MKTG 304 FINAL REVIEW
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Start of Chapter 15: Marketing Communications
Promotion
Communication by marketers that informs, persuades, reminds, and connects with potential buyers of a product. Data and data analytics help determine how marketers distribute funding among their promotional mix tactics.
Promotional Mix
A combination of promotion tools used to reach the target market and fulfill the organization’s overall objectives.
What does the promotional mix include?
Advertising
Public Relations
Personal Selling
Sales Promotion
Direct Marketing (includes social media)
The Role of Promotion
Seeks to modify behavior and thoughts in some way
The Four Tasks of Promotion
Infom the target audience
Persuade the target audience
Remind the target audience
Connect with the audience
Informative Promotion
Create/increase awareness
Explain how product works
Suggest new uses (repositioning)
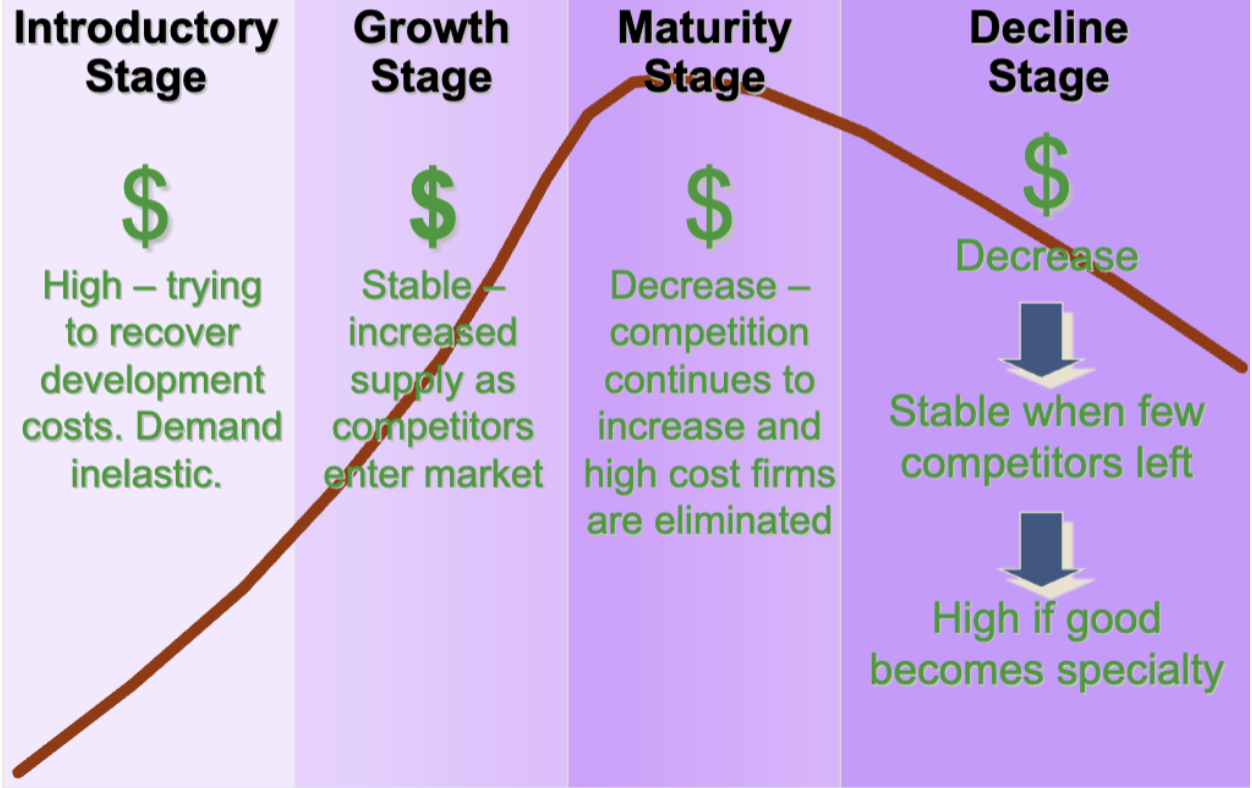
Generally more prevalent during the early stages of the product life cycle
Important for promoting complex and technical products such as automobiles, computers, and investment services
Persuasive Promotion
Simulate a purchase or an action
Typically used during the growth stage, when the target market is already aware of how the product can fulfill its wants
Messaging emphasizes the product's real and perceived competitive advantages
Messaging often appeals to emotional needs
For highly competitive products, the promotional message often encourages brand switching and aims to convert some buyers into loyal users
Reminder Promotion
Keep the product and brand name in the public’s mind
Assumes that the target market has already been persuaded of the merits of the good or service, so used during the maturity stage
The purpose is to trigger a memory that leads to a purchase
Connection Promotion
Forms relationships through social media or sales personnel
Brands are increasingly connecting with their customers in hopes that they become brand advocates who promote the brand
Important in all phases of the PLC
Advertising
Impersonal, one-way mass communication about a product or organization that is paid for by a marketer
Advertising budgets are shifting away from traditional communication media and more toward digital options
One of the primary benefits of advertising is its ability to communicate to large numbers of potential customers
Cost per contact is typically very low, but the total cost is usually very high
Major Public Relations Tools
New-product publicity helps advertisers about their new product by prompting free news or positive words (via news releases or news conferences)
Product placement: a public relations strategy that involves getting a product, service, or company name to appear in a movie, television show, radio program, magazine, newspaper, video games, video or audio clip, book or commercial for another product
Consumer education events
Sponsorship: a public relations strategy in which a company spends money to support an issue, cause, or even that is consistent with corporate objectives, such as improving brand awareness or enhancing corporate image
Sales Promotion
Short-term incentive to motivate consumers to do something (purchase a product, visit a store, etc.) immediately. Typically, it involves lowering the price or adding value.
Common Forms of Consumer Sales Promotions

Common Consumer Sales Promotion Objectives
Induce the customer to try the product
Reward brand loyalty (frequent buyer/loyalty programs)
Encourage the consumer to trade-up or purchase larger sizes
Stimulate repeat purchases
Reaction to Competitor Efforts
Direct Marketing
Allows the organization to communicate directly with customers and offer targeted promotions
Direct mail, emails, text messaging, social media, telemarketing
Technology provides more ways to directly communicate with consumers
The Internet and the Promotional Mix
The internet has changed how businesses promote their brands
Types of Media:
Paid, Earned, Owned
Paid Media
a category of promotional tactic based on the traditional advertising model whereby a brand pays for media space
(Ex. Banner ads, Sponsored posts)
Earned Media
a category of promotional tactic based on a public relations or publicity model that gets customers talking about products or services
(e.g. getting customers to share your stories, media coverage, SEO, publicity activities, WOM)
Owned Media
a new category of promotional tactic based on brands becoming publishers of their own content in order to maximize the brands’ value to customers
(Ex. Web Sites, Blogs, Social Media Presence)
Integrated Marketing Communications
Coordinates and integrates all elements of the promotion mix so that the organization presents a consistent message
Seeks to manage all sources of brand or company contacts with existing and potential customers
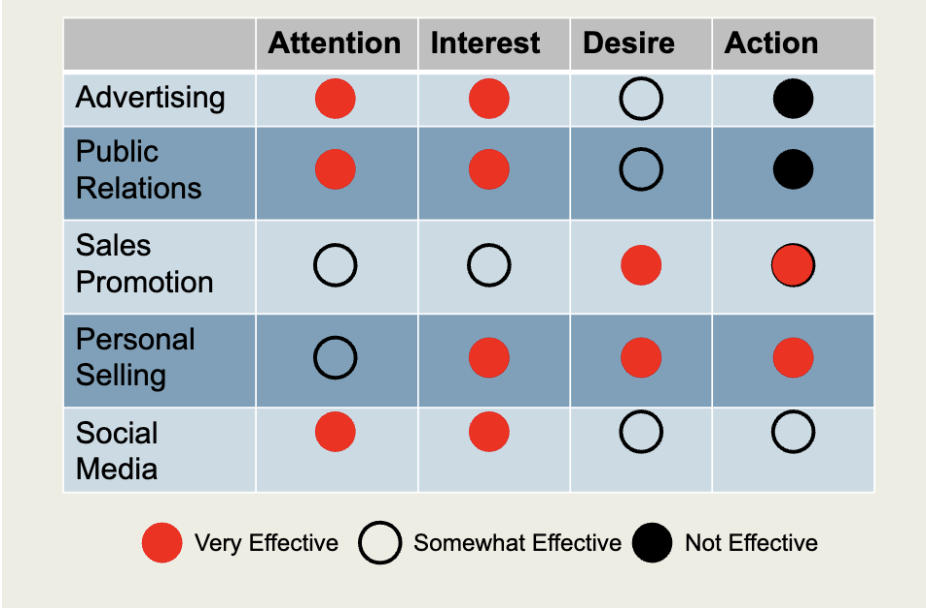
AIDA concept
a model that outlines the process for achieving promotional goals in terms of stages of consumer involvement with the message; the acronym stands for attention, interest, desire, and action
The Definition of AIDA
Attention: The advertiser must first gain the attention of the target market
Interest: Create interest in the message and the product
Desire: Show how product features will satisfy customer needs
Action: A special offer or strong closing sales pitch may drive the consumer to purchase the product
Effectiveness of AIDA Model
Factors Affecting the Choice of Promotional Tools
Nature of the product
Stage in Product’s Life Cycle
Target market characteristics
Type of buying decision
Promotion funds
Push or pull strategy
Effective Promotion for Routine Consumer Decisions & Basic/Easy/Convenience Products
Most effective promotion calls attention to the brand
Advertising and sales promotion are the most productive promotion tools
Complex/Extensive Consumer Decisions & Complex/Hard-To-Use Products
Rely on large amounts of information to help them reach a purchase decision
Personal selling is effective in helping these consumers decide
As a general rule, as the costs or risks of buying and using a product or service increase, personal selling becomes more important
Target Market Characteristics
Target market characterized by widely scattered potential customers, highly informed buyers, and brand-loyal repeat purchasers requires a promotional mix with more advertising and sales promotion and less personnel selling.
Product Life Cycle and the Promotional Mix
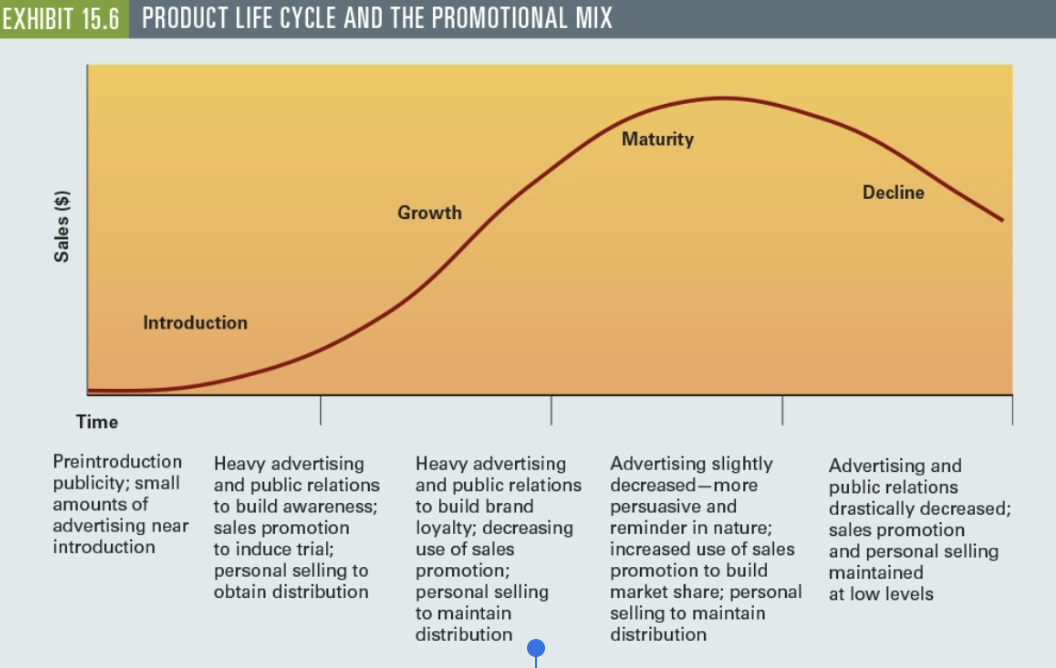
End of Chapter 15: Marketing Communications
Push and Pull Strategy
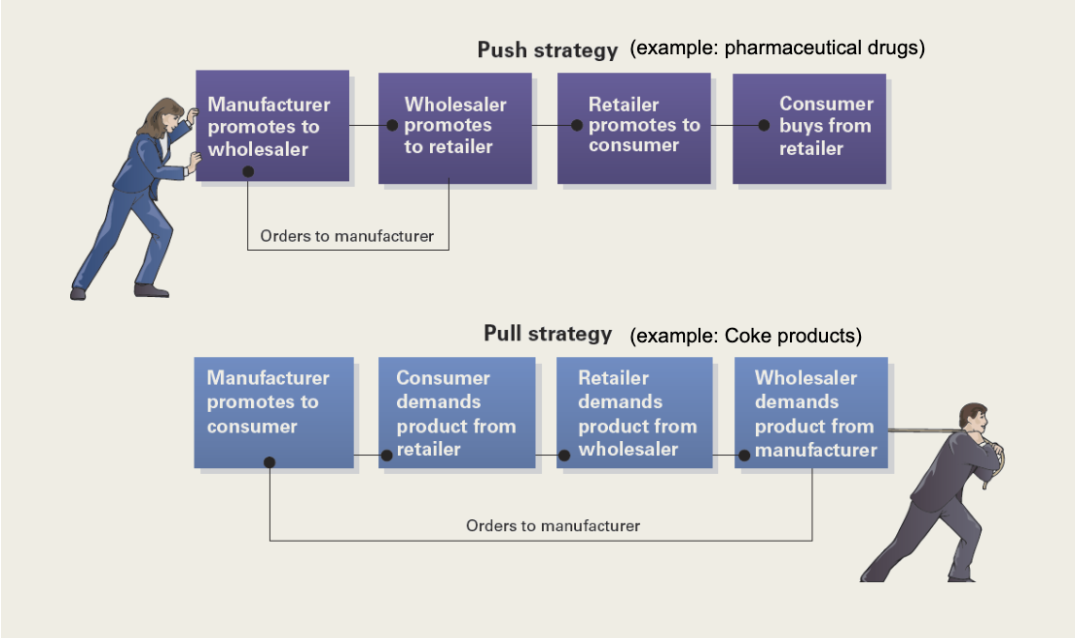
Start of Chapter 16: Advertising & Sales Promotions
What is advertising used for?
creating/maintaining brand awareness and market share
Why do new brands w/ small market shares spend more on advertising?
Advertising Response function & requirements of a minimum level of exposure to measurably affect purchase habits (i.e. consumers need to be exposed to your brand multiple times for it to impact their willingness to purchase)
Advertising response function
a phenomenon in which spending for advertising increases sales or market share to certain level but then produces diminishing returns
Effects of Advertising on Consumers
Advertising may change a consumer’s negative attitude toward a product or reinforce a positive attitude, but is not good for really connecting with consumers/creating long-term relationships and cannot change deeply rooted values.
Advertising can affect consumer ranking of a product’s attributes
Car ads used to emphasize attributes such as roominess, speed, and low maintenance, but todays car ads often show technology, safety, fuel efficiency
Institutional advertising
a form of advertising designed to enhance a company’s image rather than promote a particular product
Advocacy advertising
a form of advertising in which an organization expresses its views on controversial issues
Product advertising
a form of advertising that touts the benefit of a specific good or service
Types of Product Advertising
Pioneering, Competitive, Comparative
Pioneering Product Advertising
Stimulates primary demand for new product or category. Used in the introductory stage of PLC. Offers in-depth info about benefits.
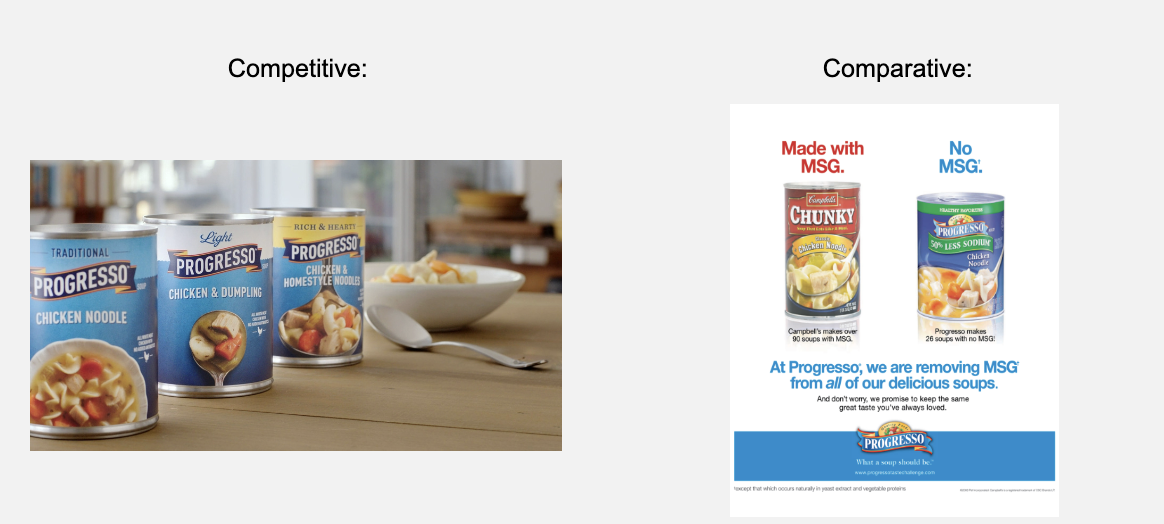
Competitive Product Advertising
Stimulates secondary demand. Influences demand for a specifc brand in the growth phase of the PLC. Often uses emotional appeal. Emphasis on branding. GEICO ad
Comparative Product Advertising
Compares two or more competing brands’ product attributes. Used if growth is sluggish, or if competition is strong. 21st century ad
Competitive vs. Comparative Advertising
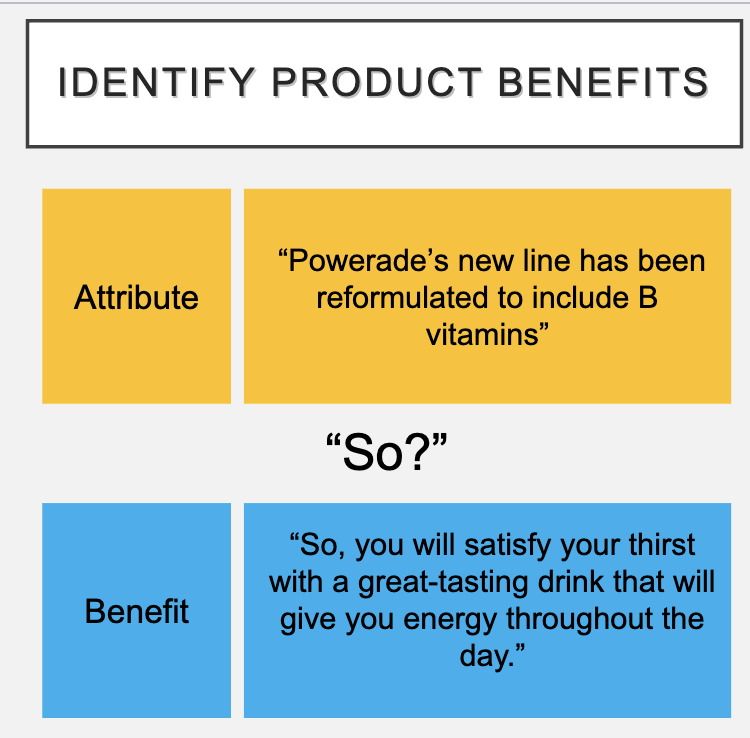
Identify Product Benefits
An advertising campaign should sell a product’s benefits, not its attributes. A benefit is what consumers will receive or achieve by using the product.
A benefit should answer “What’s in it for me?”
Ask “So?” to determine if advertising offers attributes or benefits
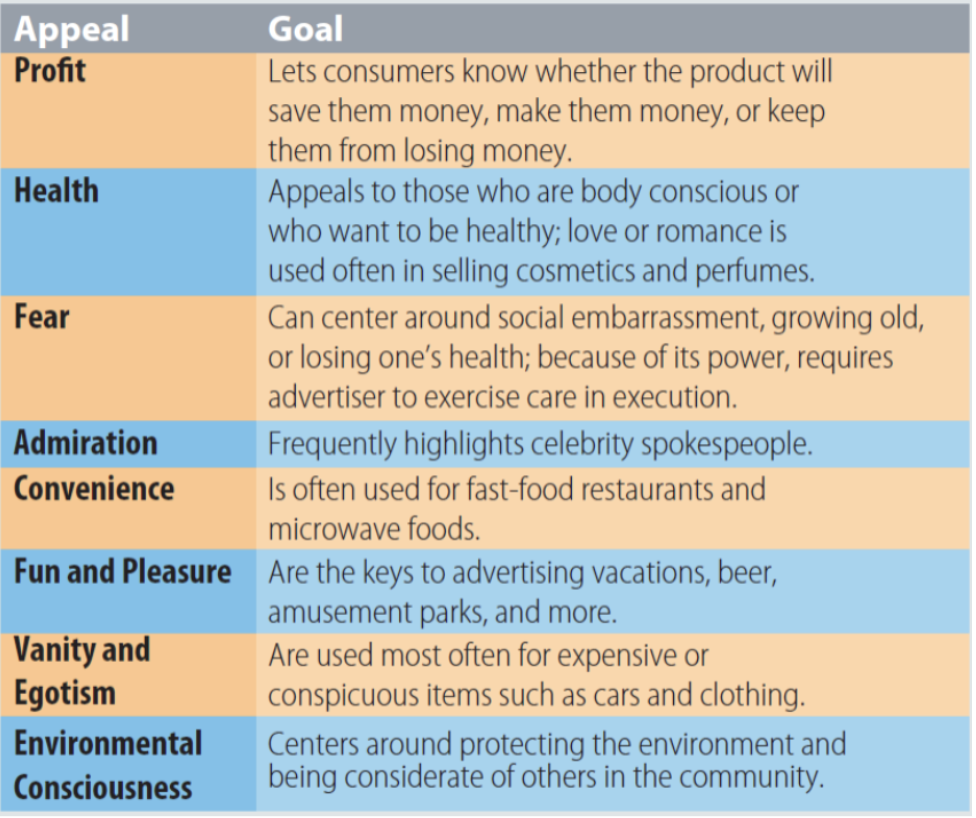
Advertising Appeal
identifies a reason for a consumer to buy a product
How are you going to make your product appeal to your consumers?
requires market research to determine how your specific target market will respond to different types of appeals; must make a positive impression on the target market, while being unique, distinguishable from competitor’s messages, and believable
Common Advertising Appeals
Unique Selling Proposition
A desirable, exclusive, and believable advertising appeal selected as the theme for a campaign
Snickers USP - stopping hunger, slogan - “You’re not you when you are hungry.”
Effective slogans become easily recognizable (taste the rainbow, the ultimate driving machine, just do it, i’m lovin’ it)
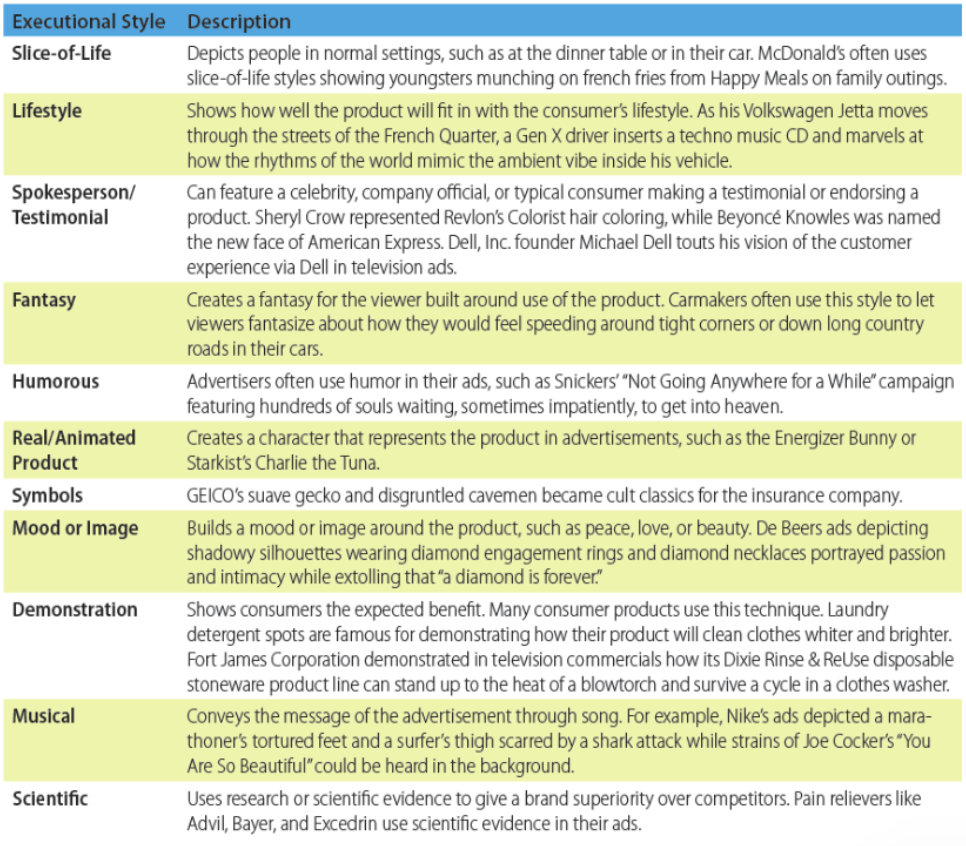
Executing the Message
The way that an ad portrays its message
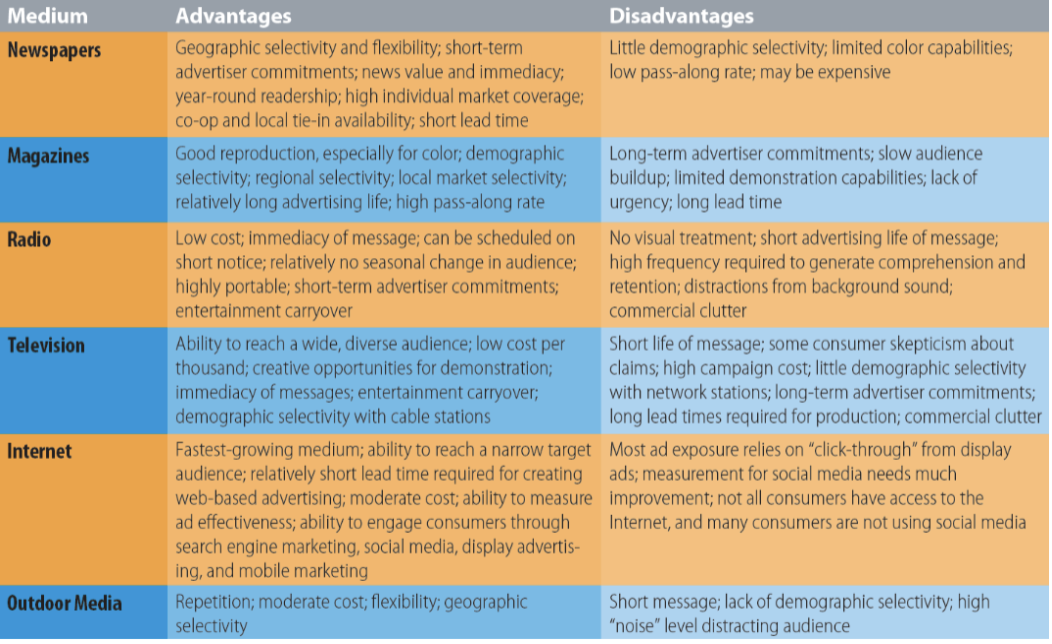
Medium
the channel used to convey a message to a target market
Selection of the medium is determined by promotional objectives and the appeal and executional style of the advertising
Media planning
the series of decisions advertisers make regarding the selection and use of media, allowing the marketer to optimally and cost-effectively communicate the message to the target audience
Advantages and disadvantages of major advertising media
Continuous Media Schedule
Advertising is run steadily throughout the period (Charmin ads)
Flighted Media Schedule
Advertising is run heavily at specific time intervals to achieve greater impact (More movie ads on Thursdays)
Pulsing Media Schedule
Advertising combines continuous with flighting (Chicken stock ads increase around Thanksgiving)
Seasonal Media Schedule
Advertising is run only when the product is likely to be used (cold medication, sunscreen)
Sales Promotion
marketing communication activities other than advertising, personal selling, and public relations in which a short-term incentive motivates consumers or members of the distribution channel to purchase a good or service immediately, either by lowering the price or by adding value
- goal is to give the consumer an incentive to make an immediate purchase ing value
Trade sales promotion
promotion activities directed to members of the marketing channel, such as wholesalers and retailers
Consumer sales promotion
promotion activities targeted to the ultimate consumer market
Types of consumer sales promotions
coupon, rebate, premium, loyalty marketing program
Coupon
A certificate that entices consumers to an immediate price reduction when they buy the product. Encourages product trail and often increases the amount of a product purchased.
Rebate
A cash refund given for the purchase of a product during a specific period. Requirers consumer to mail in proof of purchase.
Premium
An extra item offered to the consumer (gift with pruchase). Reinforce purhcase decision, increase consumption, and persuade brand switchers. Ex: McDonalds Toys
Loyalty Marketing Program
A promotional program designed to build long-term, mutually beneficial relationships between a company and key customers.
What are contests and sweepstakes for?
Designed to create interest in a brand, not effective tools for generating long-term sales. Offering several smaller prizes instead of one huge prize will increase effectiveness.
Contest
Promotions in which participants use some skill or ability to compete for prizes.
Sweepstakes
Promotions that depend on chance, with free participation.
End of Chapter 16: Advertising & Sales Promotions
Sampling
A promotional program that allows the consumer the opportunity to try a product or service for free.
Sampling is often the most successful sales promotion tactic. In a recent study in-store sampling increased sales by 116%, outperforming end cap displays (70%), ad circualrs (63%), and temporary price reductions (48%)
Start of Chapter 18: Social Media & Marketing
Influencer Effectiveness
Influencer originality, follower size, sponsor salience, influencer activeness, follower-brand fit, and post positivity (as long as it seems genuine) are positively impact SMI campaign effectiveness
Posts that announce new product launches are less effective than general brand awareness campaigns
SMI campaigns are not as effective with brands that base their marekting strategy on their heritage/history (Kiehl’s Since 1851)
- Authenticity is more important for these brands and working SMIs can diminish perceptions of brand authenticity
Brands can see backfire effects with their use of SMIs to target consumers that are already loyal brand shoppers
Social Media
any tool or service that uses the Internet to facilitate conversations
traditonal marketing media offer a mass media method of interacting with consumers, SM offer more one-to-one ways to meet consumers
Social Media’s Implications for Marketers

How Consumers Use Social Media
Which social media consumers are using and how they are using them (Target Market)
- Teens and young adults use TikTok and Instagram
- Older adults use Facebook
4.9 billion active on SM but only 2.6 billion use Internet to shop
- facebook = 2.96 billion
- instagram = 2.35 billion (growing)
- tiktok = 1.53 billion (growing)
How do companies start on social media?
Start with a strategy before diving head first into social media
Start with a marketing or communications plan
Situation analysis, objectives, and evaluation are still essential
Social media media types
Owned, earned, and paid
How to leverage social media types?
Maximize owned media
Public relations do not always translate to earned media so they must find other ways to encourage WOM
Paid media must drive customer engagement
Why develop a listening system?
An effective listening system is necessary in understanding and engaging an online audience
Social media monitoring
the process of identifying and assessing what is being said about a company, individuals, product, or brand
Involves sentiment analysis and text mining for specific key words
Google Alerts, Mention, Pulsar, and Brand Watch are some of the companies that help with social media monitoring
Failure to respond to criticism leads to larger crisis
Social media metrics
Only valuable if they are tied to performance indicators that show how SM directly impact the business
Buzz - volume of consumer created content for a brand on posts and impressions (how much are people talking about you)
Interest - number of likes and followers
Participation and engagement - number of comments, ratings, bookmarks, subscriptions, retweets, shares, and time spend on social media platform
Search engine ranks and results - how high is your ranking on search engine results for certain keywords
Influence - media mentions, bloggers reached, influence on consumers
Sentiment analysis - positive, negative, or neutral sentiment of posts
Website metrics - clicks and click-throughs
End of Chapter 18
Social Media Tools
Blog: a publicly accessible web page that functions as an interactive journal, whereby readers can post comments on the author’s entries
Microblog: blogs with post length limits
Useful for disseminating news, promoting longer blog posts, sharing link, announcing events, and promotion sales.
Facebook status updates are considered microblogging
Social networking sites: websites that allow individuals to connect–or network–with friends, peers, and business associates (LinkedIn)
Media sharing sites: websites that allow users to upload and distribute multimedia content like videos and photos (YouTube, Instagram, TikTok)
Social news sites: websites that allow users to decide which content is promoted on a given website by voting that content up or down (Reddit)
Location-based social networking sites: websites that combine the fun of social networking with the utility of location-based GPS technology (Facebook “check-ins”)
Review sites: websites that allow consumers to post, read, rate, and comment on opinions regarding all kinds of products and services
More than 70% of consumers say they trust online consumer ratings
Start of Chapter 19
What is price?
Price is that which is given up in an exchange to acquire a good or service. This is typically money but can also be time or other products.
Pricing Goals
Should be derived from overall marketing objectives, which in turn should be derived from corporate objectives
Common Pricing Goals (3):
Profit-Oriented (Achieving a target profit/return on investment)
Sales-Oriented (Achieving a target market share/sales volume)
Status Quo (Maintain current pricing or matching competition)
Profit Oriented Pricing Objectives
Profit Maximization: Setting prices so that profit is as high as possible. Increased customer satisfaction or decreased cost.
Target Return on Investment: Profits relative to investment. Firms typically aim for ROI’s between 10% & 30% but varies by industry.
Sales-Oriented Pricing Objectives
Market Share
Sales Maximization
Short-term objective to maximize sales to increase cash flow immediately. Should never be a long-run objective because it may mean little or no profit.
May be used to sell excess inventory (end of season sales)
Status Quo Pricing Objectives
requires little planning, passive policy. Suboptimal because it ignores value of product to customer.
Maintain existing prices
Meet competition’s prices
Pricing Strategies (3) Basic Approaches
Skimming Policy: Seller charges a relatively high price and then may lower the price at a later date to makes sales to more price-sensitive buyers. Ex: New Apple Products
Fits well with profit/ROI based objectives
Penetration Policy: Seller charges a relatively low price in order to grow a market, gain market share, and discourage competition from entering the market. Ex: Spirit Airlines
Fits well with market shares/sales-based objectives
Status Quo Pricing: Charging a price identical or very similar to that of your competiton
Situations When Price Skimming Is Successful
Better to test at higher prices than lower if sales are low

Advantages & Disadvantages of Penetration Pricing
Advantages:
Discourages or blocks competition from market entry
Boosts sales and provides large market share increases
Disadvantages:
Requires gear up for mass production
Strategy to gain market share may fail
Lower profit/unit
Pricing Influences
Demand/Consumer Influences
Environmental Influences (including the competition)
Product Influences (including PLC)
Promotion Influences
Place (Distribution) Influences
Demand Influences on Pricing Decisions
Primarily concerned with the nature of the target market and expected reaction of consumers to a given price or change in price.
How much of my product will consumers demand at a given price?
Primary considerations:
Demographic factors (number of buyers, expected consumption rate, willingness/ability to pay)
Used to determine market potential
Price elasticity
Demand Influences on Price: Elasticity
Price Elasticity - Consumers responsiveness or sensitivity to changes in price.
Inelastic Demand - An increase or decrease in price will not significantly affect demand. Consumers are NOT price sensitive.
Elastic Demand - Consumers buy more or less of a product when the price changes. Consumers are price-sensitive.
Factors that Affect Elasticity of Demand
Availability of substitutes - more subs (easy to switch) makes demand more elastic and vice versa.
Price relative to purchasing power - if a price/price change is so low that it is an inconsequential part of one’s budget, demand will be inelastic and consumers will not be sensitive to $ changes
Product durability - if the cost of a new product increases, people might elect to repair the product making people sensitive to $ (elastic)
Product Considerations in Pricing
Perishability
Stage in the Product Life Cycle
Distinctiveness
Perceived Quality & Value
Perishability
Discounting the products as they approach being no longer fit for sale
Products are perishable if the demand for them is confined to a specific time period (seasonal products)
Distinctiveness
Marketers can charge higher prices if they can successfully distinguish their products from those of their competitors
Branding and brand equity are used to make products distinctive
Prestige Pricing
Consumers typically have strong price/quality associations (i.e. high price = high quality)
Prestige pricing involves charging a high price to create a signal that the product is high quality or special/unique
Particularly effective when customer uncertainty is high
Pricing In the Product Life Cycle
Environmental Influences on Pricing: The Internet
Internet auctions - eBay
Second opinions from expert sites (KBB.com)
Increased product selection/comparison
Shopping bots – search the web for the best price
Promotional Influences
Tactics for fine-tuning the base price (base price - general price level at which the company expects to sell goods/services)
Discounts
Geographic Pricing
Special pricing tactics
Discounts, Allowances, Rebates and the Types
Discounts are used to encourage customers to do what they would not ordinarily do.
Quantity Discounts: Discounts for buying in quantity
Cash Discounts: Discounts for payment of a bill in cash
Functional Discounts (Trade Discount): Discounts
for performing functions, such as in-store display
Seasonal Discounts: Discounts for buying out of season
Special Pricing Tactics
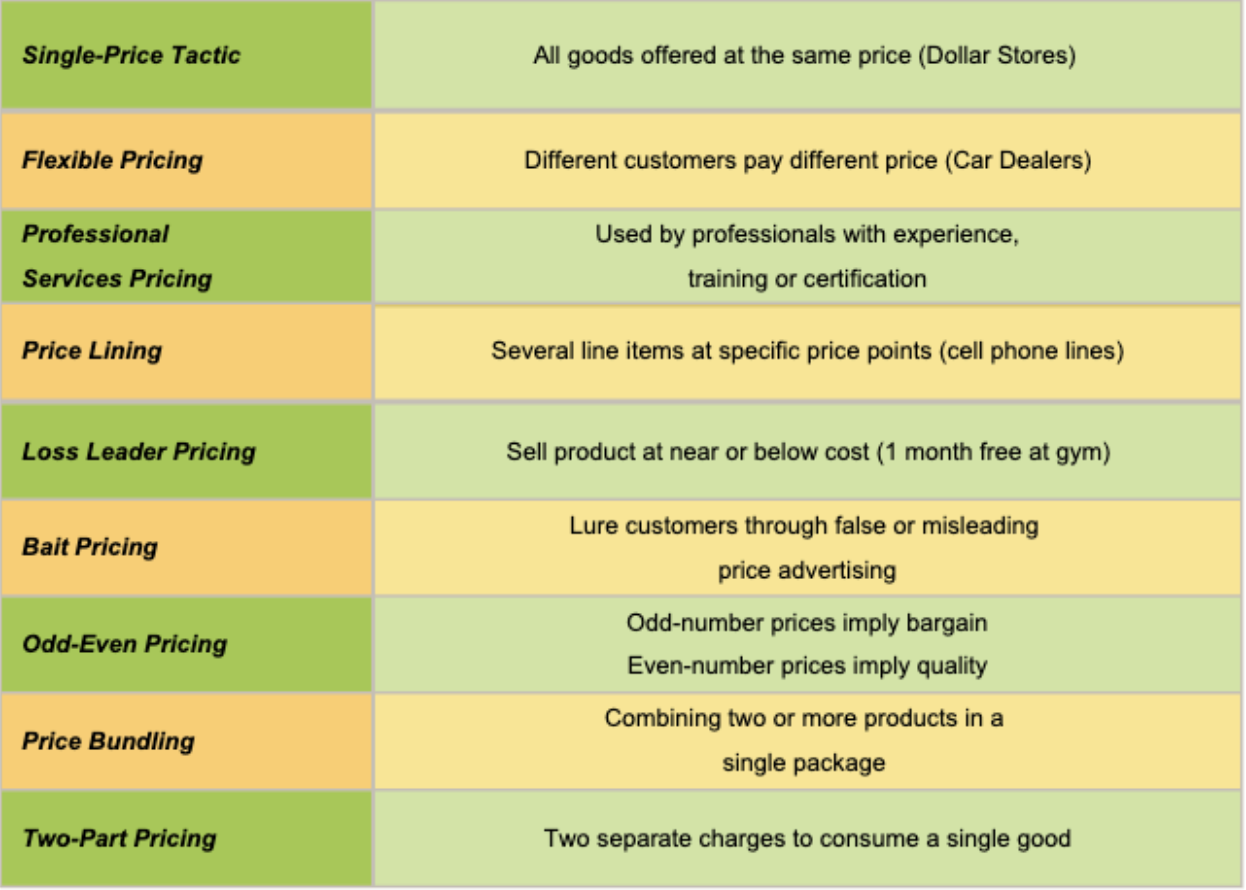
Even/Odd Pricing
Prices are set at one or a few cents below a round number in order to create the perception that the price is low (getting a good deal) or pricing evenly at the dollar to give a perception of high quality.
End of Chapter 19
Bundle Pricing
involves selling several products together at a single price in order to suggest a good deal