Unit 1 - Practice Exam A
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is the molar hydroxide ion (OH-) concentration of an aqueous solution at pH 6?
A. 1 x 10^-2
B. 1 x 10^-6
C. 1 x 10^-8
D. 1 x 10^-10
E. 1 x 10^-12
C. 1 x 10^-8
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A. In liquid water, every water molecule participates in 4 hydrogen bonds.
B. The hydrogen bond has a directional preference for the atoms on either side of the hydrogen to be in a 120° configuration.
C. The hydrophobic effect is due to a favorable increase in the entropy of water when it is released from non-polar molecules.
D. A pH change from 5.0 to 6.0 corresponds to an increase in the hydrogen ion concentration by a factor of 10.
E. A hydrogen bond is shorter than a covalent bond.
C. The hydrophobic effect is due to a favorable increase in the entropy of water when it is released from non-polar molecules.
At what pH would a 1 L solution of 1 M histidine (side chain pKa = 6) have 80% of its side chains in the protonated form? Choose the closest answer.
A. 2.1
B. 4.3
C. 5.4
D. 6.6
E. 7.7
C. 5.4
Calculate the pI of glutamate given its pKa values of 2.2, 9.2, and 4.2 (side chain).
A. 2.5
B. 3.2
C. 5.7
D. 6.7
E. 7.2
B. 3.2
To calculate the isoelectric point (pI) of glutamate, we need to find the average of the two pKa values that surround the zwitterionic (neutral) form — the point where the molecule has no net charge.
Given the pKa values listed below, what is the isoelectric point of the following peptide?
Choose the closest answer.
Glutamine-Aspartate-Alanine-Glycine
Glutamine: 2.0, 9.1
Aspartate: 1.9, 9.6, 3.7 (R-group)
Alanine: 2.3, 9.7
Glycine: 2.3, 9.0
A. 2.3
B. 3.0
C. 5.9
D. 7.5
E. 9.4
B. 3.0
Which of the following statements regarding the peptide bond is CORRECT:
A. The peptide bond is formed through hydrogen bonding.
B. The peptide bond can freely rotate.
C. The peptide bond is formed through a hydrolysis reaction.
D. The peptide bond has partial double bond character between the carbonyl carbon and the amide nitrogen.
E. The peptide bond is “puckered” or non-planar.
D. The peptide bond has partial double bond character between the carbonyl carbon and the amide nitrogen.
The folding of a globular, soluble protein is thermodynamically favorable due to:
A. Charge-dipole interactions with water
B. Ionic interactions
C. The hydrophobic effect
D. Restricted rotation of the peptide bond
E. Hydrogen bonding
C. The hydrophobic effect
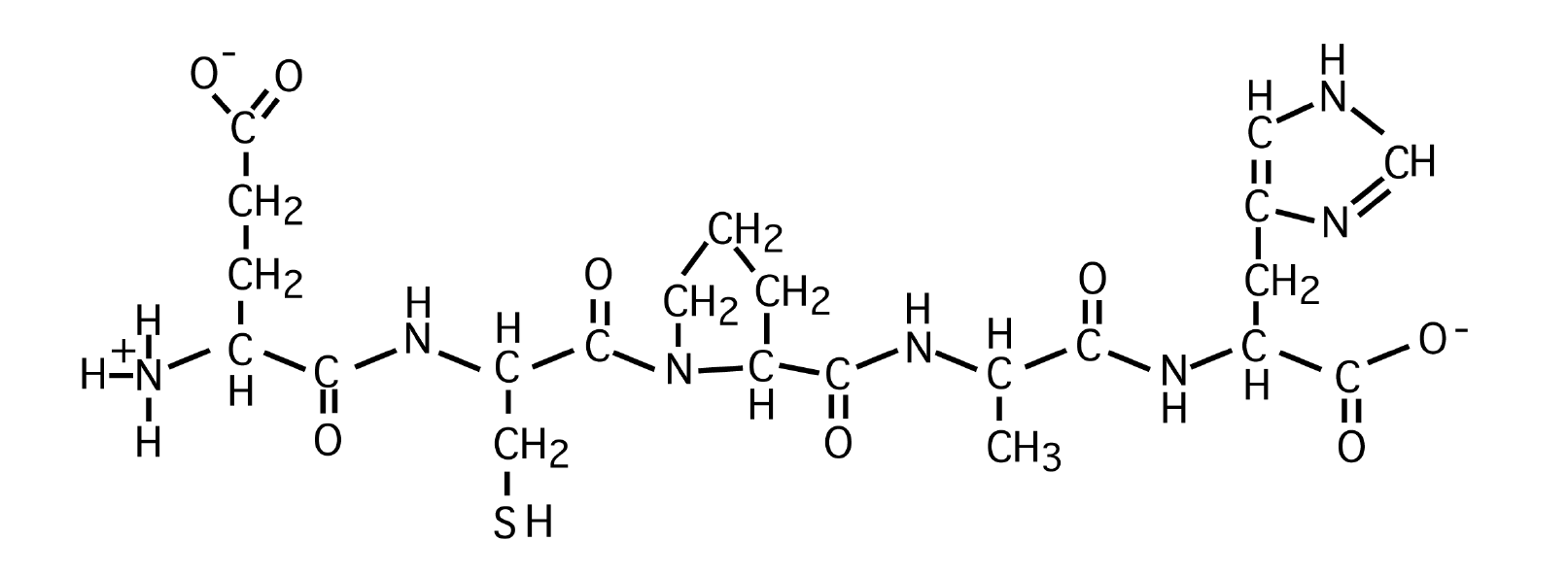
What is the sequence of the following peptide?
A. Glutamate-Cysteine-Tyrosine-Glycine-Phenylalanine
B. Aspartate- Serine -Proline-Alanine-Histidine
C. Glutamate- Cysteine - Phenylalanine - Glycine-Histidine
D. Glutamate- Cysteine - Proline -Alanine-Histidine
E. Aspartate-Cysteine-Proline-Glycine-Phenylalanine
D. Glutamate - Cysteine - Proline - Alanine - Histidine
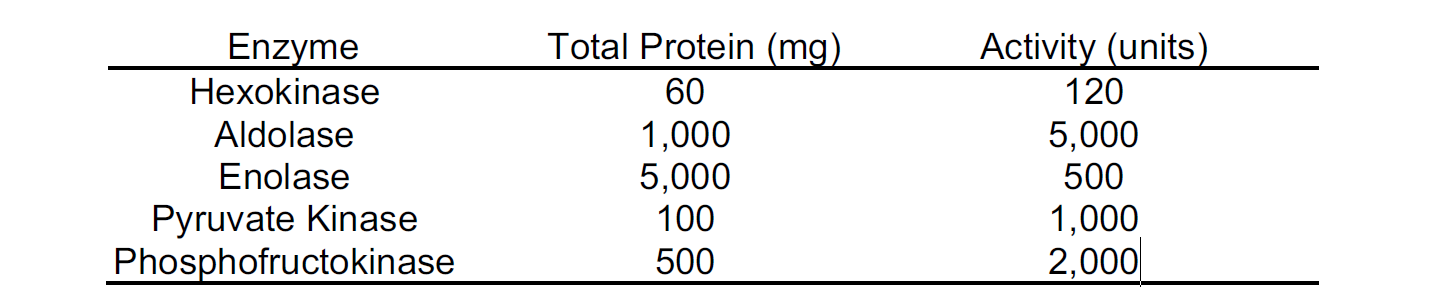
Following purification, which of the following enzymes has the highest specific activity?
A. Hexokinase
B. Aldolase
C. Enolase
D. Pyruvate Kinase
E. Phosphofructokinase
D. Pyruvate Kinase
How many hydrogen bonds would be found in a 100 amino acid alpha helix?
A. 20
B. 25
C. 96
D. 100
E. 104
C. 96
Which of the following methods could be used to separate a mixture of proteins by size?
A. Isoelectric focusing
B. Affinity chromatography
C. UV spectrophotometry
D. SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
E. Ion exchange chromatography
D. UV spectrophotometry
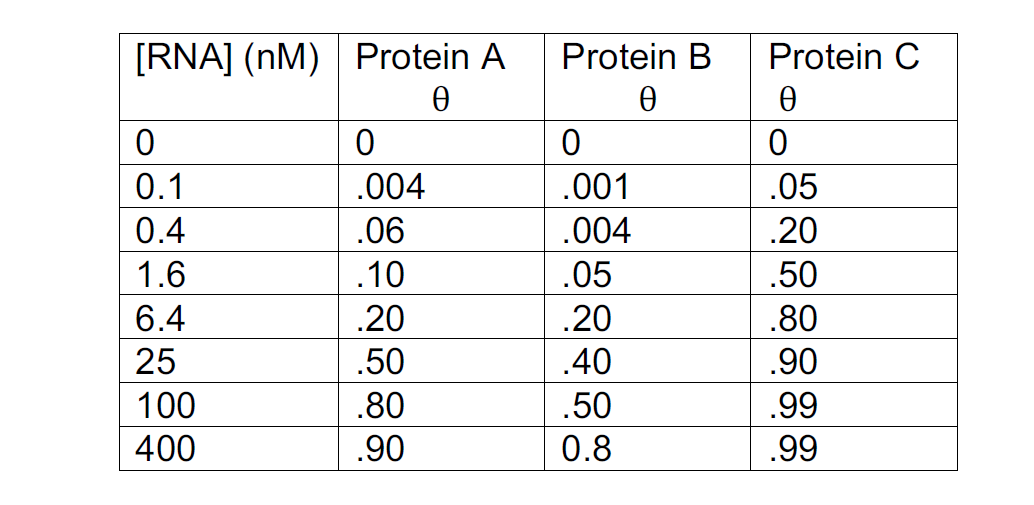
Proteins A, B and C bind to an RNA ligand. Fractional saturation of binding (q) was measured for a range of given RNA concentrations. From the data in the table, which protein binds most tightly to the RNA? What is the Kd of that protein?
Note that q x 100 is % RNA bound and a calculator is not required for this problem.
A. Protein A, Kd = 25 nM
B. Protein B, Kd = 100 nM
C. Protein C, Kd = 1.6 nM
D. Protein A, Kd = 400 nM
E. Protein C, Kd = 100 nM
C. Protein C, Kd = 1.6 nM