Physics Test: Electromagnetic Waves
4.9(13)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:33 PM on 11/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
Electromagnetic waves
a wave that is partly magnetic and partly electric
2
New cards
Radio
Largest electromagnetic waves (size of buildings-humans)
3
New cards
Microwave
Second largest electromagnetic waves (size of honey bee)
4
New cards
Infrared
Third largest electromagnetic wave (size of a pinpoint)
5
New cards
Visible light
Middle of the electromagnetic spectrum (roygbiv)
6
New cards
Ultraviolet
Third smallest electromagnetic wave (size of molecules)
7
New cards
X-ray
Second smallest electromagnetic wave (size of atoms)
8
New cards
Gamma ray
Smallest electromagnetic wave (size of atomic nuclei)
9
New cards
Radiation
emitting electromagnetic waves
10
New cards
low
Radio waves have high or low frequency?
11
New cards
high
Gamma ray waves have high or low frequency
12
New cards
3 x 10^8 m/s
What is the speed of light?
13
New cards
700 nm - 400 nm
Range of visible light? (nanometers)
14
New cards
white
our eyes interpretation of every color wave at once
15
New cards
black
no light waves, everything is absorbed
16
New cards
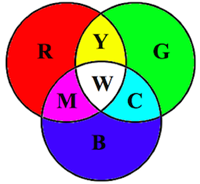
red, green, blue
three primary colors
17
New cards
yellow, cyan, magenta
three secondary colors
18
New cards
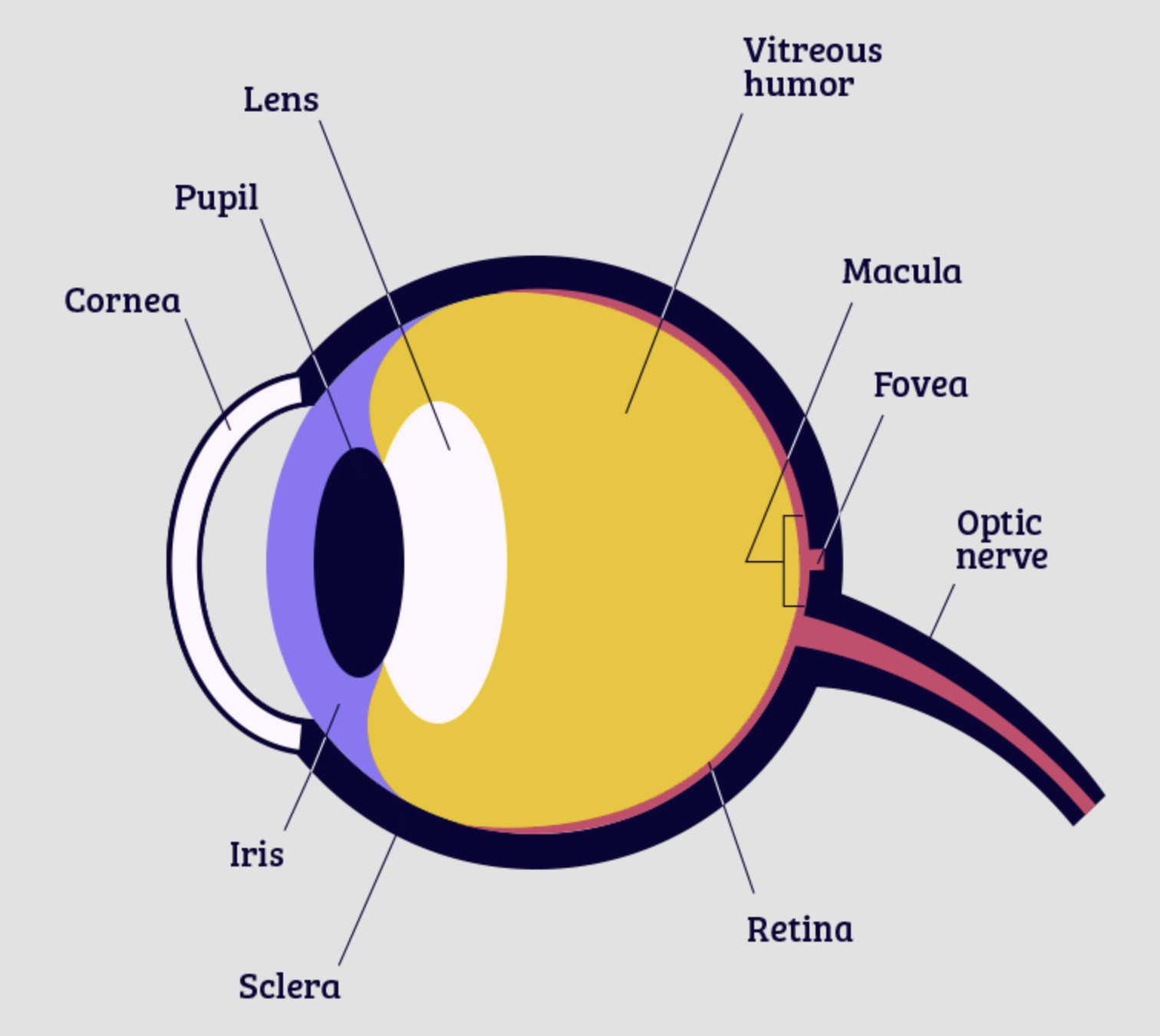
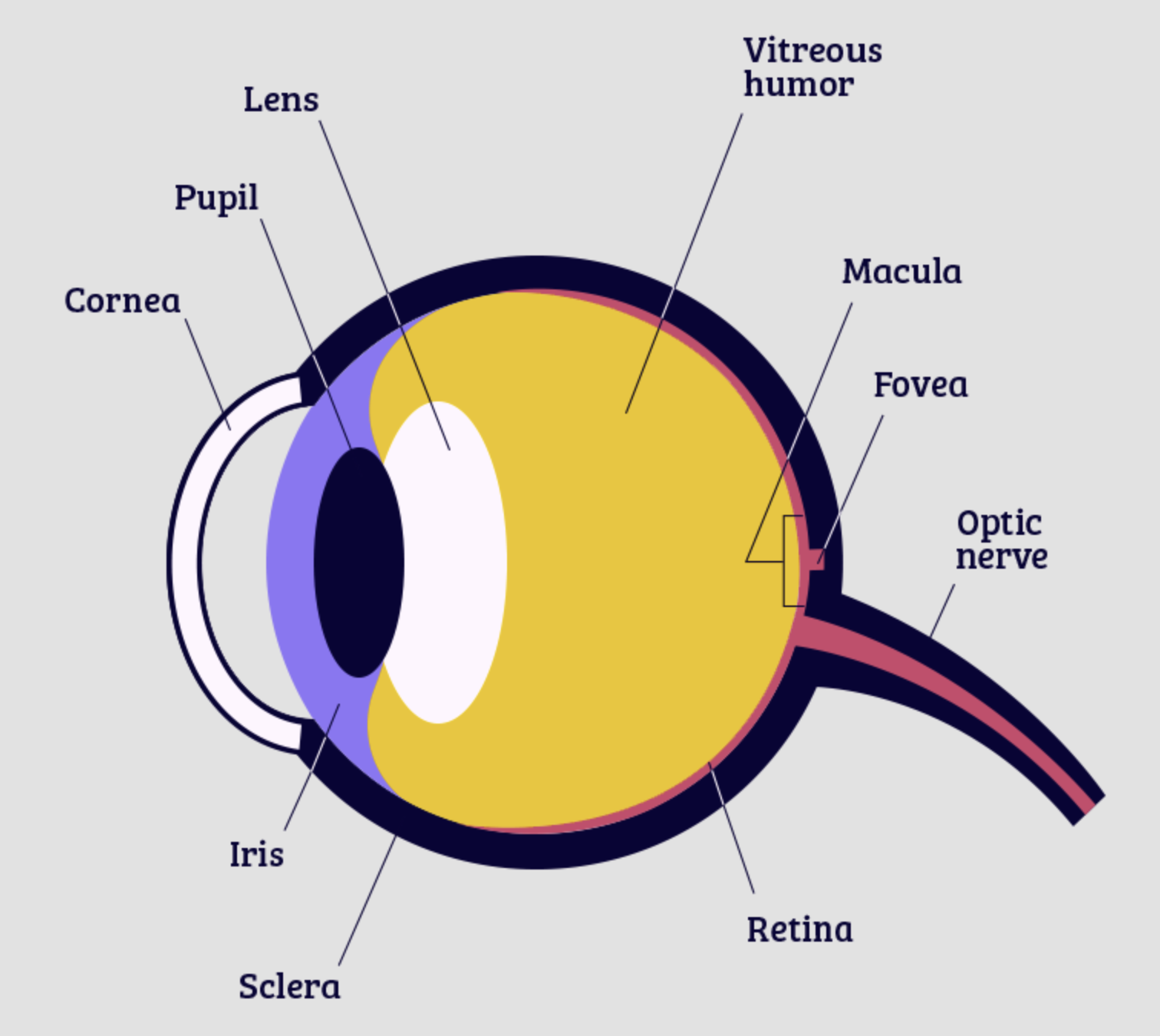
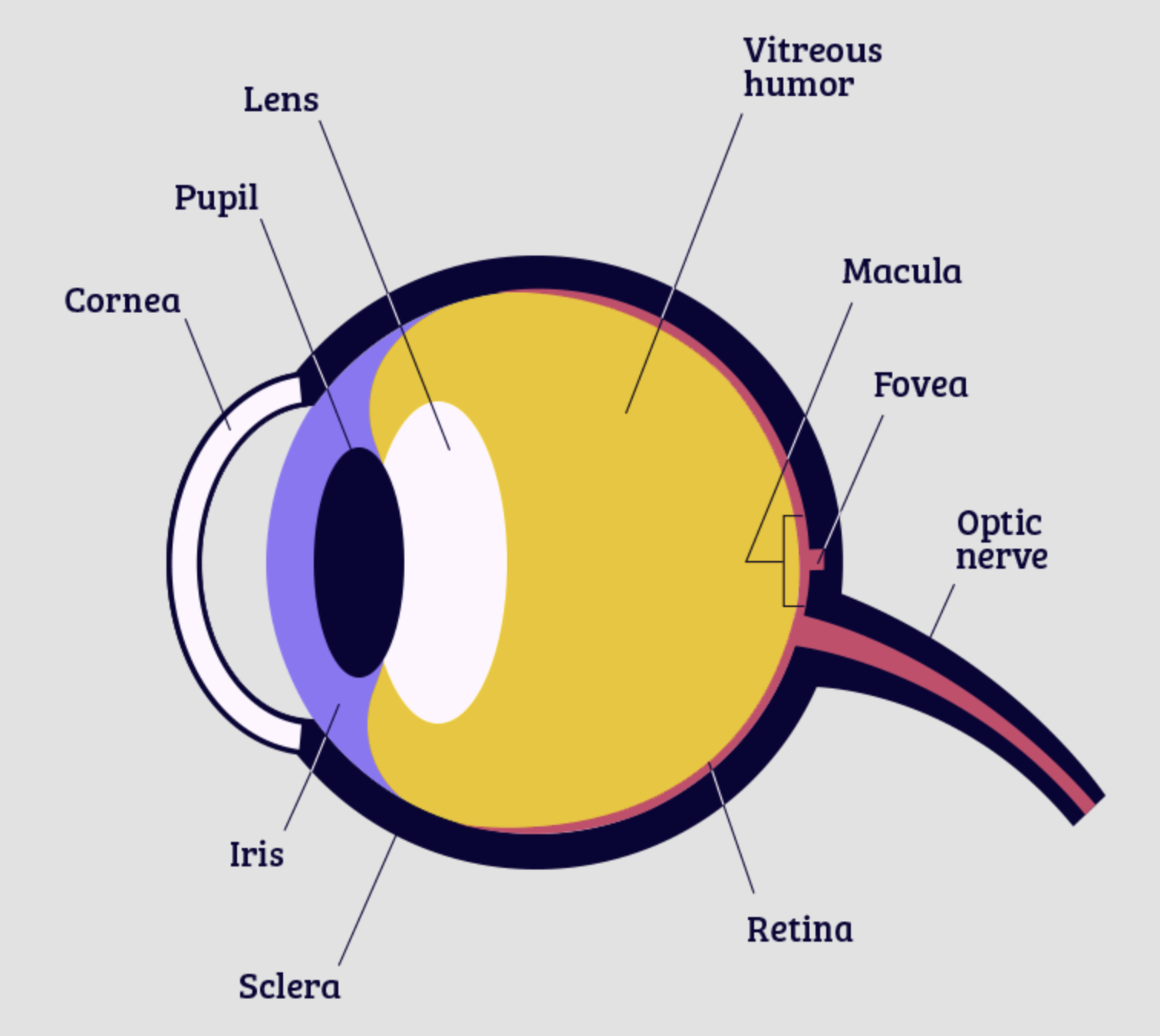
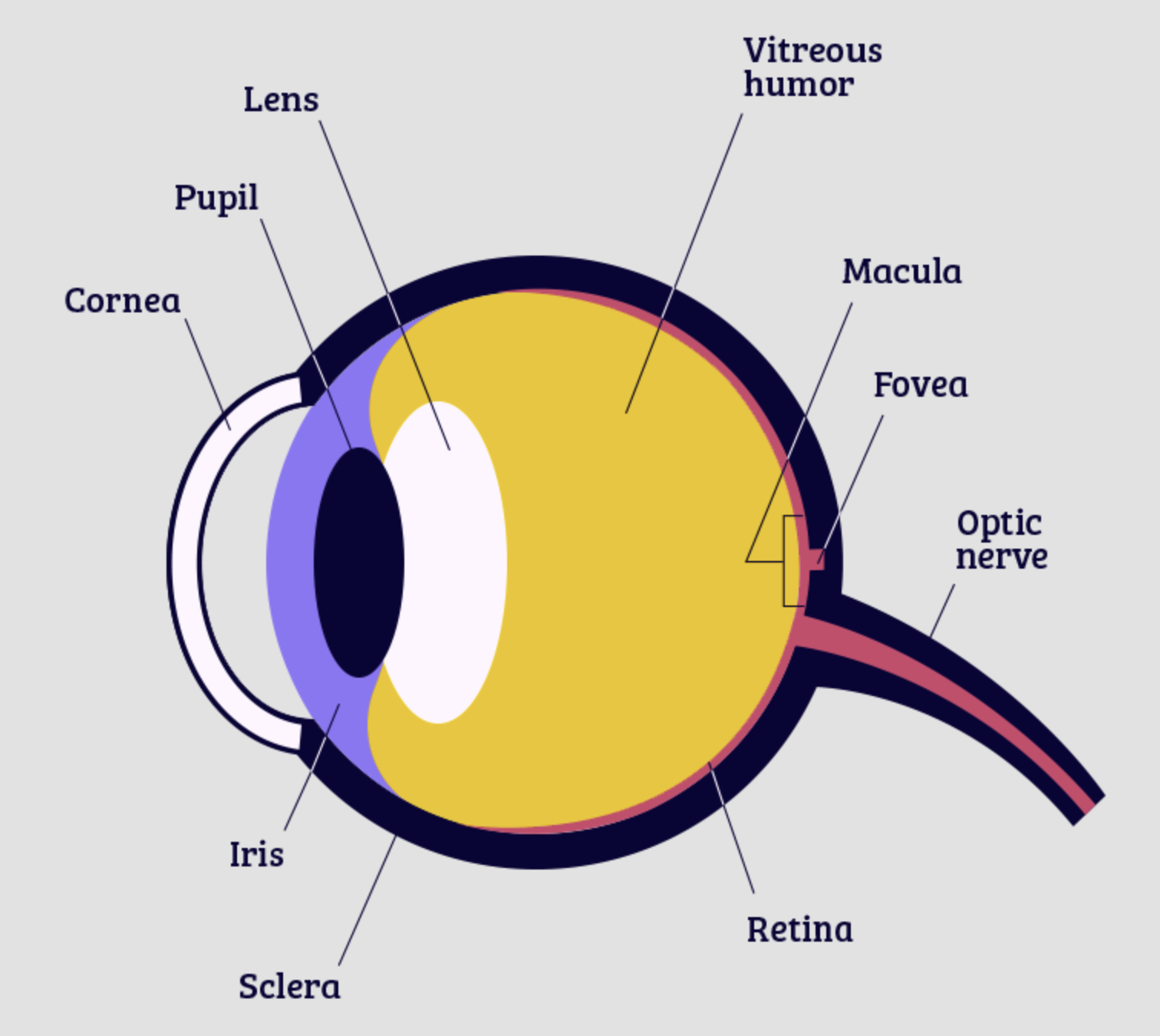
Cornea
part of eye that lets light through, protective layer
19
New cards
lens
part of eye that focuses the image
20
New cards
retina
part of the eye that the image is focused on, contains rods and cones
21
New cards
optic nerve
bundle of nerves that connects to the brain
22
New cards
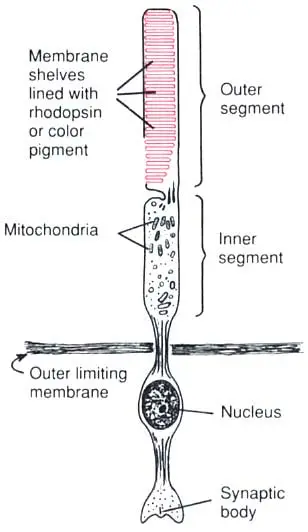
rods
cells on outside of retina that see bright and dark
23
New cards
cones
cells on the center of the retina that react to colors, three types (red green, blue)
24
New cards
color-blindness
missing or damaged cones leads to...
25
New cards
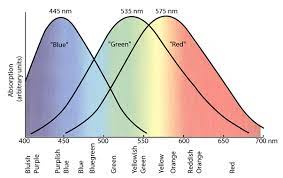
yellow
Red-high, Green-high, B- none
26
New cards
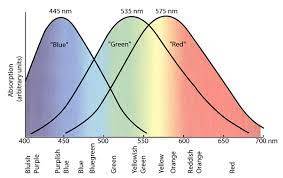
cyan
Red-low, Green-mid, Blue-mid
27
New cards
Reflection
light hits a surfaces and bounces off, the incident ray and second ray have the same angle
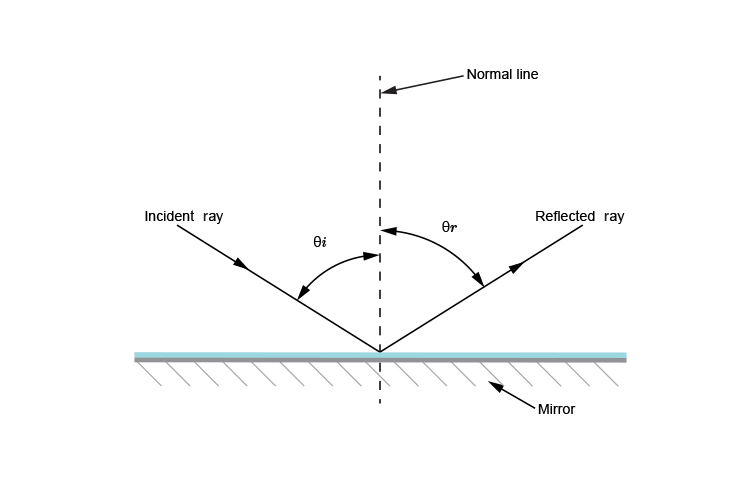
28
New cards
Refraction
the medium changes so the direction of the wave changes, light "curves"
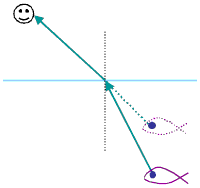
29
New cards
Diffraction
bending of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves past small openings

30
New cards
Polarization
reflection of light of non-metallic surfaces, results in removal of light waves that aren't a certain direction
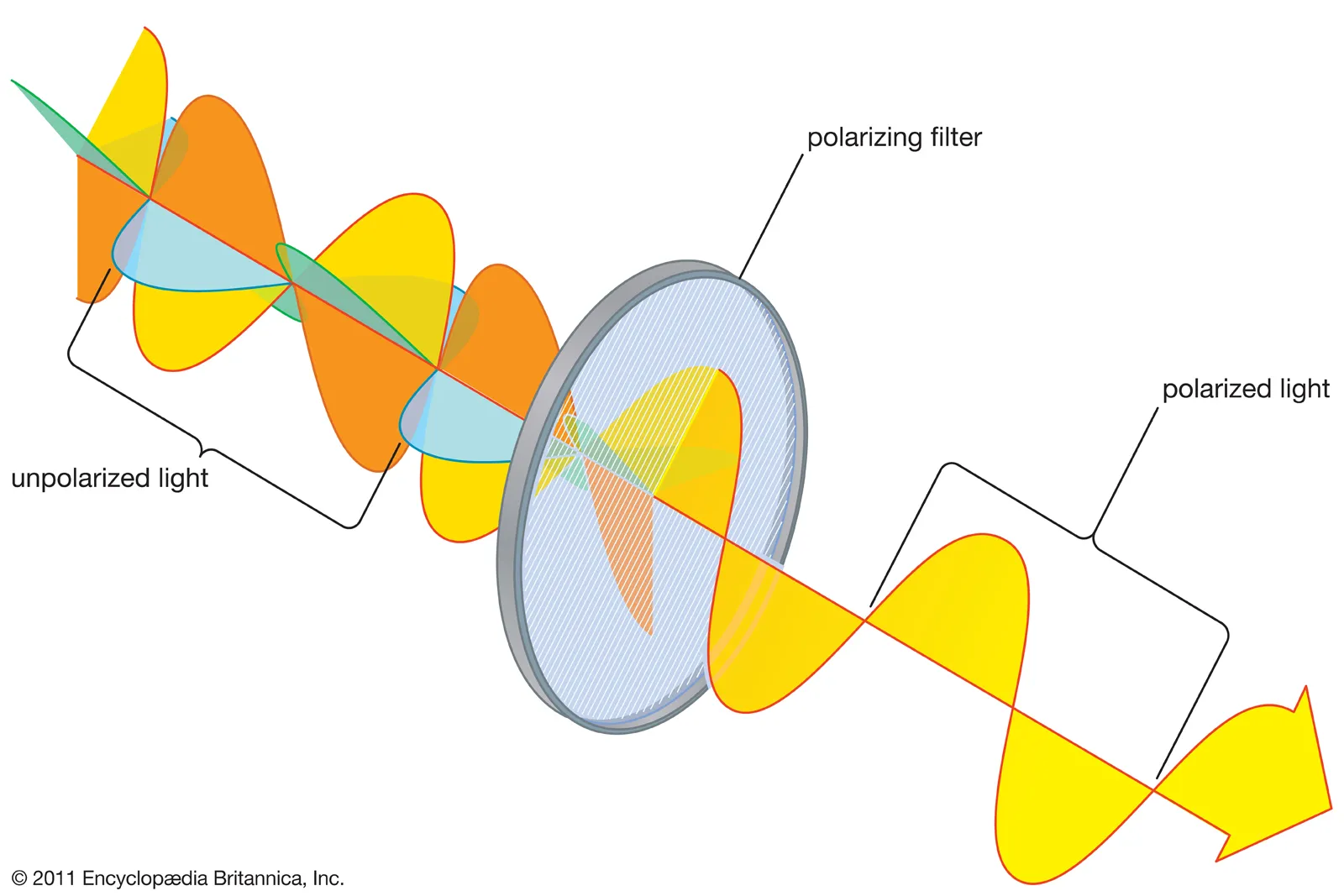
31
New cards
Blind spot
The optic nerve in your retina causes a...
32
New cards
medium
the substance waves are traveling through
33
New cards
Spectrum
range of things
34
New cards
Velocity = frequency x wavelength
Speed of a wave formula
35
New cards
because blue waves are small but our eye picks them up more than violet waves.
Why is sky blue and not violet?
36
New cards
color combinations