EVALUATING MESSAGES AND IMAGES OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF TEXTS Chapter 5
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Evaluating messages and images of different types of text
Chapter 5
Text
provide the means for communicating and form an important part of study in any given course.
Pardo (2004)
explains that these types of texts share characteristics that may include an understanding of the author’s intent, the social purpose of the text, how it is structured, how well it is written, the subject matter, vocabulary, language choices, the reading level, and other surface features.
Print-based
refers to those texts that are prepared in prints, but any printed text is a multimodal text since it involves various communication modalities.
Multimodal texts
When a text combines two or more semiotic systems (linguistic, visual, audio, gestural, spatial), it is considered ________.
Semiotic
is the study of meaning-making. It explores signs and symbols as important components of communication.
Syllabus of the Australian Curriculum
mentions that language modes such as, listening, speaking, reading, writing, viewing, and representing are often integrated and interdependent activities used in evaluating texts in order to shape meaning and that any combination of the modes may be involved in responding to or composing print, sound, visual or multimedia text. Hence, multimodal texts can be print, digital, or live.
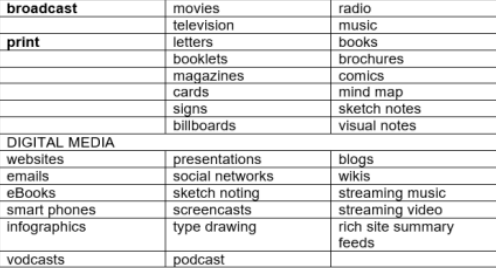
Forms of multimodal texts
Paper
Digital
Live
Two or more of the following semiotic systems are included in a multimodal text.Linguistic system
Visual system
Audio system
Gestural System
Spatial system
CRITICAL READING AND LISTENING
Multimodal texts require readers and listeners to become critical readers and listeners. Since comprehension is the central goal of both reading and listening, the ability to comprehend multimodal texts develops students to become critical readers and listeners as well as active evaluators of multimodal texts.
Critical reading
is the process of reading that goes beyond comprehension of a text.
Critical Reading involves
1. Carefully considering and evaluating a reading text;
2. Identifying the strengths and implications of the text;
3. Identifying the weaknesses of the text; and
4. Looking at the image and deciding how the reading fits into the greater academic context.
critical reader
is inquisitive, always asks questions about the texts. Hence, the ________ closely examines the key elements of the text. These elements may affect how strong the message is, that is, how convincing it is. However, before you consider the message, you should build up a background information about the text or an image.
Source
Readers or listeners of a text should ask first about its authorship. There is a need to identify if the ______ is an individual or a team although the number of writers does not warrant credibility of the text.
Who created the message? Is the source reliable? Was it by a news organization, a public citizen, an editorial team of a scientific journal, or an advertiser?
Message
After evaluating the source, the content of the text should be examined in order to get its ________. There are various questions that one may ask in getting the _________ of the text
2. What does the message say (subject, main point, support)?
3. Is the information fair and logical?
4. What points of view are shared in the message? Which ones are left out?
5. What images or sounds catch your attention?
Medium
The ______ in transmitting the message may be conventional or digital although they are often mixed up in a communication situation. Sometimes, print-based communication needs to be backed up by a digital form in order to achieve a better and faster communication
6. What type of text is used to deliver the message?
7. What are the advantages and limitations of the text format?
Audience
in the communication situation refers to the receiver of the message. It may be a person or a group for whom a message is created. Some texts like a personal email, an invitation to deliver a talk, or a thank-you note target just one person, but other texts are meant for larger audiences like research reports, advertisements, signages, books, brochures, among other communication forms. Two important questions guide audience adaptation in multimodal communication
8. Who is the target audience of the message?
9. How might other people interpret the message of the text?
Context
in this section includes the purposes and authorship of the text. A text serves at least one of three purposes: to inform, to entertain, or to persuade. Often, a text fulfills all three purposes at once. Magazines, for example, may entertain its readers, but it may also inform and persuade them. Consider and analyze the purpose before sending any messages.
10. What is the purpose of the message?
11. Who controls the transmission of this message?
Listening
is a voluntary active process, it is psychological.
Critical listening
requires active thinking because it goes far beyond just hearing a speaker’s message.
Identify support for the claims
This means performing research to determine the process the speaker used to actually gather facts and information. Look for things like dates and sources.
Evaluate the argument of the speaker or the text
Try to figure out whether the speaker is using emotional appeals, a logical argument or actual evidence to state the case. Sometimes, a speaker uses overstatements to stress a point and to make it more appealing. It is perfectly legal, but it can be misleading. This is especially true if you have not done your homework. When it comes to evaluating an argument, there are a few things you can do to get the most information.
main point
is no less the main idea or the claim of the source. It can be explicitly or implicitly expressed in the text.
explicit main point
is well expressed in the text. Certain features of the text would lead to an overt statement of the main point, for instance, orthographic features like sentences, phrases, clauses that provide an immediate extract of the main point is an explicit expression of the main point.
implicit main point
is covertly expressed in the text and can only be extracted based on suggestive features such as, graphics, images, or sound effects.
fact
is a statement about the real world that can be shown to be true and can be checked for accuracy through gathering of evidence.
opinion
however, is a self-report or attitudinal statement of feelings or personal judgement.
claim
is a debatable statement that can be supported with evidence and reason.
Visual elements
lighting
camera angle
composition
body
Lighting
Low ________ suggests sadness or fear, while bright ________ conveys happiness or joy. Soft ________expresses beauty and romance. Use color and tone to reflect the mood you are trying to create in your image.
Camera Angle
This visual element is used to position the viewers so that they can understand the relationship between the characters. It is very important in shaping meaning in film as well as in other visual texts. A low-______ view makes people or things appear larger than they actually are, often indicating importance. Conversely, a high ______ view makes people or things appear smaller and less significant.
Composition
Visual elements should be arranged in a manner that they do not affect the viewer’s perception. Arrangements such as, close ups of a face convey tension or intimacy, wider views showing people or things and their surroundings usually express significance of the setting
Body Language
Non-linguistic elements like the body language are more revealing than words. They seem to be more catchy than the words provided in the text
Sound Effects
This sound technique that is added after the filming enhances a scene making it realistic although the effects themselves are often artificially produced.
Music
This is another sound technique that affects the mood and intensity of a scene. Fast-paced music use rhythm and volume to heighten drama and often accompany car chases, fight scenes, and other action-packed scenes. Slower, softer, intentionally expressive compositions can create tension and foreboding, as in gothic film
To inform
The message provides the audience with a clear understanding of the concept presented by the source.
To entertain
The message or the text amuses the audience.
To persuade
The audience is provided with well-argued ideas that can influence their own beliefs and decisions.
Government
Multimodal texts that were created by __________ offices are state owned and must be carefully evaluated for propaganda—publicity, advertising, marketing, and information dissemination.
Corporations
Most of the media messages are controlled by private companies. Different forms of multimodal texts like videos, newspapers, magazines, movies, web sites are controlled by giant __________.
Individuals
Personal creations are independent media forms.
Paper
This form is print based, such as, books, comics, posters, magazines.
Digital
It is computer-based like slide presentations, emails, ebooks, blogs, e posters, web pages, social media, animations, films, movies, video games.
Live
It is a form of actual performance or an event.
Linguistic system
It refers to the linguistic components like vocabulary, structure, and grammar of a text.
Visual system
It pertains to the color, vectors and viewpoint in still and moving images.
Audio system
This mode refers to the volume, pitch, and rhythm of music and sound effects of a presentation.
Gestural system
It denotes the movement, facial expression, and body language of the characters.
Spatial system
It indicates proximity, direction, position of layout, and organization of objects in space.
Conventional Media