Chapter 2: atomic structure
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Dalton
Billard ball model
Thomson
plum pudding model
discovered electrons
experience of deflection of cathode rays by magnetic field
Rutherford
model named after the guy
heavy nucleus, most mass centered in the nucleus
discovered the scattering of alpha particles by heavy atoms
Bohr
electrons in few, discreet orbits around the nucleus (kind of like planets but modified)
model leading to accurate calculation of the wavelength of light emitted by hydrogen
l values based on orbitals
s orbital = 0
p orbital =1
d orbital = 2
f orbital =3
etc.
ml
values for __ go from -l to +l
angular nodes
#of __ = l
radial
number of __ nodes = n-l-1
total number of nodes
n-1
cannot
s orbitals __have angular nodes, however, p,d,f etc. orbitals can have them, you just can’t see it without cutting them open.
n
the number of radial nodes depends on the angular momentum l, aka the type of orbital, but also on __
Dmitri Mendeleev
established periodic law and organization of elements
1869
proipertiesofelementrs reur at regular intervals
Julius Lothar Meyer
Independently contributed to the organization of the elements
ordered in order of atomic weight and grouped based on similar properties
before
the elements were organized in a table ___ the electrons were discovered by Thomson
light
electromagnetic energy
white __ can be separated into component colors based on wavelengths distribution`
decreases
E = hc/lamba
As the wavelength increases, the frequency and energy ___, and vice versa.
atomic line spectra
unique spectral signature corresponding to a specific energy emitted from an excited atom
yellow
Na+ ions emit a ___ light, specific to sodium.
Balmer series
Lines of the H atom spectrum in the visible range
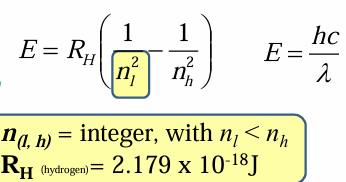
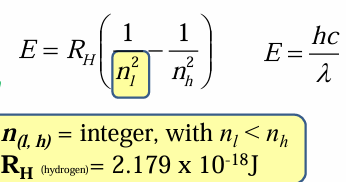
1,2,3
When calculating spectral lines, the Lyman series starts at n=__, Balmer series start at n=___ and the Paschen series starts at n=__
When calculating, nl is considered the starting point of the series, but it is not the start of the entire spectra, so nh will be nl+# of the line you wish to calculate.
Rydberg
__ generalized Balmer equation which made predicting new atomic lines possible
The Rh constant named after him.
Paschen
series for H lines in the IR range
Paschen
series for H lines in UV
before
Elements were organized following the periodic law, and spectral lines discoveries happened __ the discovery of electrons by Thomson
Thomson
discovered the electrons
played with cathode rays to prove that the electrons have a negative charge
plum pudding model
Millikan
measured the electron its charge and figured out its mass of 9.11×10^-31 kg
oil droplets and X-rays experiements
Rutherford
established the nuclear model of the atom: a very small, heavy nucleus surrounded by mostly empty space
reflection of alpha particles on foil
discovered protons and neutrons aka heavy nucleus
1911
Bohr
propose an atomic model where the electrons can only exist in discrete orbits
electrons jump from one orbital to the next& each jump correspond to a specific amount of energy
discrete stationary states called orbital
QUANTIZED energy levels
limitations of the Bohr atom
only works for 1 electron system like the H atoms
electron is treated as a particle “in orbit” around the nucleus
orbit is always circular (true for s orbitals, not the other types)
De Broglie
electrons are discrete bits of matter (particles) which also have wave-like properties with wavelength and frequency
Einstein
light is an electromagnetic wave and a localized pack of discrete energy (particle-like)
photoelectric effect
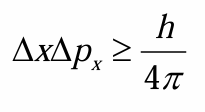
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
we never know where the electron is located exactly, always uncertainty about that