Human Blood and Immunology: Key Concepts and Cell Types
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Plasma is closest in composition to
interstitial fluid.
The most abundant component of plasma is
water.
Plasma composes about ________ percent of whole blood and water composes ________ percent of the plasma volume.
55; 92
Surgical removal of the stomach could cause
pernicious anemia.
________ is a condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is reduced.
Anemia
A bruise appears as a greenish spot in the skin because
the heme group in the hemoglobin has broken down into biliverdin.
Pernicious anemia caused by a lack of intrinsic factor is specifically treated by
injections of vitamin B12.
A person's blood type is determined by the
presence of specific glycoproteins on the cell membrane.
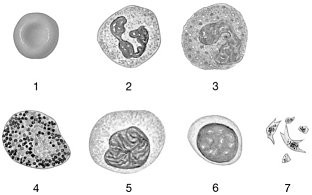
Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed ElementsUse Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:Identify the cell labeled "6."
lymphocyte
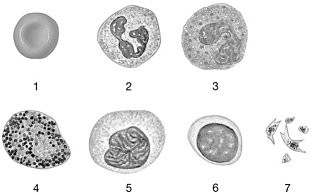
Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed ElementsUse Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:Identify the cell labeled "5."
monocyte
Non-specific immunity, such as phagocytosis, is a function of which blood cells?
neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes
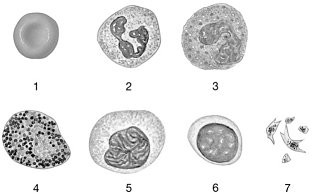
Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed ElementsUse Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:Identify the cell labeled "2."
neutrophil
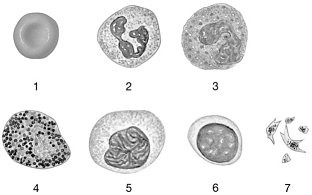
Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed ElementsUse Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:Identify the cell labeled "3."
eosinophil
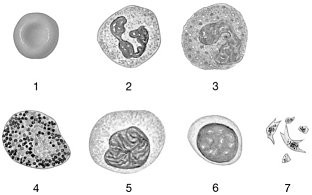
Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed ElementsUse Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:Identify the cell labeled "4."
basophil
The blood cells involved in specific immunity are the
lymphocytes.
Most of the protein factors that are required for clotting are synthesized by
the liver.
The ________ is a procedure that is used to determine the number of each of the various types of white blood cells.
differential count
A fibrin network that contains trapped blood cells and platelets is called a(n)
blood clot.
The phase of hemostasis that involved clotting of blood is called
coagulation.
Proteins in the blood for defense are called
immunoglobulins.
Fifty to seventy percent of circulating white blood cells are
neutrophils.
Which of the following statements is true regarding the ABO blood types and the Rh blood types?
An Rh- person has to be exposed to Rh+ blood in order to produce anti-Rh.
A cross-match test is performed between donor blood and recipient blood, even though the ABO and Rh blood types match between the two because
there are many more surface antigens on red blood cells other than A, B and Rh.
Reticulocytes complete their development into ________ in the circulation.
erythrocytes
The plasma protein involved in blood clotting is
fibrinogen.
The enzyme that can digest fibrin and dissolve a clot is
plasmin.
Which of the following vitamins is needed for the formation of clotting factors?
vitamin K
How would removal of calcium ions from a blood sample affect coagulation?
Coagulation would be prevented.
A substance that activates plasminogen might be useful to
cause clot dissolution to proceed faster.
Some rat poisons contain a toxin that blocks the liver's ability to utilize vitamin K. Animals that consume this poison would die of
hemorrhage.
The process of fibrinolysis
dissolves clots.
The common pathway of coagulation begins with the
activation of Factor X, production of prothrombin activator.
________ involves a cascade of reactions leading to the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
Coagulation
During a bacterial infection you would expect to see increased numbers of
neutrophils.
Eosinophils function in
destroying antibody-labeled antigens.
An infected wound contains typically contains
All of the answers are correct.
Which of the following is not true of monocytes?
about same size as basophils
Which of the following is true of basophils?
All of the answers are correct.
Which of the following is not true of neutrophils?
less abundant than lymphocytes
A genetically engineered hormone that stimulates the production of neutrophils is
G-CSF (Neupogen).
White blood cells that are increased in allergic individuals are the
eosinophils.
Which of the following descriptions best matches the term colony stimulating factor?
hormone that regulates white blood cell formation
The most numerous white blood cells in peripheral circulation are the
neutrophils.
All of the following are true of neutrophils except that they are
important in coagulation.
Type AB blood has which of the following characteristics?
RBCs have both the A & B surface antigens and no ABO plasma antibodies.
Blood type is identified primarily by
both the ABO and Rh blood groups.
People with type AB blood are considered the "universal recipient" for transfusions because
their blood lacks A or B agglutinins.
Bill wants to determine his blood type, so he takes a few drops of blood from a puncture wound in his finger and mixes it with various antisera. His blood cells agglutinate when mixed with the anti-A sera but not with the anti-B or anti-D sera. What does this mean?
Bill's plasma contains B antibodies.
Which of the following blood count values would be a sign of anemia?
3.5 million RBC
Each hemoglobin molecule contains
four iron atoms.
Erythropoiesis is stimulated when
blood flow to the kidney declines.
The developmental stage at which erythrocytes enter the circulation is as
reticulocytes.
The process of red blood cell production is called
erythropoiesis.
In adults, erythropoiesis exclusively takes place in
red bone marrow.
Most of the iron that is removed from degraded hemoglobin is
recycled to the red bone marrow.
The waste product bilirubin is produced from
heme molecules lacking iron.
Aged and damaged erythrocytes are broken down by macrophages in the
spleen, liver, and bone marrow.
The function of hemoglobin is to
carry dissolved blood gases.
More than 95 percent of the protein in a red blood cell is
hemoglobin.
If bile ducts are blocked,
more bilirubin appears in the plasma.
Each heme ring in hemoglobin encloses an atom of
iron.
In adults, the only site of red blood cell production, and the primary site of white blood cell formation, is the
red bone marrow.
The function of red blood cells is to
carry oxygen to the cells and then carry away carbon dioxide.
The average life span of a red blood cell is
4 months.
An obstruction in blood flow to the kidneys would ultimately result in
increased erythropoiesis.
Which plasma protein transports fatty acids and some hormones?
albumin
The disease sickle cell anemia is an example of what can happen if
a gene for adult hemoglobin is abnormal.
Which of these proteins functions to store or transport iron?
ferritin, hemosiderin, and transferrin
Red blood cell production is regulated by the hormone
erythropoietin.
All the circulating red blood cells in an adult originate in the
red bone marrow.
A plasma protein essential for blood coagulation is
fibrinogen.
Plasma proteins essential in body defense are the
immunoglobulins.
The most abundant proteins in blood plasma are
albumins.
Which organ secretes most of the plasma proteins?
liver
Transferrin is an example of which kind of plasma protein?
metalloprotein
Thyroid-binding globulin is an example of which kind of plasma protein?
hormone-binding
The percent fraction of formed elements relative to whole blood is the
hematocrit.
Which of the following is not one of the formed elements of blood?
antibodies
The chief difference between plasma and interstitial fluid involves the concentration of
proteins.
Which of the following statements about blood is false?
The normal pH of blood is 6.8 to 7.0.