Chapter 4 Anatomy (tissues and integumentary)
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Epithelium
Simple cells that cover a body surface or line a body cavity. Divided into simple (one cell layer for diffusion) and stratified (multiple cell layers for protection)
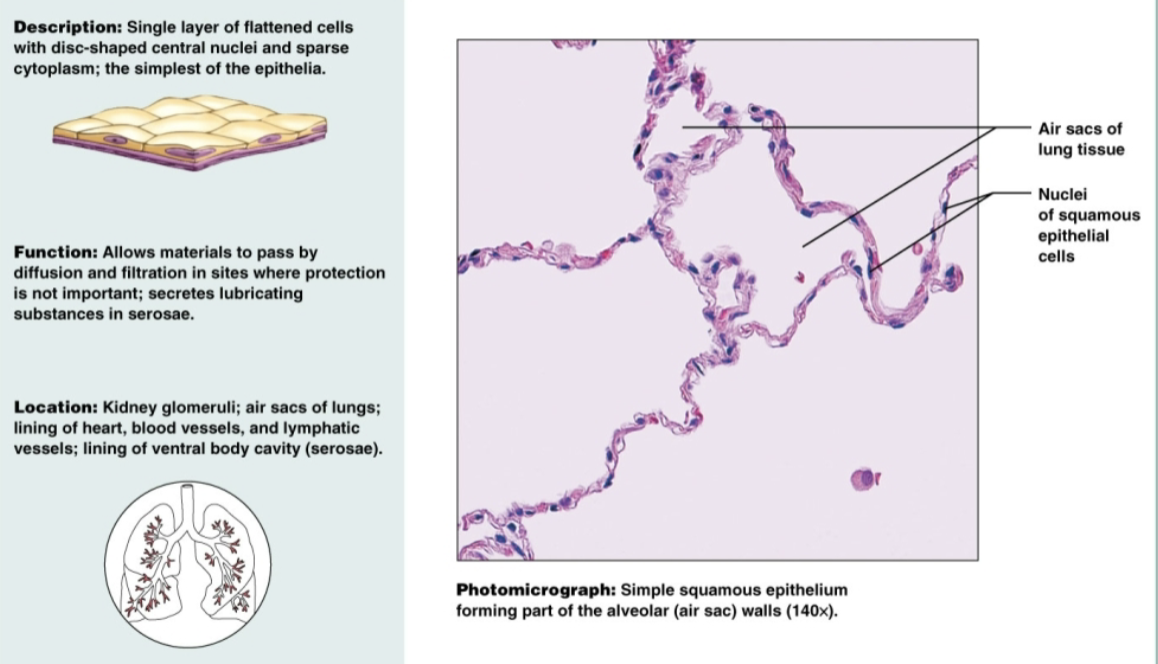
Simple squamous epithelium
single-layer of flat, sheet-like cells that line various surface in the body. Allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration
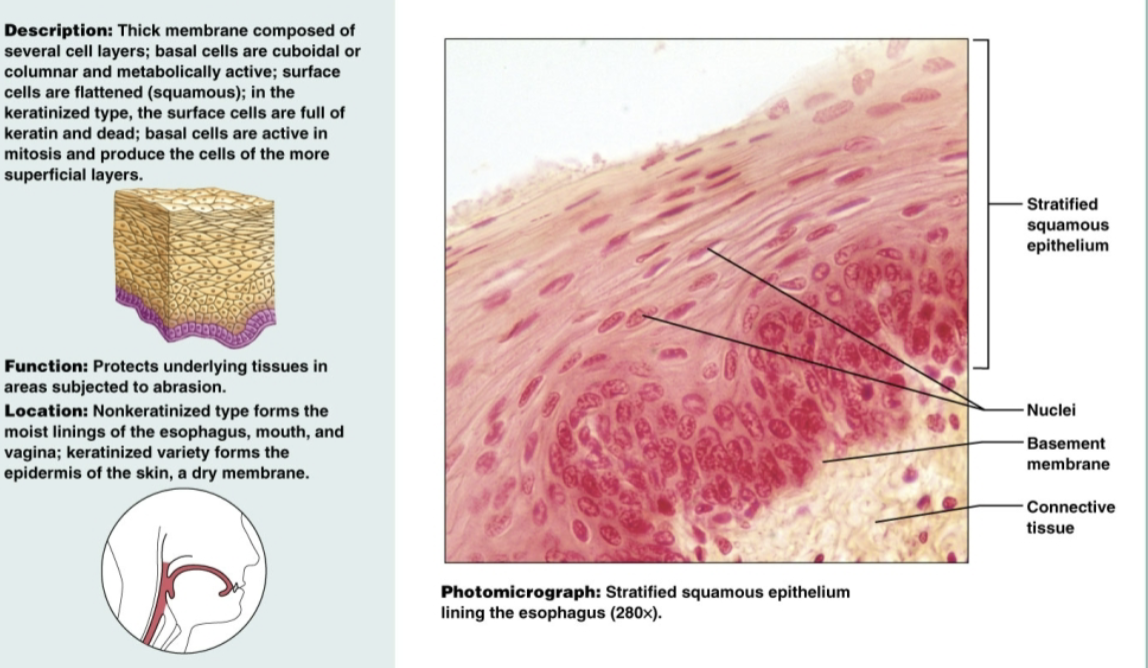
Stratified squamous epithelium
multiple layers of flat, sheet-like cells that serve as protection for underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion. Non-keratinized types form moist linings of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina. Keratinized forms the epidermis of the skin
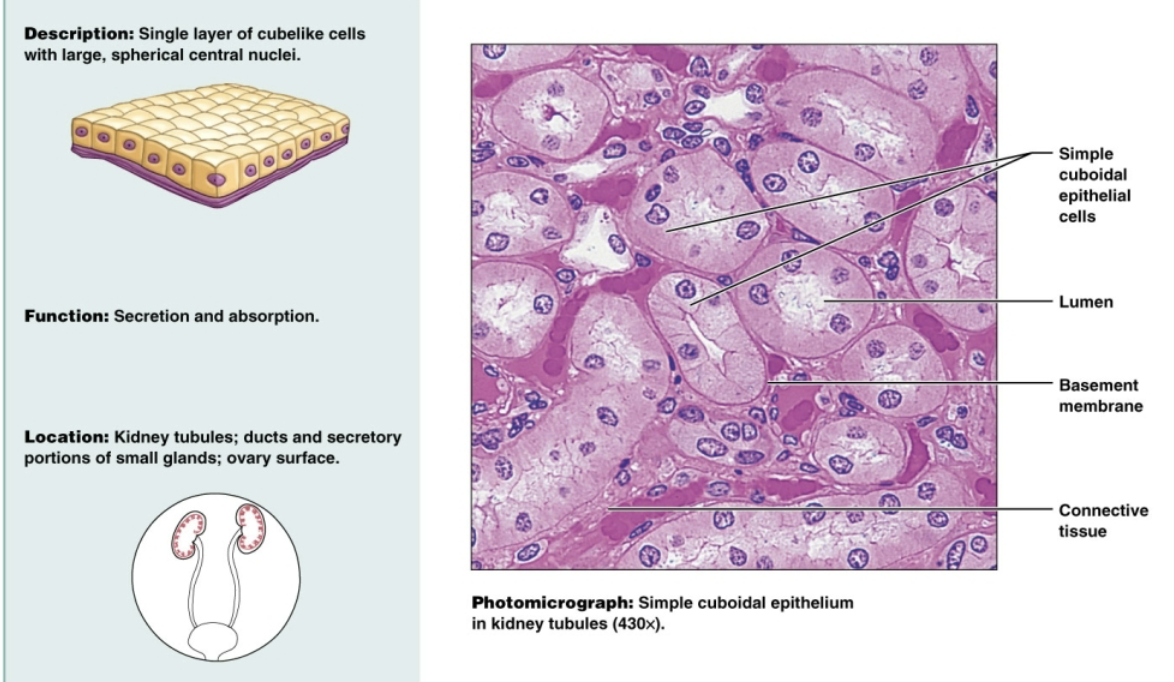
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Single layer of cube-shaped cells with large, spherical central nuclei. Functions to secrete and absorb in the kidney tubules, ovary surfaces, and secretory portions of small glands
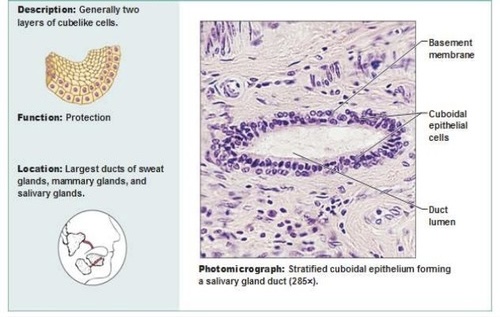
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Two layers of cube-like cells. Functions to protect large ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands
Simple columnar epithelium
single-layer of elongated, cylindrical cells with oval nuclei. Functions to absorb and secrete mucus in the digestive tract, gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands
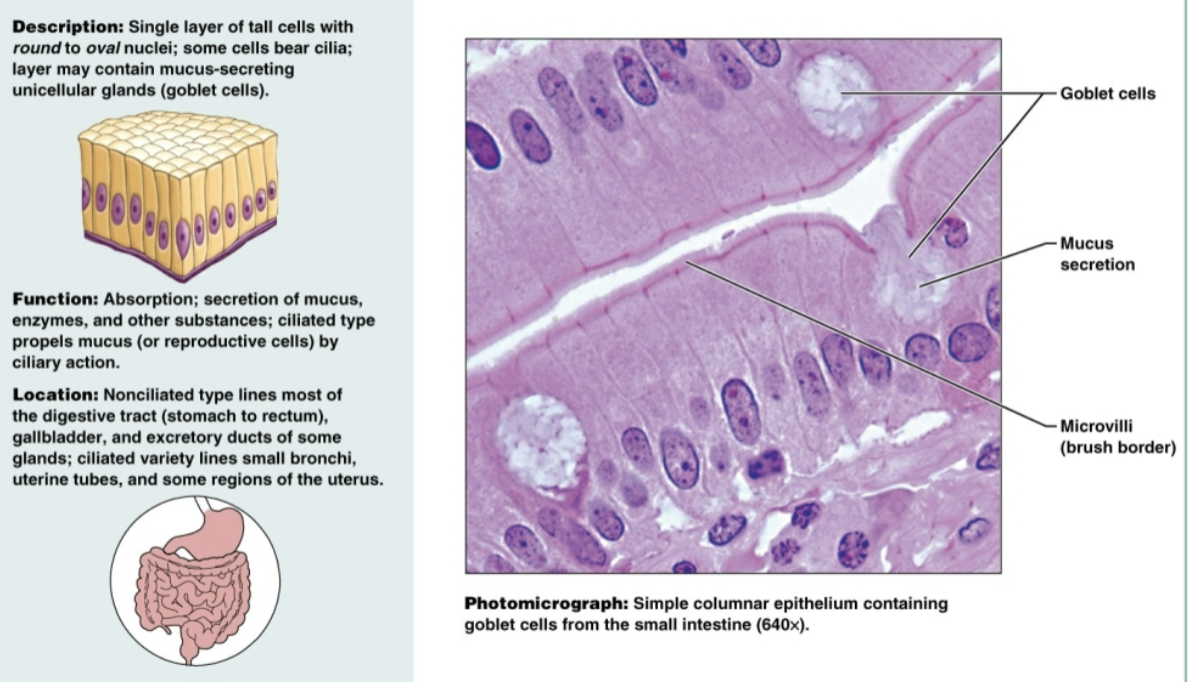
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
Single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching free surface; nuclei seen at different levels. Functions to secrete substances, particularly pushing mucus in trachea
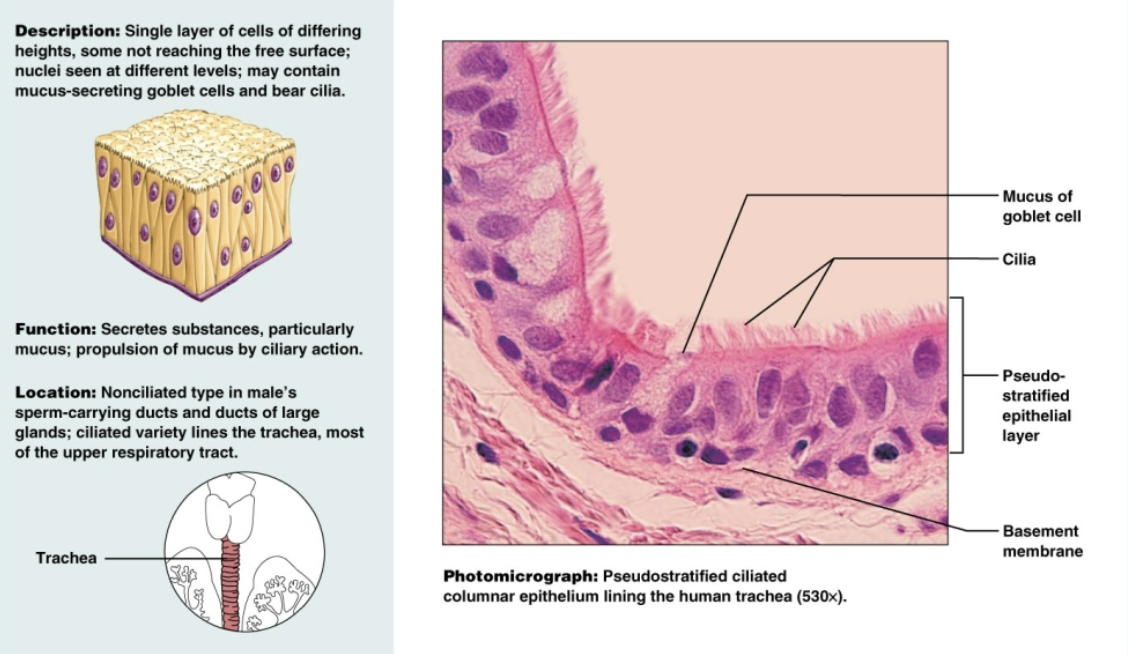
Transitional epithelium
a specialized type of epithelium that combines both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal cels. Functions to stretch readily to accommodate volume changes in urinary tract
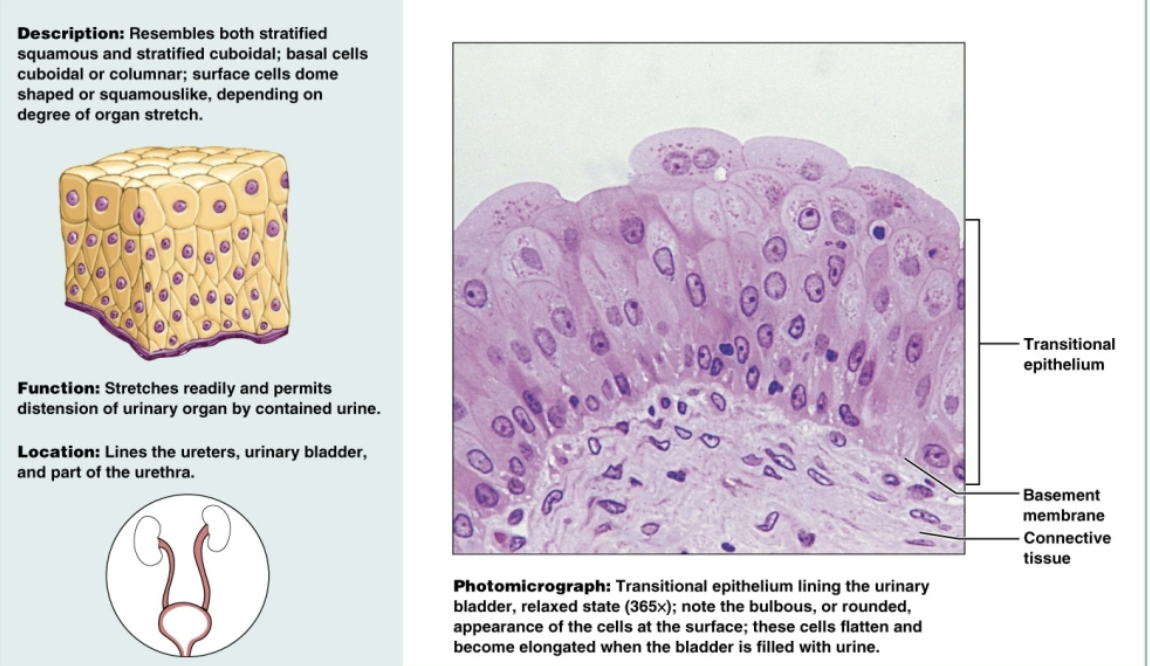
Stratified columnar epithelium
several cell layers; basal cells usually cuboidal, superficial cells elongated and columnar. Functions to protect and secrete. Is rare in body and covers small amounts in male urethra and large ducts in some glands
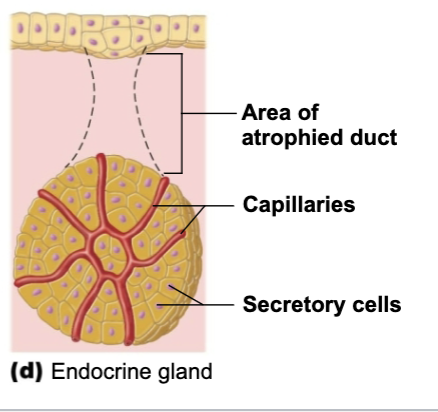
Endocrine gland
gland that’s ductless and opens to surface of cavity. Enters blood or lymph system
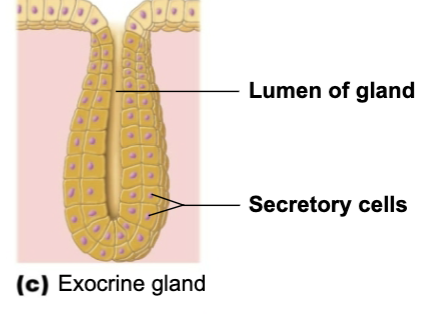
Exocrine gland
gland that secretes surface of skin
Glands
Makes and secrete product/hormones. Considered epithelial
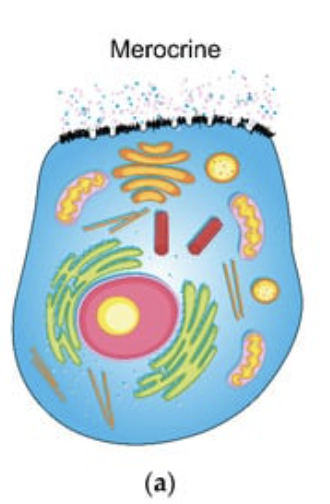
Merocrine gland
Type of exocrine gland that secretes substances directly into the duct by exocytosis (fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane)
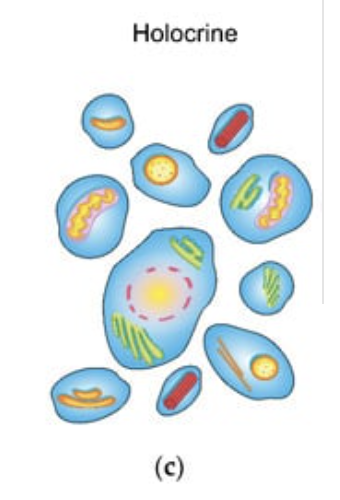
Holocrine glands
Type of exocrine gland that secretes substances by rupturing the entire cell
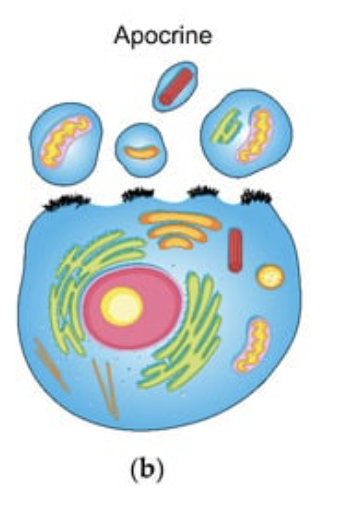
Apocrine glands
Type of exocrine gland that secretes substances by budding off a portion of the cell membrane and cytoplasm into the duct
Collagen fibers
the most abundant and strongest component of connective tissue. Found in bones, tendons, cartilage
Elastic fibers
component of tissue that stretches and recoils easily. Found in skin, lungs, blood vessels
Reticular fibers
component of tissue that are a network of thin strands used as supportive framework. Every tissue type has a mix of these fibers. Found in lymphoid organs, bone marrow, and liver
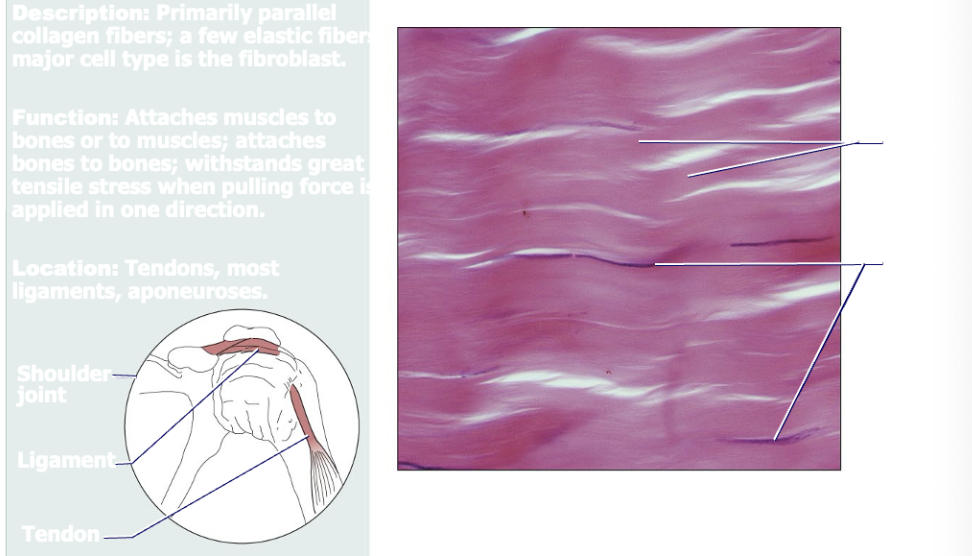
Dense regular tissue
Primarily parallel collagen fibers; a few elastic fibers. Major cell type is fibroblast. Functions to attach muscles to bones, muscles to muscles, and bones to bones. Very strong
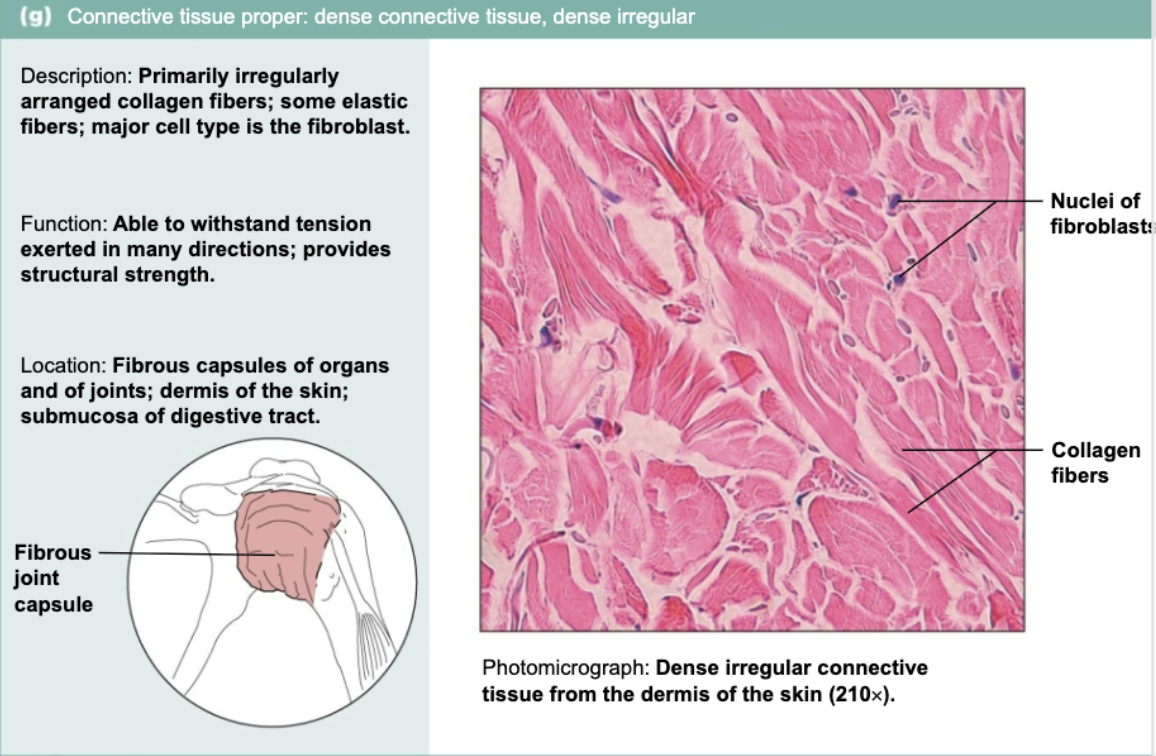
Dense irregular connective tissue
Primarily irregularly arranged collagen fibers and some elastic fiber. Major cell type of fibroblast. Moves in all different directions to support joints
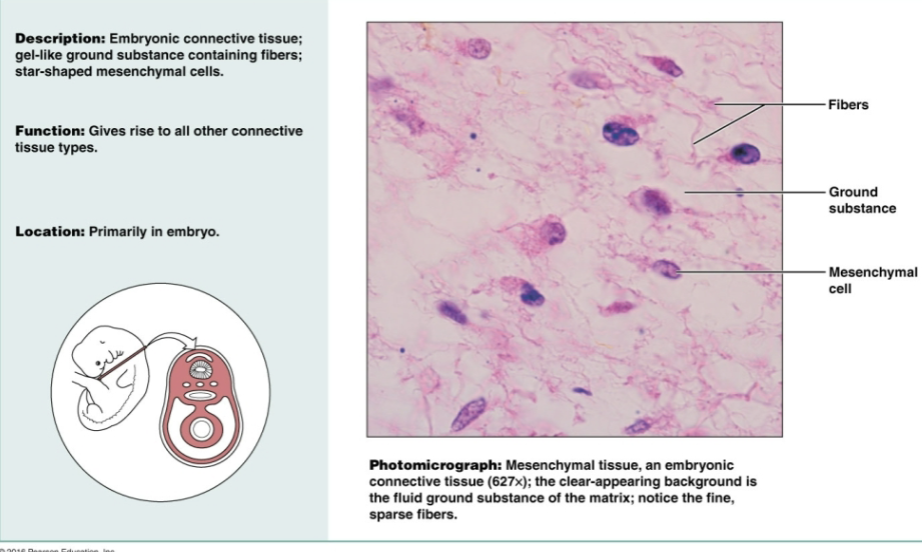
Embryonic connective tissue
Gel-like ground substance containing fibers, star-shaped mesenchymal cells. Functions to give rise to all other connective tissue types in embryo
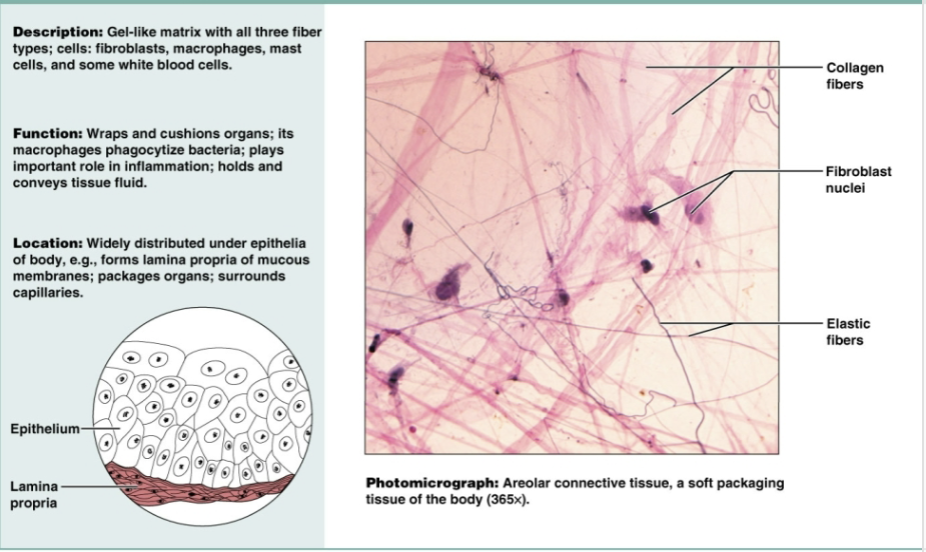
Areolar loose connective tissue
Gel-like matrix with all three fiber types. Functions to wrap and cushion organs; plays important role in inflammation that holds and conveys tissue. Widely distributed under epithelial of body
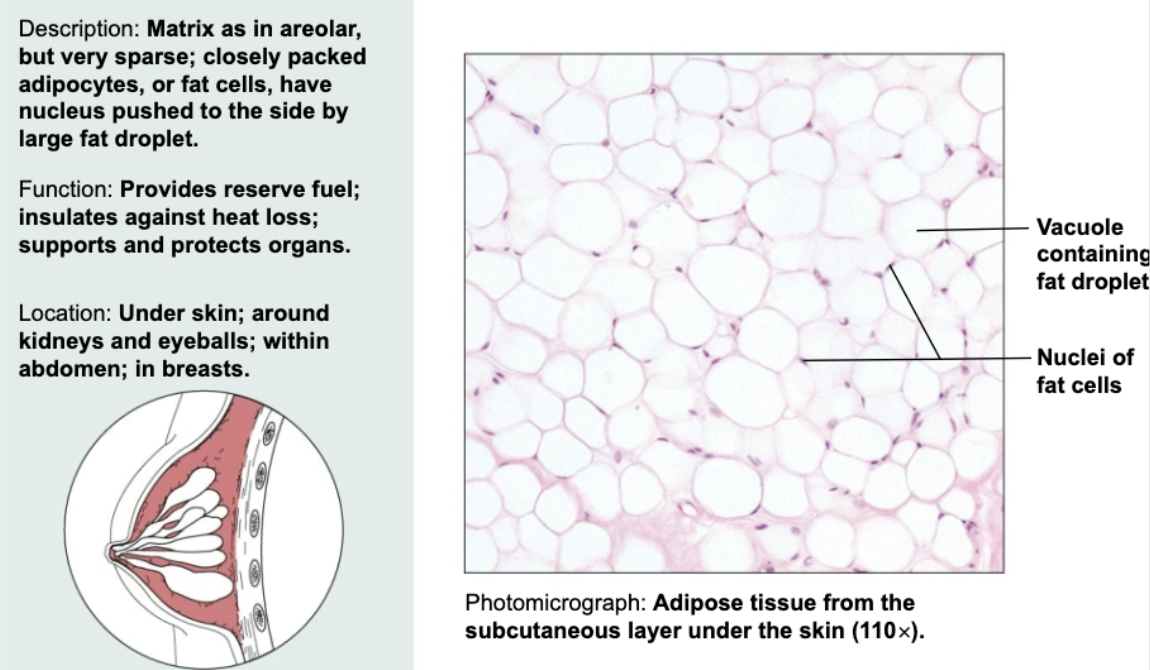
Adipose loose connective tissue
Matrix but very sparse. Closely packed fat cells have nucleus pushed to the side by large fat droplets. Functions to reserve fuel, insulate heat loss, and support organs. Found under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, and within breasts
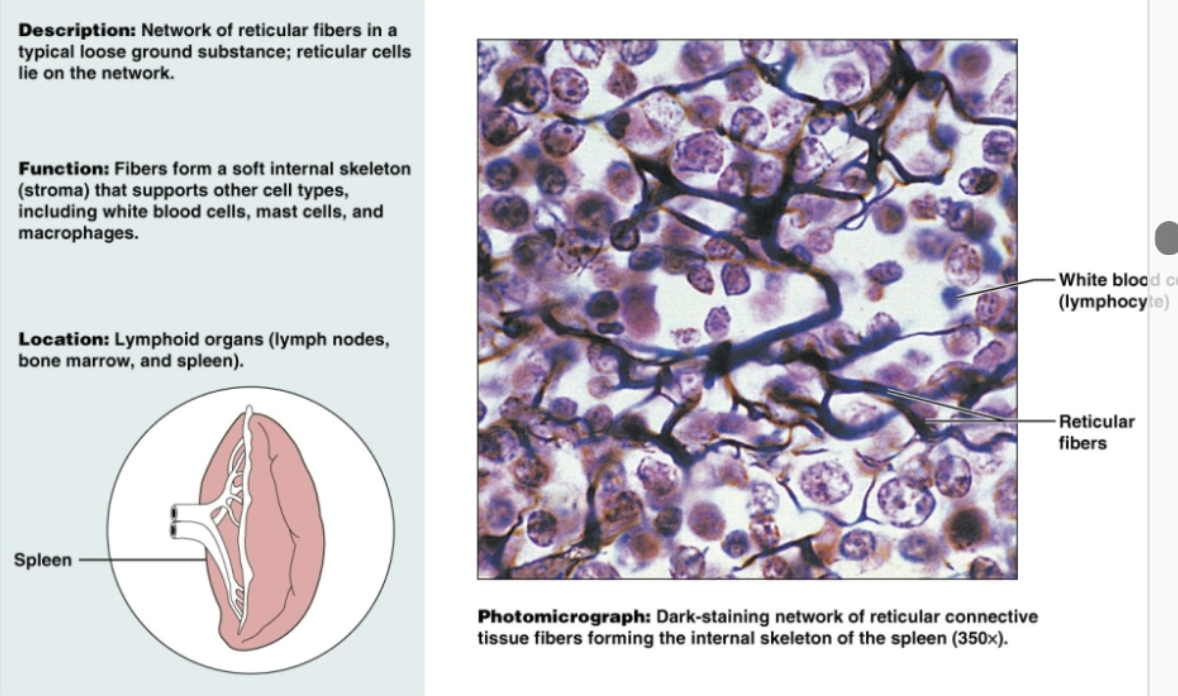
Reticular loose connective tissue
Network of reticular fibers in a loose ground substance. Functions to form soft internal skeleton that supports other cell types, including white blood cells and mast cells. Found in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen)
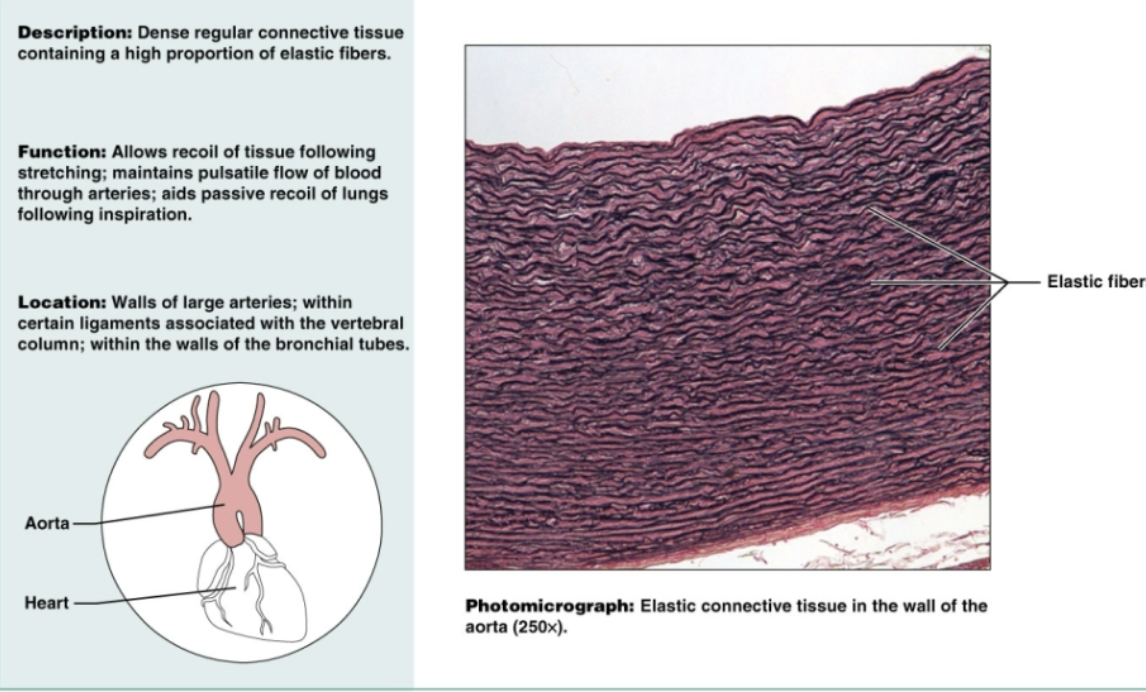
Elastic connective tissue
Dense regular connective tissue containing a high proportion of elastic fibers. Allows recoil of tissue following stretching, maintains pulsatile flow of blood throw arteries, and aids passive recoil of lungs following inspiration. Located on walls of large arteries
Hyaline cartilage connective tissue
Amorphous but firm matrix; collagen fibers form an imperceptible network. Supports and reinforces, serves as resilient cushion, and resists compressive stress. Located at end of long bones in joint cavities
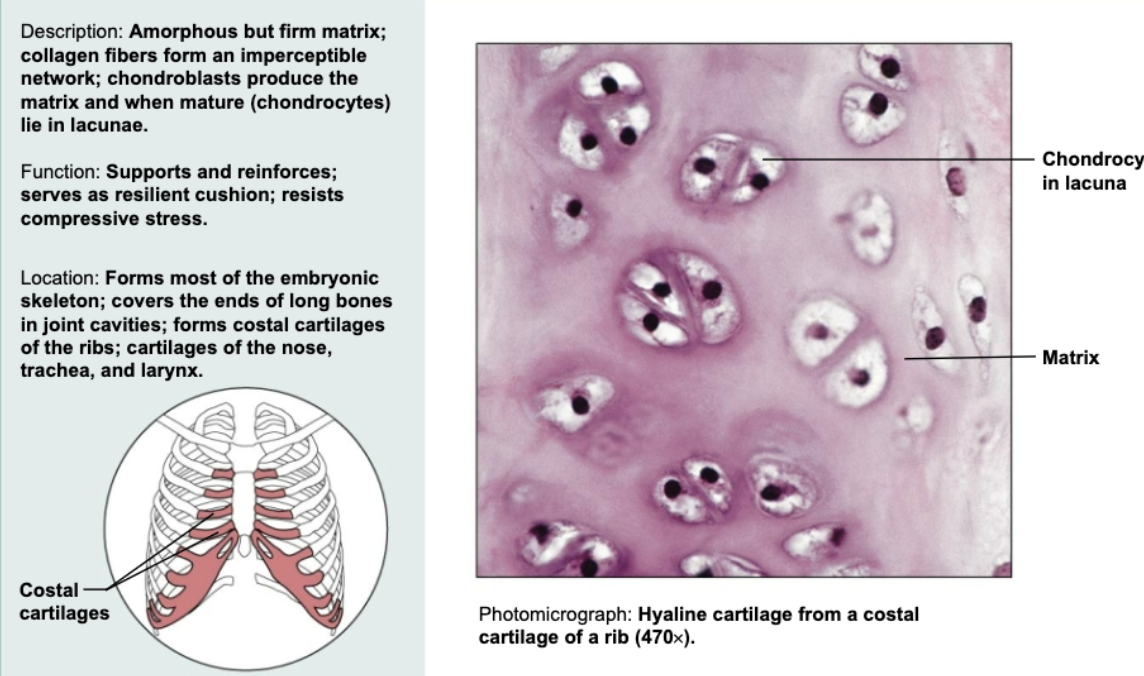
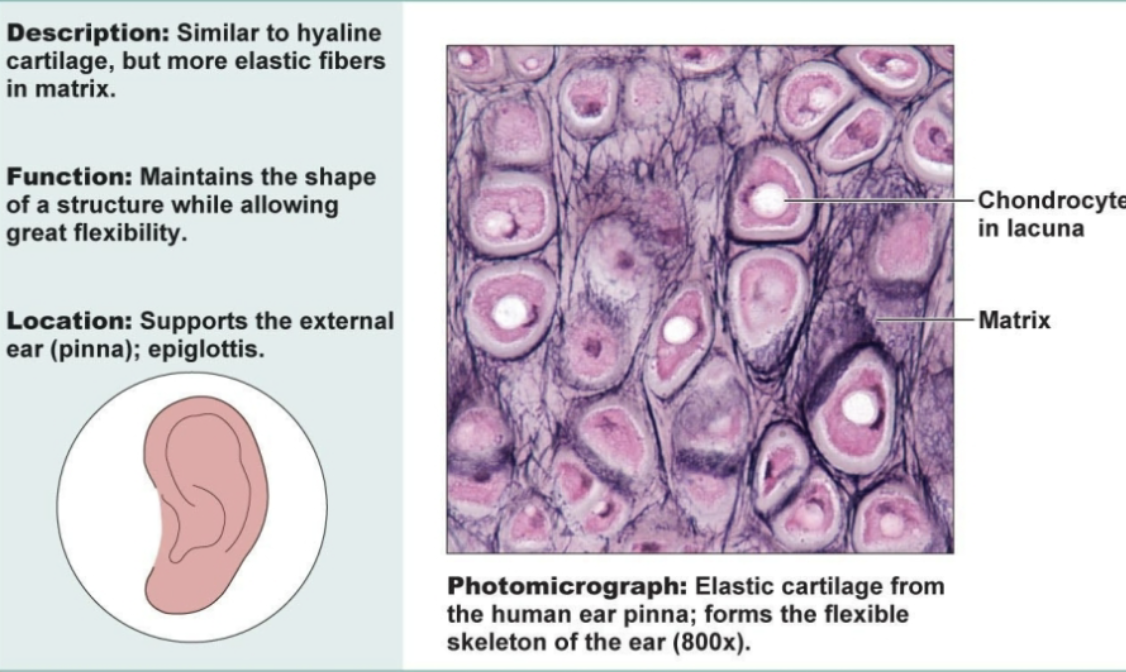
Elastic cartilage connective tissue
Similar to hyaline cartilage but more elastic fibers in matrix. Functions to maintain the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility. Supports ear
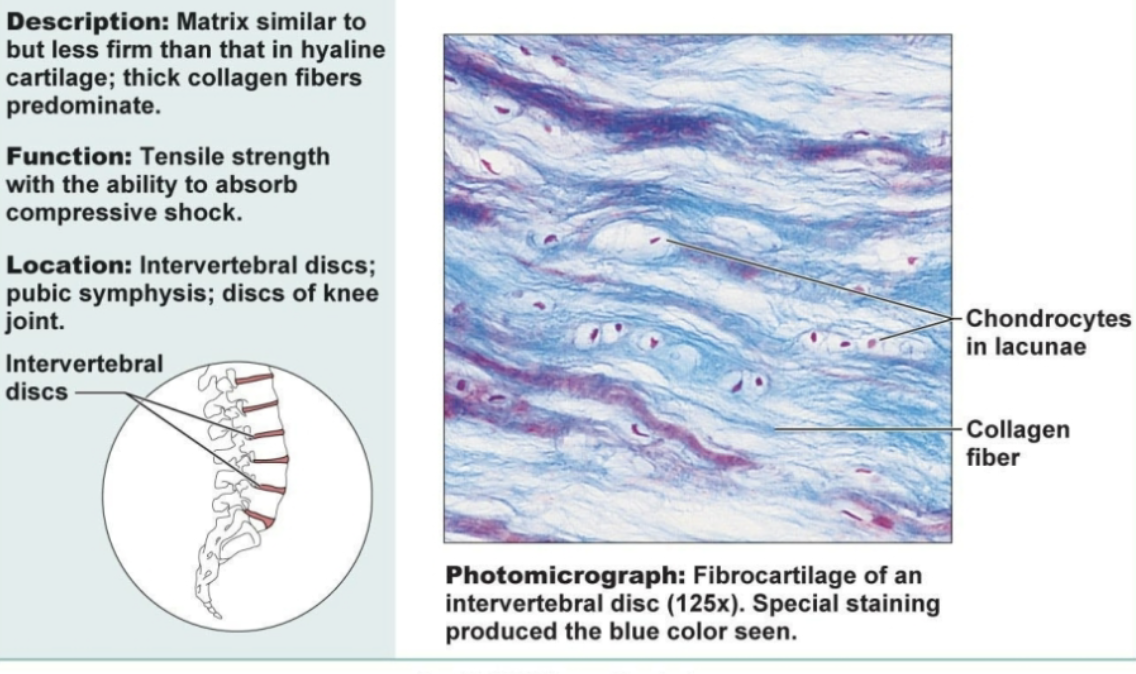
Fibrocartilage connective tissue
Matrix similar to but less firm than that in hyaline cartilage; thick collagen fibers dominate. Functions to be strong and absorb compressive shock. Located in invertebral disks
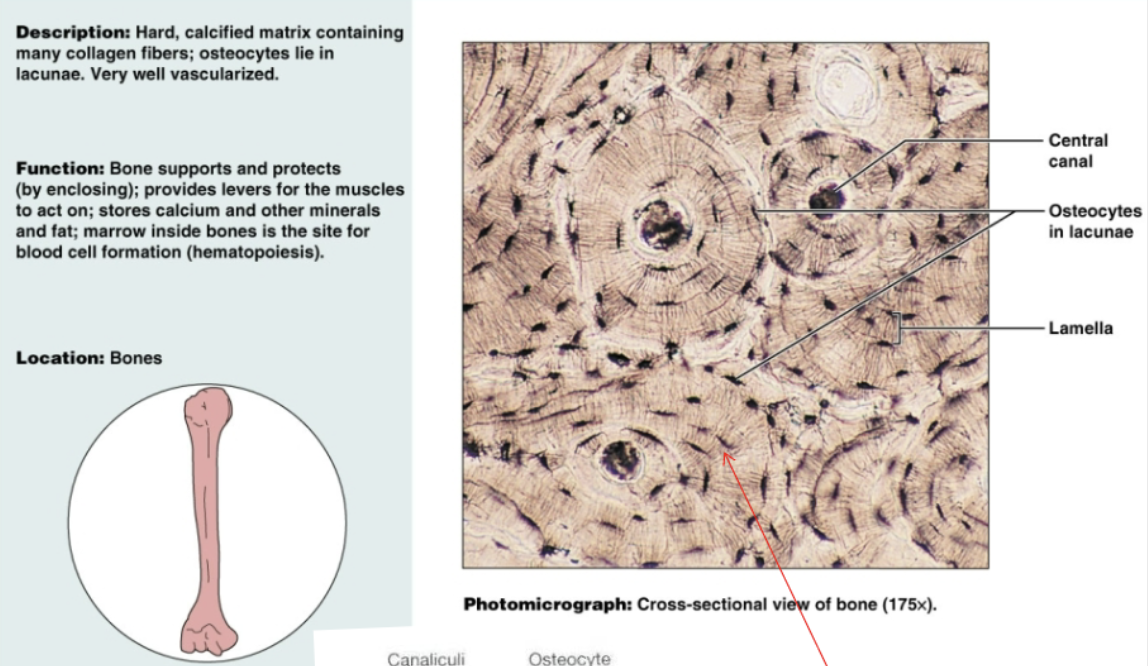
Osseous connective tissue (bones)
Hard, calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers. Functions as bone support and protects. Provides levels for muscles to act on, stores calcium/minerals and marrow.
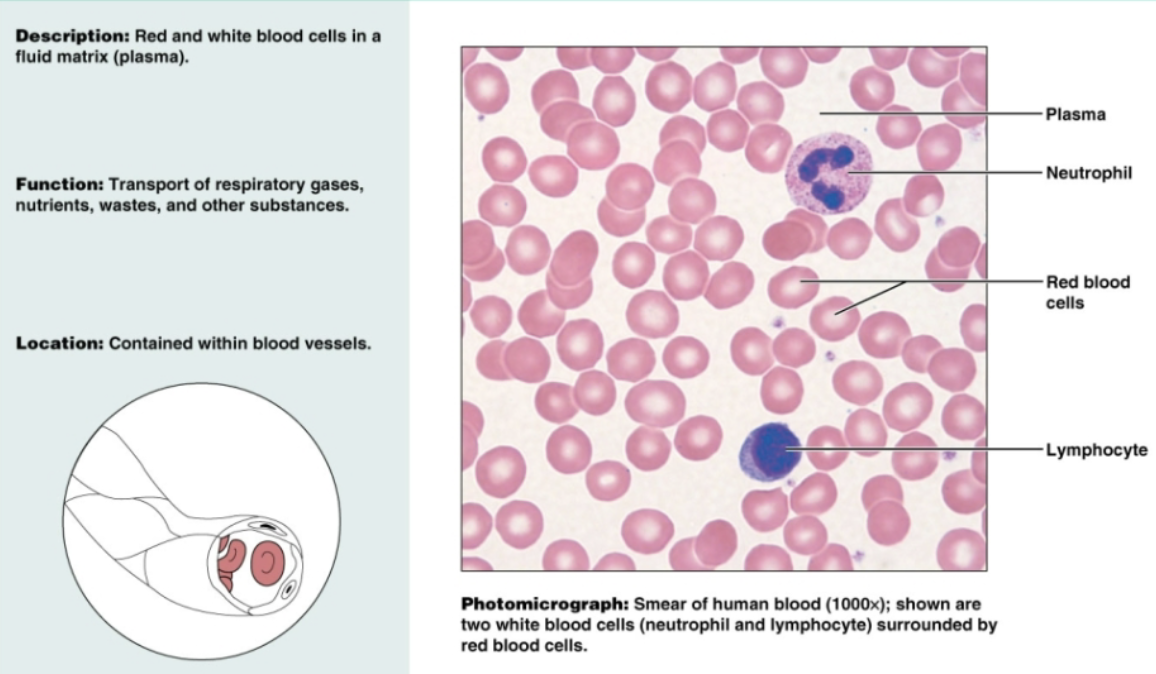
Blood (connective tissue)
Red and white blood cells in fluid matrix (plasma). Transports respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Contained within blood vessels
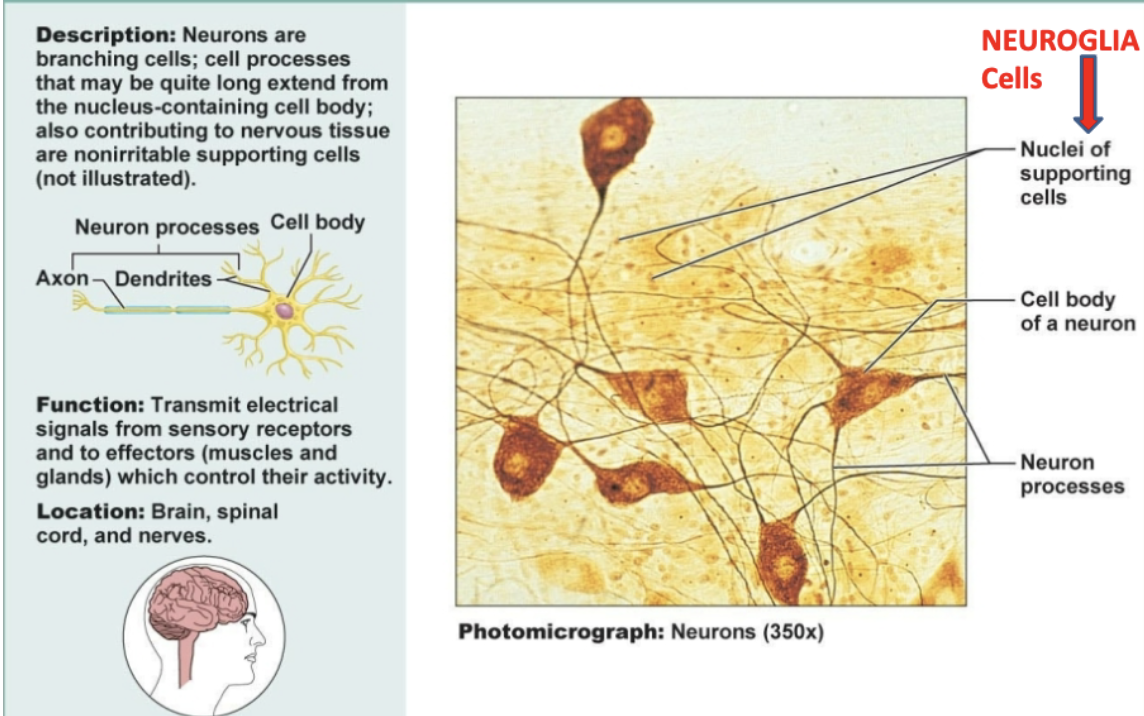
Nervous connective tissue
Neurons are branching cells containing cell body. Functions to transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors which control their activity. Located in brain, spinal cord, and nerves
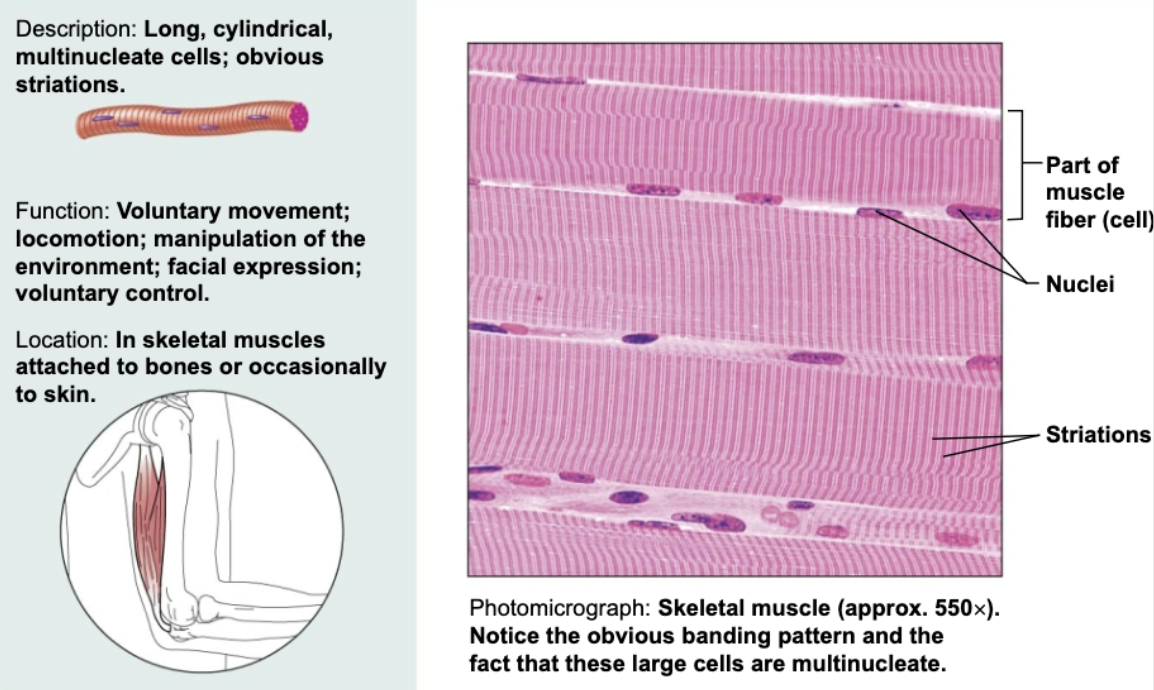
Skeletal muscle
Long, cylindrical multinucleate cells; obvious striations. Functions to produce voluntary movements, locomotion, manipulation of environment.
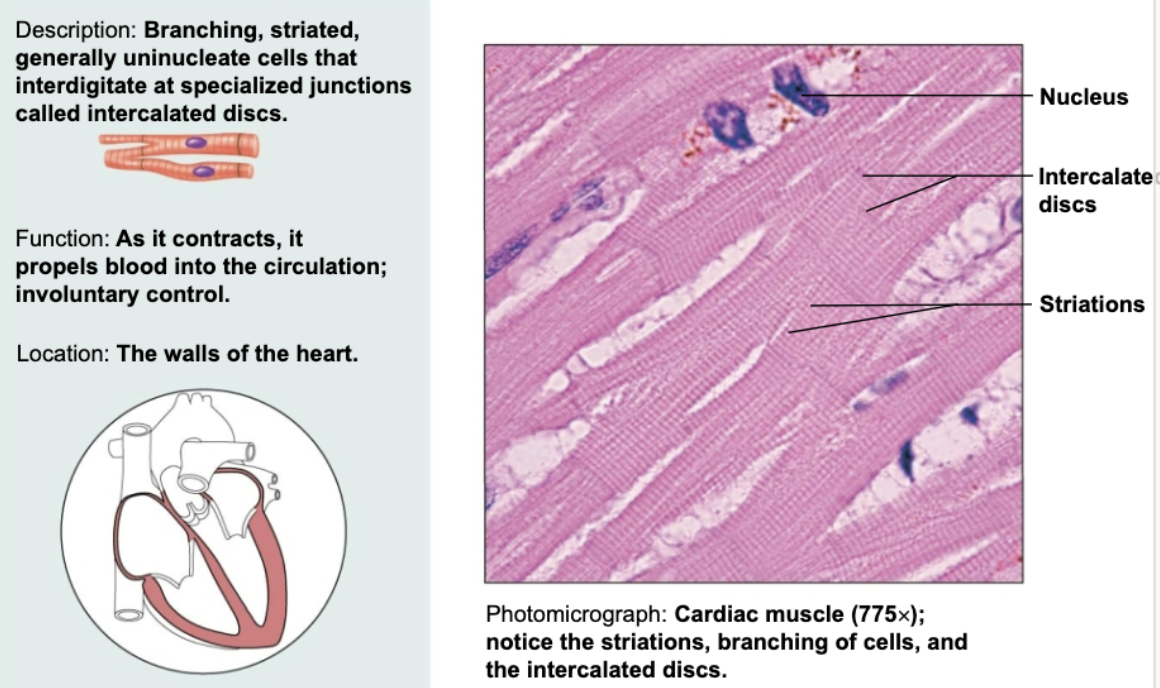
Cardiac muscle
Branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that interdigitate at specialized junctions. Functions to contract and propel blood into circulation involuntarily.
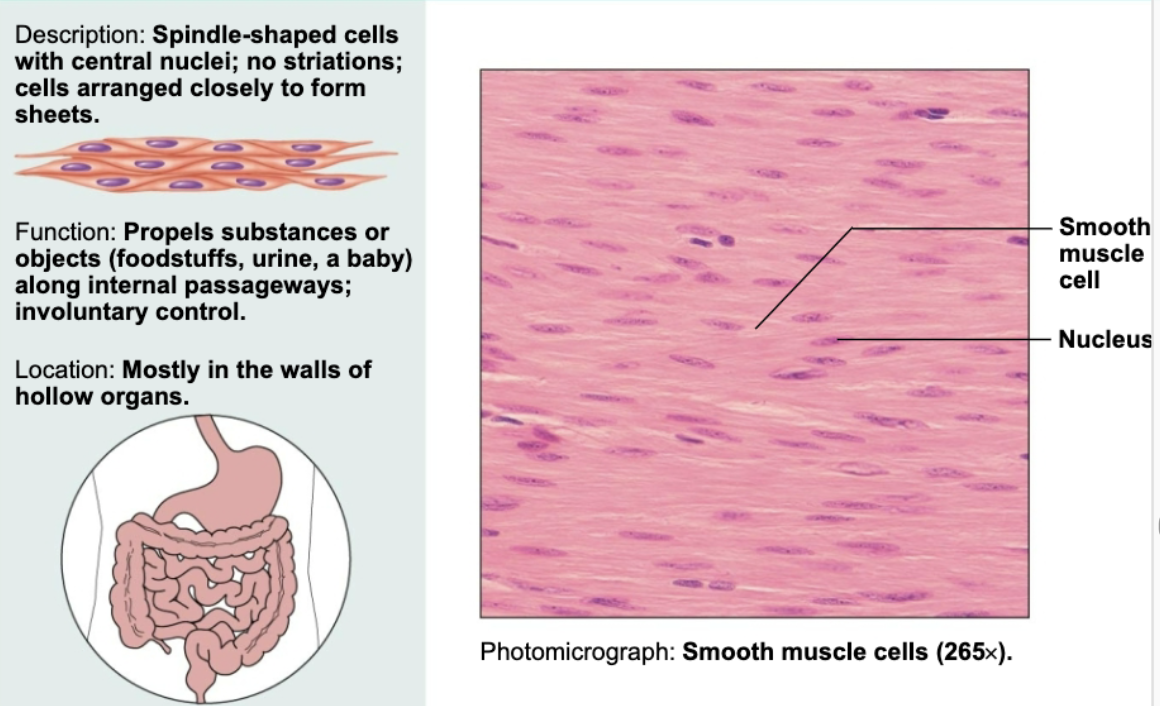
Smooth muscle
Spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheet. Functions to propel substances or objects like foodstuffs, urine, or a baby along internal passageways
Cutaneous membrane
Membrane on surface (ex. skin)
Mucous membrane
Membrane in digestive and respiratory system
Serous membrane
Membrane that lines ventral body cavities (pleura, peritoneum, pericardium)
Inflammation
When you get a cut, the surrounding skin gets inflamed. You release a bunch of cells to inflamed areas to resolve the cut
Organization
Tissue is reorganized to clot blood, stop bleeding, get rid of clot, open it back up, and refill with tissue
Regeneration
Tissue is regenerated. You may get scar tissue (dense, irregular connective tissue)
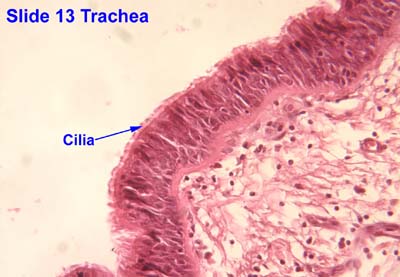
Cilia
A modification in the epithelium that is a short hair-like vibrating structure found in large numbers on the surface of certain cells that function in locomotion, movement of fluids and particles, signal transduction, and environmental sensing
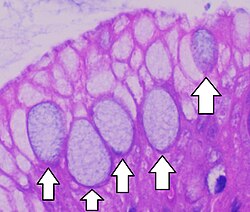
Goblet cells
A modification in the epithelium that is goblet-shaped cells that secrete mucins (main component of mucus) to lubricate and protect lining of various organs
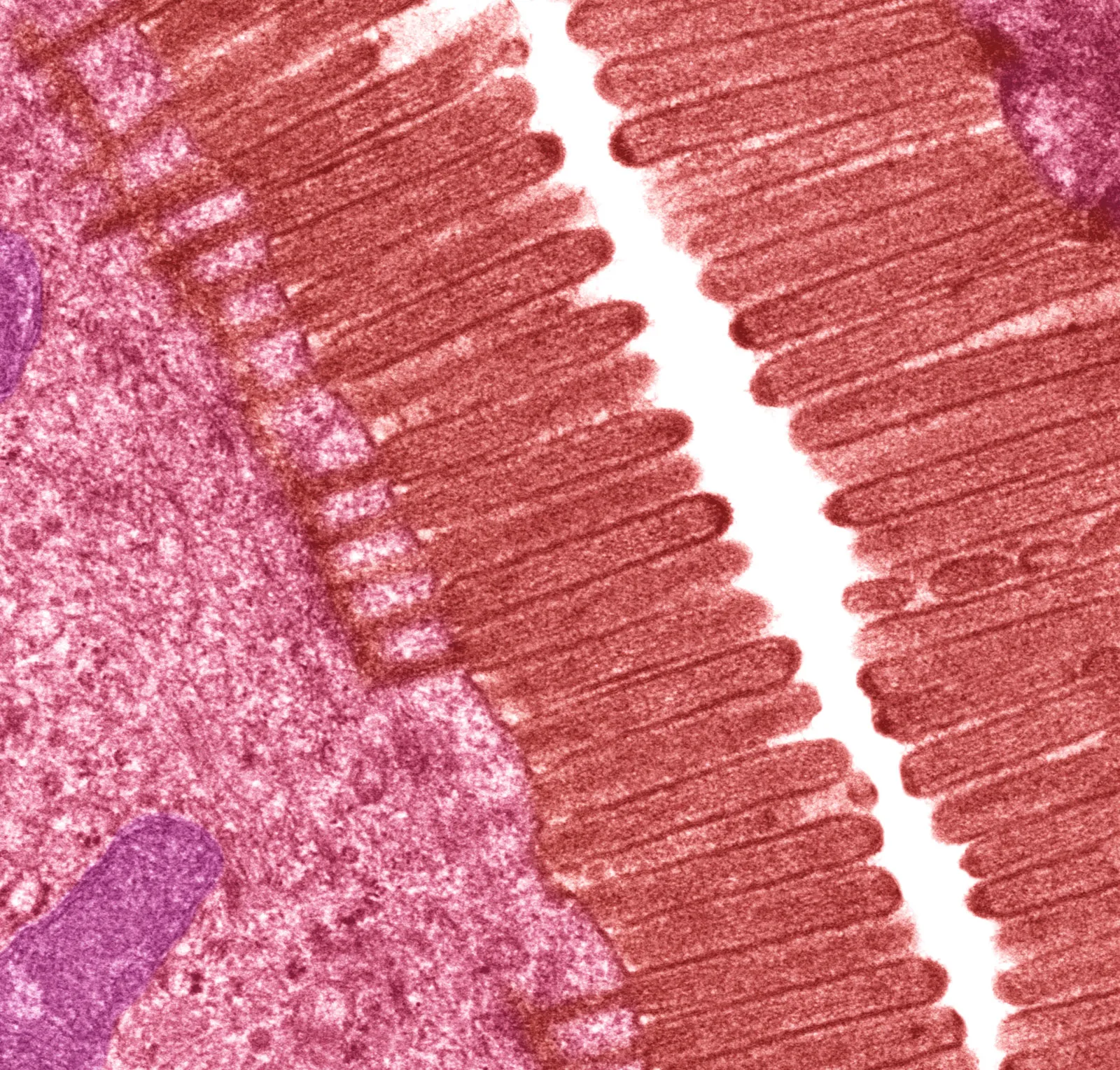
Microvilli
A modification in the epithelium that are finger-like protrusions from the surface of certain cells . Functions to increase cell’s surface area for absorption of nutrients
Protection
Function of integumentary system that protects body with low pH and bactericidal substances, keratinized layers, and immune cells/melanin
Body temperature/regulation
Function of integumentary system where sudoriferous glands and blood vessels dilate/constrict
Cutaneous sensation
Function of integumentary system where Meissner and Pacinian Corpuscles function and free nerve endings
Messiner’s (aka Tactile) corpuscles
Rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors in the dermal papillae, detecting light touch and low-frequency vibrations
Pacinian (aka Lamellar) corpuscles
Large, deep-skin receptors that detect high-frequency vibrations and deep pressure, and are found in various internal organs
Metabolic functions
Function of integumentary system where vitamin D is created
Blood reservoir
Function of integumentary system including dermal blood vessels, which are networks of arteries, veins, and capillaries located in the skin's dermis layer that supply the skin with nutrients and oxygen, remove waste products, and regulate body temperature by controlling blood flow near the surface
Excretion
Function of integumentary system where ammonia, urea, and uric acid exit the skin mainly through sweating
Superficial epidermis
One of two distinct skin regions that’s composed of epithelium
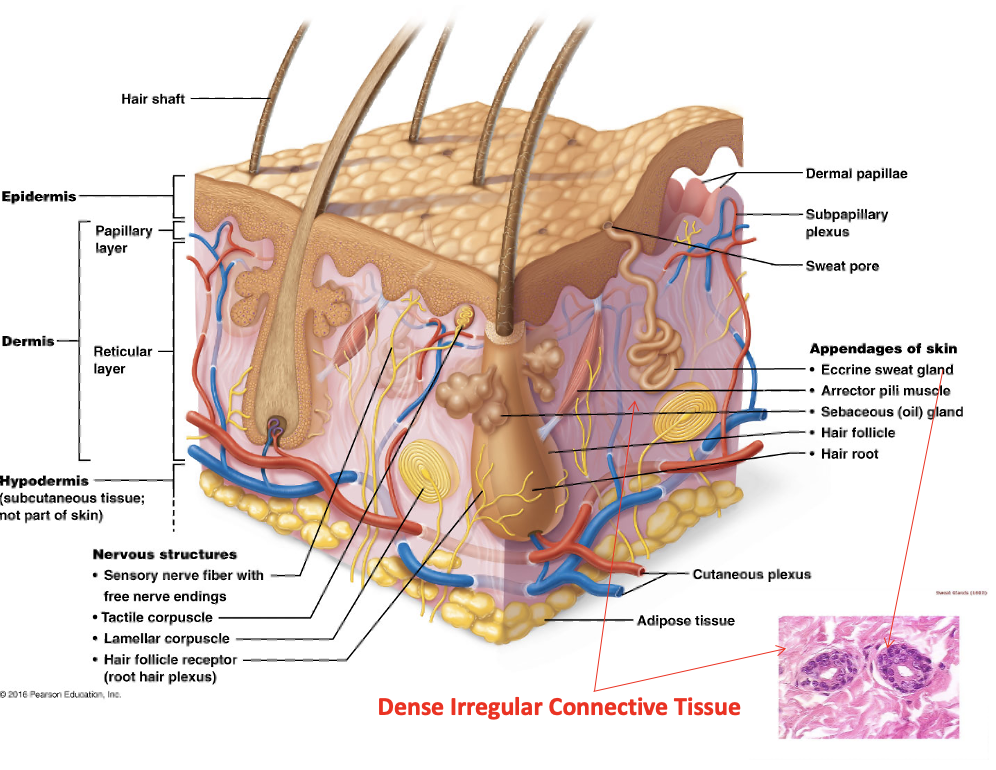
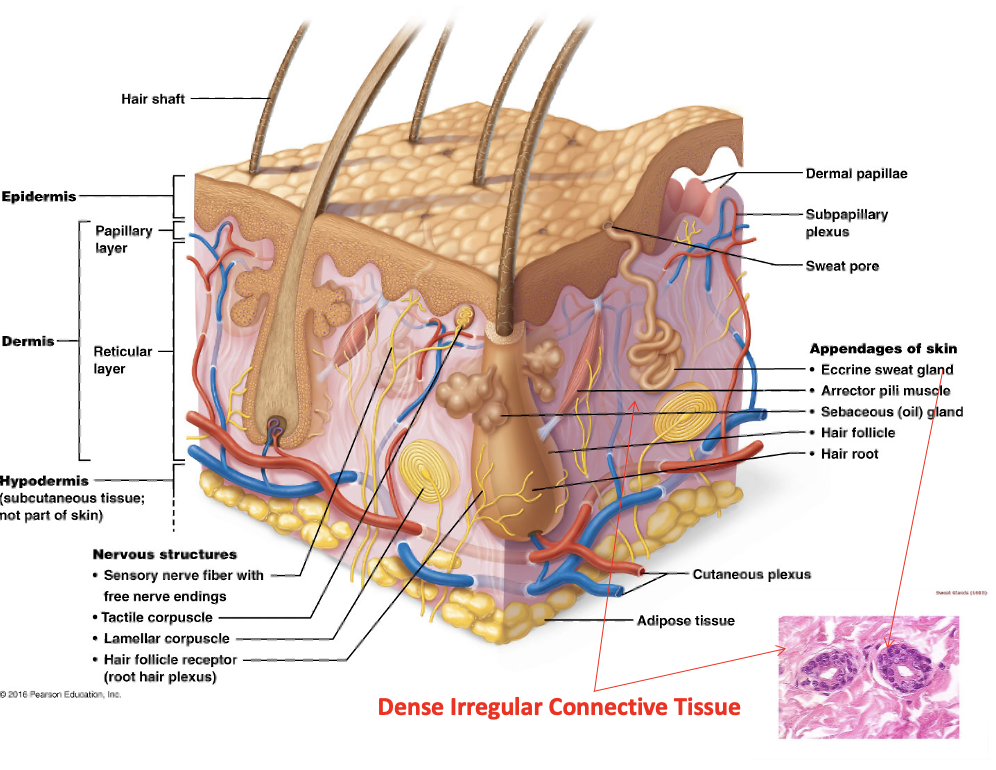
Dermis
One of two distinct skin regions that’s composed of underlying connective tissue
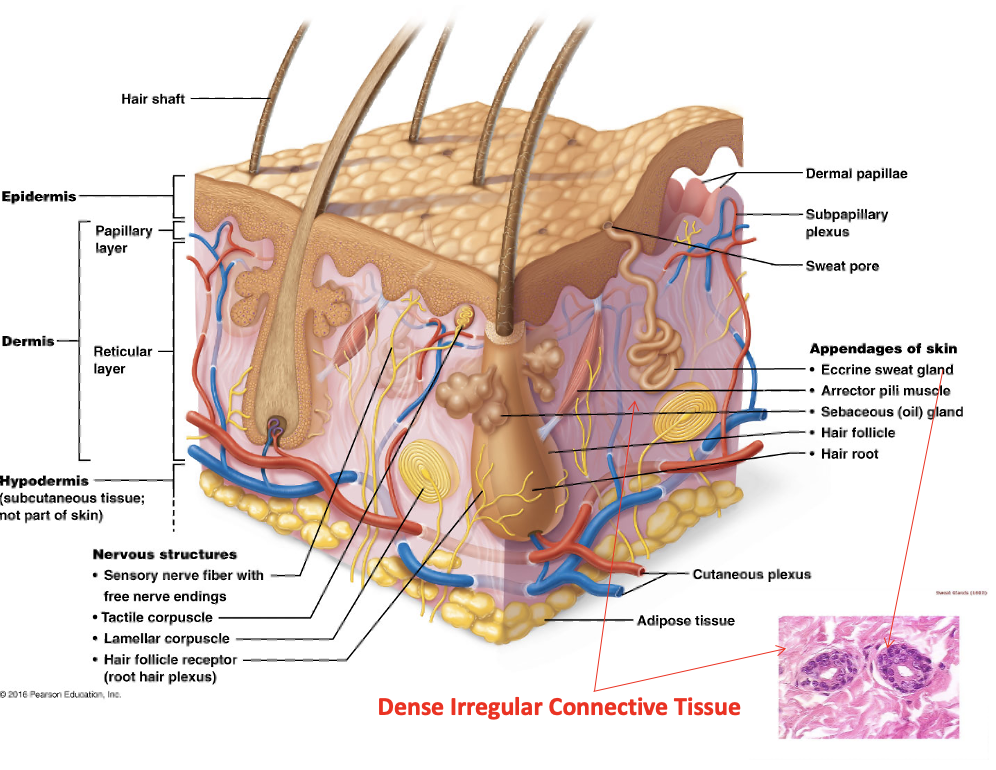
Subcutaneous layer/hypodermis
deepest layer of the skin that lies beneath the dermis and not considered part of the skin. Primarily consists of adipose tissue
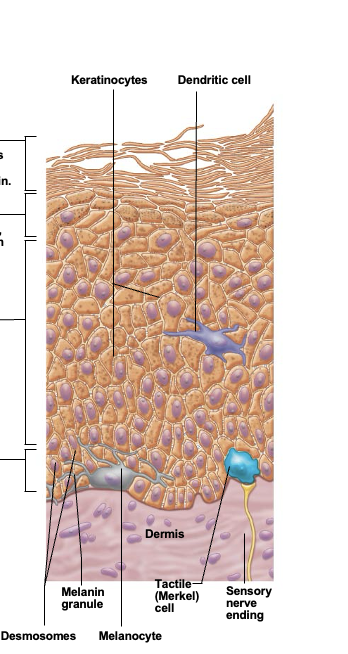
Keratinocytes (kertain cells)
most abundant epidermal cell. Functions to product kertain, a fibrous protein that gives the epidermis durability and protective capabilities
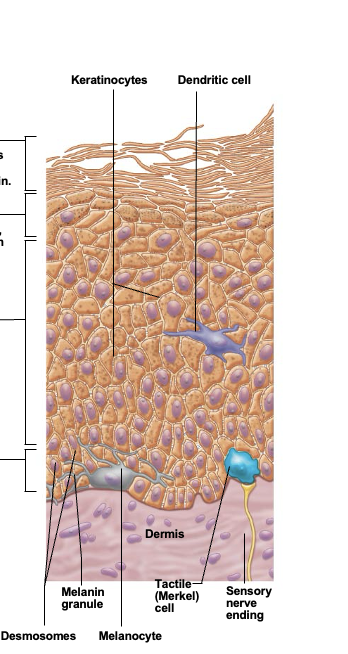
Melanocytes
spidery black cells that produce brown-to-black pigment called melanin. Skin tans because melanin production increases when the skin is exposed to UV in sunlight
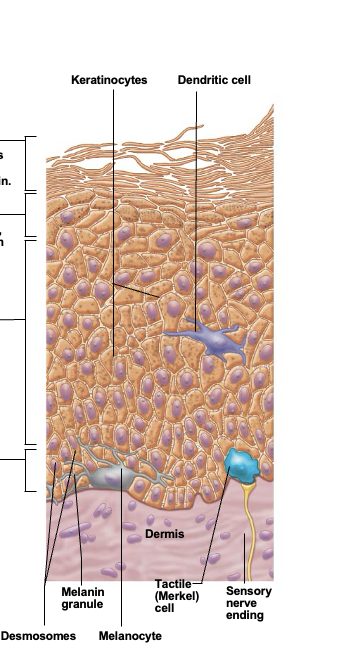
Dendritic cell (Langerhans cell)
cells that arise from bone marrow and migrate to the epidermis. Ingest foreign substances and play key role in activating the immune response
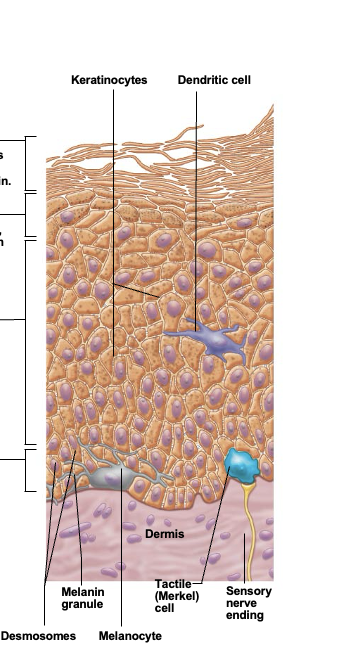
Tactile epithelial cells
Occasional spiky hemispheres that, in combination with sensory nerve endings, form sensitive touch receptors located at the epidermal-dermal junction
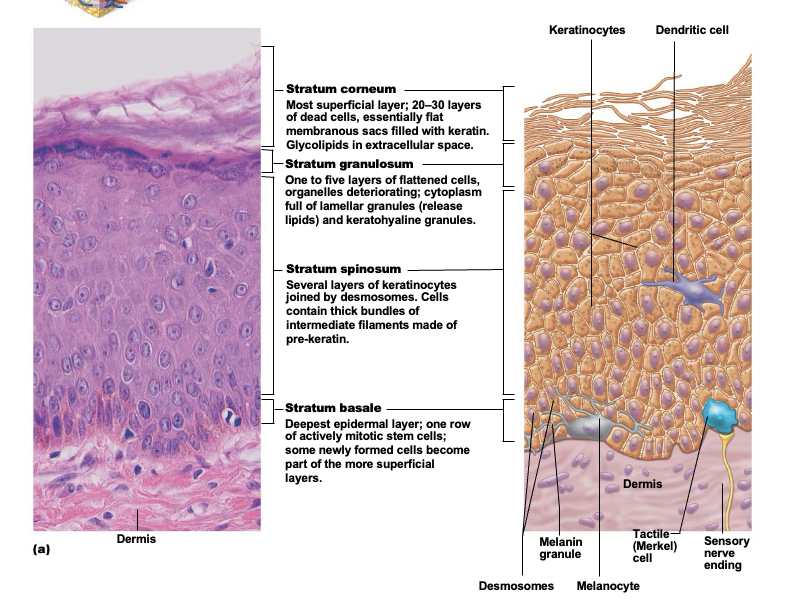
Stratum corneum (horny layer)
The outermost epidermis layer consisting of 20-30 layers of dead, scalelike keratinocytes. They are constantly being exfoliated and replaced by the division of the deeper cells
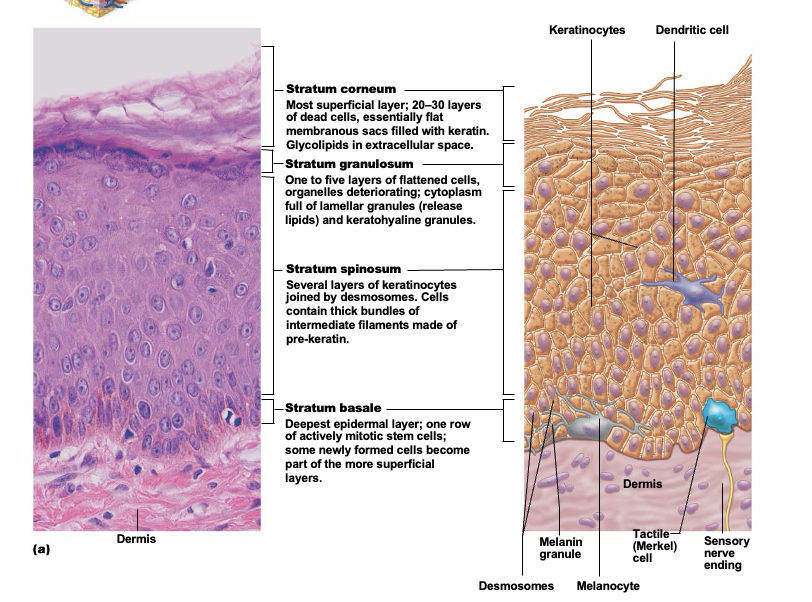
Stratum lucidum (clear layer)
Layer of epidermis that’s present only in thick skin. A very thin transparent bank of flattened, dead keratinocytes with indistinct boundaries. Below stratum corneum
Stratum granulosum (granular layer)
1-5 layers of flatten cells of epidermis; named for abundant granules its cells contain. Includes lamellar granueles and keratohyaline granules. At upper border of this layer, cells are beginning to die
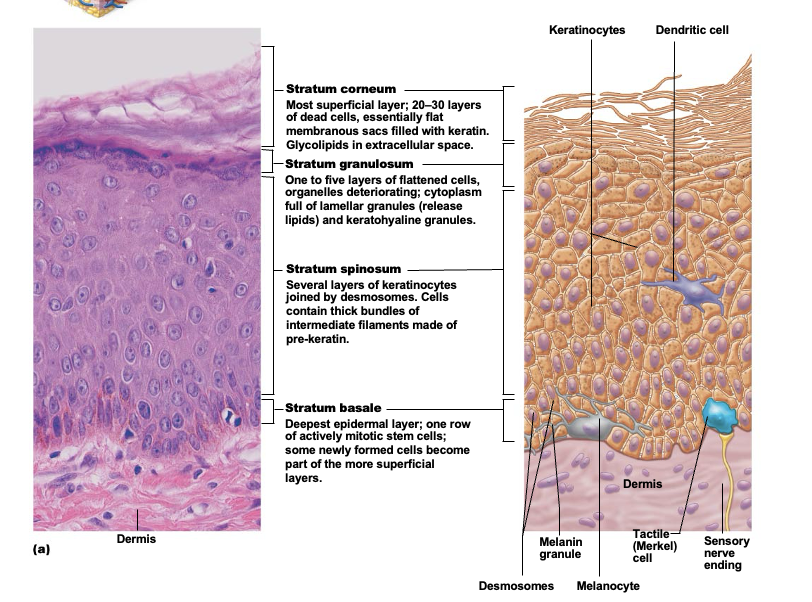
Lamellar granules
Found in stratum granulosum and contains waterproofing glycolipid that’s secreted into extracellular space
Keratohyaline granules
Found in stratum granulosum and form kertin in more superficial layers
Stratum spinosum (spiny layer)
Several layers of cells that contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of a pre-keratin protein. Joined together by desmosomes. Cells in this layers and the basal layer are the only ones to recieve adequate nourishment from diffusion of nutrients from the dermis
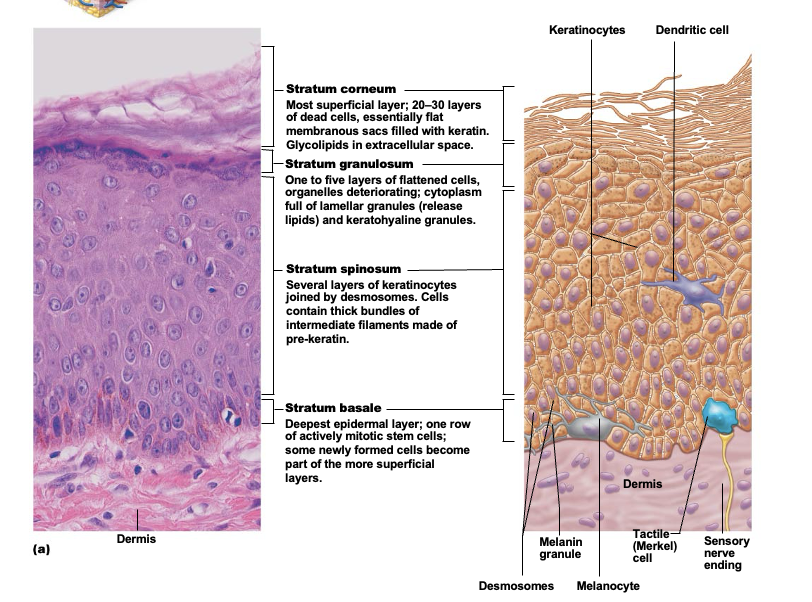
Stratum basale (basal layer)
Single row of cells immediately above dermis. Cells are constantly undergoing mitosis to form new cells. 10-25% of cells in this layer are melanocytes with occasional tactile epithelial cells
Papillary dermis
Upper region of dermis and composed of areolar tissue. Is very uneven and has fingerlike projections. The dermal papillae attach it to the epidermis above
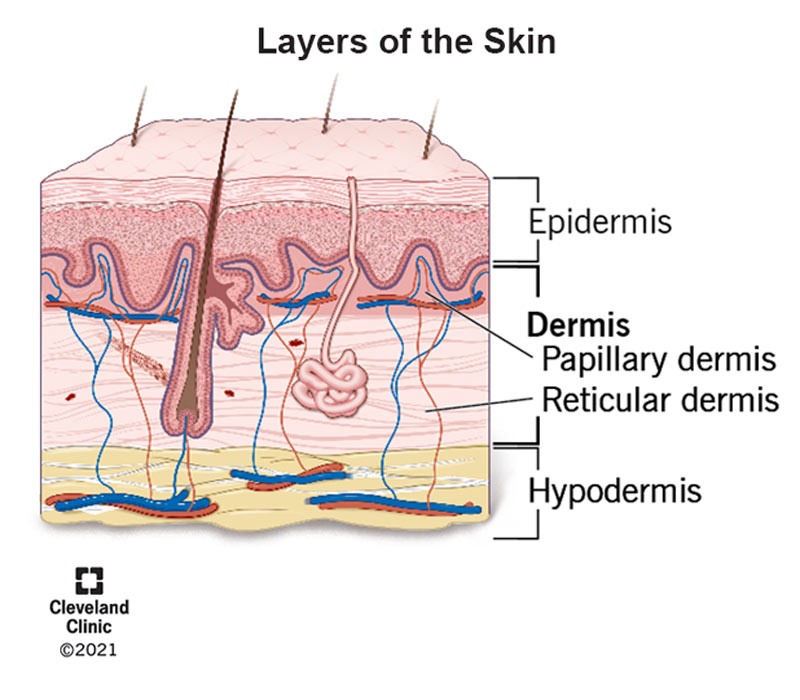
Reticular dermis
Bottom region of dermis composed of dense irregular connective tissue and contains many arteries and veins, sweat and sebaceous glands, and pressure receptors (lamellar corpuscles)
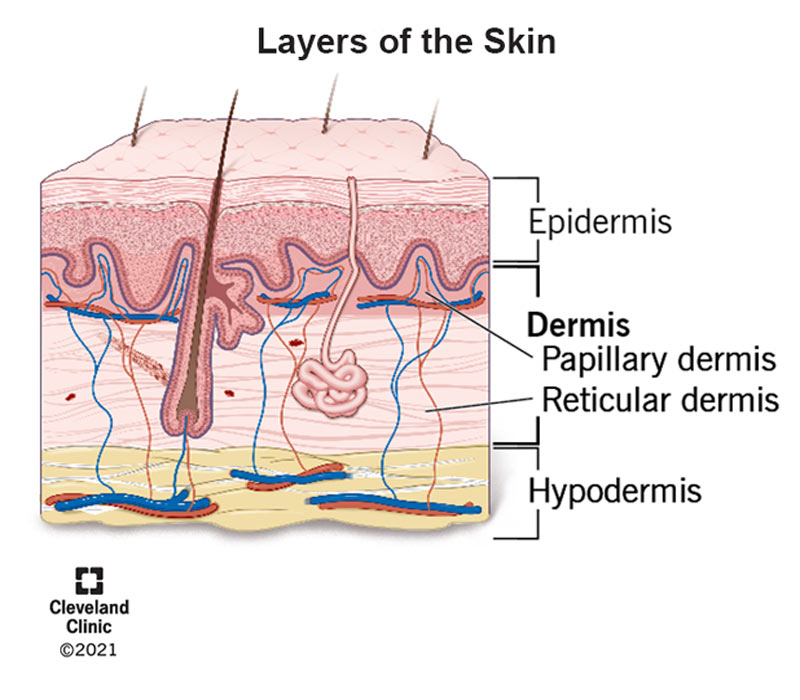
When body temperature is high, the arterioles dilate and the capillary network of the dermis becomes engorged with heated blood, allowing body heat to radiate away from skin
How does the dermal blood supply regulate body temperature?
Skin color
the result of relative amount of melanin in skin, the relative amount of carotene in skin, and degree of oxygenation of the blood.
Carotene
a yellow-orange pigment present primarily in stratum corneum and in the adipose tissue of the hypodermis. Presence is most noticeable when large amounts of carotene-rich foods (ie. carrots) are eaten.
Cyanosis
A condition where blood is inadequately oxygenated and blood and skin take on a bluish cast. Occurs during asphyxiation and serious lung disease
Jaundice
Tissue becomes yellowed and is almost always a diagnostic for liver disease
Addison’s disease
a bronzing of the skin that hints a person’s adrenal cortex is hypoactive
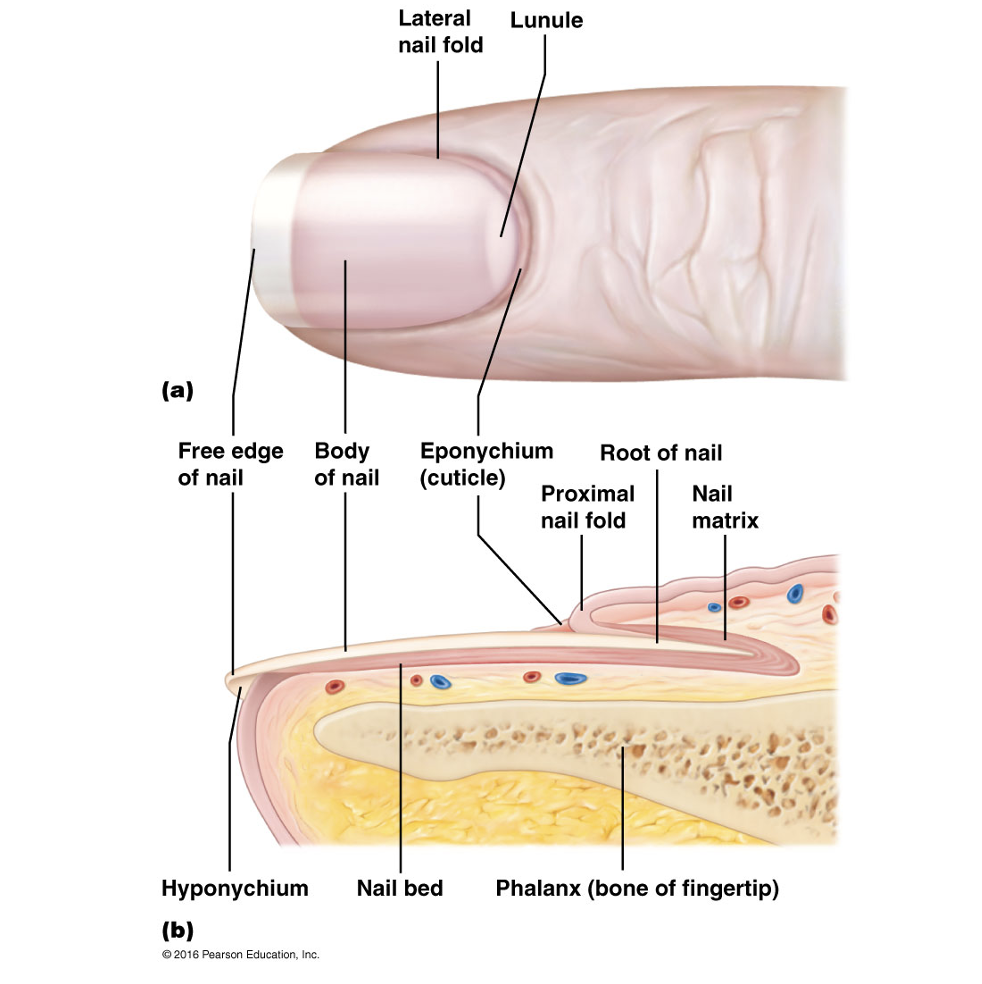
Nail plate
Visible attached portion of nail
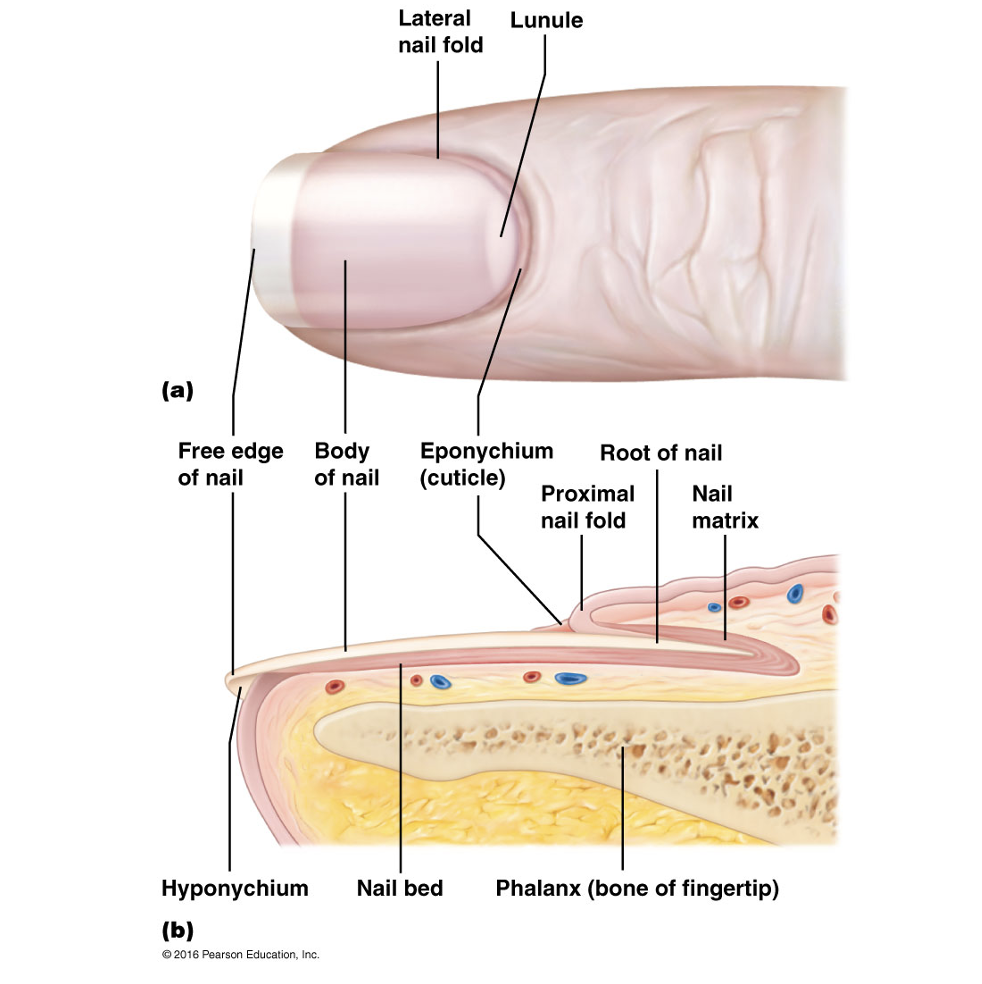
Free edge
portion of nail that grows away from body
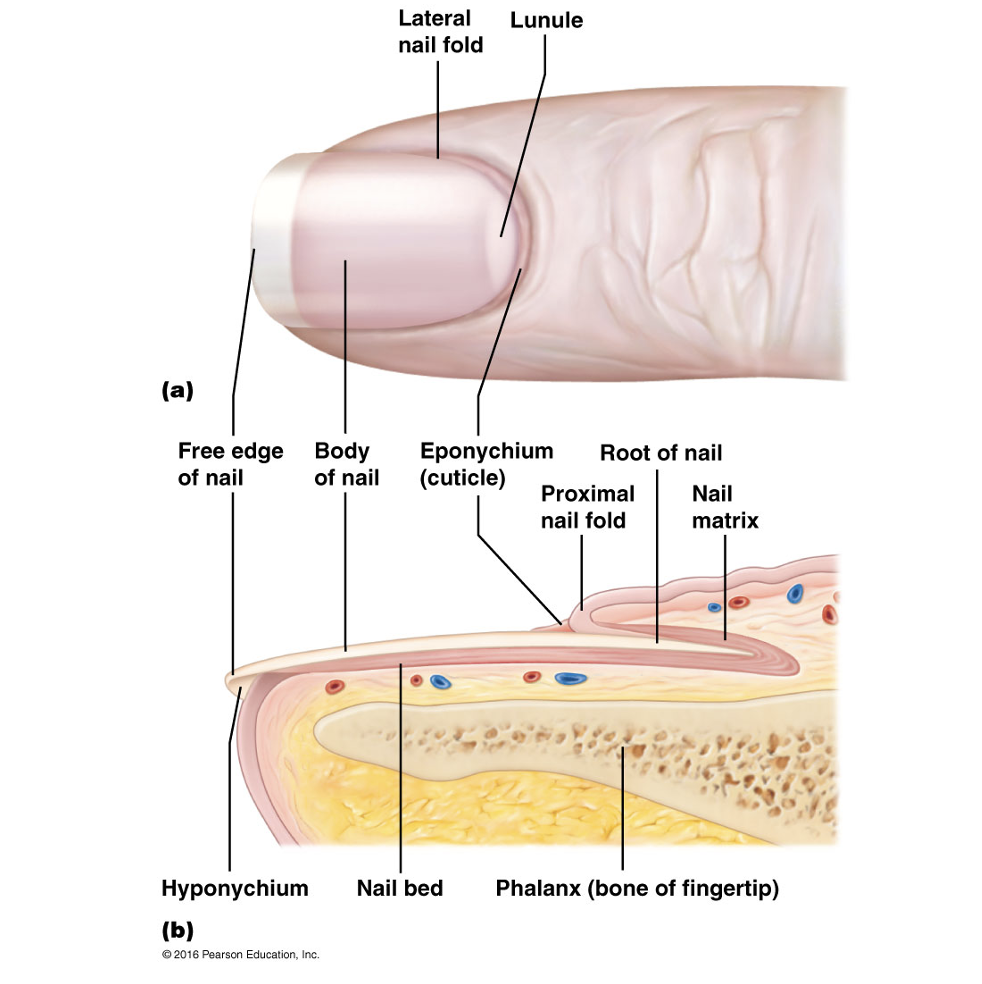
Hyponychium
Region beneath the free edge of the nail
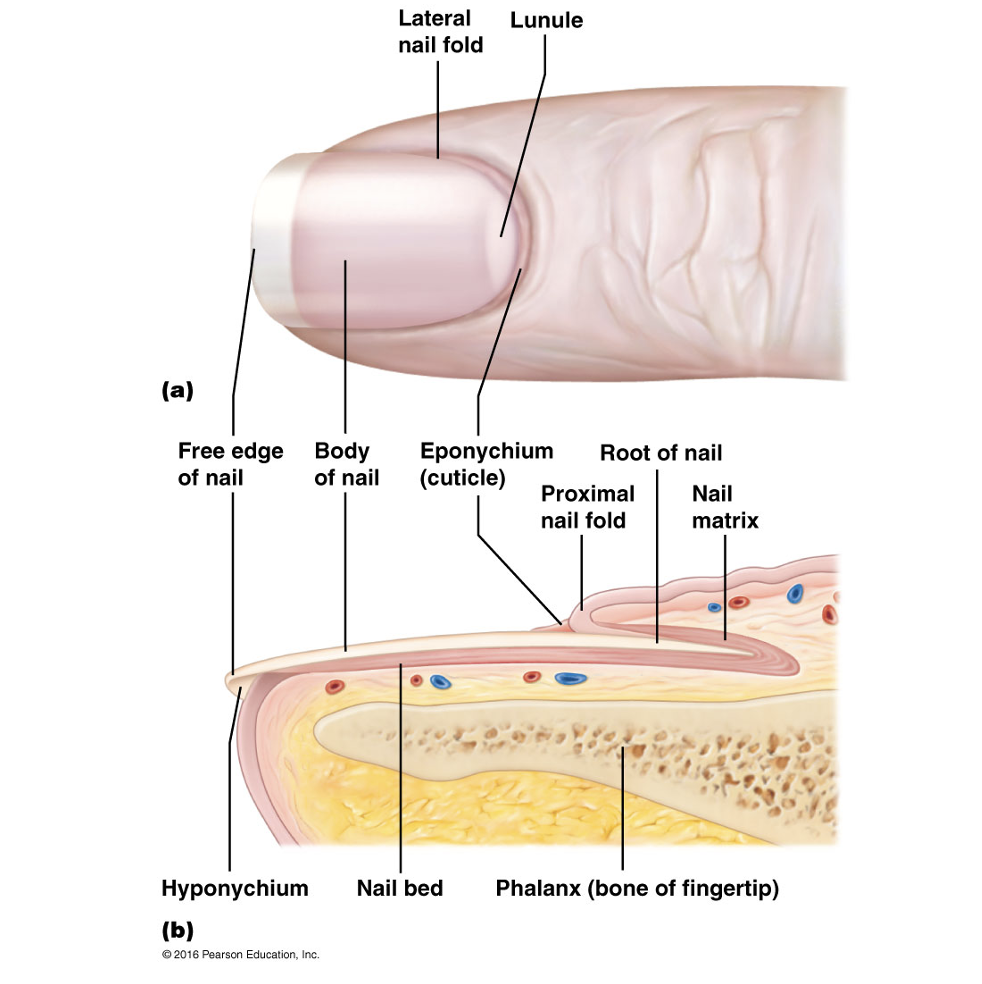
Nail root
Part that is embedded in the skin and adheres to an epithelial nail bed
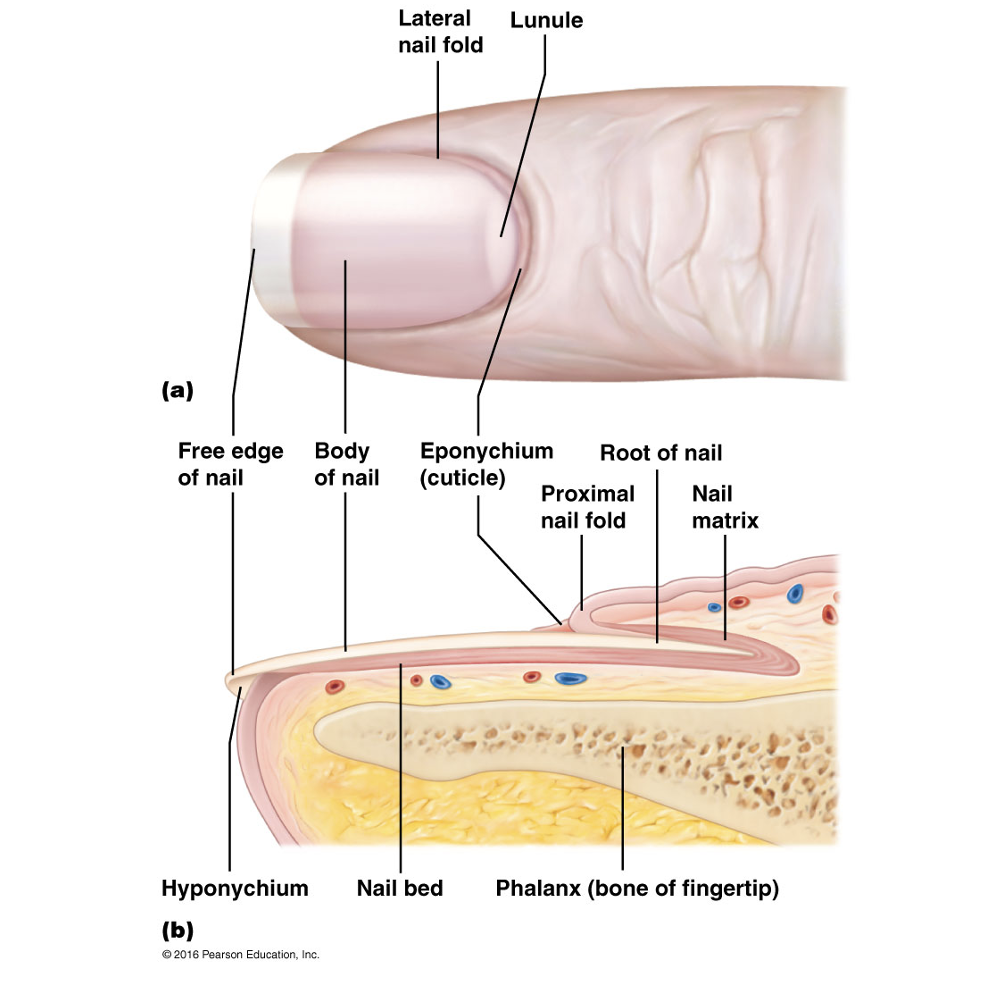
Nail folds
skin folds that overlap with borders of the nail
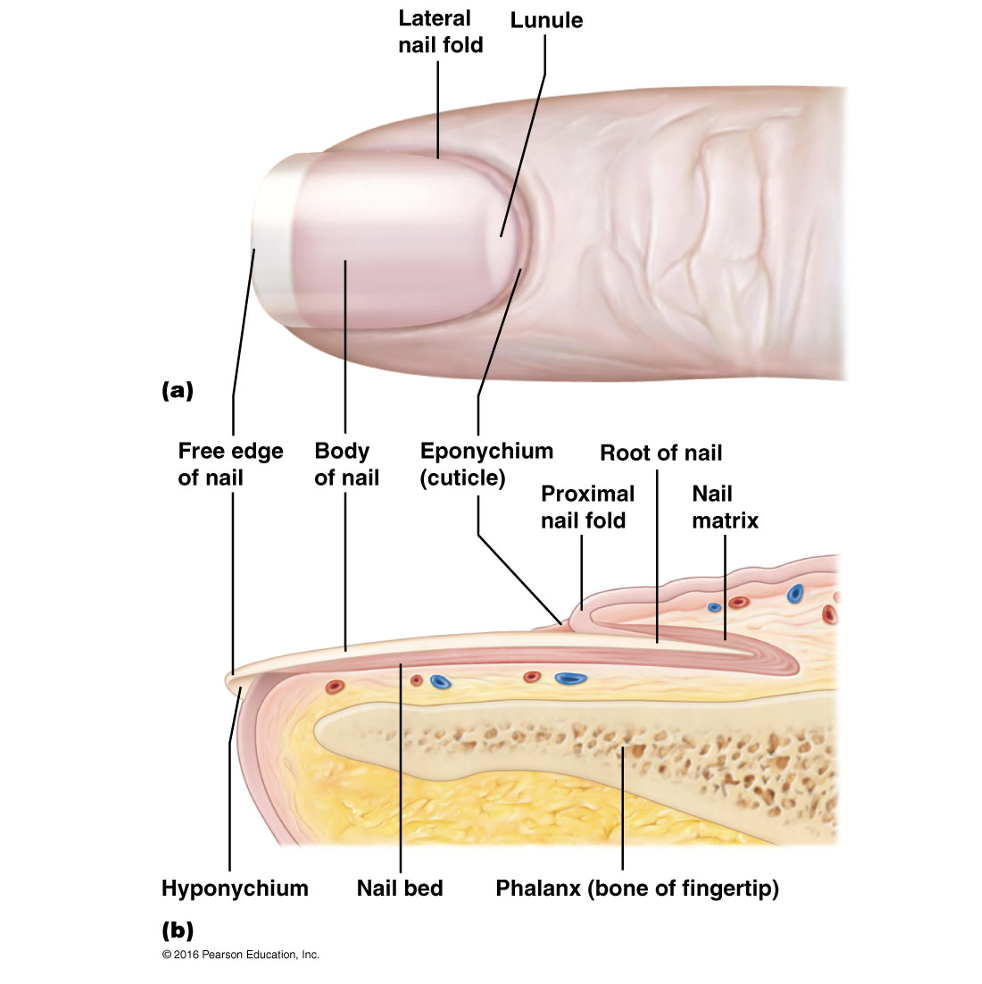
Eponychium
Part of nail that projects the thick proximal nail fold. Commonly called the cuticle
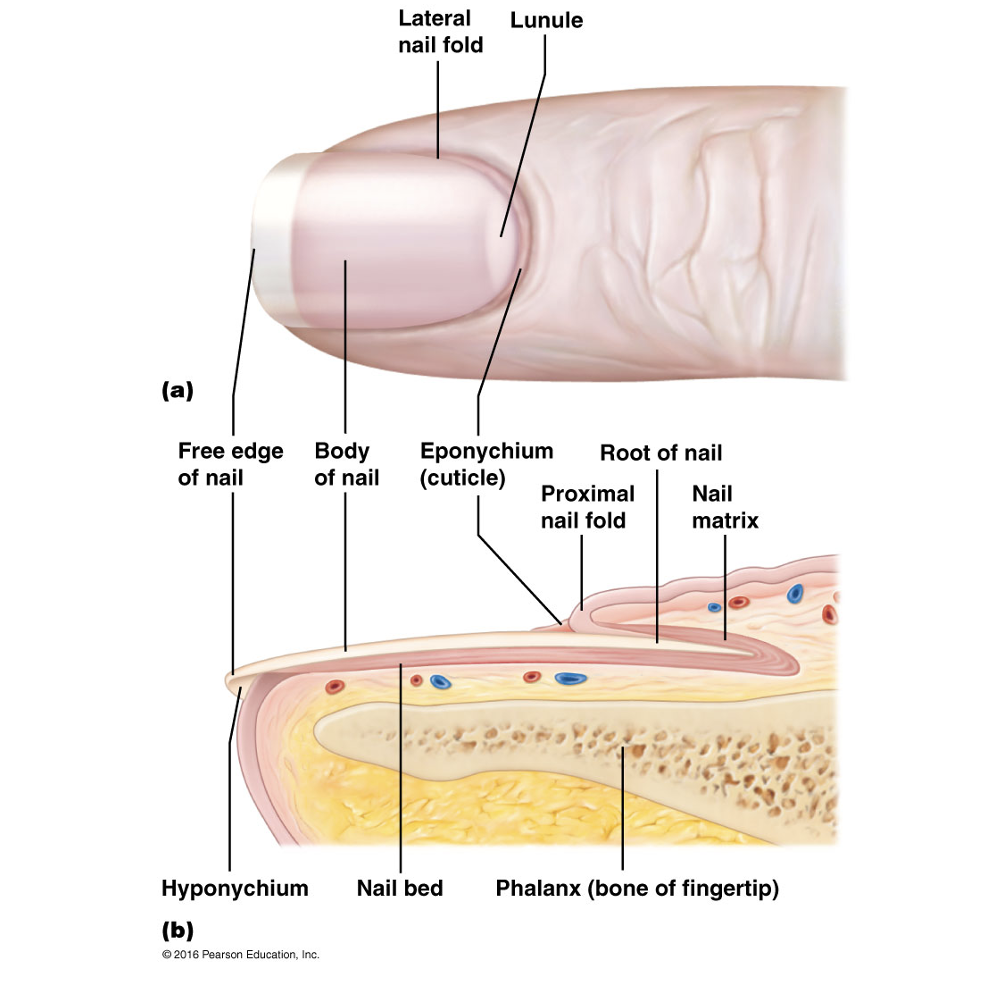
Nail bed
Extension of the stratum basale beneath the nail
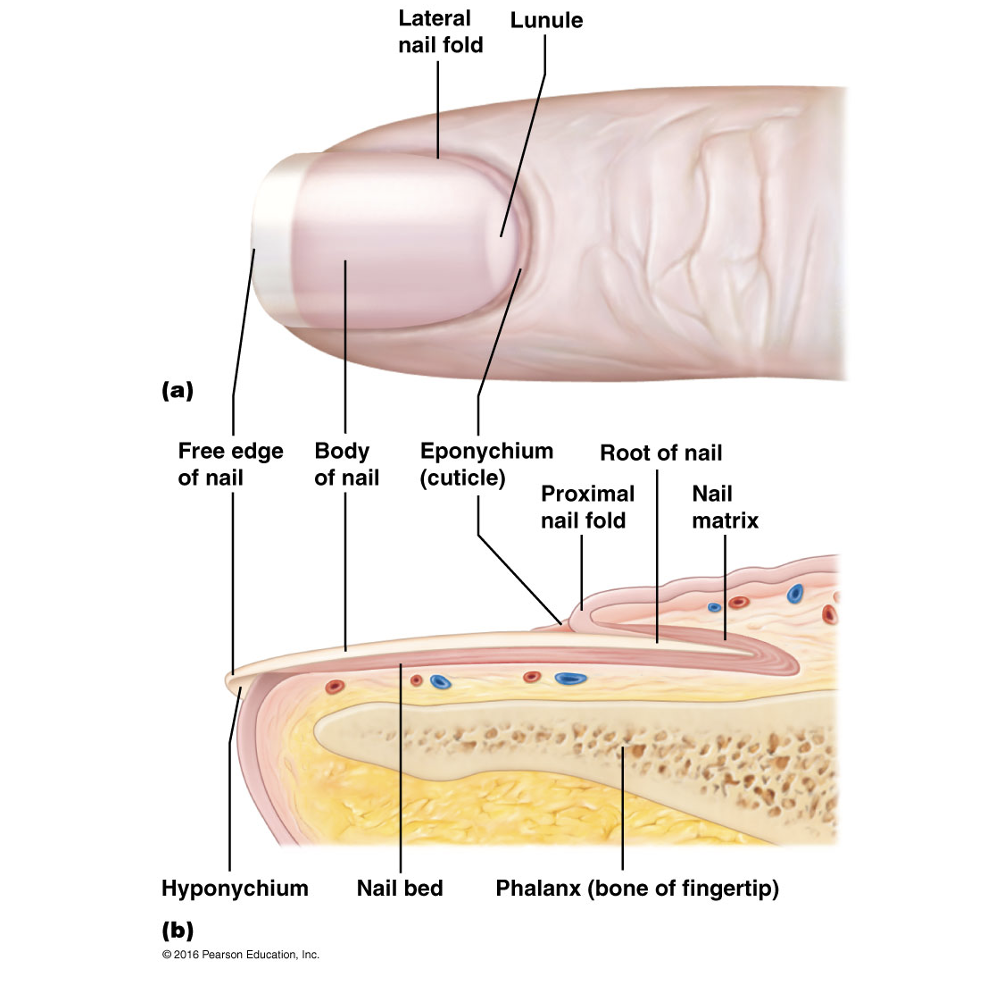
Nail matrix
Thickened proximal part of nail bed containing germinal cells responsible for nail growth. As the matrix produces the nail cells, they become heavily keratinized and die.
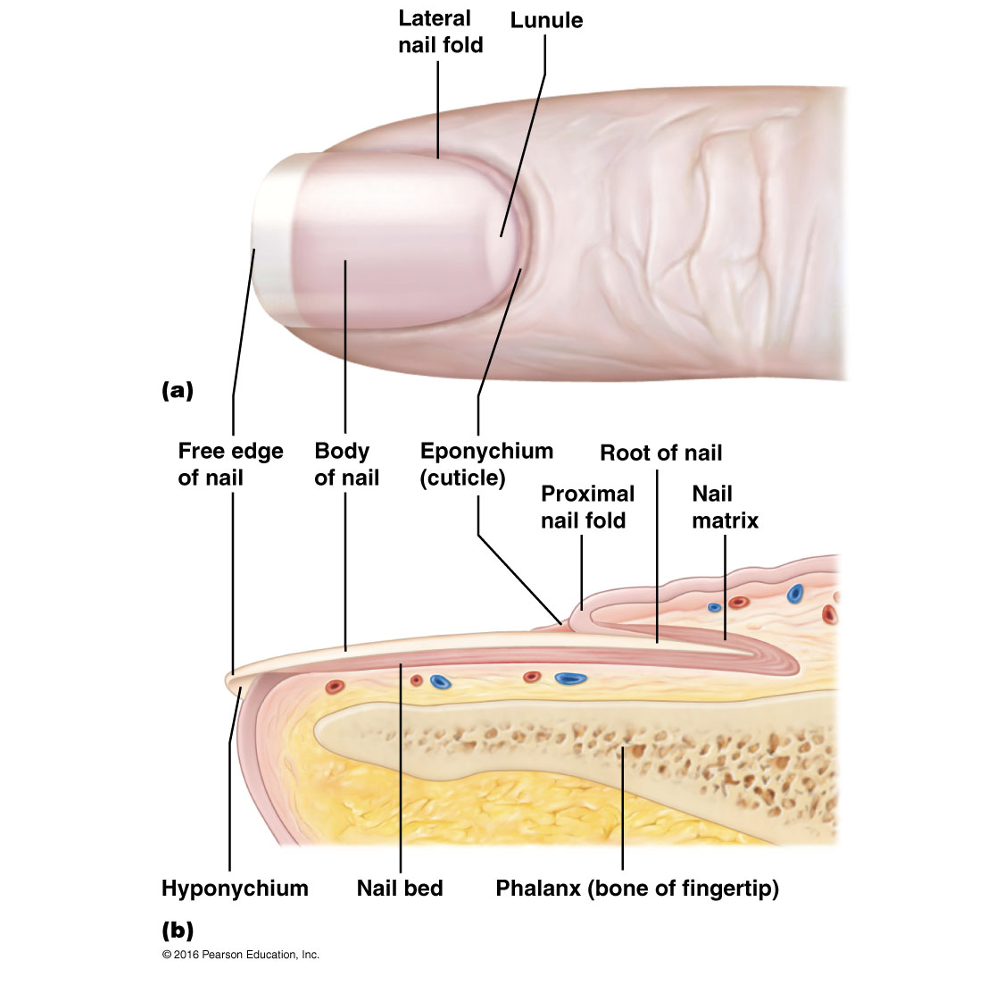
Lunule
Proximal region of thickened nail matrix, which appears as a white cresent moon.
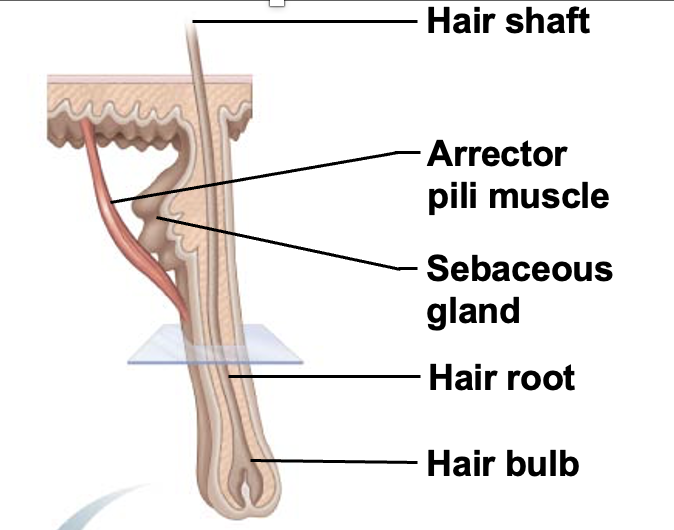
Hair shaft
the visible, exterior portion of a hair strand that extends from the skin's surface and is composed of three distinct layers: the medulla, cortex, and cuticle
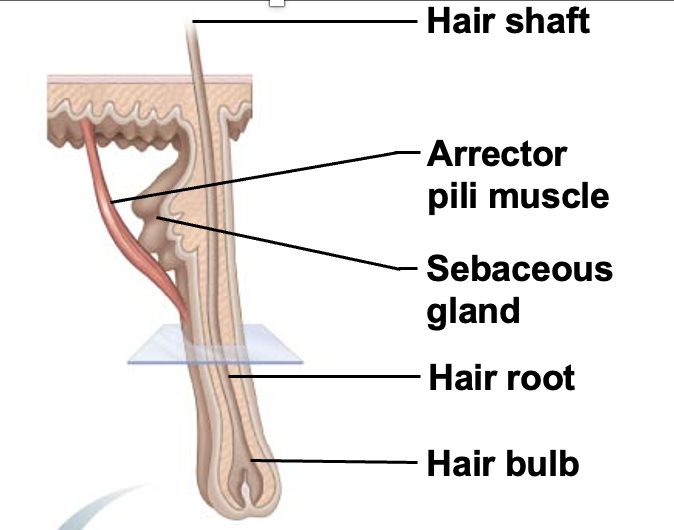
Hair root
the living part of a hair strand located beneath the skin's surface within a hair follicle
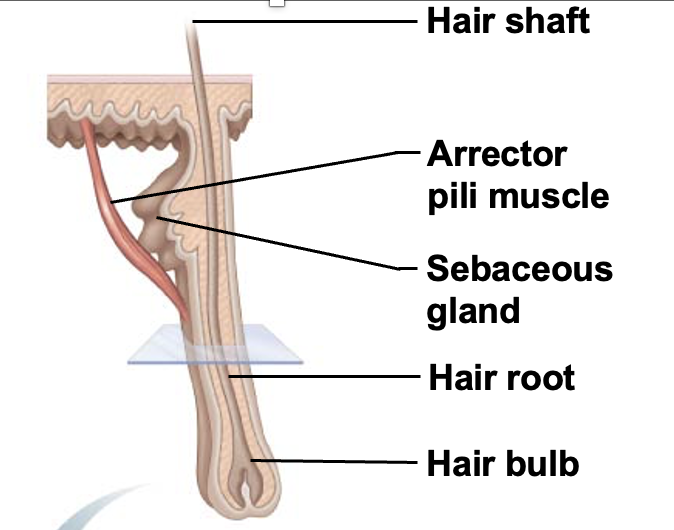
Hair bulb
collection of well-nourished epithelial cells at the base of the hair follicle
Medulla
The center of the hair follicle
Cortex
Surrounds the medulla
Cuticle
Protective part of hair follicle surrounding cortex. Abrasion causes split ends
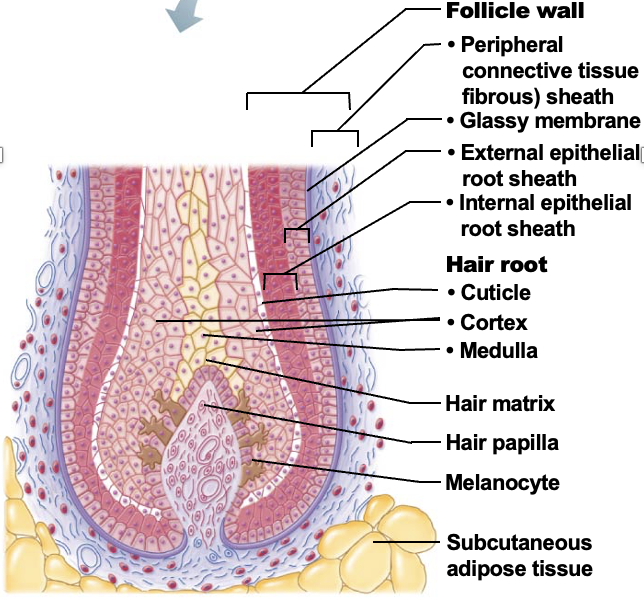
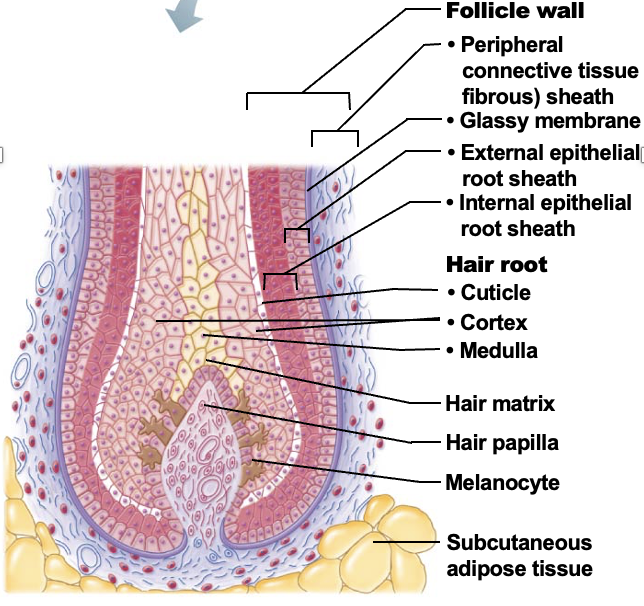
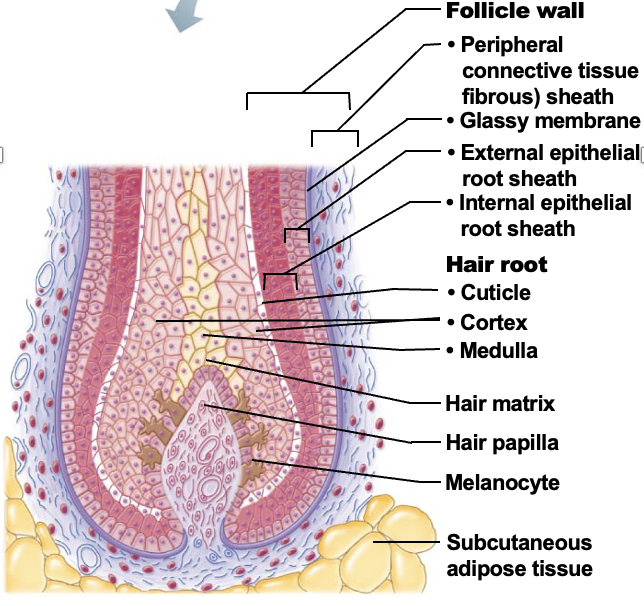
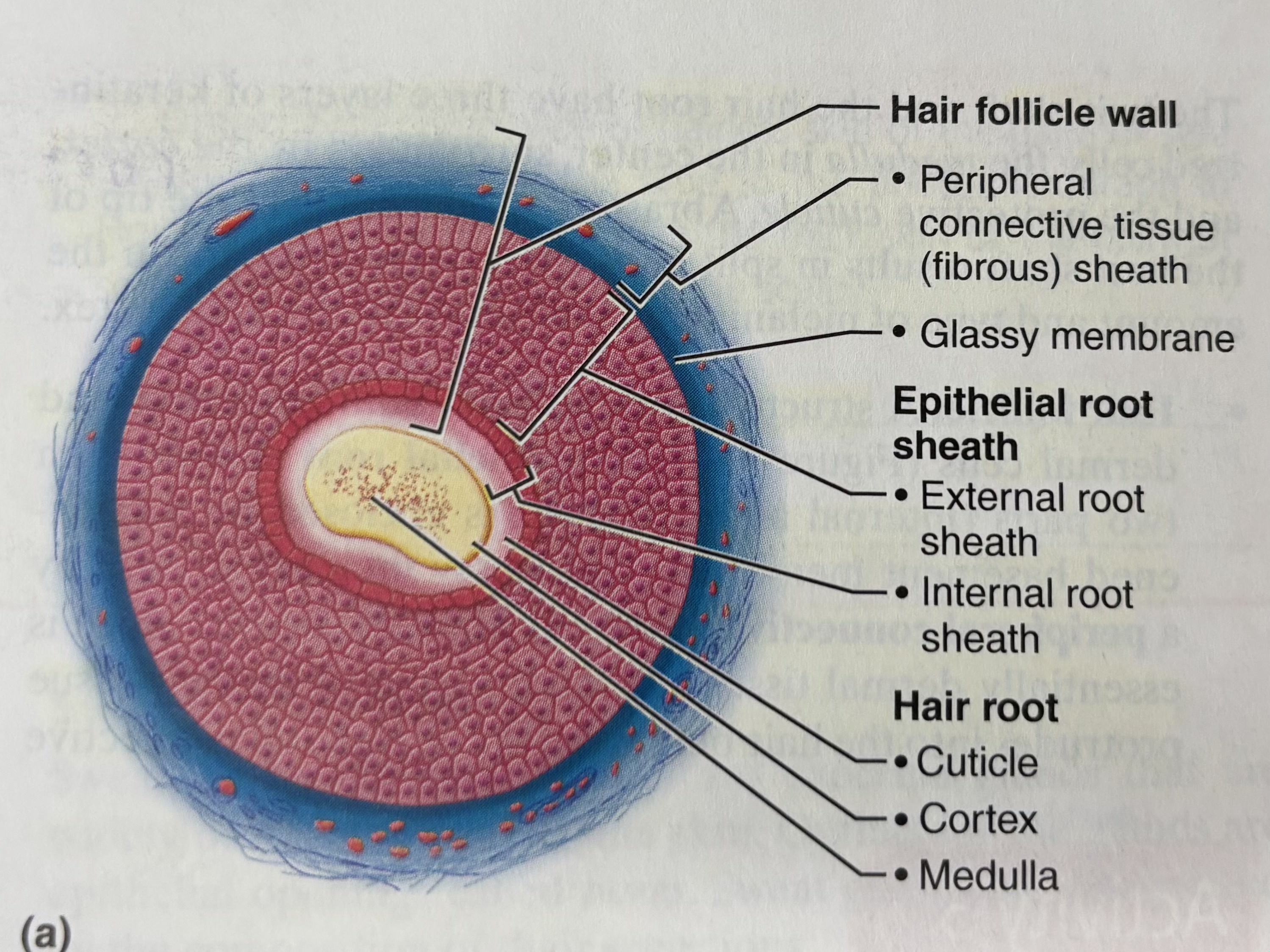
Hair follicle
structure formed by both epidermal and dermal cells. Contains the hair follicle wall & peripheral connective tissue (fibrous) sheath), epithelial root sheath (with external and internal root sheat) and hair root (medulla, cortex, cuticle)
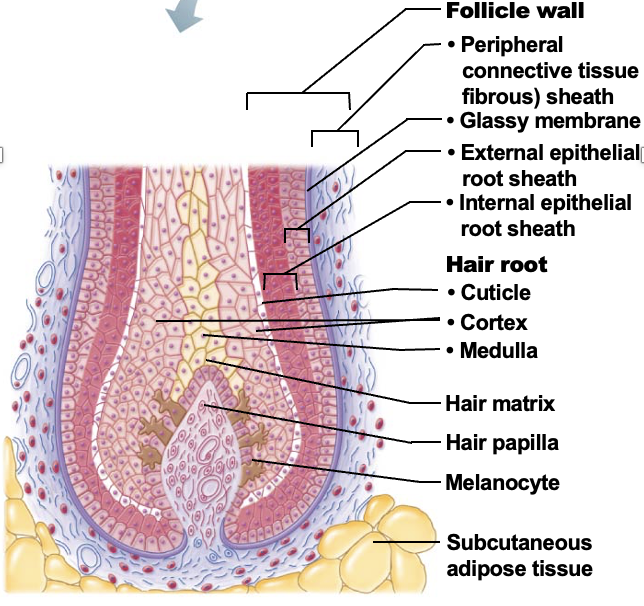
Hair papilla
A small nipple of dermal tissue that protrudes into the hair bulb from the peripheral connective tissue sheath and prvoides nutrition to the growing hair
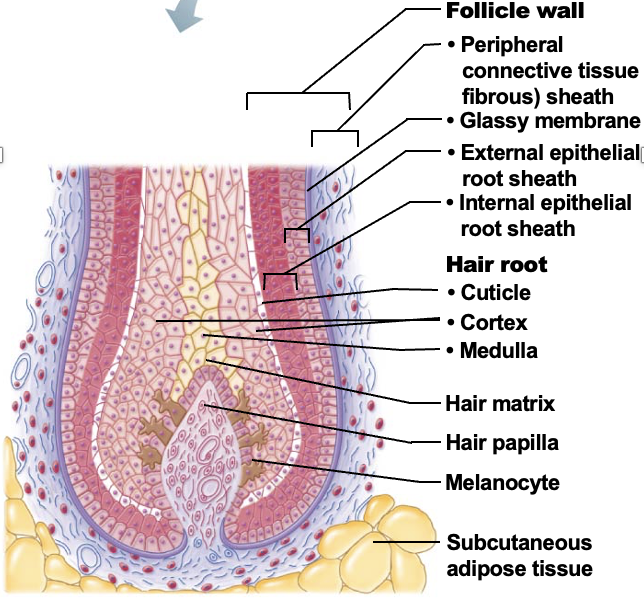
Hair matrix
A layer of actively dividing epithelial cells located at the top of the hair papilla
Arrector pili muscle
Small bands of smooth muscle cells that connect each hair follicle to the papillary layer of the dermis. When these muscles contract during cold or fright, the slanted hair follicle pulls upright and creates goose bumps
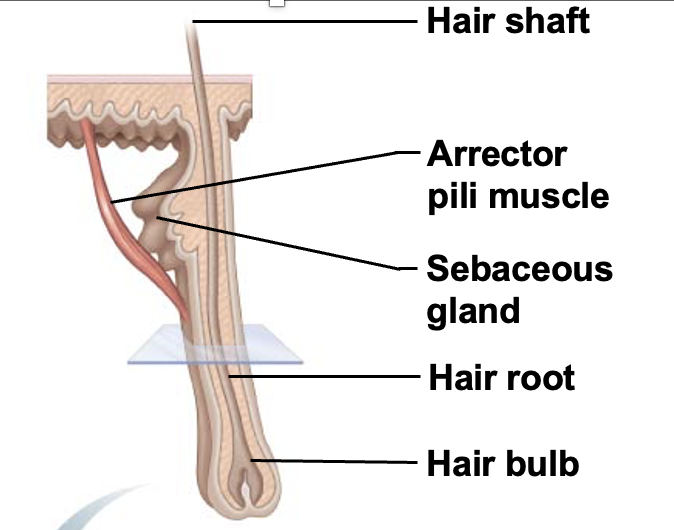
Cutaneous gland
exocrine glands found in the skin that secrete substances to protect, lubricate, and regulate body temperature. Divided into sebaceous gland and sweat gland
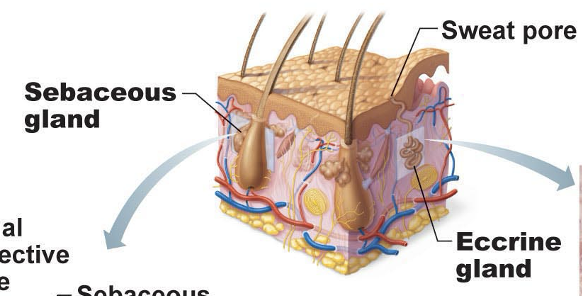
Sebaceous gland
cutaneous gland found nearly all over the skin, except for palms of hands and soles of feet. Ducts usually empty into a hair follicle, but some directly on the skin surface
Sebum
the product of sebaceous glands. It’s a mixture of oily substances and fragmented cells that act as lubricant to keep the skin soft, moist, and keep the hair from becoming brittle. Become particularly active during puberty
Blackheads
the accumulation of dried sebum, bacteria, and melanin from epithelial cells in the oil duct.
Acne
active infection of sebaceous glands
Sudoriferous (sweat) glands
exocrine glands that are widely distributed all over the skin. Outlets for the glands are epithelial openings called pores. Categorized by eccrine and apocrine sweat glands
Eccrine/merocrine sweat glands
Sweat glands distributed all over body that produce clear secretion consisting primarily of water, salts, and urea. Is an important part of the body’s heat-regulating apparatus and excrete sweat when external temperature or body temperature is too high
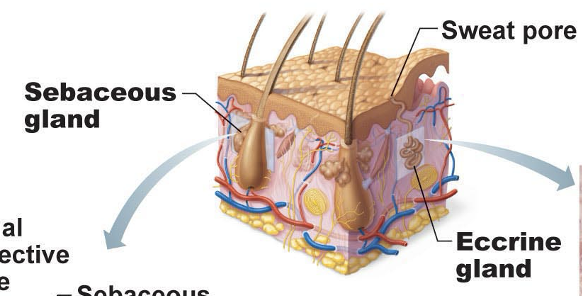
Apocrine sweat glands
Sweat glands found primarily in axillary or genital areas. Secrete basic components of eccrine sweat plus proteins and fat-rich substances. Initially odorless, but when bacteria breaks it down into organic components, it smells unpleasant (BO)