HOST Semester One
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:35 PM on 1/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
1
New cards
Chronometer
________ was invented, and then accurate timekeeping was there to use the sextant.
2
New cards
Astrolabe
Used measurements of stars and time to find longitude and latitude (especially at sea), not very accurate but gave users a good sense of where they were.
3
New cards
Tare
Setting a scale to zero (Can be used to set items to zero so that they are not counted in the measurement)
4
New cards
Aristocrat
Inherits money, title, and power.
5
New cards
Weights and Measures
Standard units that tell you how much you have of something.
6
New cards
Concave
________- Slightly dish- shaped (Like a dent)
7
New cards
Astrology
Trying to predict the future and personalities through star position.
8
New cards
Technology
Designing tools to solve problems.
9
New cards
Eratosthenes
276 B.C.E, head librarian at the library of Alexandria, Ptolemy.
10
New cards
Optics
The technology of seeing things (HOST def .)
11
New cards
Investigator
________ addresses consumer complaints.
12
New cards
Stonehenge
Giant stone structure, tracks solstices and served as a burial ground.
13
New cards
Contaminant
A something in a substance that makes it ________ (Not pure)
14
New cards
Net
________- Total amount after something is subtracted from Gross (________ Worth)
15
New cards
Sextant
Can be used to find longitude/latitude or the time with advanced calculations. Much more accurate than the astrolabe, but needed more advanced calculations.
16
New cards
Glass
Silica melted into a transparent material, often from sand with the contaminants removed.
17
New cards
Resources
Objects/Talents to use for practical purposes.
18
New cards
Metric System
A common measurement system almost used everywhere.
19
New cards
Tertiary Effect
Even larger changes caused by earlier sets of changes.
20
New cards
Vernal Equinox
First day of Spring, day /night same length.
21
New cards
European army officers
________ were almost always aristocrats and did not always know what they were doing.
22
New cards
Rectilinear Propagation of Light
Light always travels in a straight line.
23
New cards
Paleolithic
Old Stone Age
24
New cards
Neolithic
New Stone Age
25
New cards
Equator
The line that splits the Earth into the Northern and Southern hemisphere.
26
New cards
Metrology
The study of measurement
27
New cards
Periscope
A device equipped with mirrors to allow to see above or below obstacles.
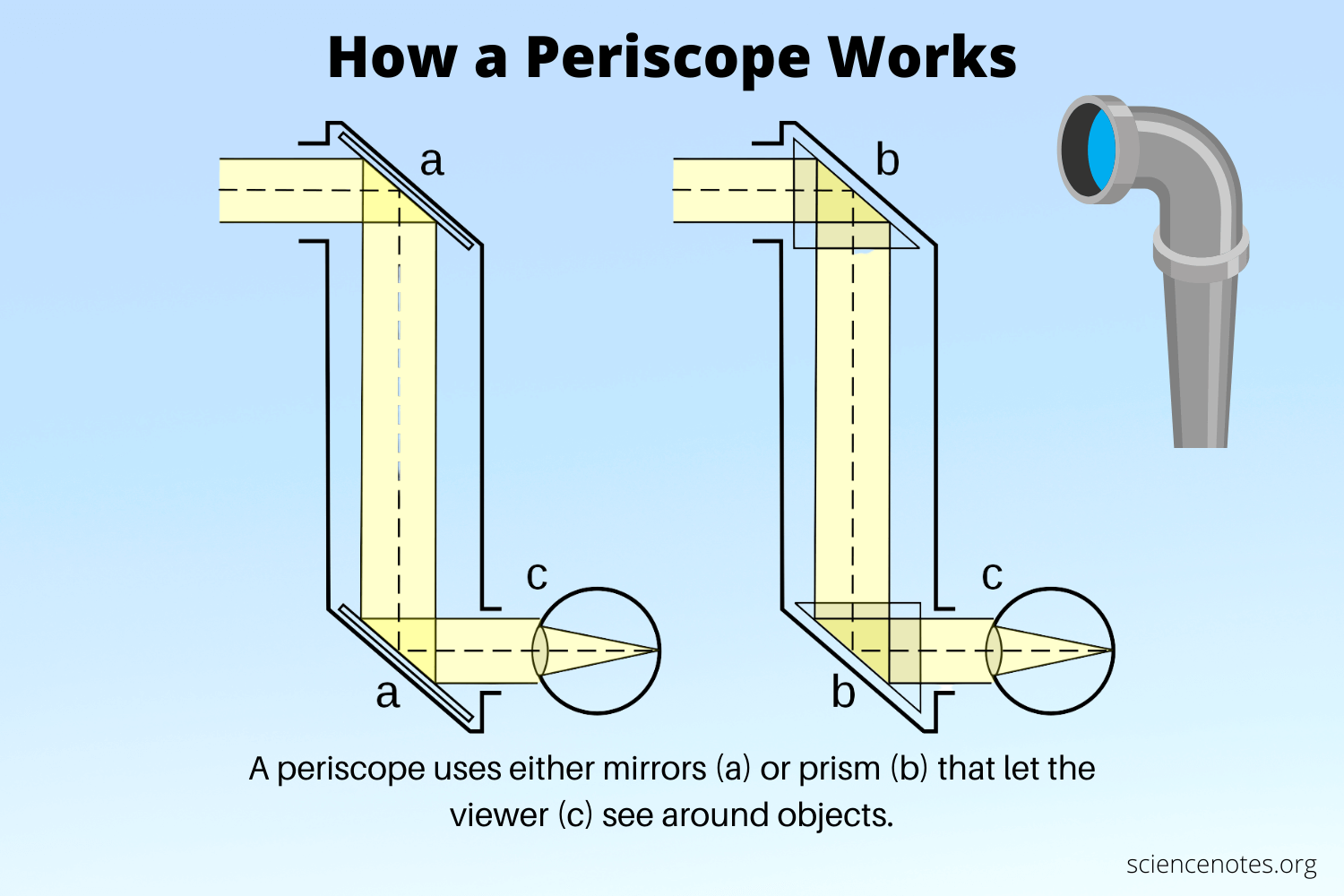
28
New cards
Prism
Solid geometric figure that reflects all light.
29
New cards
Chronometer
Accurate timekeeping device that could be used at sea
30
New cards
Aristocrat
Inherits money, title, and power
31
New cards
Technology
Designing tools to solve problems
32
New cards
Resources
Objects/Talents to use for practical purposes
33
New cards
Primary Effect
First, most immediate change caused by an event
34
New cards
Secondary Effect
Bigger changes caused by the first set of changes
35
New cards
Tertiary Effect
Even larger changes caused by earlier sets of changes
36
New cards
Idea
Imagining something that could be
37
New cards
Tare
Setting a scale to zero (Can be used to set items to zero so that they are not counted in the measurement)
38
New cards
Gross
Total Amount
39
New cards
Net
Total amount after something is subtracted from Gross (Net Worth)
40
New cards
Weights and Measures
Standard units that tell you how much you have of something
41
New cards
Metric System
A common measurement system almost used everywhere
42
New cards
Smoot
Height/length of Oliver R. Smoot, 5ft 7in
43
New cards
Optics
The technology of seeing things (HOST def.)
44
New cards
Stonehenge
Giant stone structure, tracks solstices and served as a burial ground
45
New cards
Astrolabe
Used measurements of stars to find longitude and latitude (especially at sea)
46
New cards
Sextant
Can be used to find longitude/latitude or the time with advanced calculations
47
New cards
Concave
Slightly dish-shaped (Like a dent)
48
New cards
Convex
Slightly bump-shaped
49
New cards
Rectilinear Propagation of Light
Light always travels in a straight line
50
New cards
Summer Solstice (Midsummer)
Longest day, shortest night (June 21), beginning of Summer
51
New cards
Winter Solstice (Yule)
Shortest day, longest night (December 21), beginning of Winter
52
New cards
Autumnal Equinox
First day of Autumn, day/night same length
53
New cards
Astronomy
Study of stars
54
New cards
Astrology
Trying to predict the future and personalities through star position
55
New cards
Eratosthenes
276 B.C.E, head librarian at the library of Alexandria, Ptolemy
56
New cards
Primary Effect of the Sextant
Users know where they were
57
New cards
Secondary Effect of the Sextant
Time was needed to use the sextant, which started a motion to invent an accurate clock that could work at sea
58
New cards
Tertiary Effect of the Sextant
Royal Naval Observatory, science/math linked to Navy
59
New cards
GMT
Greenwich Mean Time
60
New cards
Lenses
A clear piece of glass or plastic that changes the focus of an image
61
New cards
Primary Effect of Lenses
Images could be made to look larger or closer
62
New cards
Secondary Effect of Lenses
Grinding lenses was invented, or making lenses concave or convex
63
New cards
Tertiary Effect of Lenses
Important lens inventions were invented (Eyeglasses, binoculars, telescope, microscope, contact lenses)
64
New cards
Contaminant
A something in a substance that makes it contaminated (Not pure)
65
New cards
Glass
Silica melted into a transparent material, often from sand with the contaminants removed
Explore top notes
Federal Board Chemistry Class 9th PDF Book - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - TOUSEEF AHMAD
Updated 380d ago0.0(0)
Federal Board Chemistry Class 9th PDF Book - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - TOUSEEF AHMAD
Updated 380d ago0.0(0)