Ch 8 - Visual Motion Perception
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
motion aftereffect (MAE)
the illusion of motion of a stationary object that occurs after prolonged exposure to a moving object
interocular transfer
the transfer of an effect (such as adaptation) from one eye to the other
middle temporal area (MT/V5)
an area of the brain thought to be important in the perception of motion
apparent motion
the illusory impression of smooth motion resulting from the rapid alternation of objects that appear in different location in rapid succession
i.e. stop motion movies
aperture
a windowlike opening that allows only a partial view of an object
correspondence problem
in reference to motion detection, the problem faced by the motion detection system of knowing which feature in Frame 2 corresponds to a particular feature in Frame 1
aperture problem
the fact that when a moving object is viewed through an aperture (or a single receptive field), the direction of motion of a local feature or part of the object may be ambiguous
first-order motion
the motion of an object that is defined by changes in luminance (reflected light)
luminance-defined object
an object that is outlined by differences in reflected light
second-order motion
the motion of an object that is defined by changes in contrast or texture, but not by luminance
texture/contrast-defined object
an object that is defined by differences in contrast, or texture, but not by luminance
akinetopsia
a rare neuropsychological disorder is which the affected individual cannot perceive motion
double dissociation
the phenomenon in which one of two functions, such as first and second-order motion, can be damaged without harm to the other, and vice versa
optic array
the collection of light rays that interact with objects in the world that are in front of a viewer
optic flow
the changing angular positions of points in a perspective image that we experience as we move through the world
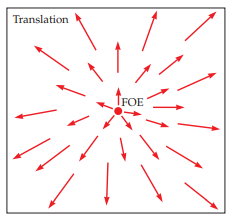
focus of expansion
the point in the center of the horizon from which, when we’re in motion (i.e. driving on the highway), all points in the perspective image seem to emanate
one aspect of optic flow
time to collision (TTC)
the time required for a moving object to hit a stationary object
= distance / rate
tau
information in the optic flow that could signal time to collision without the necessity of estimating either absolute distances or rates
the ratio of the retinal image size at any moment to the rate at which the image is expanding is this
biological motion
the pattern of movement of living beings (humans and animals)
saccade
a type of eye movement, made both voluntarily and involuntarily, in which the eyes rapidly change fixation from one object or location to another
smooth pursuit
a type of voluntary eye movement in which they eyes move smoothly to follow a moving object
superior colliculus
a structure in the midbrain that is important in initiating and guiding eye movements
microsaccade
an involuntary, small, jerky eye movement
reflexive eye movement
a movement of the eye that is automatic and involuntary
optokinetic nystagmus (OKN)
a reflexive eye movement in which the eyes will involuntary track a continually moving object
vergence
a type of eye movement in which the two eyes move in opposite direction
ex. both eyes turn toward the nose (convergence) or away from the nose (divergence)
saccadic suppression
the reduction of visual sensitivity that occurs when we make a saccadic eye movement
eliminates the smear from retinal image motion during an eye movement
efference copy
the phenomenon in which outgoing signals from the motor cortex are copied as they exit the brain and are rerouted to other areas in the sensory cortices
comparator
an area of the visual system that receives one copy of the command issued by the motor system when the eyes move (other copy goes to the eye muscles)
compares the image motion signal with the eye motion signal and can compensate for the image changes caused by the eye movement