physics p2 : forces
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
unit : s
unit : m/s ^2
unit : m
unit : m/s
unit : m/s
whats a force
a push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object
what are contact forces
forces that act between two objects that are physically touching each other
what are non contact forces
forces between two objects that aren’t touching
whats an example of a contact force
friction
what are examples of non contact forces
electrostatic, magnetic and gravitational forces
whats an interaction pair
a pair of equal and opposite forces acting on two different objects
whats a resultant force
the overall force on a point or object
is a force a vector or a scalar
vector
what is a free body force diagram
a diagram of an object with arrows drawn to show the direction and size of the forces acting on the object
whats a non zero resultant force
it means the forces are unbalanced
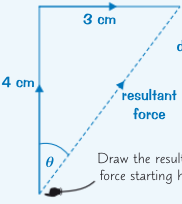
how do you use scale drawings to find the resultant force
draw a scale diagram drawing the forces tip to tail and using a sensible scale (e.g. 1cm=1N)
measure the length if the resultant force by measuring from the start of the first force to the end of the last force
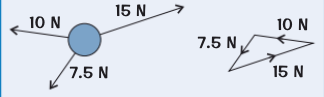
when is an object in equilibrium
if all the forces on an object are balanced
the forces acting on an object are drawn to scale and tip to tale, forming a closed loop. What does this say about the resultant force acting on an object
the resultant force is 0 as the forces are balanced
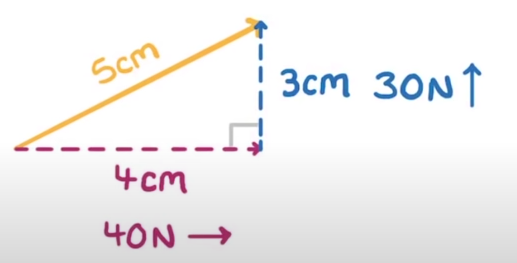
what does it mean when you resolve a force?
you split the force into 2 forces that are at right angles to each other. The two forces have the same original effect as the original force
whats newtons first law
an object will remain stationary or at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force
whats newtons second law
the force acting on an object is equal to its rate of change of momentum (meaning any resultant force will produce an acceleration)
whats the formula for newtons second law
force = mass x acceleration (F=ma)
what happens if there is no resultant force on a moving object
it will carry on moving at the same velocity
what do you need to keep moving when there is friction
a driving force (e.g. thrust)
what does an object do if the driving force is equal to the friction force
the object will stay at a steady speed
what does an object do if the driving force is greater than the friction force
the object will accelerate
what does an object do if the driving force is less than the friction force
the object will decelerate
what is terminal velocity
as the air resistance increases, so will the air resistance
terminal velocity is when the air resistance equals the weight and the resultant force equals 0
whats the resultant force
the combination of all the forces acting on an object
what causes air resistance
the moving object colliding with the particles of air
The size of the air resistance is dependent on the object's ______.
surface area and it velocity
We say an object has reached 'terminal velocity' when it is falling with a _________ velocity.
constant
what is inertia
how difficult it is to change an objects velocity
whats the forumla for interial mass
force / acceleration
whats newtons 3rd law
when two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal and opposite
whats the normal contact force
the force that surfaces exert to prevent solid objects from passing through each other
how do objects move forward if according to newtons 3rd law the forces objects exert on each other are equal and opposite
a high force or a small mass
whats the equation for momentum
momentum = mass x velocity
whats the unit used for momentum
kgm / s
kiloram metres per second
whats the law of conservation of momentum
in a collision when no other external forces act, momentum is conserved (the total moment after the collision if the same as it was before it)
whats the equation linking change in momentum, force and time
force x time = change in momentum
whats an elastic collision
where the total energy in the kinetic energy stores colliding is the same before and after the collision
whats a inelastic collision
where some of the energy in the kinetic energy stores is transferred to others stores
what is gravity
the force of attraction between masses
what is meant by the weight of an object
the force acting on an object due to gravity
what is the equation for gravitational force (weight)
weight = mass x gravitational field strength
w = mg
what is gravitational potential energy
the energy it has due to its height in a gravitational field
what is the equations for gravitational potential energy
gravitational potential energy = mass × gravitational field strength × height
gpe = mgh
what 2 factors affect the strength of gravitational attraction between 2 objects
the mass
the distance
whats kinetic energy
the kinetic energy of an object is the energy it possesses due to motion
whats the formula for kinetic energy
kinetic energy = 1/2 × mass × (speed)2
what is power
the rate at which energy is transferred, or the rate at which work is done
whats the formula for power
power = energy / time
p = E/t
what is work done
refer to the energy transfer that occurs when a force is used to move an object by a certain distance
whats the unites for work done
watts
whats the equation for work done
work done = force × distance
W = F s
whats inelastic deformation
the change in the shape of an object which can not be reversed once the forces that are stretching it have been removed (object will not return to original shape)
what does spring contant mean
a measure of how many newtons or force