biotechnology: DNA and RNA anaylis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Biotechnology
use of basic science from the feild of biology to solve human problems
DNA/RNA analysis
takes a sample of DNA and learn about it
PCR
Gel Electrophoresis
Sequencing
DNA manipulation
Gene cloning
CRISPR
Why is DNA/RNA anyslis risky and how is it overcome
Forensic sceintits have little DNA avaible and if Analysis fails then there is no DNA left
To combat this they make copies of the DNA
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Makes more copies of the DNA
DNA replciation in a test tub
Ingredients in PCR
Crim scene DNA
Primers
DNA polymerase
Nucleotides
Buffer/cofactors
3 steps of PCR
Denaturation
Annealing
Elongation
Denaturation
Mimics helicase in DNA replication
Heated to 95 degrees
Hydrogen bonds and broken and DNA is speerated into 2 strands
Annealing
Sample is cooled (55 C) and primers bind
Primers are DNA based
Elongation
72 C
DNA polymerase uses the free -OH group at the end of the primers to crete two new DNA strnads
Is PCR reusable
Yes! PCR can be cycled again and again this time replicating the newly made DNA strands
30 cycles of PCR significance
Single strand can be replicated into more than a billion copies
Thermocycler
Machine for PCR
Will cycle through the temperatures needed for PCR to repeat the process over and over again
DNA sequencing
Allows scientists to determine the exact order of nucleotides in a given DNA sample
Can be preformed to short DNA molecules as well as an organisms entire geonone
DNA sequencing purpose
Can detect mutations
Useful for detecting small changes in DNA that have big consequences
Can detect 3 nucleotides in a gene that codes for a chloride transport protein that results in Cystic Fibrosis
RNA sequencing
What protiens are being made (cancer detection)
Preformed in a similar manner to DNA sequencing but reveals changes in gene expression
mRNA from cells can be collected and sequenced to determine if gene expression has changed
RNA sequencing steps
mRNA are isolated from tissue being studid
mRNA are cut into simular sized smaller fragments
mRNAs are reverse transcribed into cDNAs of the same size
cDNAs are sequenced
Short sequences are mapped by computer onto the genome sequence
cDNA and stability
cDNA is more stable than RNA
restriction enzymes
special class of enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences
significane of restriction enzymes
Cut the DNA into diffrent sized peices or fragments
Different combination of fragment sizes is unique to each person
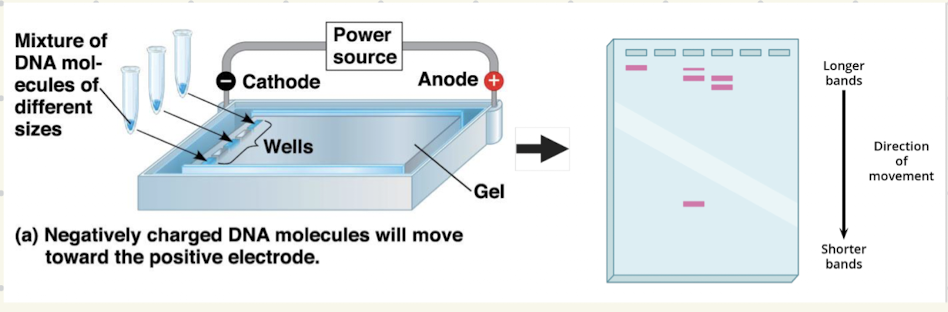
Gel Electrophoresis
A type of sceincy machine that can comapre the DNA fragments of diffrent sizes and line them up
Gel electrophoresis Steps
Crime scene DNA is copied and then cut with restriction enzymes
DNA from potential suspects is collected and cut with the same restriction enzyme
RNA samples are loaded into a gel block
Run through gel electrophoresis machine
DNA spreads out due to the size of bands
Large fragments travel slower through the gel, while smaller fragments travel faster.
Each person produces a unique banding pattern in gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis image