BM U4: Marketing
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Market growth
Refers to an increase in the size of a market, usually measured by the rise in total sales revenue of the market or industry.
Market leader
Refers to the business with the largest market share in a given industry.
Market orientation
This is an approach to marketing that focuses on meeting the specific demands (desires and needs) of customers and potential customers.
Market share
Refers to the sales revenue that an organization accounts for within a given market or industry. It is measured by expressing the firm’s sales revenue as a percentage of the whole industry’s sales revenue.

Market size
The total number of individual customers or the total value of sales revenue in a certain market.
Marketing
The management process of identifying, anticipating, and satisfying customer requirements in a profitable way. It is the art of determining the goods and services required to meet the needs and wants of customers in a sustainable way.
Needs
These are the things people need in order to survive, e.g., food, water, and shelter.
Product orientation
This is an approach to marketing that focuses on making products a business knows how to make well, rather than primarily concentrating on the needs and desires of potential customers.
Sales revenue
Refers to a firm's income from selling its goods and/or services, i.e., the value of its sales.
Sales volume
Refers to the volume (quantity) of sales of a particular business.
Wants
These are human desires, i.e., things that people would like to have, or have more of.
Market Growth
An increase in the size of a market, usually measured by the rise in total sales revenue of the market or industry.
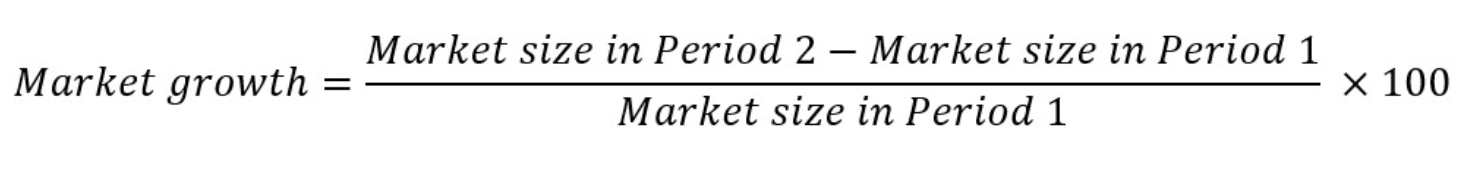
Consumer profiles
The demographic and psychographic characteristics of consumers in different market segments.
Demographic segmentation
The process of splitting consumers according to statistical characteristics of the population, such as age, gender, family size, religion, and ethnicity.
Differentiation
The process of distinguishing an organization’s products from those of other firms in the same industry.
Geographic segmentation
The marketing process that involves characterising consumers according to their different geographical locations.
Market
A market is the collective term for the buyers and sellers of a particular good or service.
Market segment
A distinct group of customers with similar characteristics, tastes, and preferences.
Market segmentation
The process of dividing a market for a product into smaller or distinct groups of customers in an effort to meet their specific desired needs and wants.
Marketing objectives
These are the goals or targets that help to give marketing teams (or marketing departments) a sense of purpose and direction.
Marketing plan
A document that shows the marketing objectives and marketing strategy of a particular business.
Marketing planning
The structured process of formulating marketing objectives and appropriate marketing strategies to achieve these goals.
Marketing strategies
The different long-term actions used by an organization to achieve its marketing goals.
Mass markets
A marketing approach that focuses on supplying to wide-ranging groups of customers in a market, without having split them into separate market segments, such as the markets for bottled water or breakfast cereal.
Niche markets
Marketing approach that focuses on supplying highly specialised products to cater for a small and select target market.
Product differentiation
Refers to the process by which firms attempt to make their goods and services different from those provided by other firms in the market in order to increase their own sales revenue.
Production position map
Also known as a perception map, this is a graphical illustration of customer perceptions of a business, its products, and/or brands in comparison to other firms in the industry.
Psychographic segmentation
Segmentation that involves characterising consumers according to people’s lifestyle choices and personal values.
Socio-economic segmentation
The process of splitting the market according to consumer or household income levels. This is often linked to their type of profession and/or their level of educational attainment.
Target market
The group of customers that an organization focuses on selling its products to.
Targeting
Targeting is the marketing practice of creating and using an appropriate marketing mix and marketing strategies to cater for different market segments.
Unique selling point
An exclusive feature or aspect of a business, its products or brands that makes it distinct from others in the same industry.
Focus groups
Forming small discussion groups to gain insight into the attitudes and behaviour of respondents. The group is typically made up of participants who share a similar customer profile.
Government publications
A type of secondary market research, referring to official documents and publications released by government entities and agencies.
Market analysis
a form of secondary market research that reveals the characteristics, trends, and outlook for a particular product or industry, such as market size, market share, and market growth rate.
Market research
Marketing activities designed to discover the opinions, beliefs, and preferences of potential and existing customers.
Media articles
a type of secondary market research referring to the documents (articles) in print or online media. They are written by skilled journalists and authors.
Observations
a method of primary research that involves watching how people behave or respond in different situations.
Population
all potential customers of a particular market.
Primary market research
gathering new data for a specific purpose, using methods such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observations.
Qualitative market research
getting non-numerical responses from research participants in order to understand their behaviour, attitudes, and opinions.
Quantitative market research
collecting and using factual and measurable information rather than people’s perceptions and opinions.
Quota sampling
using a certain number of people (known as the quota) from different market segments for primary market research purposes.
Random sampling
gives everyone in the population an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
Sample
a selected group or proportion of the population used for primary market research purposes.
Sampling
a primary research technique that selects a sample of the population from a particular market for research purposes.
Sampling errors
caused by mistakes made in the sample design, such as an unrepresentative sample being used or the sample size being too small.
Secondary market research
the collection of second-hand data and information that already exists, previously gathered by others, such as media articles and government publications.
Survey
a document that contains a series of questions used to collect data for a specific purpose. Surveys are the most common method of primary research.
Above the line promotion (ATL)
Form of promotion that refers to any form of paid-for promotional technique through independent consumer media.
Advertising
A form of visual and/or audio marketing communication used to inform and persuade people to buy a certain good or service.
After-sales care
These are value-added services offered to customers subsequent to the sale of a product, e.g., guarantees and warranties, maintenance services, and technical support.
Agents
Also known as brokers, these independent intermediaries help to sell a vendor’s products in return for commission, e.g., real estate agents.
Below the line promotion (BTL)
Form of promotion that refers to all forms of advertising or promotion that do not use external media agents.
Brand awareness
The degree of customer knowledge and recognition of a particular brand in order to gain more customers.
Brand development
Part of a firm’s marketing strategy in communicating the value of a brand and what the brand stands for.
Brand value
The expected earning potential of a brand, i.e., the likely future earning potential (value) of a particular brand.
Branding
This is the practice of using an exclusive name (brand), symbol, or design which identifies a specific product or business.
Competitive pricing
This pricing method involves a business setting the price of its products at the same or similar level charged by competitors in the market.
Consumer goods
These are products bought for personal consumption, rather than for business use, e.g., home appliances, furniture, food and drink, and house plants.
Contribution pricing
A pricing method that involves setting the price of a product at a level higher than the direct costs. Hence, the sale of each product earn the firm a positive contribution towards paying its indirect costs.
Cost-plus pricing
Adds a profit margin to the costs of production, thereby ensuring that each unit sold contributes towards the profits of the firm.
Customer care
Refers to the attentiveness and courtesy of employees towards meeting the needs of their customers in the delivery of a good or service.
Direct mail
The use of postal correspondence for promotional purposes.
Direct marketing
Refers to a business communicating information about its products straight to customers.
Distribution (place)
The marketing process of getting the right products to the right customers in the right place and at the right time, e.g., wholesalers, retailers, agents, e-commerce, and vending machines.
Distribution channel
Also known as a channel of distribution, this refers to the path taken for a product to get from the producer to the consumer.
Dynamic pricing
This refers to charging customers different prices based on changing demand at different times of the day, week, month, or year.
Extension strategies
Marketing approaches used to prolong or lengthen a product’s life cycle, e.g., price reductions or new promotional strategies.
Informative promotion
Describes one of the purposes of promotion in the marketing mix, which is used to notify or tell customers about a firm’s products.
Intermediary
A third-party person or business that offers distribution services as part of a channel of distribution, such as agents, wholesalers, and retailers.
Loss leader pricing
Pricing a product below its cost of production so as to attract customers to also buy other items (with a higher profit margin).
Mail order
A form of distribution channel that enables customers to receive their goods via postal services.
Mark-up (profit margin)
The difference between the price and the cost per unit.
Merchandise
Refers to a retailer’s range of goods that are available for sale, often used for promotional purposes, e.g., Disney toys sold at their theme parks.
Multi-channel distribution strategy
This refers to a firm’s use of a different distribution channels to get its products to customers.
Payment methods
As part of “process” in the marketing mix, this refers to the different methods that customer can pay for the purchase of goods and services, e.g., cashless payment options.
Penetration pricing
A pricing method that involves a firm setting low prices so as to gain entry in a new market. The firm will then raise the price once the product or brand has established itself in the industry.
Personal selling
The use of sales personnel to sell goods and services with customers on a face-to-face basis.
Persuasive promotion
Describes one of the purposes of promotion in the marketing mix, which is used to encourage or convince customers to make a purchase and to improve customer loyalty.
Point of sale (POS)
The promotion of products in retail outlets where customers can buy the goods.
Predatory pricing
A strategy that involves charging a low price, sometimes even below the cost, so as to damage the sales of rivals.
Premium pricing
A pricing method that involves a firm charging significantly higher prices than similar or competing products in the market. This is usually due to the prestige or quality associated with the product or brand.
Price
The value of a good or service that is paid by the customer.
Price elasticity of demand
PED measures the extent to which the demand for a good or service is responsive to changes in the price of that product.
Price leadership
A strategy of following the price set by the dominant firm in the industry (the firm with the largest market share).
Process
This refers to the ways in which a service is provided or delivered, such as various payment systems, queuing systems, after-sales care, and delivery service options.
Producer goods
These are products purchased by a business for its commercial use, rather than for private consumption, e.g., machinery, equipment, tools, fixtures and fittings, and office stationery.
Product
This refers to both physical (goods) and non-physical (services) items sold by a business or purchased by a customer.
Product life cycle (PLC)
Marketing theory showing the different stages that most products go through from their research and development (R&D) stage to their final removal from the market.
Product portfolio
The range and mix of products sold by a business, including the various brands of all the products it owns.
Promotion
The various marketing processes used to inform customers about a product and persuading them to purchase the product.
Promotional mix
The range of above and below the line methods used to promote a product as part of a larger marketing mix.
Public relations
The management function overseeing public attitudes and opinions of an organization to gain public understanding and support.
Retailers
These are commercial businesses that sell a manufacturer’s products directly to consumers.
Sales promotion
A short-term promotional tactic used to entice customers to buy a certain product.
Social media marketing (SMM)
The use of online content that users can upload and share to a website using a suitable medium platform, e.g., Facebook, Google. Instagram, Twitter, and YouTube.
Sponsorship
A promotional strategy that involves a business providing financial support to another organization or event in return for marketing exposure.
Telemarketing
A direct promotional marketing strategy that involves salespeople using the telephone to call existing and potential customers about a firm’s latest product offerings.
Test marketing
This is part of the pre-launch stage in a product’s life cycle, when a business trials a new product with a small number of customers, usually in a specific geographical location prior to the official launch.