Social Influence (complete)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
* identification
* internalisation
* superficial and temporary
* to fit in or avoid disapproval
* public behaviour changes
* sometimes remains the same privately
* public and private beliefs change
* remains when not around the group
what are the main theorists that investigated conformity?
asch 1951
zimbardo 1971 (conformity to social roles)
what was the procedure of asch’s investigation into conformity?
123 male students in a ‘visual perception task’
in lab setting = groups of 7
asked to judge the length of the lines - answer easy and obvious
all but one were confederates that gave the wrong answer
real ppt seated 2nd to last
majority can influence a minority even is answer is obvious
what are 5 evaluations of Asch’s study?
strengths
lab - high control → can control where ppt was sat and people in the room meaning you can establish cause and effect, validity
weaknesses
1951 so lack temporal validity - findings influences by post-war social attitudes when people conformed and worked together. findings may not be as relevant in society today (can’t generalise)
lacks ecological validity - artificial and not representative of day to day, hard to generalise results
biased example - all ppts male so lacks population validity
contradictory evidence - perrin and spencer demonstrate the effects of individual differences meaning generalisation may be limited
what were the alternative explanations for asch’s conformity
perrin and spencer 1981 - replicated study with maths, chem and engineering students and found much lower conformity rate
engineering student more confident in their opinion and answer
individual differences affect the conformity rates for certain tasks
What three variables did Asch investigate affecting conformity?
unanimity
task difficulty
group size
How did Asch investigate effects of unanimity in his experiment?
agreement by all people involved
levels increase when majority are unanimous and vise versa
‘rebel’ condition = having one confederate give the correct answer
found conformity rates dropped to 5.5%
How did Asch investigate effect of group size in his experiment?
conformity rates increase with the group size up to a point
manipulated this by having a different number of confederates
1 confederate = 3%, 2 = 13%, 3 = 32%
From there on additional confederates made little difference
How did Asch investigate the effects of task difficulty in his experiment?
rates increase when task is more difficult (link to ISI as an ambiguous situation)
manipulated this my making comparison lines more similar in length
conformity rates increased
What are the two explanations for conformity?
normative social influence (NSI)
informational social influence (ISI)
what is normative social influence?
when people conform to be part of the majority and not stand out
based on the desire to be liked
follow ‘norms’ and fit in with others
people want approval and acceptance from others to avoid rejection
often results in compliance
what is informational social influence?
occurs when people conform as they don’t know how to behave and use the majority to decide
based on desire to be right
people want to feel like ideas and beliefs are correct and believe others know more than them - need for certainty particularly in ambiguous situations
results in genuine long lasting change in beliefs or opinions - internalisation
what is the difference between ISI and NSI
ISI = desire to be right
NSI = desire to be liked
What are three strengths of the explanations for conformity (NSI and ISI)?
research evidence from Asch’s study = conformity rates increased when majority were unanimous explained by NSI = they felt self-conscious giving the right answer. task difficulty also increased conformity explained by ISI - ambiguous situation so people looked to others for guidance.
Lucas et al (2006) asked people to give answers to maths problems (hard or difficult) where people could see previous answers. found ppts conformed more on the harder questions
practical applications = can account for behaviour in the real world eg ISI = in ambiguous situations.
What are the weaknesses of the explanations for conformity?
explanations overlap and work together = sometimes we use NSI and ISI, me may look to others for info and don’t want to be different - makes distinguishing between explanations difficult
contradictory evidence = research shows NSI doesn’t affect everyone in the same way, some people are more concerned with being liked and underlies the reason for conformity more than in others
what are social roles?
the ‘parts’ people play as part of a social group that have expectations of what is appropriate behaviour - learnt by observation of others
each situation has its own social norms
become like internal mental scripts
conformity to social roles therefor involves identification
Who investigated explanations for obedience?
stanley milgram 1963
What is obedience?
taking direct orders from someone with perceived authority
what was the procedure for Milgram’s obedience experiment?
sample obtained with public announcement (‘we will pay you $4, persons needed for a study of memory’) - volunteer sampling
’teacher’ was told to shock the ‘student’ every time got an answer to a question wrong increasing voltage each time
‘experimenter’ would tell ‘teacher’ they must continue and that they (the experimenter) would be responsible for the consequences.
What were the results of Milgram’s experiment on obedience?
thought that 1% would deliver the lethal shock
2/3 ended up delivering it (65% obedience rates)
people will rather obey authority over their morals
what are the social psychological explanations for obedience?
legitimacy of authority
agentic state
What is legitimacy of authority (with reference to milgram’s study)?
there are people in certain positions of authority in society like the police
this authority is legitimate as agreed in society to help it function smoothly
we learn acceptance of authority from parents, teachers etc
in milgram’s experiment experimenter was considered legitimate as they worked at the university/controlled experiment
what is agentic state?
in an autonomic state behave voluntarily and are aware of our actions (feel responsible)
in an agentic state (opposite to autonomic) =
act on behalf of an authority figure
don’t feel responsible for our actions
don’t act according to our conscience and feel authority figure is responsible
deindividuated = loose sense of individuality
may experience high anxiety (moral strain) but feel powerless to disobey
Name a strength of the social psychological explanations for obedience…
research support →
blass and smitt (2001). showed a film of milgram’s study asking who was responsible for the person’s harm. students blame the experimenter.
also indicated responsibility was due to legitimate authority as experimenter was top if the hierarchy.
Name a weakness of the social psychological variables for obedience…
limited explanation
agentic shift doesn’t explain all findings eg. doesn’t explain why some didn’t obey
means cannot account for all cases of obedience
What is minority influence?
a person or small group influences the beliefs and behaviors of other people.
usually brings about social change rather than majority influence which remains the status quo.
what are characteristics of successful minority groups?
consistency
flexibility
commitment
What is consistency as a characteristic of minority groups?
minorities must be clear certain and stable to draw attention to their view
everyone is saying the same thing
should not deviate from their view
view must remain for a long time
Who provided research evidence for consistency in minority groups?
Moscovici et al (1969) demonstrated importance of consistency
What was moscovici’s procedure in his study on minority influence?
32 groups of 6, 4 real ppt, 2 confederate (minority). shown 36 slides that were shades of blue and asked to state the colour of the slide.
there were 3 conditions →
consistent = confederates stated all slides green
inconsistent = confederates stated 24/36 slides green
control = only participants
What were the findings of moscovici’s experiment into consistency in minority influence?
consistency increases rate of agreement
condition 1 = 8.42%
condition 2 = 1.25%
condition 3 = 0.25%
What is flexibility as a characteristic of minority groups?
minorities must not rigidly repeat the same argument
must listen to counter-arguments and be prepared to adjust viewpoint/compromise
strike a balance between consistency and flexibility
What is commitment as a characteristic of minority groups?
minorities are more likely to be influential if they are seen to have made sacrifices for their benefits and not out of self interest
place themselves at some risk or inconvenience
usually begins with a successful minority and eventually view is accepted as the majority
eg. Rosa parks, suffragettes
what is the role of minority influence on social change?
C,C+F are more likely to be successful in creating social change
snowball effect = increasing numbers convert form majority into minority
This creates a new majority and indicates change has happened.
people remember this change but not how is happened and the origin of the ideas = cryptoamnesia
What is the role of conformity on social change?
conformity means people are encourage by what others are doing
people look to others for guidance if the situation is unclear or new. people might believe that others now better (ISI) or that they want to be part of a group (NSI)
What is the role of obedience on social change?
changes due to the law → individuals obey the law due to perceived authority of government.
police can enforce this with their authority and legitimacy of authority
What was the aim of the stanford prison experiment, conducted by zimbardo 1971?
investigate conformity to social roles
understanding why people develop norms
understand effects of roles, labels and social expectations in a simulated prison environment
How did zimbardo increase levels of dehumaisation in the stanford prison experiment?
ppts given uniform for their social role in the experiment (eg gaurds given batons, tinted glasses and uniforms, prisoners numbered)
made them lose their identity, causing them to identify with the group and conform
What was the procedure of the stanford prison experiment?
24 US males (student volunteers from a newspaper advert and offered $15 a day, and selected on basis of physical and mental stability)
random assignment to either prisoner or guard roles
unexpectedly arrested at home and on arrival given uniform and ID numbers
prisoners given rights such as; 3 meals a day, 3 supervised toilet trips a day and 2 visitors per week.
guards given uniforms, clubs, whistles and reflective sunglasses.
zimbardo took role of superintendent (PPT observation)
planned duration was 2 weeks but ended on 6 days - study abandoned due to abuse stress and anxiety
What were the findings of the stanford prison experiment?
both the prisoners and guards quickly identified with their social roles.
Within days the prisoners rebelled, but this was quickly crushed by the guards, who then grew increasingly abusive towards the prisoners.
The guards dehumanised the prisoners, waking them during the night and forcing them to clean toilets with their bare hands
prisoners became increasingly submissive, identifying further with their subordinate role.
What were the conclusions zimbardo made from his experiment?
concluded that people quickly conform to social roles, even when the role goes against their moral principles.
situational factors were largely responsible for the behaviour found, as none of the participants had ever demonstrated these behaviours previously.
What is a strength of Zimbardo’s investigation into conformity to social roles?
allocation of participants
pts randomly allocated to their roles
zimbardo made sure that those chosen were mentally and physically healthy
means researcher bias is reduced, and validity is high - can conclude social roles were the cause of the behaviour
What are 4 weaknesses of the stanford prison experiment?
sample bias = male student only, all those that were interested in volunteering in a ‘prison’ experiment
lack population validity and may not be able to generalise to females
PPT observation = zimbardo acted as superintendent and as the researcher
zimbardo’s own behaviour impacted way events unfolded so validity of findings may be questioned
controlled experiment = ppts may have been ‘play acting’ based on stereotypical roles of prisoners and guards rather than genuine conformity to the situation
demand characteristics not reflecting real life situations
protection from harm = ppts soon became distressed and one even went on hunger strike. they were also denied right to withdraw
there was a debrief offering psychological help however levels of distress were high and hard to anticipate
there were no long-term impacts on ppts
What was the aim of Milgram’s experiment on obedience?
aim was to see how far people would go to obey authority
what are the 3 types of explanations for obedience?
social-psychological explanations
agentic state
legitimacy of authority
situational variables (investigated by milgram)
proximity
location
uniform
dispositional explanation
authoritarian personality
what are the 3 situational variables for obedience?
proximity
location
uniform
What is proximity as a situational explanation for obedience, as investigated by milgram?
a. physical closeness of authority figure to person they are giving the order to
obedience increases with proximity
encourages a move into agentic state
b. physical closeness of the teacher to the learner (victim)
obedience decreases as consequences become more obvious
prevents agentic shift, people remain more autonomous
when study was repeated with experimenter delivering orders over the phone obedience rates dropped to 20%
when study repeated with teacher and learner in same room obedience rates were 40%
What is location as a situational explanation for obedience, as investigated by milgram?
obedience is influenced by the status of the location they are in when he order is issued
coveys the legitimacy of authority figure
obedience rates higher in institutionalised settings where obedience to authority figures is instilled
when repeated in a run down office obedience rates dropped to 48%
What is uniform as a situational explanation for obedience, as investigated by milgram?
people in positions of authority often wear specific uniform, symbolic of authority
indicates to others who is entitled to their respect
conveys legitimacy of authority figure
when study repeated with experimenter played by ‘ordinary person’ in normal clothes obedience rates dropped to 20%
What are 2 strengths of the situational variables in explaining obedience?
lab experiment
used systematic/standardised procedures
allowed situational variables to be studied directly by manipulating the study
ensures cause and effect can be established
supporting evidence by slater
replicated milgram’s study finding support for proximity as an explanation of obedience
What supporting evidence did Slater (2006) provide for situational explanations of obedience?
replicated milgrams’s study using a virtual reality to make it more ethically correct.
ppts asked to administer word association memory tests to the female virtual human
she was shocked with incorrect answers increasing each time
responded with discomfort and protests
23/34 ppts saw/heard the female and 11/34 ppt communicated through text
found that all ppts in hidden condition delivered the maximum shock
provides support for proximity
What are 2 weaknesses of the situational variables in explaining obedience?
contradictory evidence - mandel 2008
situational factors do not apply to all real world events so lack ecological validity
e.g. in WW2 when soldiers carried out mass killings of Jewish they weren’t always in the presence of an authority figure
other explanations
has little focus on individual differences in obedience , dispositional explanation (authoritarian personality) focuses more on individual characteristics
Who proposed the authoritarian personality?
Adorno et al 1950
What is the dispositional explanation for obedience?
authoritarian personality
obedience is due to internal traits (eg personality type)
Adorno proposed authoritarian personality as an explanation that reflects the importance of someones personality, not the situation.
found it is shaped in early childhood as result of over-strict parenting
collection of personality traits
How is authoritarian personality measured?
potential for fascism scale (F-scale)
those that scored highly are more obedient
What are some authoritarian characteristics?
ridgid obedience to authority
submissive to authority
conventional attitudes to race/sex/gender
hostile to those of lower status
belief in the need for strong leaders to enforce traditional values
what is the supporting evidence for the dispositional explanations of obedience?
Elm’s and Milgram 1966
found ppts in milgram’s study who were highly obedient were significantly more authoritarian scoring higher on the F-scale than disobedient ppts
supports a link between obedience and authoritarian personality
What are 3 weaknesses of the dispositional explanations of obedience?
cause and effect = only a correlation between AP and obedience. it is impossible to draw the conclusion.
validity of the F-scale = has been criticised for working every item in the same ‘direction’. high score can be achieved by ticking the same line of boxes down the page. May be measuring tendency to agree
contradicted by other explanations = situational factors have a greater impact on obedience
What is the locus of control?
dispositional explanation for resistance to social influence
personality characteristics identified by rotter 1966
refers to the sense of control people have over their lives
measured on a scale between internal and external using a questionnaire
define an internal locus of control…
your actions are your own choice
have a large amount of personal control over your life
you are responsible for your actions
define an external locus of control…
your behaviour is controlled by other forces such as luck
everything in your life is caused by external influences
Is an ILOC or an ELOC more likely to resist social influence?
internal
more likely to be risk takers in society but take responsibility
have greater self confidence and don’t seek external approval
more achievement oriented and have higher intelligence
who provided supporting evidence for the explanations of resistance to social influence?
avtgis 1998 (LOC)
conducted meta-analysis and found slight correlations between internal LOC and resisting
holland 1967 (LOC)
repeated milgram’s experiment and measured whether ppts had internal or external LOC
37% of internal resisted
23% of external resisted
asch 1951 (social support)
found a drop from 33-5% in the rebel condition when one confederate gave the correct answer on the trials
milgram (social support)
found obedience levels dropped to 10% when two confederates rebelled and refused to continue
shows that having social support increase confidence and allows resistance to seem more legitimate
what are the two explanations for resisting social influence?
locus of control
social support
what are the weaknesses of LOC in explaining resistance to SI?
contradictory research - twenge 2004
analysed data from US obedience studies over a 40 year period
over this time span people became more resistant to obedience and were reporting lower levels of ILOC
challenges the link between LOC and resistance
other explanations
LOC focuses on individual characteristics, however there can be influence from the environment
means it is not a complete explanation
What is Weiners attribution model?
extension of LOC that processes sucesses and failures, and that they are due to either: ability, effort, task difficulty or luck
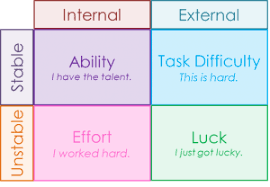
What social support?
explanation for resisting social influence
it is easier to resist if others are too
with social support people do not feel totally isolated and are more confident in their resistance