AS Physics Chapter 5
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Work Done
When a force moves the point at which it acts in the direction of the force [moves impact point, scalar]
Work Done formula
Work done = Force * Displacement in the direction of the force
Displacement
Distance moved in a particular direction [vector]
One joule of work done
When 1 Newton of force moves its point of application 1 metre in the direction of the force
Condition for an object that can do work
The object must have energy
Law of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted to one form or another
Efficiency
(Useful Energy / Total Energy) * 100
Energy
Ability to do work [scalar]
Power
Rate of energy conversion or usage, also known as the rate of work done
Watt
Unit of power and equivalent to working 1 joule per second
Deriving Equations Power
W = fx, divide both sides by time, Power = f * v
Potential Energy
Ability of an object to do work as a result of its position or shape
Gravitational potential energy
energy possessed by a mass as a result of its position in a gravitational field
Gravitational potential energy equation derivation
Work done = Fx = mg * h = mgh
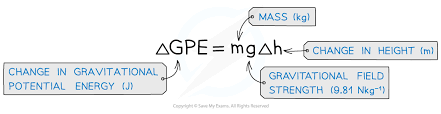
Change in gravitational potential energy
ΔE = mgΔh
[Translational] Kinetic Energy
E [k] = 1/2mv²