Lec 28 - hypertension treatments
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
factors of physiological control of BP
cardiac output
baroreceptor
blood volume
vascular tone
phases of hypertension
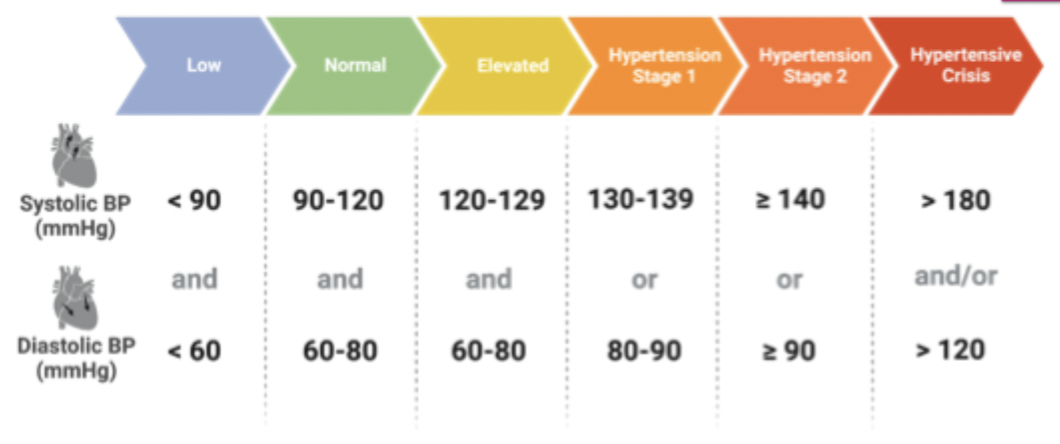
diagnosis is based on consistent elevated BO measurements over time or by 24 hour BP monitoring
primary or essential hypertension
developed over time
family history, obesity, salt intake, age, etc
secondary hypertension
occurs quickly and more severely
cause can be identified
majority of renal origin
may be possible to correct the underlying abnormality
drugs that can increase BP
NSAIDS
combined oral contraceptives
sympathomimetic agents
stimulants
why os treating hypertension important
most chronic cardiovascular condition in NZ and most people dont know thye have it - usually symptom free
silent killer - undiognosed can shorten lifespan by 10-20 years
consequences of high BP
CVD
neurological diseases
renal diseases
types of drug classes to treat hypertension
reduce blood volume - diuretics
produce vasodilation - calcium channel blockers, alpha blockers
mixed effects (RAAS modulators) - vasodilation and decreased blood volume, ACE inhibitors, ARBs
reduce HR and CO - beta blockers, calcium channel blockers
green script
lifestyle changes first
reduce weight, regular daily exercise
salt restriction
quit smoking
reduce alcohol intake
control diabetes, reduce stress, increase sleep
RAAS system
works synergistically with SNS - beta receptors stimulate renin release
renin is released and converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I which is then converted to angiotensin II by ACE
angiotensin II cauases vasoconstriction by acting directly on blood vessels, increases blood volume by acting on the kidney, causes aldosterone to be released from adrenal glands
renin
proteolytic enzyme
released from juxtaglomerular cells in response to low blood pressure, low renal blood flow, sodium in distal tubule, increased sympathetic stimulation (B1-R)
angiotensinogen
plasma protein produced in the liver
angiotensin I
inactive
gets converted to the active form angiotensin II via angiotensin converting enzyme
angiotensin converting enzyme
peptidase (removes a dipeptide)
found primarily in the lungs but also in endothelial cells throughout the body
angiotensin II
powerful vasoconstrictor
promotes Na+ ad fluid retention by nephron
stimulates release of aldosterine from adrenal cortex - plays a role in blood pressure regulation and Na+ plasma levels
enhances sympathetic activities
RAAS modulators
RAAS regulates blood pressure and fluid balance in the body - the system is crucial in responsing to low blood pressure and dehydration, when activated it causes vasoconstriction and sodium retention
renin inhibitors not approved in NZ
ACE inhibitors
Angiotensin receptor blockers
ACE inhibitors
enalapril
compete with angiotensin I for the catalytic binding site on ACE
prevents ACE from converting antiotensin I to II
downregulates angiotensin II provoked sympathetic activity = decreased angiotensin II mediated adrenaline release
reduced aldosterone release - decrease in sodium retention, decreased blood volume → blood pressure
mostly prodrugs - monitor in patients with impaired liver function
6 available in NZ
cant be used during pregnancy
bradykinin
ACE is also responsible for breaking down bradykinin so decreased ACE = increased bradykinin
causes vasodilation - acts through NO pathway
increased vascular permeability - contributes to inflammation and swelling
pain sensitisation - stimulates nociceoptors, pro-inflammatory
smooth muscle contraction - bronchoconstricition
bradykinin and B2 receptors
Gq receptors located on vascular endothelial cells
IP3 and PKC increase calcium via VGCCs and IP3 receptors
elevated Ca2+ activates eNOS - converts L-arginine to NO
NO activated guanylate cyclase - increased cGMP, increased PKG activity, vasodilation
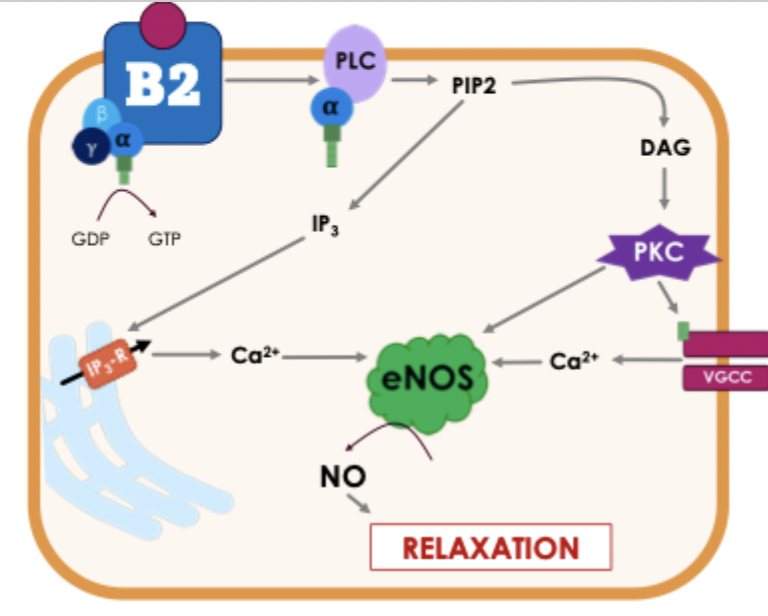
side effects of ACE inhibitors
hypotension - particularly at start
rash
cough - caused by bradykinin accumulation - airway becomes hyperresponsive, increased inflammation
angioedema - can occur after years, defective degradation of bradykinin
where are angiotensin II receptors found
many tissues including heart, brain, kidneys, blood vessels, lungs and adrenal cortex
AT1 receptors
primarily responsible blood pressure modulation effects
vasoconstriction, sodium retention, sympathetic activation, proliferation and hypertrophy, fibrosis, apoptosis, inflammation
AT2 receptors
though to have more complex functions related to cell growth and differentiation
often acting in opposition to AT1 receptors
vasodilation, natriuresis (sodium excretion)
inhibition of cell growth
anti-fibrotic
anti-inflammatory
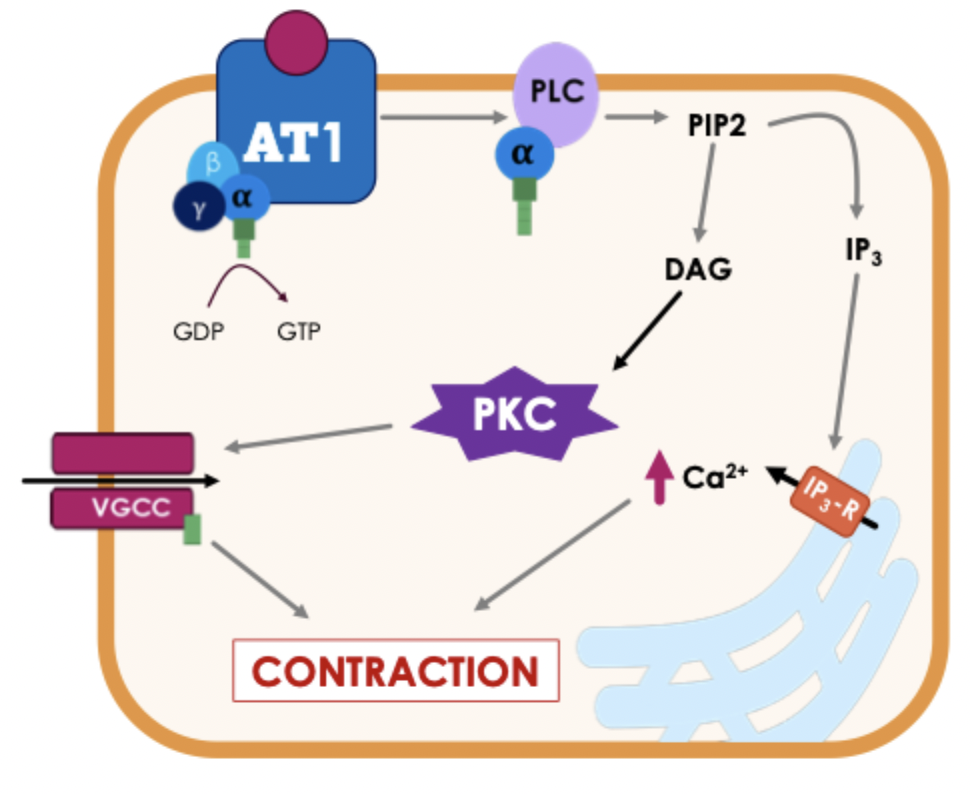
AT1 receptors - method of action in smooth muscle
Gq receptors located on vascular smooth muscle - causes vasoconstriction
phosphorylation of VGCCs
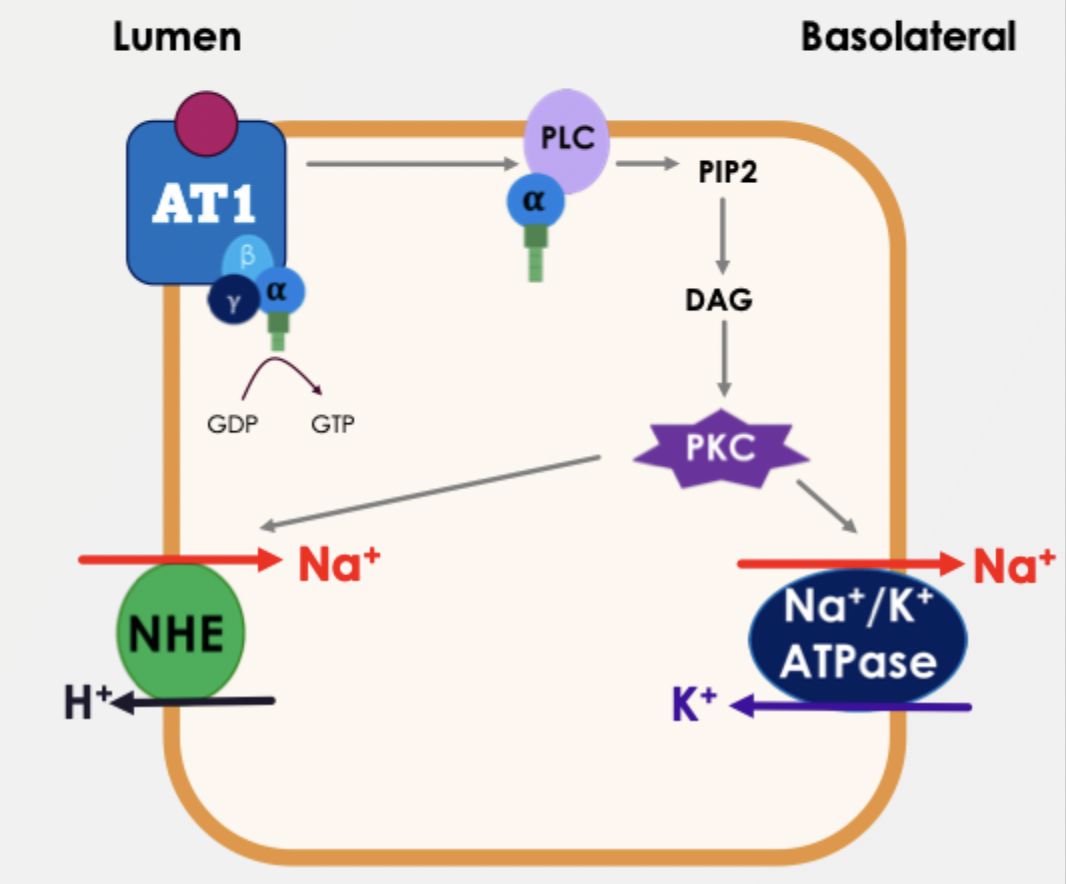
AT1 receptors - method of action in renal tubule cells
Gq receptors in distal and proximal tubules
PKC phosphorylates Na+/H+ exchanger (NH3) - increases sodium reabsorption from the tubular lumen
Na+/K+ATPase on the basolateral membrane - pumps Na+ into the bloodstream, maintaining a gradient
angiotensin receptor blockers overvoew
selective competitive antagonists for AT1 receptors
candesartan
generally well tolerated - side effects are related to hypotension
tight receptor binding and sow dissociation - long lasting RAAS suppression and bettwe 24 hour BP control
ARB vs ACE
both pretty similar - mostly up to prescriber
ARBs similar but generally better tolerated
dont have additional vasodilation effects of bradykinin but also have low risk of cough and no angioedema
ACE inhibitors also inhibit the beneficial effects of the AT2 receptors
calcium channel blockers overview
block L-type voltage gated calcium channels
vessel selective - bind to the extracellular domain outside the channel - stabilise in inactive state and more of these in the vasculature so selective against the heart
potent vasodilator, reduced BP, minimal effect on HR or contraction
what drug calcium channel blockers
amlodipine
calcium channel blockers in older patients
particularly effective
the main case of hypotension in elderly is large vessel stiffness
doesnt significantly suppress cardiac output or conduction - safer in conduction abnormalities
generally well tolerated - minimal impact on cognitive function, lipids, or electrilytes
side effects of calcium channel blockers
most are dose dependant
hypotension, facial flushing, dizziness and headache
reduced by slow release capsules
cannot be used in angina as drop in pressure causes angina symptoms
additional treatments of hypertension
alpha-1 blockers to cause vasodilation
alpha-2 agonists to decrease sympathetic outflow from the brian
beta blockers to decrease heart rate and constractility
diuretics to decrease blood volume
all decrease blood pressure