AP Psych: Motivation
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
1
New cards
Motivation
Specific need or desire, such as hunger, thirst or achivement, that prompts goal-directered behavior
(drive)
(drive)
2
New cards
Primary Drive
Unlearned drive found in all animals, motives behavior necessary for survival
EX: Hunger, thirdt and sex.
EX: Hunger, thirdt and sex.
3
New cards
Secondary Drive
Learned drive
EX: wealth, succes
EX: wealth, succes
4
New cards
Fixed Action Pattern
Specific behaviors unique to a species
5
New cards
Homeostasis
The regulation of the internal enviorment, such as body temp, salt-water blance,etc.
6
New cards
*Intrinsic Motivation*
Motivation for a behavior is the behavior itself
You do it because you enjoy it.
You do it because you enjoy it.
7
New cards
Extrinsic motivation
Behavior is performed in order to obtain a reward or to avoid punishment. You do it to get something.
8
New cards
Instinct Theory
**Views biological or genetic programming as the cause of motivation**. This claim means that all humans have the same motivations due to our similar biological programming. This theory says that the root of all motivations is the motivation to survive. / Motivated by instincs; **fixed action patterns that are not learned.**
9
New cards
PROS Instinct Theory
Explains animal motivations
10
New cards
CONS Instinct Theory
Doesnt really apply to humans. We have very few reflexes (instincts) and most fade over time. Our motivations are mostly learned.
11
New cards
Drive Reduction theory
Physiological need creates an aroused tension state (a drive) when they are not fullfield, that motivates an organism to satisfy the need.
The aim of the drive reduction is homeostasis, the maintenance of a steady internal state.
The aim of the drive reduction is homeostasis, the maintenance of a steady internal state.
12
New cards
PROS Drive Reduction theory
Biological Explanation
Explains primary drives
Explains primary drives
13
New cards
CONS Drive Reduction theory
* Does not applu secondary drives.
* Once homeostasis is achieved we never do anything, but we keep trying for more. (doesnt explain things like obesity or sexual addictions)
* Once homeostasis is achieved we never do anything, but we keep trying for more. (doesnt explain things like obesity or sexual addictions)
14
New cards
Cognitive Dissonance theory
Psychological discomfort by two conflicting thoughtd, leads to a change and/or justification of behavior.
You are motivated to decrease a mental state of discomfort.
You are motivated to decrease a mental state of discomfort.
15
New cards
PROS Cognitive Dissonance theory
* Allows you to predict how *people* might justify or change their behaviors based on motivations.
16
New cards
CONS Cognitive Dissonance theory
Cant predict which way the nehaviors will change.
17
New cards
Incentive theory
Incentuve theory says we are pulled through external forces to obtain a desire.
Do something to get something.
Do something to get something.
18
New cards
PROS Incentive theory
Helps to explain secondary drive
19
New cards
CONS Incentive theory
Over simplifies motivations and poorly explains intrinsic motivation
20
New cards
Optimum Arousal theory
There is an optimal level of arousal for best performanceon any task.
The right amount of arousal can motivate us to perform.
Yerkes-Dodson law: simple tasks require higher levels of arousal. Harder tasks require a lower level of aorusal. (too much or too little is detrimental)
The right amount of arousal can motivate us to perform.
Yerkes-Dodson law: simple tasks require higher levels of arousal. Harder tasks require a lower level of aorusal. (too much or too little is detrimental)
21
New cards
Yerkes-Dodson law
simple tasks require higher levels of arousal. Harder tasks require a lower level of aorusal. (too much or too little is detrimental)
22
New cards
PROS Optimum Arousal theory
Explains
* Performance related motivation.
* Why we seek out new experiences.
* Why seek to eliminate boredom.
* Performance related motivation.
* Why we seek out new experiences.
* Why seek to eliminate boredom.
23
New cards
CONS Optimum Arousal theory
Really specific (limited).
24
New cards
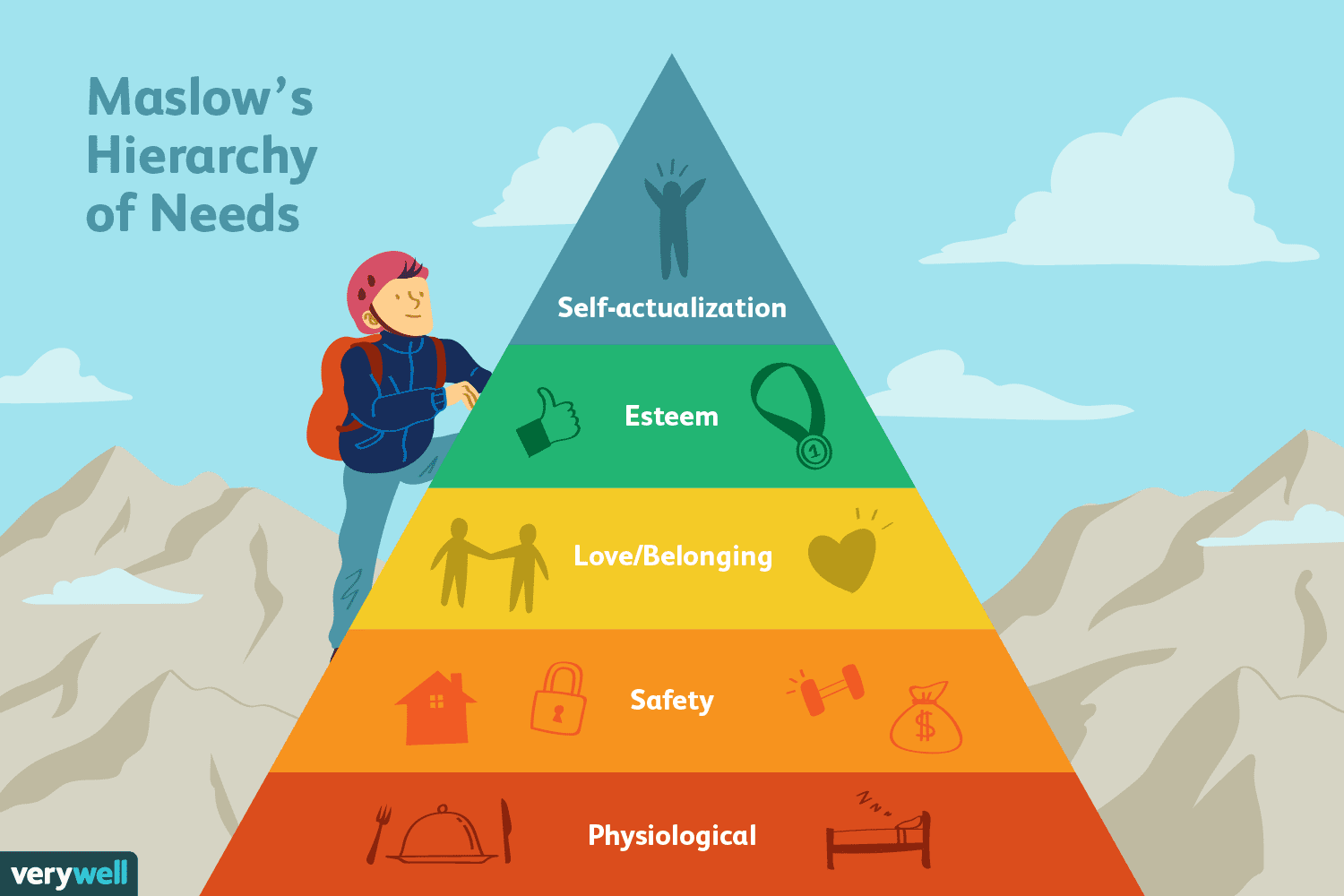
Hierarchy of needs
Suggested that human motivation is complex and for us to become our ideal selves we must meet certain needs first.
The goal is self actualization.
The goal is self actualization.
25
New cards
PROS Hierarchy of needs
* Nicely summarizes the complexity of motivations and includes intrnsic motivation.
26
New cards
CONS Hierarchy of needs
* Basic need dont always need to be met first, has been changed from Mslows original theory.
27
New cards
Self-actualization
A person motivation to reach his or her full potential.
Morality, creativity, problem solving, lack of prejudice, etc.
Morality, creativity, problem solving, lack of prejudice, etc.
28
New cards
Esteem
Confidence, self esteem, respect of others, respect by others.
29
New cards
Love / Belonging
Frienship, family, sexual intimacy.
30
New cards
Safety
Security of body, or employment, resources, family, helth or property.
31
New cards
Physiological
Breathing food, water, sex, sleep, homeostasis, etc.
32
New cards
Order of Maslow´s Hierarchy of needs
Self-Actualiztion
Esteem
Love/Belonging
Safety
Physiological
Esteem
Love/Belonging
Safety
Physiological
33
New cards
Health Psychology
Brach of psychology that addressed the factors related to well-being and illness. (Prevention, diagnosis, treatment, etc.)
34
New cards
Distress
A stress that is negative or damaging
35
New cards
Eustress
A Stress that is positive or motivating
36
New cards
Results of stress
Emotional differences:
Emotional differences:
Anxiety, depression, anger and irritability
37
New cards
Results of stress
Cognitive differences:
Cognitive differences:
Trouble concentrating and thinking clearly
38
New cards
Results of stress
Motivational differences:
Motivational differences:
Change in appetite for food and sex.
39
New cards
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
Chronic stress creates a physiological reaction that looks similar in all species.
Alarm stage
Resistance
Exhaustion
Alarm stage
Resistance
Exhaustion
40
New cards
Alarm Stage
Temporary stage of shock, immune system decreaded functioning.
41
New cards
Resistance stage
Hormones and immune function enhanced.
42
New cards
Exhauntion stage
Failure to rsist, immune system gives up.
43
New cards
Personality; Type A
Competitive and ambitious
More prone to heart disease
More prone to heart disease
44
New cards
Personality; Type B
Relaxed and easygoing
45
New cards
Coping
Efforts to control, reduce, or tolerate the threats that leads to stress.
46
New cards
Problem-Focused coping
Attempt to modify the stressful problem or source of stress.
47
New cards
Emotion-Focused coping
Attempt to menage their emotions in the face of stress, seeking to change the way they feel about or perceive a problem.
48
New cards
Approach Conflict Theories
4 kinds of conflict that cause strss and motivation.
49
New cards
Approach Approach (Win-Win)
Conflict is due to the choice between which win.
50
New cards
Approch Avoidance (Win-Lose)
Outcome is both good and bad, conflict is you having to deal with it.
51
New cards
Avoidance Avoidance (Lose-Lose)
Both outcomes are bad, have to choose one,
52
New cards
Multiple Approach Avoidance (Double Win-Lose)
Must choose between two or more approach avoidance conflicts.
53
New cards
Old Emotion Theories
James-Lange
Cannon-Bard
Cannon-Bard
54
New cards
New Emorion Theories
Schater/Two factor
Lazarus Cognitive-Appraisal Theory
\
They add the element of cognitive labeling; thinking about and labeling what the emotion is.
Lazarus Cognitive-Appraisal Theory
\
They add the element of cognitive labeling; thinking about and labeling what the emotion is.
55
New cards
James-Lange theory
Psysical Arousal happens first, leads to the emotion
\
Stimulus → Arousal → Emotion
\
Stimulus → Arousal → Emotion
56
New cards
Cannon-Bard theory
Emotional and physiological reactions occur simultaneously.
→ Arousal
Stimulus
→ Emotion
→ Arousal
Stimulus
→ Emotion
57
New cards
Schater two factor
Arousal and cognitive labeling occur simultaneously, then you experience emotion.
Arousal
Stimulus → → Emotion
Cognitive Label
\
*Direct Pathway: Amygdala*
Arousal
Stimulus → → Emotion
Cognitive Label
\
*Direct Pathway: Amygdala*
58
New cards
Lazarus Cognitive Appraisal theory
Cognitive labeling first then you experience the emotion and arousal simultaneously.
→ Arousal
Cognitive label
→ Emotion
\
*Indirect Pathway: Hypothalamus*
→ Arousal
Cognitive label
→ Emotion
\
*Indirect Pathway: Hypothalamus*
59
New cards
Le Doux Biological Explanation
The thalamus routes the perception if the stimulus to either:
1. Direct Pathway / Schacter theory : goes to the Amygdala
1. Indirect Pathway / Lazarus Theory: goes to the Frontal Lobe.
60
New cards
6 universal emotions
* Happiness
* Anger
* Sadness
* Surprise
* Disgust
* Fear
* Anger
* Sadness
* Surprise
* Disgust
* Fear
61
New cards
Evidence 6 universal emotions
Most of them are presented in infancy. Even blind children display these emotions.
62
New cards
Duchene smile
We can tell a real smile based off other features.
63
New cards
Facial Feedback hypothesis
Facial expression can influence emotions.
64
New cards
Display Rules
A social group or culture´s norms of how to express certain emotions.
65
New cards
Biology of hunger
The Glucose level in your blood is maintained by your pancreas.
Levels of glucose in the blood are monitores by neurond in the stomach, liver, and intestines. They send signals to the hypothalamus in the brain.
Levels of glucose in the blood are monitores by neurond in the stomach, liver, and intestines. They send signals to the hypothalamus in the brain.
66
New cards
Insulin
(a hormone) decreases glucose in the blood.
When you have too much glucose the body releases it.
When you have too much glucose the body releases it.
67
New cards
Diabetes
is the result of the body not producing insulin.
68
New cards
Lateral Hypothalamus
* Stimulated: Makes you hungry
* Destroyed: You no longer feel hunger.
* Destroyed: You no longer feel hunger.
69
New cards
Ventromedial Hypothalamus
* Stimulated: You feel full
* Destroyed: You never feel sated.
* Destroyed: You never feel sated.
70
New cards
Hormones that increase appetite
Released by lateral hypothalamus
\
* Gherelin
* Orexin
\
* Gherelin
* Orexin
71
New cards
Hormones that decrease appetite
Released by ventromedial hypothalamus
\
* Obestatin
* PYY
* Leptin
\
* Obestatin
* PYY
* Leptin
72
New cards
Risk of obesity
* Heart Attack
* Hypertension
* Athrosclerosis
* Alzheimers disease
* Diabetes.
* Hypertension
* Athrosclerosis
* Alzheimers disease
* Diabetes.
73
New cards
Genetics in obesity
* Identical twins reared apart still have similar body weights.
* Adopted childrens weight resembles their biological parents.
* Adopted childrens weight resembles their biological parents.
74
New cards
Psychological factors in obesity
* Learning sets from parents (no control of parents in childrens diets)
* Stress
* Lack of sleep
* Stress
* Lack of sleep
75
New cards
Societal Factors
Fast food is cheaper than the healthy food, and fast food is calorically dense and unhealthy compared to cooking in.
76
New cards
Anorexia Nervosa
Symptoms:
* Weight loss of at least 15% ideal weight (according to BMI)
* Intense fear of gaining weight
* Distorted body image
* Major caloric restriction, excessive exercise
* Weight loss of at least 15% ideal weight (according to BMI)
* Intense fear of gaining weight
* Distorted body image
* Major caloric restriction, excessive exercise
77
New cards
Bulimia Nervosa
Symptoms:
* Usually normal body weight
* Binge-Purge eating pattern;
Eating in a discrete period of time (e.g. 2 hour period) an amount of food that is definitely larger than most people would eat under similar circumstances, followed by “purging” the food through vomiting, misuse of laxatives, etc
* Usually normal body weight
* Binge-Purge eating pattern;
Eating in a discrete period of time (e.g. 2 hour period) an amount of food that is definitely larger than most people would eat under similar circumstances, followed by “purging” the food through vomiting, misuse of laxatives, etc
78
New cards
Similarities between Anorexia and Bulimia
* Recurrent inapropiate compensatory behavior to prevent weight gain.
(Self induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives, diuretics, enemas. Fasting)
* Pre occuoation with food.
(Self induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives, diuretics, enemas. Fasting)
* Pre occuoation with food.
79
New cards
Binge eating disorder
Symptoms:
* Engages in binging behaviors but no purging behaviors.
* Usually above average weight.
* Engages in binging behaviors but no purging behaviors.
* Usually above average weight.
80
New cards
Dangers of eating disorders
Extreme organ damage
* Heart
* Kidneys
* Stomach
* Esophagus
* Brain
Death.
* Heart
* Kidneys
* Stomach
* Esophagus
* Brain
Death.
81
New cards
Eating disorders are most common in:
Young
◦ Females
◦ Athletes / dancers, etc.
◦ Authoritarian parents
◦ High Neuroticism scores
i.e. high stress individuals
◦ Females
◦ Athletes / dancers, etc.
◦ Authoritarian parents
◦ High Neuroticism scores
i.e. high stress individuals
82
New cards
Causes eating disorders
* Usually triggered by another disorder or other
external event (such as parenting style, hobby,
etc.)
* Brain changes are evident – but which came
first?
external event (such as parenting style, hobby,
etc.)
* Brain changes are evident – but which came
first?
83
New cards
Biology of Sex; Hypothalamus
This part regulates a lot of functions (reward center, hormone control, homeostasis and eating beaviors)
* Stimulated--> increase in sexual behavior
* Surgical removal ---> Sexual inhibition
* Stimulated--> increase in sexual behavior
* Surgical removal ---> Sexual inhibition
84
New cards
Biology of Sex; Pitutary Gland
monitors, initiates and restrict hormones.
85
New cards
Sex Hormones
Effect the development of sexual characteristics and activate sexual behavior.
* Male; Testicles; testosterone (little estrogen)
* Female: Ovaries; Estrogen (little testosterone)
* Male; Testicles; testosterone (little estrogen)
* Female: Ovaries; Estrogen (little testosterone)
86
New cards
Human Sexual Response pattern
1. Excitement phase
2. Plateau Phase
3. Orgasm
4. Refractory (resolution)
87
New cards
Sexual Orientation
He created the Kinsey scale of sexuality… 0 to 6, where 0 is exclusively heterosexual and 6 is homosexual.
7 is Asexual.
7 is Asexual.
88
New cards
Evidence of the kinsey scale of sexual oriebtation
* Differences in Brain; Anterior hypothalamus is smaller in woman and gays.
* Twin studies; Genes (identical twins tend to have same sexuality)
* Prenatal Hormone Exposure; the more boys a womrn has, the more likely that the younger boys are gay.
* Occurs in other species in nature.
* Twin studies; Genes (identical twins tend to have same sexuality)
* Prenatal Hormone Exposure; the more boys a womrn has, the more likely that the younger boys are gay.
* Occurs in other species in nature.
89
New cards
Industrial / Organization Psychology
Is the application of concepts and methods in order to optimaze human behavior in the workplace.
90
New cards
Ergonomics (Human factors)
Intersection of engineering and psychology.
Focuses on safety and efficiency of human-machine interactions.
Safe / Comfortable work enviorment : Health and more productive employees.
Focuses on safety and efficiency of human-machine interactions.
Safe / Comfortable work enviorment : Health and more productive employees.
91
New cards
Industrial (personnel) psychology
focuses on employee recruitment, selection, placement, training, appraisal and development.
92
New cards
Organizational Psychology
Examines organizational influences on worker satisfaction and productivity, and facilitates organizational change.
93
New cards
The Hawthorne Effect
Individual productivity increases when workers are singled out and made to feel important.
Performance is subject to social pressures and group norms.
Performance is subject to social pressures and group norms.
94
New cards
Leon Festinger
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
(Psychological discomfort)
(Psychological discomfort)
95
New cards
Abraham Maslow
Hierarchy of needs
96
New cards
William Masters and Virginia Johnson
Hum,an Sexual Response Pattern
97
New cards
Alfred Kinsey
Sexual Orientation
98
New cards
Stanley Schacter
Schacter two factor theory
(cognitive labeling and arousal happen at the same time, then emotion).
(cognitive labeling and arousal happen at the same time, then emotion).
99
New cards
Richard Lazarus
Lazarus Cognitive-Appraisal Theory
(Cognitive labeling first, then arousal and emotion at the same time)
(Cognitive labeling first, then arousal and emotion at the same time)
100
New cards
Joseph LeDoux
Biological explanation of the theories of emotion.