Haloalkanes Mechanisms
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
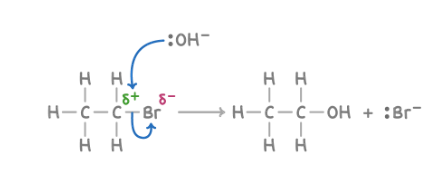
Reaction with hydroxides to form alcohols
Reagent : NaOH
Conditions : aqueous, warm
What happens : halogen atom replaced by OH group
Overall equation : CH3CH2Br + NaOH ➔ CH3CH2OH + NaBr
Mechanism : Nucleophilic Substitution
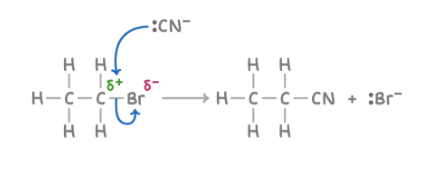
Reaction with cyanide to form nitriles
Reagent : KCN
Conditions : aqueous ethanol, warm
What happens : halogen atom replaced by CN group
Overall equation : CH3CH2Br + KCN ➔ CH3CH2CN + KBr
Mechanism : Nucleophilic substitution
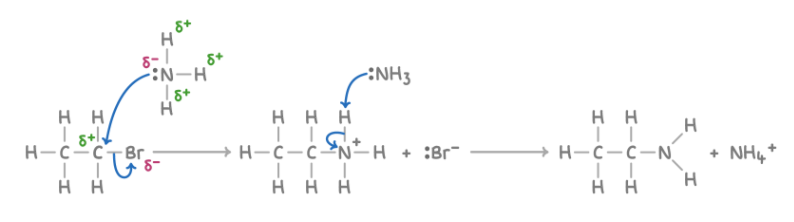
Reaction with ammonia to form amines
Reagent : NH3
Conditions : Excess concentrated ammonia dissolved in ethanol at pressure in a sealed container
What happens : first molecule of NH3: halogen atom replaced by NH3 group; second molecule of NH3: removes H+ from added NH3
Overall equation : CH3CH2Br + 2NH3 ➔ CH3CH2NH2 + NH4Br
Mechanism : Nucleophilic substitution
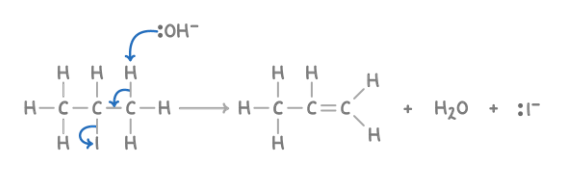
Reaction with hydroxide to form alkenes
Reagent : KOH
Conditions : Ethanolic, hot
What happens : halogen atom and one H atom from an adjacent C atom is removed giving an alkene
Overall equation : CH3CHICH3 + KOH ➔ CH2=CHCH3 + H2O + KI
Mechanism : Elimination