8- T cell receptors and MHC proteins
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:28 AM on 10/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
T lymphocytes (T cells)
-Lymphocyte
-originates in the bone marrow but matures in the thymus.
- T lymphocyte receptors.
- recognises processed antigens presented on the surface of infected cells.
- defends against intracellular pathogens.
- long life span
- involved in cell mediated immunity
- 2 types: T-helper cells and cytotoxic T cells.
-originates in the bone marrow but matures in the thymus.
- T lymphocyte receptors.
- recognises processed antigens presented on the surface of infected cells.
- defends against intracellular pathogens.
- long life span
- involved in cell mediated immunity
- 2 types: T-helper cells and cytotoxic T cells.
2
New cards
Cytotoxic T cells
-T lymphocytes
-specifically destroys virus infected cells and cancer cells
- CD8 receptors located on cell membrane
- virus infected cell or tumour cell presents antigen.
- CD8 receptors recognise and bind antigens presented with MHCI
- stimulated by cross presentation
-specifically destroys virus infected cells and cancer cells
- CD8 receptors located on cell membrane
- virus infected cell or tumour cell presents antigen.
- CD8 receptors recognise and bind antigens presented with MHCI
- stimulated by cross presentation
3
New cards
T helper cell
T-lymphocytes
-increase immune responses by recognising foreign antigens and secrete cytokines which activate T and B cells.
-CD4 receptors located on cell membrane.
- macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, B cells, neutrophils
- CD4 recognises antigens presented with MHCII.
-increase immune responses by recognising foreign antigens and secrete cytokines which activate T and B cells.
-CD4 receptors located on cell membrane.
- macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, B cells, neutrophils
- CD4 recognises antigens presented with MHCII.
4
New cards
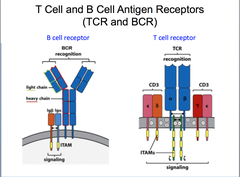
T lymphocyte receptors
member of Ig superfamily
- dimers of 2 polypeptide chains: (alpha and beta in 95% of cases, gamma delta in 5% (less diverse-fewergenes))
- alpha chain with V&J segment genes
- beta chain with V,D,J segment genes
-variable regions of both alpha and beta chains contain 3 CDR's. (CDR3 most variable in sequence and length)
-diversity brought about by junctional diversity and insertions/deletions.
- recognises and binds linear peptides processed and presented by MHC proteins.
- expressed only as membrane proteins complexed with CD3 as T cell receptor complex.
- interact with MHC proteins through CDR1 and CDR2.
- interact with foreign peptide through CDR3.
- dimers of 2 polypeptide chains: (alpha and beta in 95% of cases, gamma delta in 5% (less diverse-fewergenes))
- alpha chain with V&J segment genes
- beta chain with V,D,J segment genes
-variable regions of both alpha and beta chains contain 3 CDR's. (CDR3 most variable in sequence and length)
-diversity brought about by junctional diversity and insertions/deletions.
- recognises and binds linear peptides processed and presented by MHC proteins.
- expressed only as membrane proteins complexed with CD3 as T cell receptor complex.
- interact with MHC proteins through CDR1 and CDR2.
- interact with foreign peptide through CDR3.
5
New cards
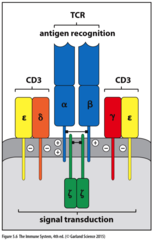
T-cell receptor complex (TCR)
CD3 is signalling protein complex that associates with T-cell receptors.
CD3 is required for T cell expression and signalling.
consists of CD3 γ, δ, ε chains and ζ chains.
ζ chains are intracellular and required for signal transduction.
γ, δ, ε and ζ chains contain ITAM motifs.
requires co-receptors (CD8/CD4) for activation.
CD3 is required for T cell expression and signalling.
consists of CD3 γ, δ, ε chains and ζ chains.
ζ chains are intracellular and required for signal transduction.
γ, δ, ε and ζ chains contain ITAM motifs.
requires co-receptors (CD8/CD4) for activation.
6
New cards
ITAMs
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs.
aggregation of T cell receptors upon responding to antigen phosphorylates ITAM motifs and allows interaction with downstream pathways, facilitating signalling.
aggregation of T cell receptors upon responding to antigen phosphorylates ITAM motifs and allows interaction with downstream pathways, facilitating signalling.
7
New cards
T cell receptor genes
T cell receptor gene rearrangement occurs in thymus
8
New cards
Major Histocompatibility proteins (MHC)
-encoded by major histocompatibility complex which are a highly polymorphic genes located on chromosome 6 and responsible for graft rejections.
- main role is in process and present antigens to T cells.
- role in T cell activation
-role in graph rejection
-role in thymic selection
- consist of 2 classes: MHCI and MHCII.
- T cells interact with MHC proteins via CDR1 and CDR2.
- main role is in process and present antigens to T cells.
- role in T cell activation
-role in graph rejection
-role in thymic selection
- consist of 2 classes: MHCI and MHCII.
- T cells interact with MHC proteins via CDR1 and CDR2.
9
New cards
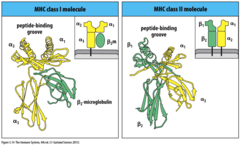
MHCI
expressed on surface of all nucleated cells.
structure:
- consist of 1 alpha membrane spanning chain and 1 beta chain (beta micro-globin).
- alpha chain domains encoded on MHC on chromosome 6 (highly polymorphic), beta chain encoded on chromosome 15.
-invariant beta micro globin stabilises membrane spanning alpha chain domain.
-single alpha chain domain (alpha 3) spans membrane.
-2 polymorphic alpha chain domains (alpha 1 &2) contain peptide binding groove and are involved in peptide presentation.
alpha chains encoded by 3 genes - HLA-B, HLA-C and HLA-A.
peptide binding groove binds short peptides of 9-10 aa long.
present endogenous antigenic peptides originating from cytoplasm to cytotoxic T cells.
associate with peptide in ER of secretory pathway.
bind CD8 receptors of cytotoxic T cells.
structure:
- consist of 1 alpha membrane spanning chain and 1 beta chain (beta micro-globin).
- alpha chain domains encoded on MHC on chromosome 6 (highly polymorphic), beta chain encoded on chromosome 15.
-invariant beta micro globin stabilises membrane spanning alpha chain domain.
-single alpha chain domain (alpha 3) spans membrane.
-2 polymorphic alpha chain domains (alpha 1 &2) contain peptide binding groove and are involved in peptide presentation.
alpha chains encoded by 3 genes - HLA-B, HLA-C and HLA-A.
peptide binding groove binds short peptides of 9-10 aa long.
present endogenous antigenic peptides originating from cytoplasm to cytotoxic T cells.
associate with peptide in ER of secretory pathway.
bind CD8 receptors of cytotoxic T cells.
10
New cards
MHCII
expressed on the surface of antigen presenting leukocytes (dendritic cells, B cells macrophages)
structure:
-consist of 2 membrane spanning alpha and beta domains.
- both encoded by MHC on chromosome 6. (highly polymorphic)
- membrane proximal domains Ig like
- membrane distal domains contain peptide binding groove and involved in peptide presentation.
alpha and beta chains encoded by HLA-D genes.
peptide binding groove binds longer proteins 13-18 aa long.
present proteins from exogenous antibodies originating extracellularly (taken up through phagocytosis) to present peptides to helper T cells.
associate with peptide in endocytic vesicle of secretory pathway.
bind CD4 receptors of helper T cells.
structure:
-consist of 2 membrane spanning alpha and beta domains.
- both encoded by MHC on chromosome 6. (highly polymorphic)
- membrane proximal domains Ig like
- membrane distal domains contain peptide binding groove and involved in peptide presentation.
alpha and beta chains encoded by HLA-D genes.
peptide binding groove binds longer proteins 13-18 aa long.
present proteins from exogenous antibodies originating extracellularly (taken up through phagocytosis) to present peptides to helper T cells.
associate with peptide in endocytic vesicle of secretory pathway.
bind CD4 receptors of helper T cells.
11
New cards
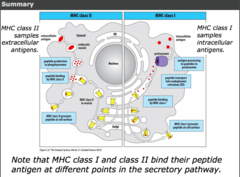
MHCI antigen presentation
immunoproteasome is induced by interferons and degrades misfolded proteins synthesised by intracellular pathogens (virus) in the cytoplasm. it processes antigen into peptides.
peptide is transported to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) from cytoplasm by TAP transporter
peptide binding to MHCI occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum.
MHCI with peptide attached to cell surface transported to cell surface of nucleated cells via Golgi body.
CD8 receptors of cytotoxic T cells recognise and bind peptides presented with MHCI at cell surface of nucleated cells.
MHCI requires peptide binding for cell surface expression.
peptide is transported to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) from cytoplasm by TAP transporter
peptide binding to MHCI occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum.
MHCI with peptide attached to cell surface transported to cell surface of nucleated cells via Golgi body.
CD8 receptors of cytotoxic T cells recognise and bind peptides presented with MHCI at cell surface of nucleated cells.
MHCI requires peptide binding for cell surface expression.
12
New cards
TAP transporter
transports peptides from cytosol into ER where peptide binds MHCI.
13
New cards
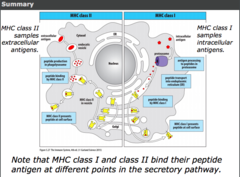
MHCII antigen presentation
extracellular antigen endocytosed/ phagocytosed by antigen presenting leukocytes.
protein degraded into peptides in endocytic vesicle or phagosome. it has correct conditions (acidic pH) to allow degradation of proteins.
peptide associated with MHCII in endocytic compartment.
MHCII with peptide attached transported to cell surface of antigen presenting leukocytes.
CD4 receptors of T-helper cells recognise and bind peptide presented with MHCII.
MHCI requires peptide binding for cell surface expression.
protein degraded into peptides in endocytic vesicle or phagosome. it has correct conditions (acidic pH) to allow degradation of proteins.
peptide associated with MHCII in endocytic compartment.
MHCII with peptide attached transported to cell surface of antigen presenting leukocytes.
CD4 receptors of T-helper cells recognise and bind peptide presented with MHCII.
MHCI requires peptide binding for cell surface expression.
14
New cards
Cross presentation
process occurring within professional antigen presenting dendritic cells whereby exogenous peptides are presented (from extracellular antigen) is presented by MHCI to naïve cytotoxic T cells.
activates naïve cytotoxic T cells even if antigen presenting cell isn't infected.
activates naïve cytotoxic T cells even if antigen presenting cell isn't infected.
15
New cards
Co-receptors (CD4 and CD8)
required by T cell receptor complex (TCR) for activation:
1. stabilise interaction between T-lymphocyte and antigen presenting cell.
2. facilitate signalling as they are associated with the tyrosine kinase LCK in the cytoplasmic region.
1. stabilise interaction between T-lymphocyte and antigen presenting cell.
2. facilitate signalling as they are associated with the tyrosine kinase LCK in the cytoplasmic region.
16
New cards
lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (LCK)
associated with co-receptors at the cytoplasmic region.
catalyses phosphorylation of ITAM motifs in CD3 regions of TCR upon co receptor binding to MHC protein ...
catalyses phosphorylation of ITAM motifs in CD3 regions of TCR upon co receptor binding to MHC protein ...
17
New cards
Thymic selection
process occurring in the thymus through which T cells mature.
involves both positive and negative thymic selection.
around 5% of thymocytes (immature T cells) that enter thymus survive thymic selection and migrate to lymphoid tissue.
autoimmune diseases arise when this process fails.
involves both positive and negative thymic selection.
around 5% of thymocytes (immature T cells) that enter thymus survive thymic selection and migrate to lymphoid tissue.
autoimmune diseases arise when this process fails.
18
New cards
Positive thymic selection
process of T cell development
occurs in thymus which enables maturation of thymocytes (immature T cell).
thymocytes with TCRs capable of recognising and binding MHCs are selected and
occurs in thymus which enables maturation of thymocytes (immature T cell).
thymocytes with TCRs capable of recognising and binding MHCs are selected and
19
New cards
negative thymic selection
process of T cell development
occurring in thymus which prevents formation of T-cells reactive to self proteins.
thymocytes with TCRs incapable of recognising and binding MHCs are rejected.
a negatively selected thymocyte undergoes apoptosis.
achieved by AIRE protein
occurring in thymus which prevents formation of T-cells reactive to self proteins.
thymocytes with TCRs incapable of recognising and binding MHCs are rejected.
a negatively selected thymocyte undergoes apoptosis.
achieved by AIRE protein
20
New cards
Autoimmune Regulator (AIRE)
transcription factor that transcribes tissue-specific genes om a subpopulation of epithelial cells in the thymus.
enables the developing T-cell population to become tolerant of antigens that normally occur only outside the thymus.
enables the developing T-cell population to become tolerant of antigens that normally occur only outside the thymus.
21
New cards
MHC genes
encoded by MHC on chromosome 6.
-extremely polymorphic.
-co-dominantly expressed.
-inherited in germline (limited diversity compared to T and B cell receptors) wide range of peptides recognised but not all peptides on all antigens.
- most variation of MHC proteins within peptide binding groove.
-extremely polymorphic.
-co-dominantly expressed.
-inherited in germline (limited diversity compared to T and B cell receptors) wide range of peptides recognised but not all peptides on all antigens.
- most variation of MHC proteins within peptide binding groove.
22
New cards
MHCI genes
HLA-A
HLA-B
HLA-C
encoded by MHC on chromosome 6.
each loci encodes alpha chain.
HLA-B
HLA-C
encoded by MHC on chromosome 6.
each loci encodes alpha chain.
23
New cards
MHCII genes
HLA-DR
HLA-DQ
HLA-DP
encoded by MHC on chromosome 6.
each loci codes an alpha and beta chain.
HLA-DQ
HLA-DP
encoded by MHC on chromosome 6.
each loci codes an alpha and beta chain.
24
New cards
Consequences of MHC polymorphism
-graft rejection
-MHC proteins are able to recognise and bind and binding to a wide range of foreign peptides as a result of been highly polymorphic and co-dominantly expressed ( but are inherited in germline- not as diverse as peptides recognised by TCRs and BCRs which undergo gene rearrangement during development.)
-MHC proteins are able to recognise and bind and binding to a wide range of foreign peptides as a result of been highly polymorphic and co-dominantly expressed ( but are inherited in germline- not as diverse as peptides recognised by TCRs and BCRs which undergo gene rearrangement during development.)