Mr. Rosendi CP9 Biology: DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Proteins differ from one another by the order of ___.
amino acids
Any change in a nitrogen base sequence
mutation
The function of ___ is to carry specific amino acids to the ribosome
tRNA
One tRNA molecule carries _ nitrogenous bases and _ amino acid
3;1
Proteins are linked by ___ bonds.
peptide
the entire process by which proteins are made
protein synthesis
a molecule made of linked nucleotides
ribonucleic acid
the process of reading instructions on an RNA molecule to put together the amino acids that make up a protein
translation
the process of transferring a gene's instructions for making a protein to an RNA molecule
transcription
a nitrogen base used in RNA instead of the base Thymine found in DNA
uracil
carries amino acids to ribosome, and made during transcription
mRNA
composed of two chains of nucleotides and contains Thymine
DNA
contains ribose, phosphate & ribose, and Uracil
mRNA and tRNA
involved in translation
DNA and RNA
contains Cytosine
DNA, mRNA, and tRNA
Where is DNA located?
the nucleus
Where is mRNA located?
mRNA
Where is tRNA located?
the cytoplasm
How many strands does DNA have?
2
How many strands does mRNA have?
1
How many strands does tRNA have?
1
What are some of DNA's functions?
Stores genetic information that codes for all proteins made in the cell
What are some of mRNA's functions?
Carries temporary copies of the message contained in DNA to the ribosome to be translated
What are some of tRNA's functions?
Carry amino acids to the ribosome to create the proper proteins
In eukaryotes, transcription takes place in the .
Nucleus
. Transcription begins when __ binds to the gene's promoter
RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase adds complementary as it "reads" the gene
nucleotides
a strand of nucleotides that carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the ribosomes
mRNA
the part of DNA that is transcribed into mRNA
exons
the part of DNA that is not transcribed into mRNA.
introns
DNA has the instruction to make what?
protein
The message of DNA is taken out of the nucleus by a special type of RNA called what?
mRNA
RNA is different from DNA because it is what?
single-stranded
The RNA takes the message to the , where proteins are made
Ribosome
Which molecule links fragments to DNA?
DNA ligase
Which enzyme is responsible for the process of transcription?
RNA polymerase
A mutation where 2 pieces of different chromosomes are interchanged
Translocation
A change in a single nucleotide in a DNA
A point mutation
Responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during DNA replication.
helicase
RNA contains the sugar ___.
ribose
In a school play, a promoter is like a ….
Start signal for replication, and binding site for RNA polymerase
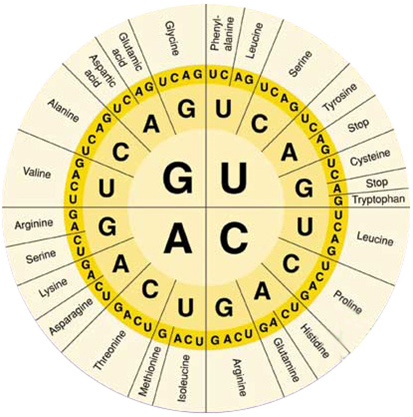
Find out which amino acid is specified by the mRNA code GCC.
Alanine
How many kinds of mutation are there?
4
A permanent change to the DNA code of a gene
Gene mutation
A mutation that involves one nucleotide
Point mutation
A mutation that involves the addition of nucleotide
Insertion mutation
A mutation in which two pieces of different chromosomes are interchange
Translocation mutation
Which of the mutations above could lead to a frameshift mutation
Inversion mutation
Which of the following BEST describes what happens in a translocation
A segment of one chromosome is moved to a different chromosome.
What results from a point mutation in a DNA sequence?
One nucleotide is changed, possibly affecting a single protein.
Pyrimidine
a one-ring mitrogenous
Purine
a two ring nitrogenous base
Complementary strands
a particular DNA strand that is able to bond to another strand according to the base-pairing rule
cell cycle
sequence of cell growth/division that occurs in a cell between the beginning of one cell division and the beginning of the next cell division
Semiconservative replication
process of DNA replication that produces one original strand and one newly created strand
Helicase enzymes
unwind and uncoil the DNA strands
Replication forks
sites along DNA where separation and replication occur
Antiparallel
sites along DNA where separation and replication occur
Leading strand
Assembled 5’ to 3’, or toward replication fork and polymerase copies it continuously
Lagging strand
Assembled 3’ to 5’, or away from replication fork and polymerase assembles Okazaki fragments
Okazaki fragments
a series of short segments of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication
ligase
enzyme that binds segments of the new DNA strand together
Histone
a small protein that associates with DNA to form a nucleosome
Chromosome
proteins and compacted DNA found in the nucleus
Nucleosome
a unit of histone proteins and its attached section of DNA
Chromatids
the short, thick rods of highly coiled, condensed DNA
Locus
the location of a gene on a certain chromosome
mRNA
messanger RNA
tRNA
transfer RNA
rRNA
ribosomal RNA
RNA splicing
the remove introns and join exons to create mature mRNA molecules