Thin lenses - power, imaging, lateral mag
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:39 PM on 9/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
1
New cards
thin lenses
-ignore the effect of thickness on lens power
-central thickness is small in relation to radii
-central thickness is small in relation to radii
2
New cards
2 curved refracting surfaces (front and back) connected together
the index of the lens is generally higher than the surrounding media
3
New cards
lens power
sum of both surface powers
Ft= F1 + F2
Ft= F1 + F2
4
New cards
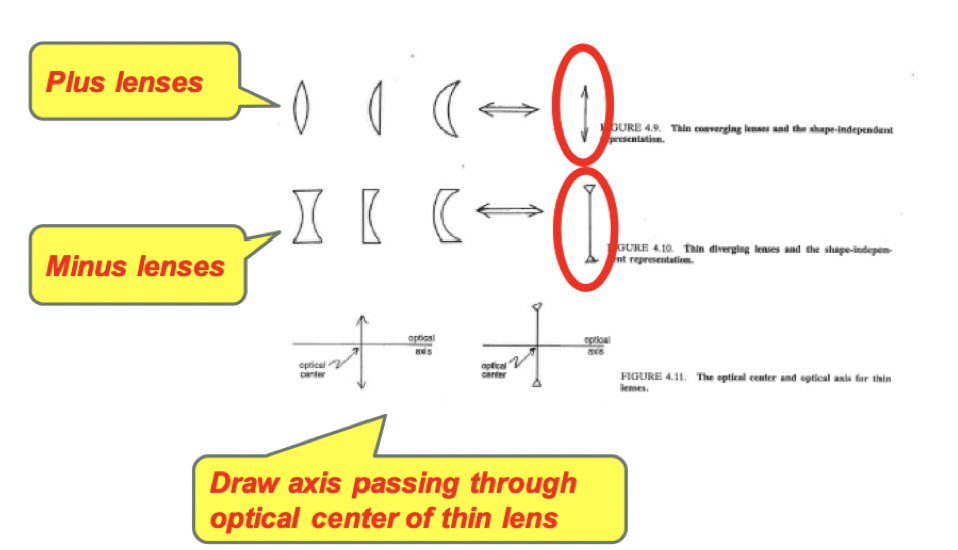
Lens designs
convex, positive, converging, or plus lenses
-thicker center, thinner edge
concave, negative, diverging or minus lenses
-thinner center, thicker edge
opthalmic lenses: usually meniscus
-minimizes off axis (peripheral) aberrations
-thicker center, thinner edge
concave, negative, diverging or minus lenses
-thinner center, thicker edge
opthalmic lenses: usually meniscus
-minimizes off axis (peripheral) aberrations
5
New cards
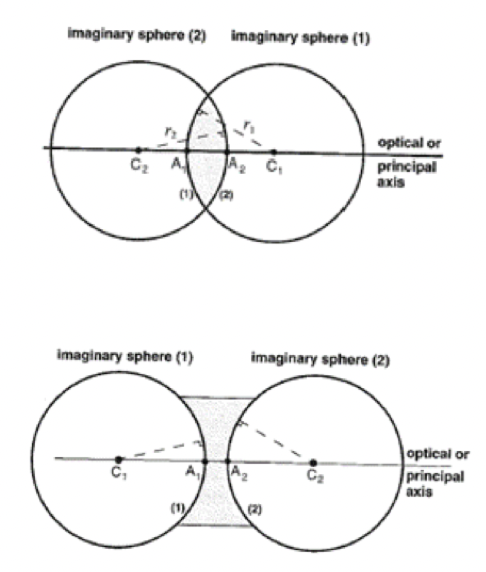
lenses have spherical surfaces
biconvex lens
- r1 is + and F1 is +
- r2 is - and F2 is +
biconcave lens
- r1 is - and F is -
- r2 is + and F2 is -
- r1 is + and F1 is +
- r2 is - and F2 is +
biconcave lens
- r1 is - and F is -
- r2 is + and F2 is -
6
New cards
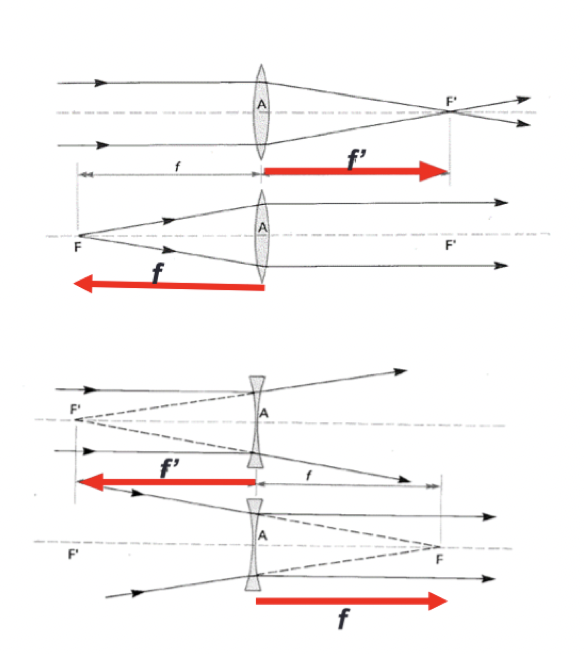
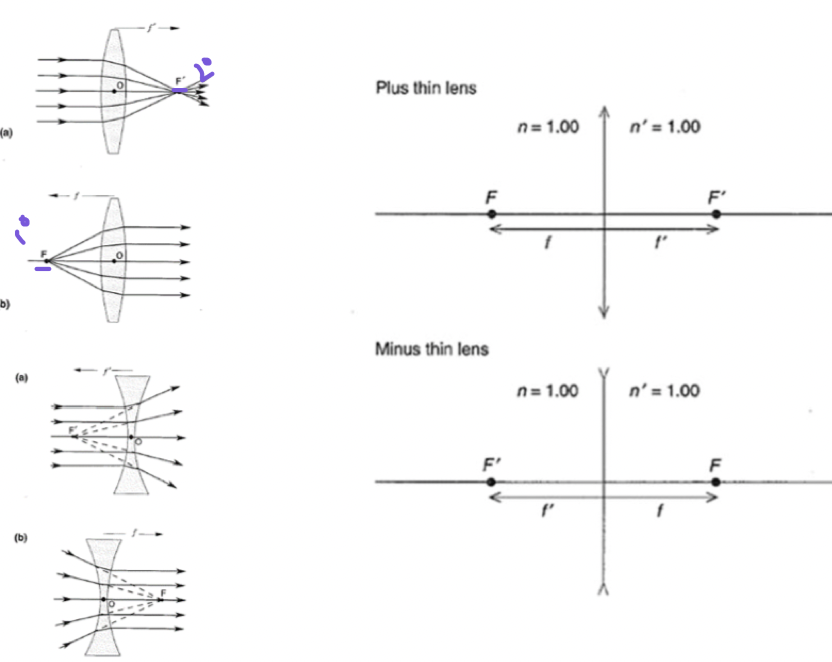
focal lengths
f' is image distance with the object at infinity
f is the object distance with image at infinity
f is the object distance with image at infinity
7
New cards
refraction occurs in _____
a single plane
we assume this
we assume this
8
New cards
focal lengths
F is the primary focal length and
F' is the secondary focal length
F' is the secondary focal length
9
New cards
Thin lens imaging
-the same as for curved surfaces
-F is now the power of the whole lens instead of just one side
- we can assume that it has air on either side unless otherwise specified
-F is now the power of the whole lens instead of just one side
- we can assume that it has air on either side unless otherwise specified
10
New cards
Thin lens imaging formula and relationship
- as RO moves from infinity to primary focal point (F), RI moves from secondary focal point (F') to infinity
- if RO is inside primary focal point (F), a VI is formed
- L'= L + F
- if RO is inside primary focal point (F), a VI is formed
- L'= L + F
11
New cards
focal length formula
f=-n/F
f'= n'/F
f'= n'/F
12
New cards
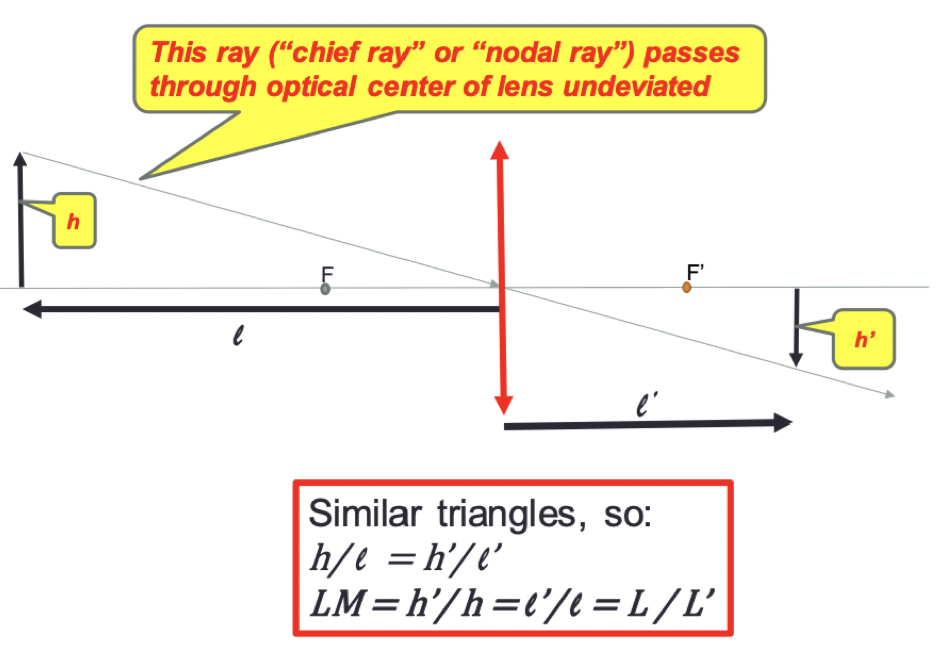
extended objects and lateral magnification
- can examine orientation and size of image compared to the object
- typically an arrow extending perpendicular to axis
- point source at tip of the arrow
- typically an arrow extending perpendicular to axis
- point source at tip of the arrow
13
New cards
Lateral magnification (LM) formula
LM= h'/h = l'/l = L/L'
14
New cards
what does LM tell us
-if LM+, image is erect
-if LM-, the image is inverted
-if LM>1, image is larger than object (h'>h)
-if LM
-if LM-, the image is inverted
-if LM>1, image is larger than object (h'>h)
-if LM
15
New cards
lateral magnification and symmetrical planes
symmetrical planes means LM = -1
if LM =-1, the l=2 f and l'=2f'
if LM =-1, the l=2 f and l'=2f'
16
New cards
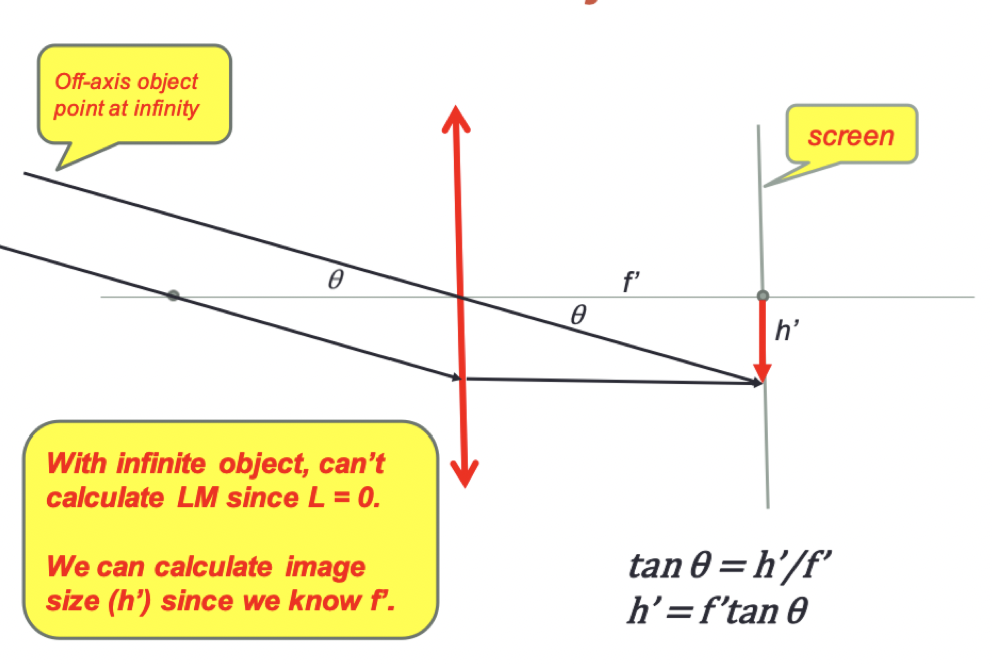
plus lens and distant object
- can't really find the lateral magnification because we need the image size or object size
- there is a special case when an object is at infinity
- there is a special case when an object is at infinity