2025 S3 Physics WA3
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is energy?
Energy is the capacity to do work.
What are the different energy pathways?
Mechanically (by a force acting over a distance)
Electrically
By Heating
Propagation of Waves (mechanical sound waves, infrared, light)
Answering Technique;
Energy in the gravitational potential store of the ball is transferred mechanically to the kinetic store of the ball by the weight of the ball acting over the distance it falls.
Energy in the chemical potential store of the cell is transferred electrically to the internal store of the bulb to increase the temperature of the filament wire and the bulb lights up. Energy is transferred by light waves to the surroundings.
What does the principle of conservation of energy state?
The principal of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed.
Energy can be transferred from one store to another.
The total energy of an isolated system is constant.
What is work done?
Work done by a constant force on an object is the product of the force and the distance moved by the object in the direction of the force.
When is work not done?
force is applied on the object, but the object does not move (s = 0)
the direction of the force is perpendicular to the direction of movement of the
object (F Ls)
example: a man carrying a suitcase and walking forward (applied force is vertically upward but direction of motion is horizontal), a student carrying a school bag and walking forward (applied force is vertically upward but direction of motion is horizontal)
What is Power?
Power is defined as the work done or energy transferred per unit time.
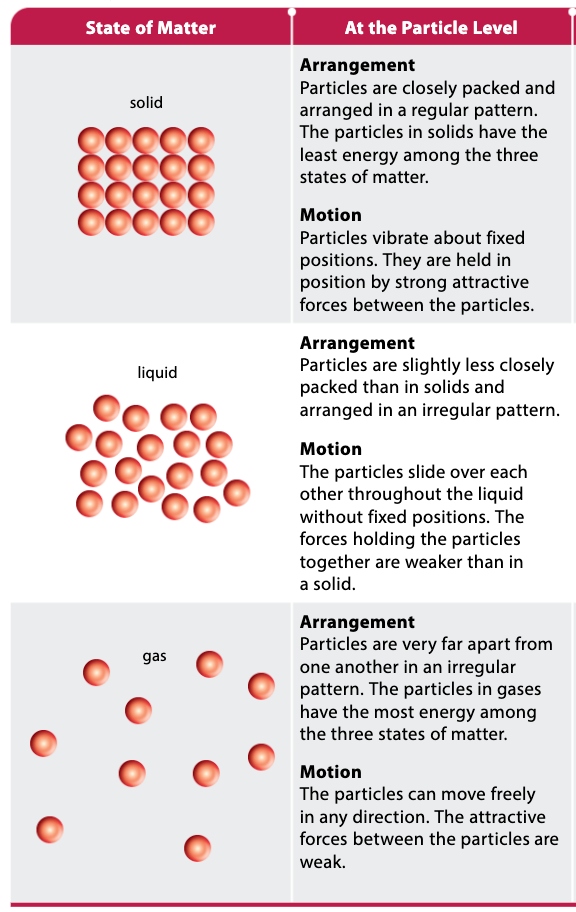
What are the arrangement and motion of each state of matter?
Solid
Arrangement: Particles are closely packed and arranged in a regular pattern.
Motion: Particles vibrate about fixed positions. They are held in position by strong attractive forces between the particles.
Liquid
Arrangement: Particles are slightly less closely packed than in solids and arranged in an irregular pattern.
Motion: The particles slide over each other throughout the liquid without fixed positions.
Gas
Arrangement: Particles are very far apart from one another in an irregular pattern.
Motion: The particles can move freely in any direction.
Relationship between temperature of substance and average kinetic energy of particles in a body.
Temperature reading of a substance is an indication of the average kinetic energy of particles in the substance.
When the temperature of a body increases, the average kinetic energy of all the particles in the body increases. This increases the energy in the internal store of the body.
Explain why when temperature increases, gas pressure increases.
When temperature increases, the average speed of the particles increases.
The particles collide more vigorously and more frequently with the container wall.
The average force exerted by the particles on the container wall increases, giving rise to a higher pressure.
Explain why when volume increases, gas pressure decreases.
When volume increases, the number of particles per unit volume decreases.
The particles collide less frequently with the container wall.
The average force exerted by the particles on the container wall decreases, giving rise to a smaller pressure.
Explain why when number of particles increases, gas pressure increases.
When the number of particles increases, the number of particles per unit volume increases.
The particles collide more frequently with the container wall.
The average force exerted by the particles on the container wall increases, giving rise to a higher pressure.
What is thermal equilibrium?
Thermal equilibrium describes a state in which two or more objects have the same temperature and that there is no net transfer of energy between them.
What is conduction?
Conduction is a process where energy is transferred through the passing on of vibrational motion from one particle to another.
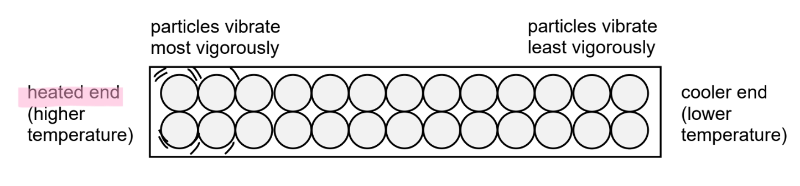
Describe the vibration of particles from the heated end to the cooler end.
When a material is heated at one end, the particles at the heated end will gain energy and vibrate more vigorously about their fixed positions.
They collide with the less energetic neighbouring particles.
Through collisions, energy is transferred from the more energetic particles to the less energetic particles.
As more energy is transferred from the heated end to the cooler end, the particles at the cooler end begin to vibrate more vigorously.
Thus, the temperature (a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles) of the cooler end increases.
Describe the movement of free electrons from the heated end to the cooler end. (only for metals)
When a metal is heated, in addition to vibration of particles, the free electrons at the heated end gain kinetic energy from interacting with the atoms and move faster.
The small size and high speed of the electrons allow them to move easily and quickly to the cooler end and transfer energy to the atoms as they collide.
Thus, the atoms at the cooler end vibrate more vigorously, and the temperature of the cooler end increases.
Why are metals generally better thermal conductors than non-metals?
Conduction by the movement of electrons is much faster than the conduction by vibration of particles as electrons are very much smaller than atoms and can move very quickly through the metal.
Conduction takes place by both mechanisms in metals.
What is convection?
Convection is a process of energy transfer by means of convection currents of a fluid (liquid or gas), due to a difference in density.
What is radiation?
Radiation is the process of energy transfer by electromagnetic waves. It does not require a medium.
What affects heat absorption by radiation?
Surface area
Colour and texture
Matt (dull), rough and dark-coloured surfaces are good absorber and emitter of radiation but poor reflector of radiation.
Shiny, smooth and light-coloured surfaces are poor absorber and emitter of radiation but good reflector of radiation.

Functions of the different parts of a vacuum flask.
Conduction
is reduced by the cap and insulated support as they are made of poor thermal conductors
is prevented by the vacuum between the silvered walls as conduction cannot take place in vacuum
Convection
is reduced by the cap as it prevents the surrounding air from coming into contact with the liquid so convection currents cannot be set up at the mouth
is prevented by the vacuum between the silvered walls as convection cannot take place in vacuum.
Radiation
is reduced by the silvered walls as silvered surfaces are poor emitter and absorber of radiation.
Note: Radiation cannot be prevented.

What is heat capacity?
Heat capacity C of an object is the change in amount of its internal energy per unit change in its temperature.

What is specific heat capacity?
Specific heat capacity c of a material is the change in amount of its internal energy per unit mass for each unit change in its temperature.

What is Latent Heat?
Latent heat L is the energy released or absorbed to change the state of a substance at constant temperature.
What is Latent Heat of Fusion?
Latent heat of fusion Lf is the amount of energy transferred to change a substance between the solid and liquid states, at constant temperature.
What is Specific Latent Heat of Fusion?
Specific latent heat of fusion is the amount of energy transferred per unit mass of a substance to change it between the solid and liquid states, at constant temperature.
What is latent heat of vaporisation?
Latent heat of vaporisation Lv is the amount of energy transferred to change a substance between the liquid and gaseous states, at constant temperature.
What is Specific Latent Heat of Vaporisation?
Specific latent heat of vaporisation lv is the amount of energy transferred per unit mass of a substance to change it between the liquid and gaseous states, at constant temperature.