Combustion of alkanes
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Types of combustion - Pollutants - Flue gas desulfurisation - Catalytic converters - Global warming and the greenhouse effect
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Why are alkanes considered as quite unreactive?
Due to the strong C—C and C—H bonds they do not react with acids, bases, oxidising agents or reducing agents
How do alkanes react (2 ways)?
They burn and they react with halogens under suitable conditions
What chain alkanes combust completely when there is an abundance of oxygen?
Shorter chain alkanes
What are the products of the complete combustion of alkanes?
Carbon dioxide and water
Complete combustion of methane CH₄
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
Complete combustion of ethane
C2H6 (g) + 3/2 O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l)
Why do combustion reactions have large negative enthalpies?
Enthalpy change = energy absorbed - energy released and the energy released for combustion reactions is larger than the energy absorbed. This means combustion has an overall negative enthalpy
What is a fuel?
A substance that releases heat energy when combusted
What are three examples of alkane fuels?
Petrol, propane or paraffin
What happens when an alkane burns with a limited supply of oxygen?
Carbon monoxide, CO is formed
What is produced when an alkane burns with even less oxygen?
Carbon, C - soot
Incomplete combustion of propane, C3H8 (two equations)
C3H8 (g) + 7/2 O2 (g) → 3CO (g) + 4H2O (l)
C3H8 (g) + 2O2 (g) → 3C (s) + 4H2O (l)
What happens when a Bunsern burner is used with a closed air hole?
There is a yellow flame and a black sooty deposit appears on the apparatus
Incomplete combustion occurs with what type of hydrocarbons and why?
Long chain hydrocarbons because they need more oxygen to burn compared to short chain hydrocarbons
Where do all hydrocarbon-based fuels derive from?
Crude oil
What causes hydrocarbon-based fuels to pollute the atmosphere when they burn?
The polluting products they may produce
What are the 7 possible pollutants from burning alkanes?
Carbon monoxide
Carbon particles (soot)
Carbon dioxide
Water vapour
Sulfur dioxide
Nitrogen oxides
Unburnt hydrocarbons
How is carbon monoxide, CO, produced and what is its risk?
Incomplete combustion of alkanes - it is a poisonous gas
What are carbon particles also called and what are their hazards (2)?
Particulates - they exacerbrate athsma and cause cancer
How is carbon dioxide produced and what is the problem?
Complete combustion of alkanes - it is a greenhouse gas
What pollutant is also a greenhouse gas besides carbon dioxide?
Water vapour
What is sulfur dioxide a contributor to?
Acid rain
How is acid rain produced?
When sulfur dioxide combines with water vapour and oxygen in the air to form sulfuric acid
How is sulfur dioxide produced?
From sulfur-containing impurities present in crude oil
How are nitrogen oxides produced?
When there is enough energy for nitrogen and oxygen in the air to combine
What is the abbreviation for nitrogen oxides and why?
NOx because they come in various proportions - NO, NO2 and N2O4
Where are nitrogen oxides commonly produced?
In petrol engines due to the high temperatures present
N2 + O2 → 2NO
Condition: high temperature
What happens when nitrogen oxides react with water?
Forms nitric acid - contributor to acid rain
How are unburnt hydrocarbons commonly ejected into the atmosphere?
Car exhausts
What happens when unburnt hydrocarbons rise up to the atmosphere?
They react with nitrogen oxides to produce photochemical smog
What is photochemical smog?
Photochemical smog is a type of air pollution that forms when sunlight reacts with pollutants like nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere.

What is the greatest contributor of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere?
Power stations
How are power stations the greatest contributor of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere?
They generate electricity by burning fuels such as coal or natural gas - coal in particular contains a large amount of sulfur, so burning it releases sulfur dioxide
Equation for when sulfur dioxide reacts in the air
Sulfur dioxide reacts with the oxgyen and water in the air to make sulfuric acid:
SO2 + ½ O2 + H2O → H2SO4
What are the gases given out by power stations called?
Flue gases
What is the process of removing sulfur dioxide from the flue gases called?
Flue gas desulfurisation
Describe the method of using a slurry of calcium oxide and water to remove the sulfur dioxide.
The slurry is sprayed into the flue gas, where they react with the calcium oxide and water to form calcium sulfite.
The calcium sulfite can be further oxidised to calcium sulfate, CaSO4∙2H2O
What is calcium sulfate, CaSO4∙2H2O, also called?
Gypsum
Overall reaction for the desulfurisation of flue gases with calcium oxide and water
CaO (s) + 2H2O (l) + SO2 (g) + ½ O2 → CaSO4∙2H2O
What is an alternative method of desulfuising flue gases?
Using calcium carbonate (limestone) instead of calcium oxide
Equation for the desulfurisation of flue gases with calcium carbonate
CaCO3 (s) + ½ O2 (g) + SO2 (g) → CaSO4 (s) + CO2 (g)
What is the problem with desulfurising flue gases with calcium carbonate?
One of the products is CO2, which is a greenhouse gas
Which method is favourable and why?
The desulfurisation of flue gases with calcium oxide and water as gypsum is very useful and can be sold so the reaction is profitable.
It also does not produce carbon dioxide in its reaction, as the desulfurisation of flue gases with calcium carbonate does.
What is gypsium used to make?
Builders’ plaster and plaster board
What are all new cars with petrol engines equipped with by law?
Catalytic converters in their exhaust systems
What does a catalytic converter do?
Reduces the output of carbon monoxide CO, nitrogen oxides NOx and any unburnt hydrocarbons in the exhaust gas mixture
What is the shape of a catalytic converter and how is this beneficial?
Honeycomb which gives a very large surface area. This maximises the opportunity for collisions between the exhaust gases and the catalyst.
What are the catalysts in the catalytic converter?
Platinum and rhodium - expensive and rare metals
What happens as the polluting gases pass over the catalyst?
They react with each other to form less harmful products
What are the two reactions that take place in a catalytic converter?
2CO (g) + 2NO (g) → N2 (g) + 2CO2
Carbon monoxide + nitrogen oxide → nitrogen + carbon dioxide
Hydrocarbons + nitrogen oxide → nitrogen + carbon dioxide + water
How does the visible radiation from the sun interact with the gases in the atmosphere?
The visible radiation penetrates the gases in the atmosphere. After infrared radiation is emmited by the earth as it cools down; some infrared radiation passes out into space but a portion is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
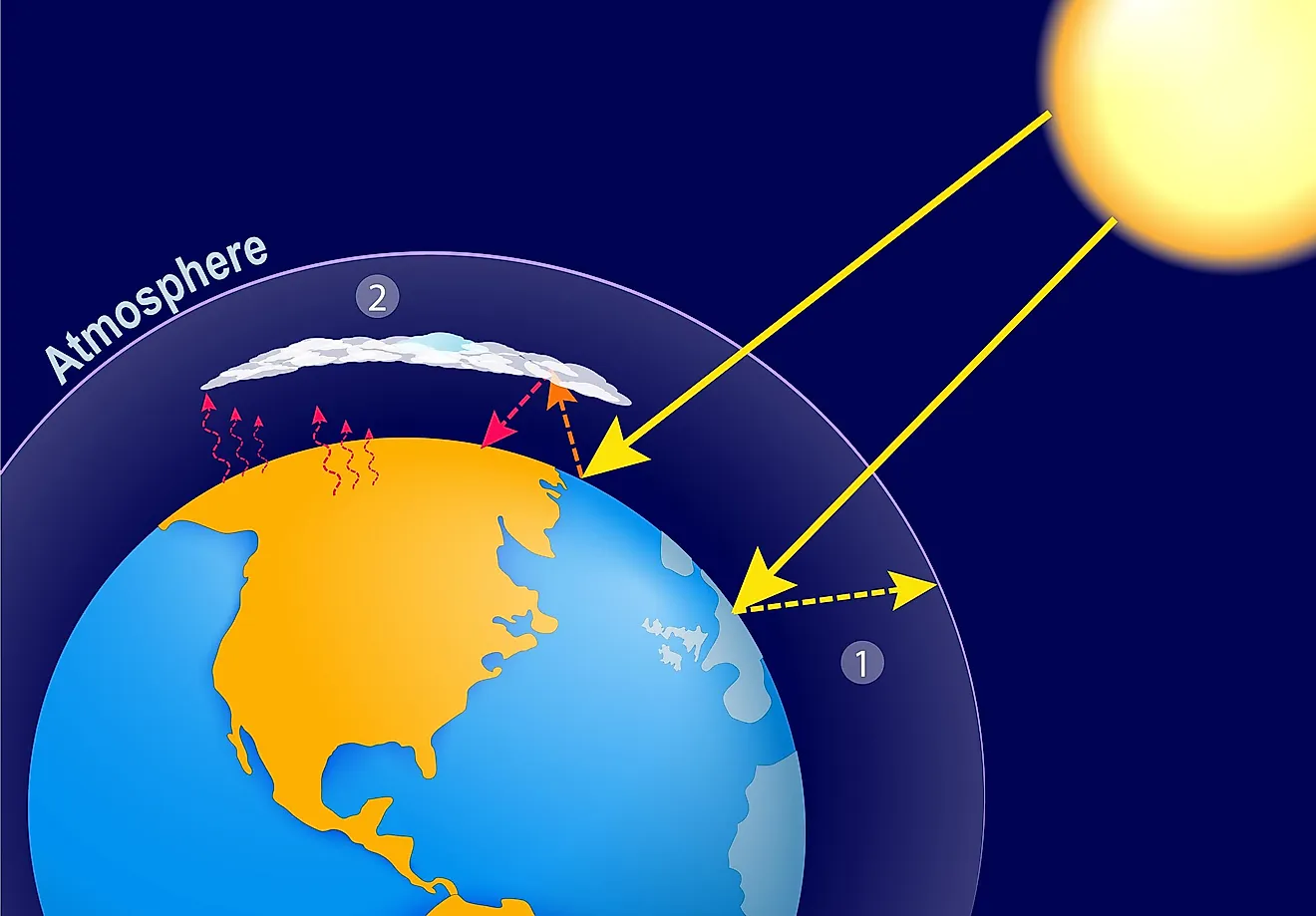
How is the Earth warmed up and why is it important?
By the greenhouse gases trapping some infrared radiation within the atmosphere. This is important so that the Earth is habitable enough to sustain life
What are the three greenhouse gases?
Carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapour (H2O) and methane (CH4)
Which two greenhouse gases are more effective in trapping infrared radiation than the other gas?
Water vapour and methane is more effective than carbon dioxide
Why then is carbon dioxide considered to be the greatest problem?
Levels of methane and water vapour in the atmosphere have not changed in the recent years. However since the Industrial Revolution, more fossil fuels have been burnt to fuel industrial plants and so the level of carbon dioxide has risen drastically.
As the Earth’s temperature gradually rises (global warming), what do the majority of scientists believe is the cause?
Increasing level of carbon dioxde is the cause for global warming
What will happen to the amount of water vapour in the air if the temperature of the Earth rises?
More water vapour in the air - therefore more global warming
What is a carbon footprint?
The total amount of greenhouse gases produced directly and indirectly by human activities, usually expressed in equivalent tons of carbon dioxide (CO2).
What are carbon neutral activities?
Activities that have no carbon dioxide emissions overall - eg. photosynthesis