Physics (Electricity)
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is current?
The rate of flow charge carriers.
What is charge?
Can be positive or negative, property of matter.
What is voltage?
The measure of energy transferred to or from the charge in a circuit.
What is resistance?
The measure of how much a circuit component prevents current passing through.
What is the unit for energy?
Joules (J)
What is the unit for charge?
Coulombs (C)
What is the unit for current
Amps (A)
What is the unit for time?
Seconds (S)
What is the unit for voltage?
Volts (V)
What is the unit for resistance?
Ohms (Ω)
What is the equation for charge?
current/ time OR Q=I/T
What is the equation for voltage?
current x resistance or V=IR
What is the equation for resistance?
Voltage/Current OR R=V/I
What is a series circuit?
One loop of current.
What is a parallel circuit?
More than one loop of current.
What is the series circuit rule?
Current is the same everywhere.
What is the series voltage rule?
Total voltage across all components must add up to the total voltage across the power supply.
What is the parallel circuit rule?
In a branch the current is the same everywhere. At a junction, the total current arriving is the same as the total current leaving.
What is the parallel voltage rule?
The voltage across each branch is the same across the power supply.
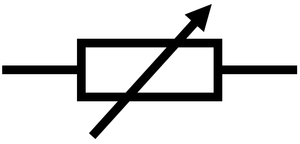
What is this?
Variable resistor
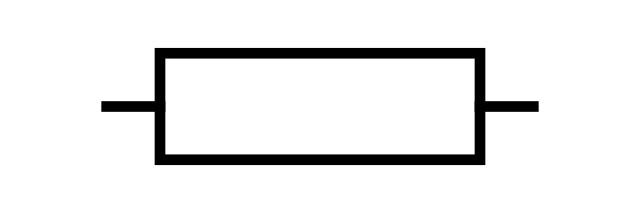
What is this?
Resistor
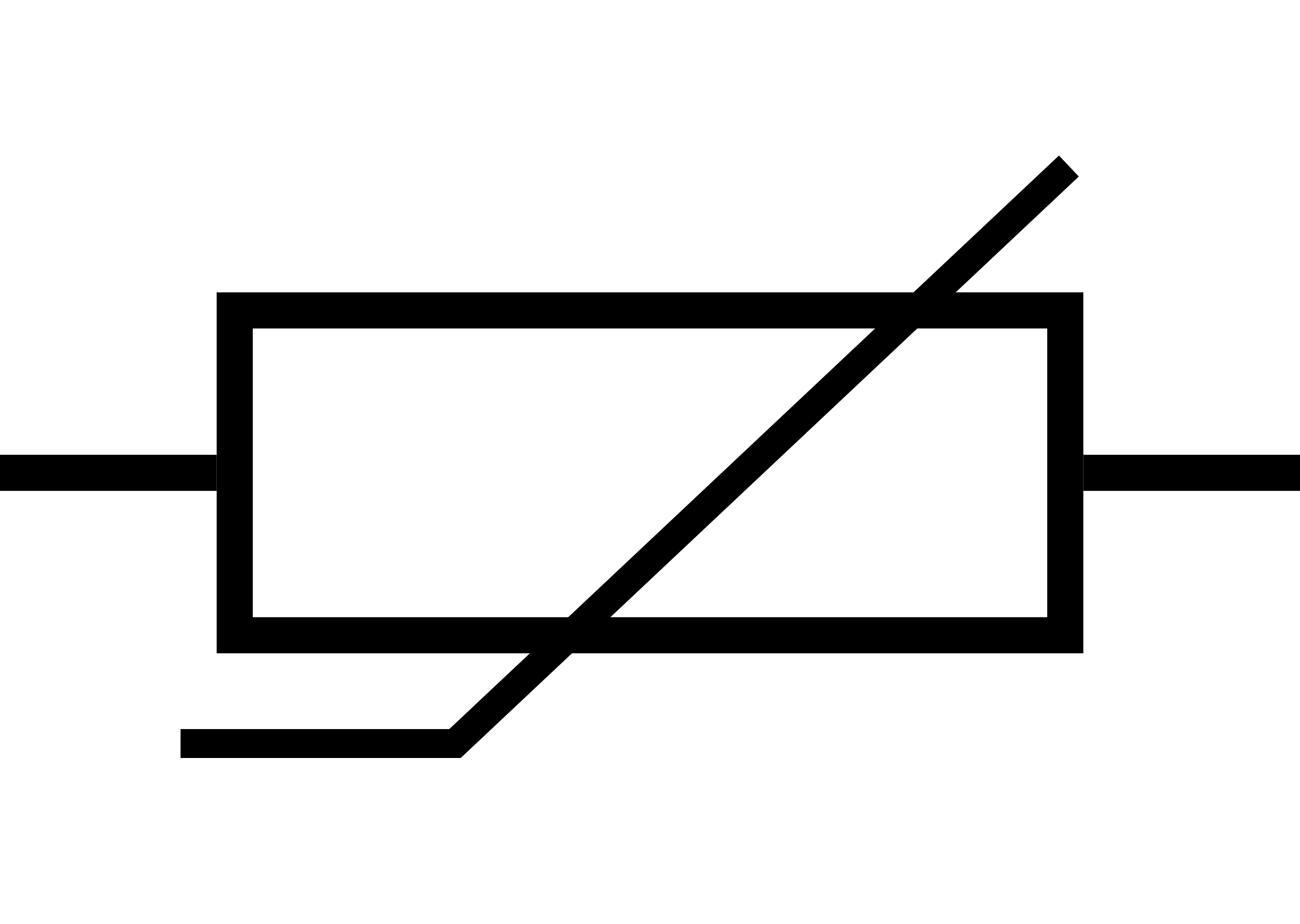
What is this?
Thermistor
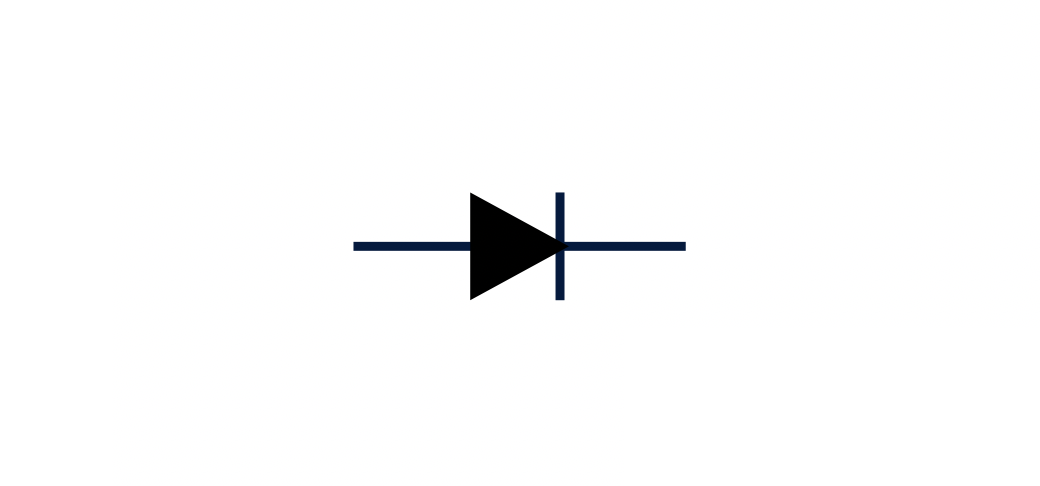
What is this?
Diode
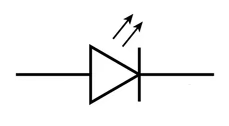
What is this?
Light emitting diode (LED)
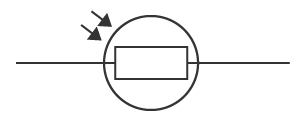
What is this?
Light dependent resistor (LDR)
What is a diode?
One way switch, current can flow easily in one direction but not in the opposite
What happens when length of wire increases
Resistance increases
What is a thermistor?
Type of variable resistor
What happens as the temperature of the thermistor increases?
Resistance decreases
What happens as the light on the LDR gets brighter?
Resistance decreases