SQA-Midterm
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
The SQA Plan (SQAP)
Deals with the activities and tasks the SQA function is required to carry out over the next year
1. SQA Process Implementation Activity Elements 2. Product Assurance Activity Elements 3. Process Assurance Activity Elements
The activity elements are classified into three (3) groups:
The Project Plan
Deals with the activities and tasks to be performed by the project team throughout the project’s life cycle
Software product risks to users
presents a project list, where for each project, an evaluation of software product risks has to be performed by the SQA function.
Development equipment and tools of software projects
presents a list of projects, where for each project, a list of equipment and tools will be determined based on an analysis of the nature.
Standards, practices, and conventions for software projects
refers to the activity that will evaluate lists of standards, practices, and conventions
Resources and schedule estimates for the SQA function
presents resources and schedule estimates for the SQA function activities planned for the next year.
Conformance Evaluation of project plans
lists the SQA function’s conformance evaluation tasks of the project plan tasks
Conformance evaluation of products
lists the evaluations of software development products
Evaluation of product for acceptability
lists evaluation of the required confidence level of a software project product
Conformance evaluation of product maintenance plan
lists evaluation of conformance of maintenance plans
Measurement plans for products
lists the measurement plans and required data collection for software products
Conformance evaluation of life cycle processes
deals with the evaluation tasks of life cycle processes, models, and procedures
Conformance evaluation of environment
deals with the evaluation of the adequacy of the environment of development, test, and support services
Conformance evaluation of subcontractors’ participation in project implementation
presents the SQA function evaluation tasks aimed to determine the adequacy of the pre-contract activities.
Measurement of development, testing, and operation processes
lists the measurement plans and required data collection for software life cycle processes
Assessment of staff skills and knowledge requirements and resulting training needs
deals with the evaluation of skills and knowledge
The project manager
usually the person responsible for preparing the project plan
Project Products
A development plan includes the following products: - Deliverables, - Software products of each activity, - Development process mapping - Development resources estimation
Control Methods
The project manager and the department management control project implementation
Mapping the Development Process
involves preparing detailed definitions of each of the project’s activities.
Estimating Development Resources
The type of professional resources required and the estimated quantity are: - Internal (developer) staff and their professional skills, - External (subcontractor) staff and their professional skills
Project Staff Organization
The organization plan includes: - Organizational structure, - Professional requirements for each team, - Number of team members required for each period of time, - Name of team leaders, and, if possible, the name of team members
Project Interfaces
Include: - Software interface, - Hardware interface, - Teams interface
Product Risks
a state where the software product may cause damage to the developer and/or to the user of the software.
Development Risks
a state of a development task or environment, which, if ignored, will increase the likelihood of project failure
Project Milestones
events of importance in the development process, that is, the completion of the design phase.
Project Cost Estimation
includes human resources costs, subcontractor costs, costs of purchased software, and costs of additional resources, such as travel costs and equipment costs.
Project Methodology and Development Tools
The methodology and development tools have to be applied for each phase of the project.
Software Development Standards and Procedures
are determined by the customer as part of the requirements stated in the project contract.
Required Development Facilities
include hardware, laboratories, software and hardware development tools, office space, and other items.
Documentation Control
The planner is required to define the list of the projects controlled documents and quality records.
Security Including Virus Protection
The planner is required to define security controls related to the project documents, code in processes, and software products.
Quality Goals
are the developed software system’s substantive quality requirements.
Procedures and Work Instructions
The relevant procedures and work instructions should be defined according to the combined quality assurance and development considerations.
Criteria for Ending each Project Stage
A criterion for ending each of the development stages, accepted by the customer and developer
Project Life Cycle SQA Activities
The quality plan should provide a complete listing of all planned review activities
Configuration Management Tools and Procedures
The quality plan should specify configuration management tools and procedures, including the timing of baseline version releases.
Monitoring Measurement Activities
The planners should define software quality metrics for quality, productivity, schedule keeping, and so forth.
Person(s) Responsible for Approving Project Outputs
The person(s) authorized to approve each of the project products, documents, and code files, especially deliverable items, should be determined.
Training in Use of New Development Tools
The need to apply new development tools for given development activities creates a training requirement.
Change Management
procedures to be applied throughout the project should be defined and agreed upon with the customer.
Cost of Software Quality
is the financial assessment of software quality development and maintenance
Cost of Software Quality Measurement Objectives
It is the - Control organization-initiated costs to prevent and detect software errors, - Evaluate financial damages of software failures as a basis for revising the SQA budget, - Evaluate plans to increase/decrease SQA activities, or to invest in new/updated SQA infrastructure.
The Classic Model of Cost of Software Quality
developed in the early 1950s by Feigenbaum and others, provides a methodology for classifying the costs associated with product quality assurance from a financial point of view.
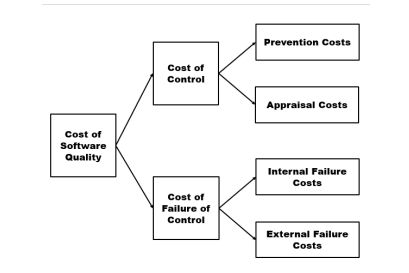
Costs of Control
relate to costs controlled by the software developer and includes the following subclasses: - Prevention Costs, - Appraisal Costs
Costs of Failure of Control
- relate to the costs of correcting failures that occurred due to unsuccessful prevention activities. The model further subdivides these costs into two subclasses: - Internal Failure Costs, - External Failure Costs
Prevention Costs
include investments in establishing, updating, and improving a software quality infrastructure, as well as for performing the regular activities required for its operation.
Appraisal costs
include the cost of activities performed for a specific project or software system to detect software errors that need to be corrected.
Internal failure costs
are those incurred through correcting errors that were detected through design reviews, software tests, and acceptance tests performed before the software was installed at customer sites.
External failure costs
include all costs of correcting failures detected by customers or maintenance teams after the software system has been installed at customer sites
Management Control Costs
relate to costs that are controlled by the management
Extended Model for Cost of Software Quality
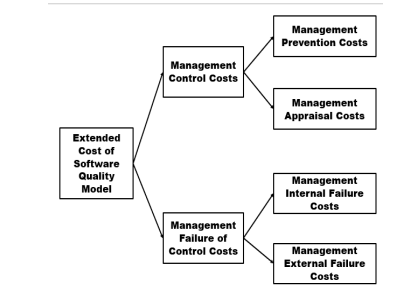
Management Prevention Costs
are associated with activities performed to prevent managerial failures or reduce prospects of their occurrence.
Management Appraisal Costs
are associated with activities performed to prevent managerial failures or reduce prospects of their occurrence.
Management Failure of Control Costs
relates to the costs of correcting failures that occurred due to unsuccessful prevention activities.
Management Internal Failure Costs
may be incurred throughout the entire course of software development.
Management External Failure Costs
Naturally, most managerial external failure costs incurred after completion of software development and system installation.