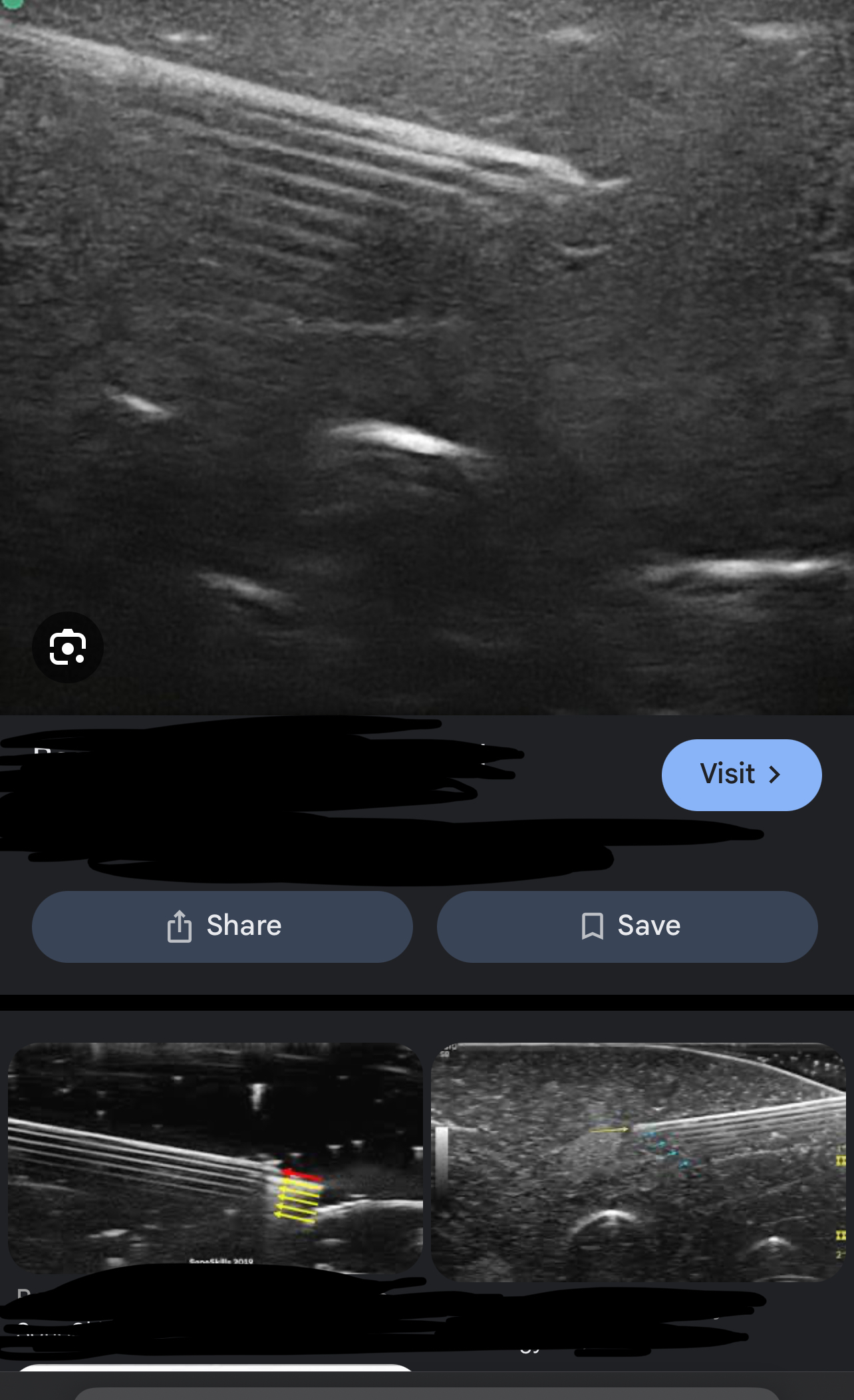
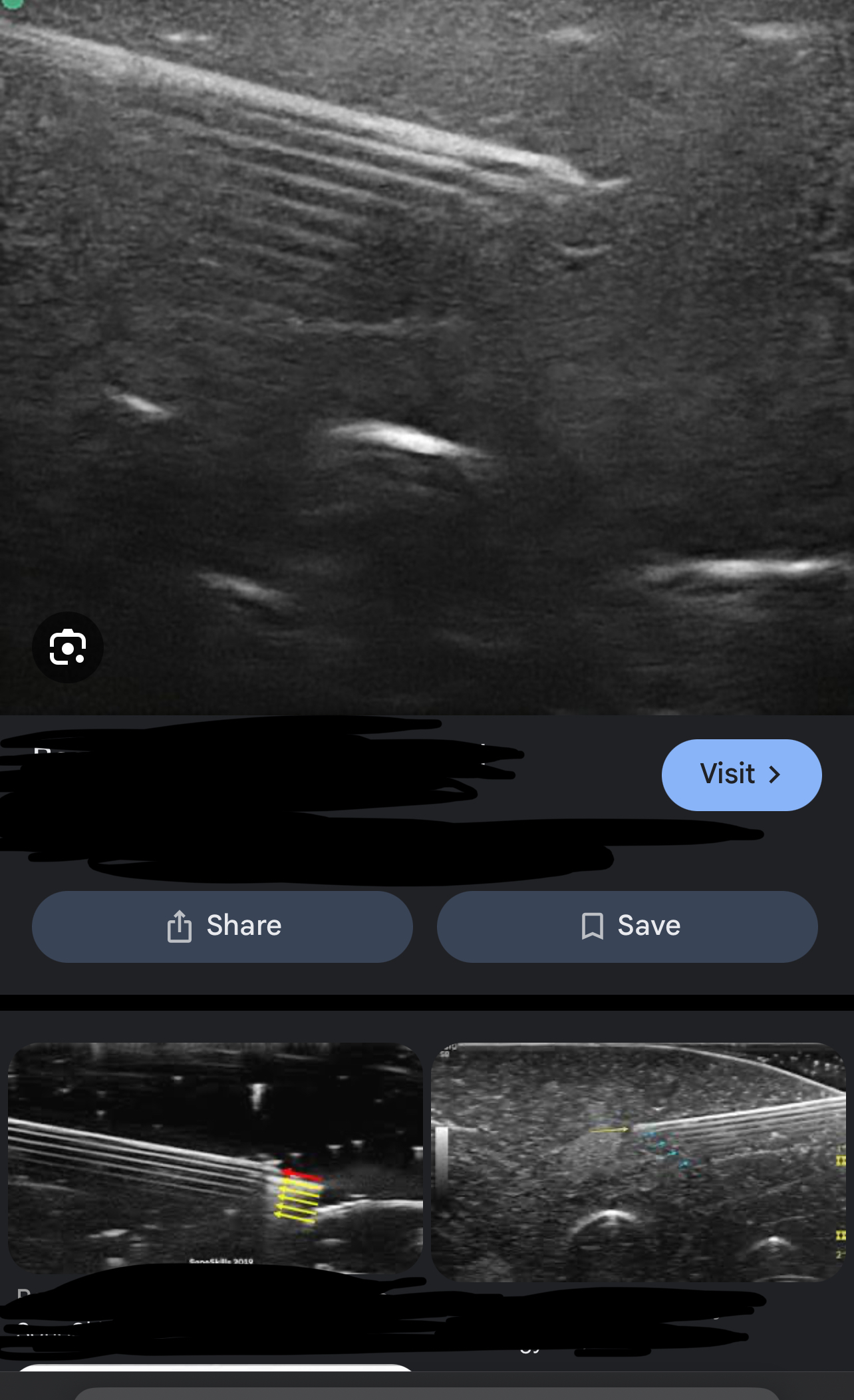
What assumption does reverberation violates & how do we correct it?
#2( sound travels directly to a reflector and back) and correct it by Harmonics, decrease depth, decrease 2D gain, TGC, or move angle of the tx
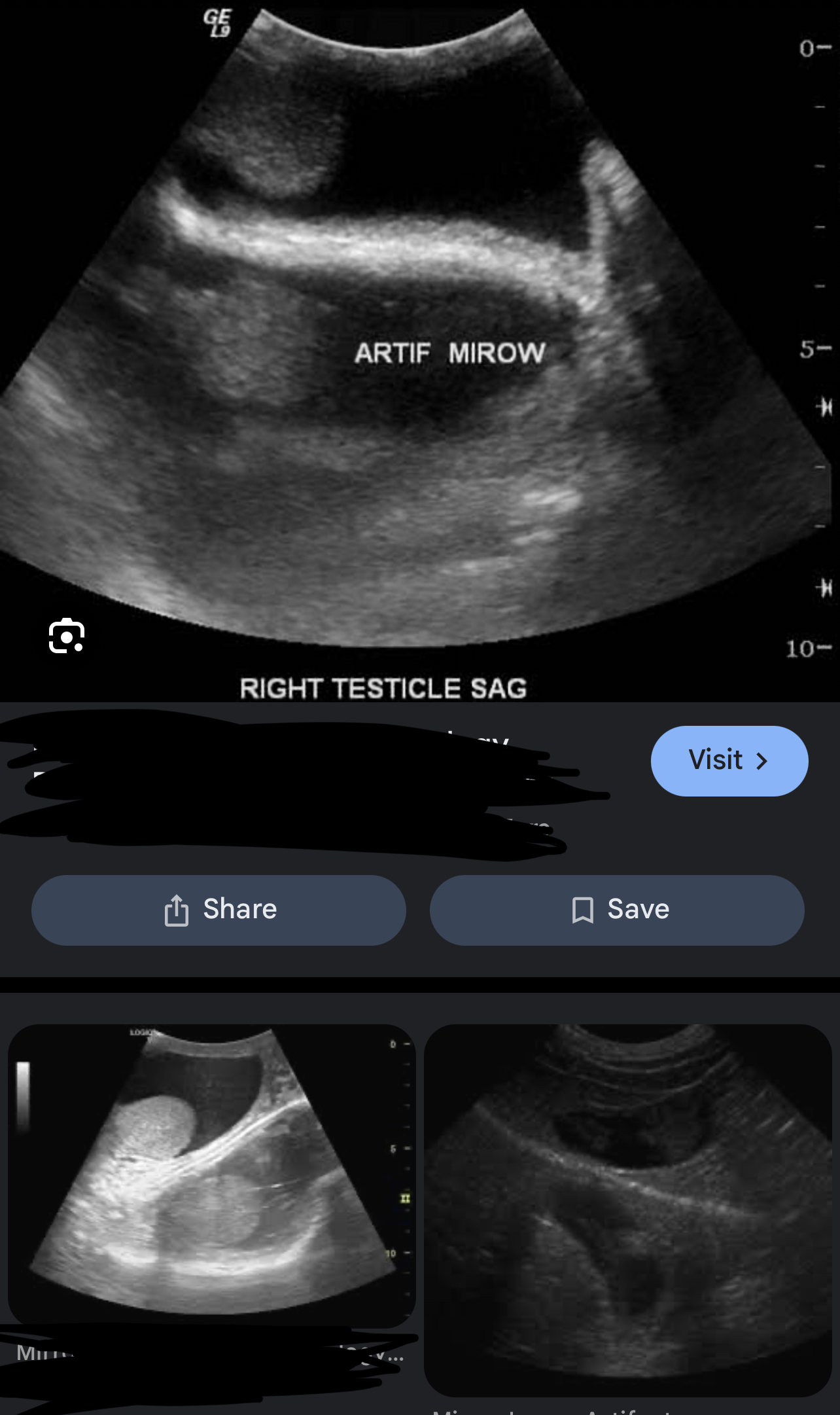
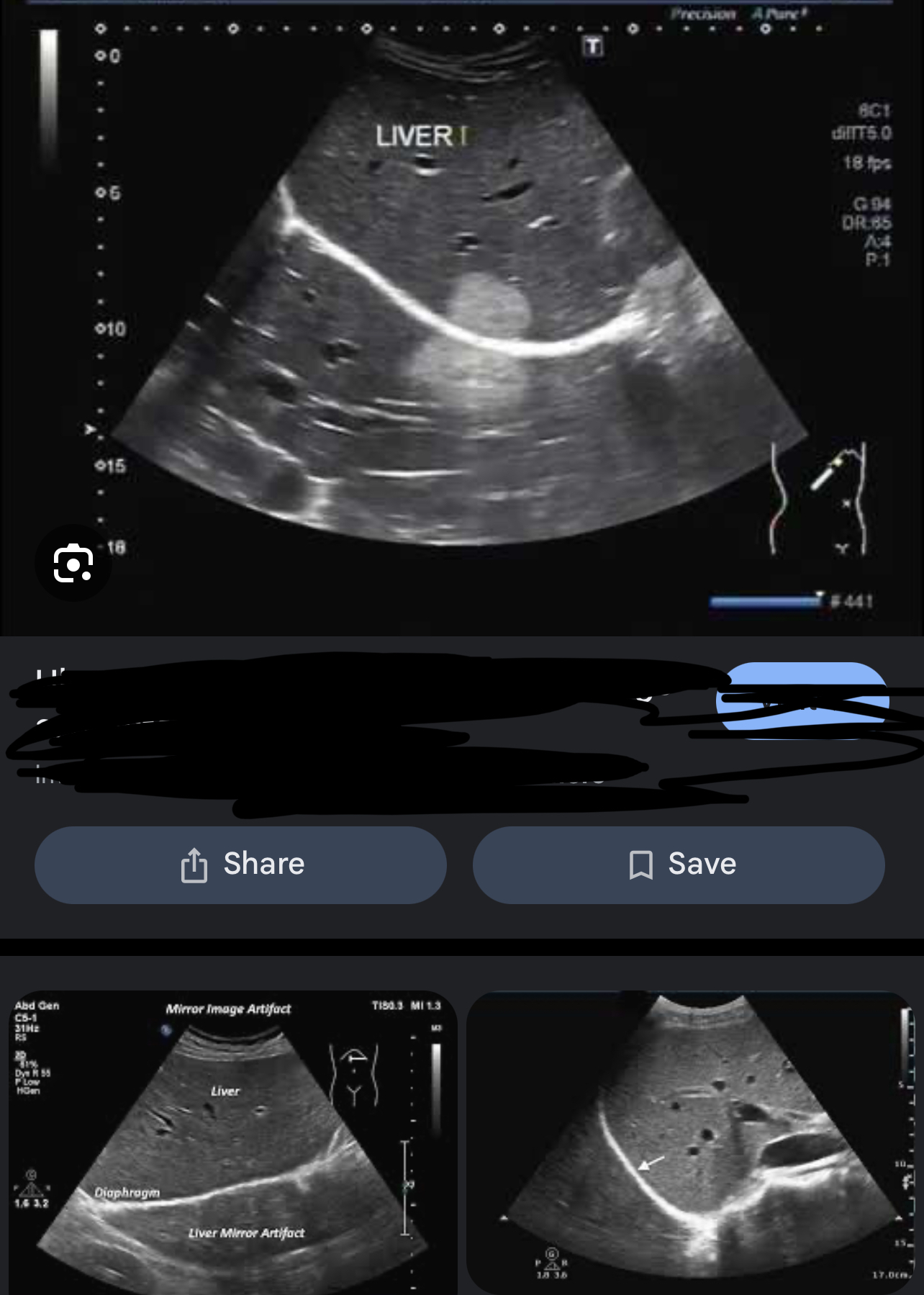
Mirror Image
When sound reflects off a strong reflector, which acts like a mirror, a mirror image artifact is created → the sound is redirected towards a second structure, this redirection causes a replica or second copy, which is the mirror image
artifact is placed deeper than the real anatomic structure, & always located along a straight line between the transducer & the artifact
Artifact may appear in Color doppler
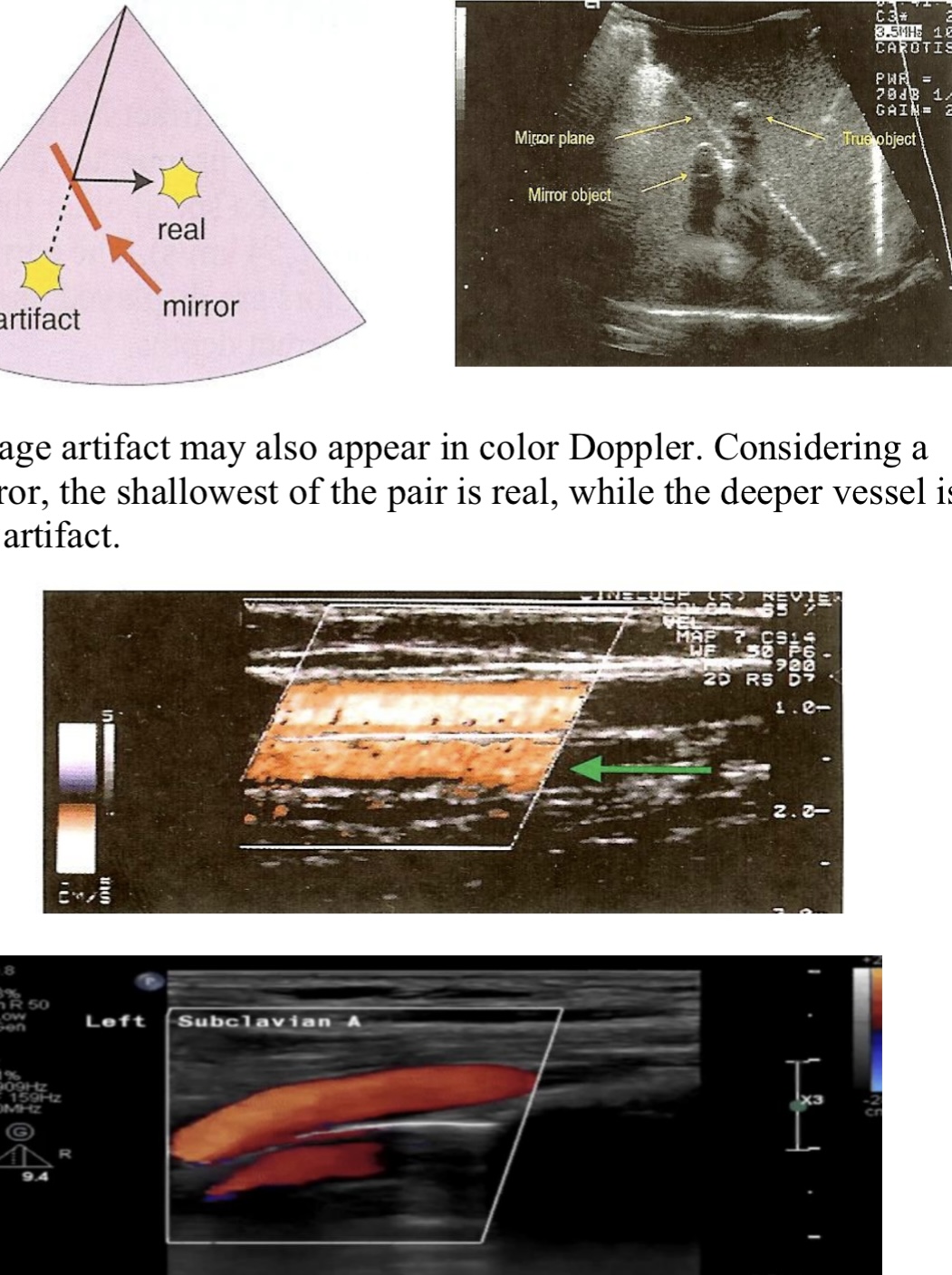
In Mirror image which assumption is it failing and how do we correct it?
#2 ( states that a sound travels directly to a reflector and back ) & moving tx in 90 degrees, spatial compounding, devrease Color doppler gain, or dive (heel/ toe) tx