AP Macroeconomics Unit 6: Open Economy - International Trade and Finance
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Net exports
Exports - imports
Trade surplus
Exporting > importing
Trade deficit (trade gap)
Exporting < importing
Balance of payments
A summary of the country’s international trade for a given year.
Current Account (CA)
A record of a country’s physical trading. Composes of 3 parts:
Net exports
Investment income (income from the factors of production, or WRIP)
Net transfers (money flows such as donations and remittances)
Capital and Financial Account (CFA)
Measures the purchase and sales of financial assets abroad.
Foreign Direct Investment
When a foreign company buys business in a different country.
Net capital outflow
The difference between the purchase of foreign assets by a country and the purchase of that country’s assets by a foreign country.
Financial Account Surplus
Inflow > Outflow
Financial Account Outflow
Inflow < Outflow
CA + CFA should equal this amount
0
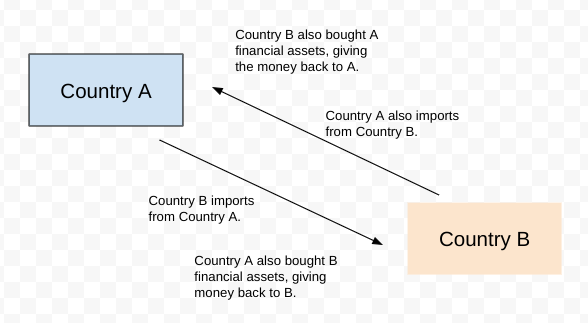
Why CA and CFA balance out
The money comes back full circle to the country, whether it be through exports, or through a foreign country buying financial assets from that country.
Exchange rate
The price of one currency relative to another.
Depreciation
The loss in value of a country’s currency when compared to another country. More of that currency is now needed to buy one unit of the foreign country’s currency. The currency “weakens.”
Appreciation
The increase in value of a country’s currency when compared to another country. Less of the currency is needed to buy one unit of the other country’s currency. The currency “strengthens.”
FOREX Market
A huge market conisting of every country’s currency,
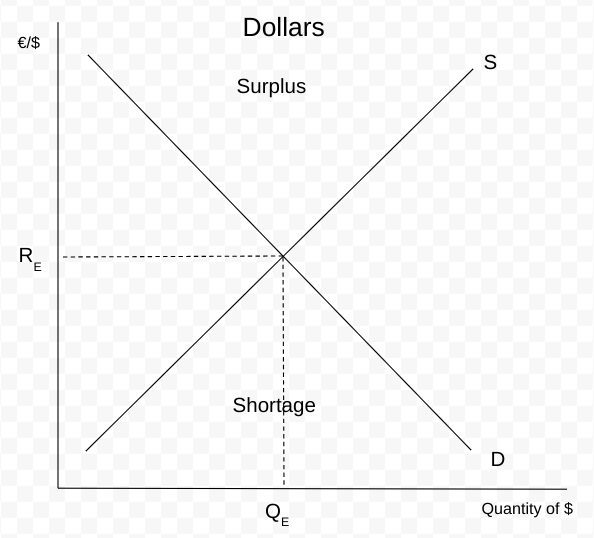
FOREX Demand
Foreigners
An inverse relationship between the exchange rate and quantity demanded.
FOREX Supply
By the home country
A direct relationship between the exchange rate and quantity supplied.
If you want to buy goods from a foreign country
You must supply that country with their currency (or exchange your currency for that country’s currency using the exchange rate)
FOREX Shifters
Change in Tastes
Change in Relative Incomes
Change in Relative Price level
Change in Relative Interest Rates
Fixed exchange rate
When the government manages the country’s currency.
Floating exchange rate
Where the market determines the value of the country’s currency.
FOREX Double shifters
Changes in price levels
Changes in interest rate
Tariff
A tax on imports
Quota
A limit on the number of imports coming in
Both tariffs and quotas:
Decrease the FOREX supply of the country restricting trade since fewer trading takes place.
When currency appreciates:
US products become more expensive
Countries buy less products from the US
US net exports decrease
When currency depreciates:
US products become less expensive
Countries buy more products from the US
US net exports increase
When interest rates increase:
Foreign countries will buy more domestic assets
Citizens will want to buy less foreign assets
Capital inflow increases
Net capital outflow decreases
When net capital outflow decreases:
FOREX demand for that currency decreases
That currency’s exchange rate goes up
The currency appreciated
When interest rates decrease:
Foreign countries will buy less domestic assets
Citizens will buy more foreign assets
Capital outflow increases
Net capital outflow increases
When net capital outflow increases:
FOREX supply increases
Exchange rate decreases
The currency depreciated