final exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/182
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
1
New cards
Ego-Dystonic
those who have them are aware they have a problem and tend to be distressed by their symptoms.
2
New cards
Ego-syntonic
the person experiencing them doesn't necessarily think they have a problem
3
New cards
DSM-5 Clusters
Contains ten distinct personality disorder daignoses, grouped into three clusters.
4
New cards
Charles Dawrin
introduced the theory of evolution; believed that reproduction was based on the "survival of the fit"
5
New cards
Simon and Binet
developed first IQ test commonly used today, first modern intelligence test
6
New cards
Ego-Dystonic
those who have them are aware they have a problem and tend to be distressed by their symptoms.
7
New cards
Personality disorders
Psychological disorders marked by inflexible, disruptive, and ednuring behavior patterns that impair social and other functioning; -Whether the sufferer recongizes that or not.
8
New cards
Personality disorder not otherwise specified (PDNOS)
The prevalence of this diagnosis suggests that while clinicians can identify a personality disorder in a patient, figuring out the details of the condition can be messy and difficult.
9
New cards
Dimentional Model
Would assess a patient not with the aim of diagnosing one disorder or another, but instead simply finding out that they rank high on narcissism and avoidance.
10
New cards
Four Dimensions on a scale
Culture
mind
life
Matter
mind
life
Matter
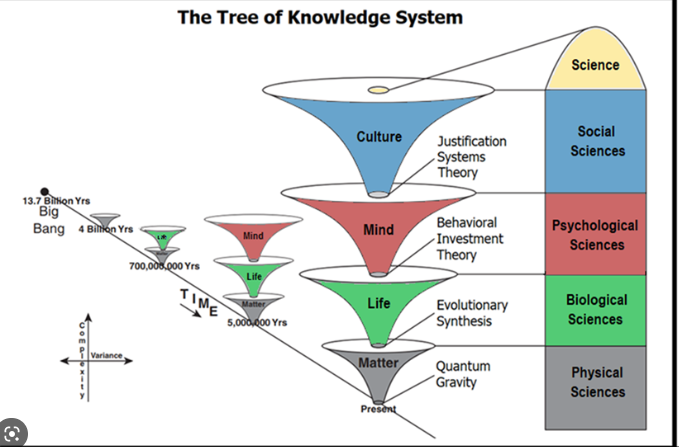
11
New cards
Border line personality Disorder (BPD)
A complicated set of learned behaviors and emotional responses to traumatic or neglectful environments, particularly in childhood. In a sense, people with this disorder learn that rage or self-harm helped them cope with traumatic situations, but as a result, they also end up using them in non-traumatic situations.
12
New cards
Antisocial Personality disorder
A personality disorder in which a person (usually men) exhibits a lack of conscience for wrongdoing, even toward friends and family members. Their destructive behavior surfaces in childhood or adolescence, beginning with excessive lying, fighting, stealing, violence, or manipulation.
13
New cards
Impairment in fear conditioning
Lower than normal response to things that typically startle or frighten children like loud and unpleasant noises.
14
New cards
Conduct Disorder in kids
A conduct disorder is characterized by a recurring pattern of behaviour that violates the fundamental rights of others. Children with conduct disorders are self-centered and indifferent to the feelings of others, and they may bully, damage property, lie, or steal without remorse.
15
New cards
Elizabeth Cochran
a journalist assumed the alias Nellie Bly and feigned a mental illness to report on the truly awful conditions inside psychiatric hospitals in the US, which were known as asylums at the time. She found rotten food, cold showers, prevalent rats, abusive nurses, and patients being tied down in her famous expose "Ten Days in a Mad House".
16
New cards
David Rosenhan
did study in which healthy patients were admitted to psychiatric hospitals and diagnoses with schizophrenia; showed that once you are diagnosed with a disorder, the label, even when behavior indicates otherwise, is hard to overcome in a mental health setting.
17
New cards
distinctions between cults and traditional religions
A religion is part of a larger culture, and its members are free to come and go as they like. A cult is often anti-social, confining its devotees' social lives to other cult members. \n -A cult is often led by a human leader who is
18
New cards
Charles Darwin
Darwin proposed that species can change over time, that new species come from pre-existing species, and that all species share a common ancestor.
19
New cards
Natural selection
the process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change.
20
New cards
Psychology Disorder
deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional patterns of thoughts, feelings, or behaviors.
21
New cards
Deviant
A person who breaks significant societal or group norms
it's used to describe thoughts and behavior that are different from most of the rest of your cultural context.
it's used to describe thoughts and behavior that are different from most of the rest of your cultural context.
22
New cards
Disorder
a disturbance in the normal function of a part of the body
23
New cards
Dysfunction
when a person's ability to work and live is clearly, often measurably, impaired.
24
New cards
Medical model
The Medical Model champions the notion that psychological disorders have physiological causes that can be diagnosed on the basis of symptoms, and treated, and sometimes even cured.
25
New cards
Biopsychological model
a model that addresses how biological, psychological, and social factors interact and affect psychological health
26
New cards
DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders)
Each new edition incorporates changes based on the latest research but also how our understanding of mental health and behavior evolves over time.
27
New cards
social psychology
which focuses on the power of the situation. It examines how we think about, influence, and relate to one another in certain conditions.
28
New cards
Attribution theory
This theory simply suggests that we can explain someone's behavior by crediting either their stable, enduring traits - also known as their disposition - or the situation at hand.
29
New cards
fundemnetal attribution Error
The tendency for observers when analyzing another's behaviour to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition
30
New cards
central route persuasion
Involves calling on basic thinking and reasoning to convince people.
31
New cards
peripheral route persuasion
influences people by way of incidental cues like a speaker's physical attractiveness or personal relatability
32
New cards
How do attitudes and behaviour connect
Our attitudes can be affected by our behaviours
33
New cards
Foot-in-theDoor phenomenon
The tendency for people to more readily comply with a certain big request after they've first agreed to smaller, more innocuous requests
34
New cards
Standford Prison Experiment
philip zimbardo randomply assigned college students to either be prisoners or guards and watched how they became the characters they were assigned--lasted only 6 days
35
New cards
Theory of cognitive dissonance, how it eases individual tension
The notion that we experience discomfort, or dissonance, when our thoughts, beliefs, or behaviours are inconsistent with each other.
36
New cards
Prejudice
''Prejudgement'' an unjustified, typically negative, attitude toward an individual or group
37
New cards
The four four categories of prejudice
1. unprejudiced nondiscriminators,
2\. unprejudiced discriminators,
3\. prejudiced nondiscriminators, and
4\. prejudiced discriminators.
\
38
New cards
Dual thought process
while we're aware of our explicit thoughts, or implicit cognition still operates under the radar, leaving us clueless about its effect on our attitudes and behavior.
39
New cards
Discrimination
in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a conditioned stimulus and stimuli that do not signal an unconditioned stimulus
40
New cards
Implicit Association Test (IAT)
A test implemented in the late 1990's to try to gauge implicit attitudes, identities, beliefs, and biases people are unwilling or unable to report.
41
New cards
Strereotypic condition
Your keystrokes correspond to stereotypical pairs.
42
New cards
Counter-stereotypic condition
situation in which an individual behaves in a way that contradicts the stereotypes associated with their group.
43
New cards
just-world phenomenon
the tendency for people to believe the world is just and that people therefore get what they deserve and deserve what they get
44
New cards
In-group out group phenomenon
Prejudices can also be driven by the "us vs. them''.
45
New cards
Social constructs
Something that we as a society create and enforce
46
New cards
Gender stratification
The unequal distribution of wealth, power, and privilege across genders.
47
New cards
Gendered media influence
representation of gender roles, identities, and stereotypes in various forms of media such as television, movies, music, and advertising.
48
New cards
Sexism
the belief that one sex is innately superior to the other
49
New cards
Raewyn Connell
In Australia, she is a sociologist who is most known for developing concept of hegemonic masculinity as a part of men's studies.
50
New cards
Patriarchal dividends
Benefits that accrue to men simply because they are men
51
New cards
anticipatory socialization
processes of socialization in which a person rehearses for future positions, occupations, and social relationships
52
New cards
Second Shift
In which women come home from work to more work - Cooking laundry, childcare- whereas men are more likely to spend their time in leisure after work.
53
New cards
emphasized femininities
dominant images of the supposedly ideal woman; includes dependence, sexual receptivity, motherhood, and subordination by men
54
New cards
Title IX
Passed in 1972, Title IX is a law that prohibits discrimination on the basis of sex in public schools.
55
New cards
Impact of Title IX
Title IX required that schools offer girls just as many opportunities to play sports as boys.
* it also forced colleges to increase their funding for female sports scholarships, increase in women pursuing higher education.
* it also forced colleges to increase their funding for female sports scholarships, increase in women pursuing higher education.
56
New cards
Pink collar jobs
These jobs with the highest concerntrations of women tend to come with both lower prestige and lower pay.
57
New cards
glass ceiling
The invisible barrier that stops women's advancement to the top levels of an organization.
58
New cards
Gender wage gap
the difference between wages earned by men and wages earned by women
\-Fewer women are offered higher paying job positions
\-Fewer women are offered higher paying job positions
59
New cards
Socialization of women
Gender socialization is also part of why women might choose to opt out of the workforce, to care for children.
60
New cards
Crisis of masculinity
The idea that men's perception of what a man is and how he ought to behave has been undermined by social and economic changes.
61
New cards
benevolent sexism
acceptance of positive stereotypes of males and females that leads to unequal treatment
62
New cards
Rebecca Cann
Discovered mitochondrial eve
63
New cards
Louis & Mary Leakey
anthropologists that were the discovers of the bones of early man, they defined a creature called homo erectus (upright man).
64
New cards
Jane Goodall
English zoologist noted for her studies of chimpanzees in the wild
65
New cards
Hans Seyle
Created General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)- alarm, resistance, exhaustion
66
New cards
Lorge-Thorndike Intelligence Test
Nonverbal intelligence test that measures cognitive ability in children and adults who have difficulty with verbal tasks, such as those who have limited language skills or hearing impairments
67
New cards
Sigmund Freud
Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a method of treating mental illness through talk therapy and understanding the unconscious mind and its influence on behaviour and emotions
68
New cards
Cults vs. Religions
A religion is part of a larger culture, and its members are free to come and go as they like. A cult is often anti-social, confining its adherents' social lives to other cult members and worshipping a living leader.
69
New cards
neurosis vs psychosis
*Neurosis* is a general term referring to mental distress that, unlike psychosis, does not prevent rational thought or daily functioning.
*Psychosis* is a generic psychiatric term for a mental state involving the loss of contact with reality, causing the detioration of normal social functioning
*Psychosis* is a generic psychiatric term for a mental state involving the loss of contact with reality, causing the detioration of normal social functioning
70
New cards
distiction between nature and nurture
"nature" is Determined by genetic structure that a child inherits from their parents at the time of conception;•Can occur no matter where or how your grow up; while "nurture" is Learning that occurs when our behaviour changes as a result of experiences.
71
New cards
Intrinsic
Need for self-esteem, self-fulfillment and self-determination
Approach emphasizes personal freedom, choice, self-determination and striving for personal growth;
Approach emphasizes personal freedom, choice, self-determination and striving for personal growth;
72
New cards
Different types of intelligence
analytical, or problem-solving intelligence,
creative intelligence, or the ability to adapt to new situations,
practical intelligence for everyday tasks
creative intelligence, or the ability to adapt to new situations,
practical intelligence for everyday tasks
73
New cards
Abraham Maslow
1. Physiological needs: basic needs for survival such as food, water, shelter, and sleep
2. Safety needs: needs for security and stability, such as safety from physical and emotional harm
3. Love and belonging needs: needs for social interaction, love, and a sense of belonging
4. Esteem needs: needs for self-esteem, self-respect, and respect from others
5. Self-actualization needs: needs for personal growth, self-fulfillment, and realizing one's potential.
74
New cards
Eugene Aserinsky
He was the first to observe periods of rapid eye movements in sleeping infants in the early 1950s.
75
New cards
Nathaniel Kleitman
sleep researcher who first discovered that dreams occur in REM and about the REM rebound effect
76
New cards
Francis Crick
English biochemist who (with Watson in 1953) helped discover the helical structure of DNA (born in 1916)
77
New cards
Erich Fromm
his theory centered around the need to belong and the loneliness that freedom can bring
78
New cards
Rosalind Cartwright
She hypothesized that dreaming, particularly during REM sleep, is a way to process emotions experienced during the day.
79
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
Developed an experiment testing the concept of the conditioned reflex.
80
New cards
Jonathan Winson
Developed an experiment testing the concept of the conditioned reflex.
81
New cards
B.F. Skinner
Behaviorist that developed the theory of operant conditioning by training pigeons and rats
82
New cards
Jenson & Shockley
Shockley is credited with inventing the junction transistor and later the three-layer diode, which formed the basis for all modern electronic devices.
83
New cards
George Gerbner
communication professor who was a leading researcher on media violence; he estimated that by the age of 18, the average U.S. viewer has witnessed 32,000 murders and 40,000 attempted murders on television
84
New cards
Auguste Comte
founder of sociology
85
New cards
Herbert Spencer
English philosopher and sociologist who applied the theory of natural selection to human societies (1820-1903)
86
New cards
Emile Durkheim
\-Father of sociology, pioneer of modern social research and established the field as separate and distinct from psychology and politics
\-Major proponent of functionalism
\-Argued that modern society was more complex than primitive societies because they were all similar, shared a common language. Even when people were dissimilar, they relied on each other to make society function.
\-Major proponent of functionalism
\-Argued that modern society was more complex than primitive societies because they were all similar, shared a common language. Even when people were dissimilar, they relied on each other to make society function.
87
New cards
Karl Marx
founder of modern communism
88
New cards
Weber & Blumer
Weber: known for his contributions in the areas of social action, social stratification, and the concept of the "ideal type."
Blumer: is best known for his concept of "symbolic interaction" which emphasizes how people interact with one another and interpret their experiences
Blumer: is best known for his concept of "symbolic interaction" which emphasizes how people interact with one another and interpret their experiences
89
New cards
Alfred Bandura
behaviorist who looked at personality and self-efficacy and reciprocal determinism
90
New cards
Homo Habilis
(man of skill) first to make stone tools
91
New cards
Neanderthal
Closest extinct human relative. Fossils found in Neander Valley Germany. Lived in Europe, Asia, Middle East. Cold-weather adapted. Social structure, tools, buried dead, hunted.
92
New cards
Cro-Magnon
a species also referred to as Homo Sapiens; seem to have replaced Neanderthals
93
New cards
Homo Erectus
extinct species of primitive hominid with upright stature but small brain
94
New cards
Australopithecus
The earliest humanlike creature that flourished in eastern and southern Africa 3 to 4 million years ago
95
New cards
Sahelanthropus tchadensis "Toumai"
6-7 million year old skull, oldest possible human ancestor yet found
96
New cards
Hans Selye
(1907-1982) Psychologist who researched a recurring response to stress that he called the general adaptation syndrome.
97
New cards
Lorge-Thorndike
Intelligence Test is a nonverbal measure of general intelligence that was developed by Ivan Lorge and Robert Thorndike in the 1940s.
98
New cards
emotions
mental and physical reactions to something in our environment or something we think of or remember
99
New cards
STRESS
the reaction of the body and mind to everyday challenges and demands
100
New cards
EUSTRESS
A positive stress that energizes a person and helps a person reach a goal